目录
一.常用数学函数
#include / #include
二.常用字符串处理函数
#include / #include
2.1常见的内存函数:
(1)memcpy库函数
(2)memcmp库函数
(3)memset
2.2字符串常见库函数
(1)strlen
(2)strcpy
三、其他常用函数
四、实现键盘和文件输入/输出的成员函数
一.常用数学函数
头文件:
#include<math> / #include<math.h>
| 函数原型 | 功能 | 返回值 |
| int abs(int x) | 求整数x的绝对值 | 绝对值 |
| double acos(double x) | 计算arcos(x)的值 | 计算结果 |
| double asin(double x) | 计算arsin(x)的值 | 计算结果 |
| double atan(double x) | 计算arctan(x)的值 | 计算结果 |
| double cos(double x) | 计算cos(x)的值 | 计算结果 |
|
| 计算x的双曲余弦cosh(x)的值 | 计算结果 |
| double exp(double x) | 求e的x次方的值 | 计算结果 |
| double fabs(double x) | 求实数x的绝对值 | 绝对值 |
| double fmod(double x,double y) | 求x/y的余数 | 余数的双精度数 |
| long labs(long x) | 求长整型数的绝对值 | 绝对值 |
| double log(double x) | 计算In(x)的值 | 计算结果 |
| double log10(double x) | 计算log10(x)值 | 计算结果 |
| double modf(double x, double *y) | 取x的整数部分送到y所指向的单元格中 | x的小树部分 |
| double pow(double x, double y) | 求x的y次幂的值 | 计算结果 |
| double sin(double x) | 计算sin(x)的值 | 计算结果 |
| double sqrt(double x) | 求根号下x的值 | 计算结果 |
| double tan(double x) | 计算tan(x)的值 | 计算结果 |
| fcvt | 将浮点型数转化为字符串 |
二.常用字符串处理函数
头文件
#include<string> / #include<string.h>
| 函数原型 | 功能 | 返回值 |
| void *memcpy (void *p1, const void *p2 size_t n) | 存储器拷贝, 将p2所指向的共n个字节拷贝到p1所指向的存储区中 | 目的存储区的起始地址 (实现任意数据类型之间的拷贝) |
| void *memset (void *p ,int v, size_t n) | 将v的值作为p所指向的区域的 值,n是p所指向区域的大小 | 该区域的起始地址 |
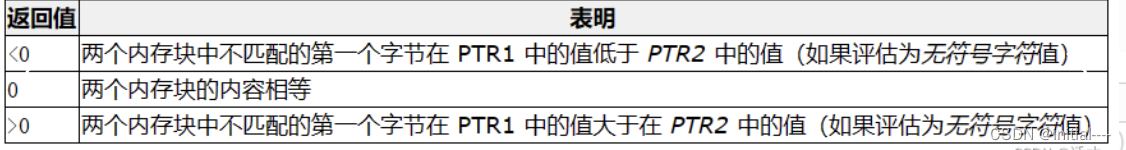
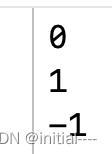
| int memcmp ( const void * ptr1, const void * ptr2, size_t num ); | 比较两个内存大小: | 1,0,-1 |
| char *strcpy (char *p1, const char *p2) | 将p2所指向的字符串拷贝到 p1所指向的存储区中 | 目的存储区的起始地址 |
| char *strncpy (char *p1, const char *p2,int n) | 目的存储区的起始地址 | |
| char *strcat (char *p1, const char *p2) | 将p2所指向的字符串连接到 p1所指向的字符串后面 | 目的存储区的起始地址 |
| int strcmp (const char *p1, const char *p2) | 比较p1,p2所指向的两个 字符串的大小 | 两个字符串相同,返回0;若p1所指向的字符串小于p2所指的字符串,返回负值;否则,返回正值 |
| int strlen(const char *p) | 求p所指向的字符串的长度 | 字符串所包含的字符个数 (不包括字符串结束标志’\n’) |
| char *strncpy (char *p1, const char *p2, size_t n) | 将p2所指向的字符串(至多n个字符)拷贝到p1所指向的存储区中 | 目的存储区的起始地址 (与strcpy()类似) |
| char *strncat (char *p1, const char *p2, size_t n) | 将p2所指向的字符串(至多n个字符)连接到p1所指向的字符串的后面 | 目的存储区的起始地址 (与strcpy()类似) |
| char *strncmp (const char *p1, const char *p2, size_t n) | 比较p1,p2所指向的两个字符串的大小,至多比较n个字符 | 两个字符串相同,返回0;若p1所指向的字符串小于p2所指的字符串,返回负值;否则,返回正值 (与strcpy()类似) |
| char *strstr (const char *p1, const char *p2) | 判断p2所指向的字符串是否是p1所指向的字符串的子串 | 若是子串,返回开始位置的地址;否则返回0。 |
2.1常见的内存函数:
(1)memcpy库函数
void * memcpy ( void * destination, const void * source, size_t num );
第一个参数p1:目的地—指向要在其中复制内容的目标数组的指针,类型转换为 void* 类型的指针。
第二个参数p2:来源地—指向要复制的数据源的指针,类型转换为 const void* 类型的指针。
第三个参数n:字节数—要复制的字节数。size_t 是无符号整数类型。
各类型字节长度:
byte 1字节 、 short 2字节 、int 4字节 、long 8字节 、float 4字节(精确到7位有效数字) 、 double 8字节 、char 2字节 、boolean 1位
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;int main(){int arr1[]={1,2,3,4,5,6,7};int arr2[3]={0};memcpy(arr1,arr2,12);for(int i=0;i<sizeof(arr1)/sizeof(arr1[0]);i++){cout<<arr1[i]<<endl;}return 0;
}

(2)memcmp库函数
比较两个内存大小:
int memcmp ( const void * ptr1, const void * ptr2, size_t num );
第一个参数p1:指向内存块的指针。
第二个参数p2:指向内存块的指针。
第三个参数n:要比较的字节数。
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;int main(){int p[5]={1,2,3,4,5};int arr1[]={1,2,3,4,5,6,7};int arr2[3]={1,2,2};int arr3[4]={2,2,3,4};int n1=memcmp(p,arr1,20);int n2=memcmp(p,arr2,12);int n3=memcmp(p,arr3,16);cout<<n1<<endl<<n2<<endl<<n3<<endl;return 0;
}
(3)memset
填充内容:
void * memset ( void * ptr, int value, size_t num );
第一个参数p1:指向要填充的内存块的指针。
第二个参数v:要设置的值。该值作为 int 传递,但该函数使用此值的无符号 char 转换填充内存块。
第三个参数n:要设置为该值的字节数。size_t 是无符号整数类型。
返回值:返回指针类型
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;int main()
{char str[21] = "nice to meet you";//在str字符串后面添加三个感叹号memset(str + 16, '!', 5);printf("%s\n",str);return 0;
}

2.2字符串常见库函数
(1)strlen
获取字符串长度,计算‘\0’之前的字符。
int strlen ( const char * str );
str:字符串起始地址,会计算该字符串’\0‘之前的字符个数。
返回值:返回一个无符号数值。
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;int main()
{char str[20] = "nice to meet you";int len=strlen(str);cout<<len;return 0;
}

(2)strcpy
复制字符串的功能。
char * strcpy ( char * destination, const char * source );
第一个参数p1:目的地,指向要在其中复制内容的目标数组的指针。
第二个参数p2:来源地,要复制的字符串。
返回值:返回一个指针
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;int main()
{char str1[] = "nice to";char str2[]="meet you";strcpy(str1,str2);cout<<str1<<endl;return 0;
}

三、其他常用函数
头文件#include <stdlib> 或者 #include <stdlib.h>
| 函数原型 | 功能 | 返回值 | 说明 |
| void abort(void) | 终止程序执行 | 不能结束工作 | |
| void exit(int) | 终止程序执行 | 做结束工作 | |
| double atof(const char *s) | 将s所指向的字符串转换成实数 | 实数值 | |
| int atoi(const char *s) | 将s所指向的字符串转换成整数 | 整数值 | |
| long atol(const char *s) | 将s所指的字符串转换成长整数 | 长整数值 | |
| int rand(void) | 产生一个随机整数 | 随机整数 | |
| void srand(unsigned int) | 初始化随机数产生器 | ||
| int system(const char *s) | 将s所指向的字符串作为一个可执行文件,并加以执行 | ||
| max(a, b) | 求两个数中的大数 | 大数 | 参数为任意类型 |
| min(a,b) | 求两个数中的小数 | 小数 | 参数为任意类型 |
四、实现键盘和文件输入/输出的成员函数
头文件#include <iostream> 或者 #include <iostream.h>
| 函数原型 | 功能 | 返回值 |
| cin >> v | 输入值送给变量 | |
| cout << exp | 输出表达式exp的值 | |
| istream & istream::get(char &c) | 输入字符送给变量c | |
| istream & istream::get(char *, int , char = ‘\n’) | 输入一行字符串 | |
| istream & istream::getline(char *, int , char = ‘\n’) | 输入一行字符串 | |
| void ifstream::open(const char*,int=iOS::in, int = filebuf::openprot ) | 打开输入文件 | |
| void ofstream::open(const char*,int=ios::out, int = filebuf::openprot) | 打开输出文件 | |
| void fsream::open(const char*,int , int = filebuf::openprot) | 打开输入/输出文件 | |
| ifstream::ifstream(const char*,int = ios::in, int = filebuf::openprot) | 构造函数打开输入文件 | |
| ofstream::ofstream(const char*,int=ios::out, int = filebuf::openprot) | 构造函数打开输出函数 | |
| fstream::fstream(const char*, int, int = filebuf::openprot) | 构造函数打开输入/输出文件 | |
| void istream::close() | 关闭输入文件 | |
| void ofsream::close() | 关闭输出文件 | |
| void fsream::close() | 关闭输入/输出文件 | |
| istream & istream::read(char*, int) | 从文件中读取数据 | |
| ostream & istream::write(const char*,int) | 将数据写入文件中 | |
| int ios::eof() | 判断是否到达打开文件的尾部 | 1为到达2为没有 |
| istream & istream::seekg(streampos) | 移动输入文件的指针 | |
| istream & istream::seekg(streamoff,ios::seek_dir) | 移动输入文件的指针 | |
| streampos istream::tellg() | 取输入文件的指针 | |
| ostream & ostream::seekp(streampos) | 移动输出文件的指针 | |
| ostream & ostream::seekp(streamoff,ios::seek_dir) | 移动输出文件的指针 | |
| streampos ostream::tellp() | 取输出文件的指针 |