1. 前言
从今天起我们开始内存相关的话题,内存是个很大的话题,一时不知从何说起。内存离不开allocator,我们就从allocator开始吧。allocator目前有两种:std::allocator, std::pmr::polymorphic_allocator,各有优缺点。
上来就长篇大论容易显得枯燥,我们还是抛出一个例子然后提出问题,通过问题慢慢深入。
2. 分配器例子
下面这个例子是我很久以前从一个网站上copy下来的。是个不错的用来快速学习的例子。作者当时留了个疑问没解决:为什么预分配内存的pmr反而效率更低哪?
这也是本节我们要解决的问题,从中也可以学到allocator和polymorphic_allocator的优缺点对比。
#include<iostream>
#include<memory_resource>
#include<vector>
#include "../PerfSum.hpp"
using namespace std;void TestPmrVec(){char buffer[1000000*4] = {0};std::pmr::monotonic_buffer_resource mbr{ std::data(buffer), std::size(buffer) };std::pmr::polymorphic_allocator<int> pa{&mbr};std::pmr::vector<int> vec{pa};//vec.push_back(0);//vec.push_back(1);PerfSum t;for(int i=0;i<1000000;i++){vec.push_back(i);}std::cout<<"End"<<std::endl;}void TestStdVec(){std::vector<int> vec ;PerfSum t;//vec.push_back(0);//vec.push_back(1);for(int i=0;i<1000000;i++){vec.push_back(i);}std::cout<<"End"<<std::endl;}int main() {std::cout<<"std vector cost:"<<std::endl;TestStdVec();std::cout<<"pmr vector cost:"<<std::endl;TestPmrVec();
}
其中PerfSum.hpp在《Modern C++ idiom3:RAII》中有提到。编译运行结果:
[mzhai@std_polymorphic_pmr]$ g++ compare_speed.cpp -std=c++17 -g
[mzhai@std_polymorphic_pmr]$ ./a.out
std vector cost:
Endtook 19171 microseconds.
pmr vector cost:
Endtook 56134 microseconds.
可见pmr反而比普通的vector慢了大约3倍。
注意:pmr是c++17开始支持的standard library features, gcc9.1开始支持。
3. pmr慢的原因
启动perf, 查热点:
[mzhai@std_polymorphic_pmr]$ sudo sysctl -w kernel.kptr_restrict=0
sudo sysctl -w kernel.perf_event_paranoid=0
[sudo] password for mzhai:
kernel.kptr_restrict = 0
kernel.perf_event_paranoid = 0
[mzhai@std_polymorphic_pmr]$ perf record -a -g ./a.out
std vector cost:
Endtook 17302 microseconds.
pmr vector cost:
Endtook 58350 microseconds.
[ perf record: Woken up 1 times to write data ]
[ perf record: Captured and wrote 0.100 MB perf.data (369 samples) ]
[mzhai@std_polymorphic_pmr]$ perf report
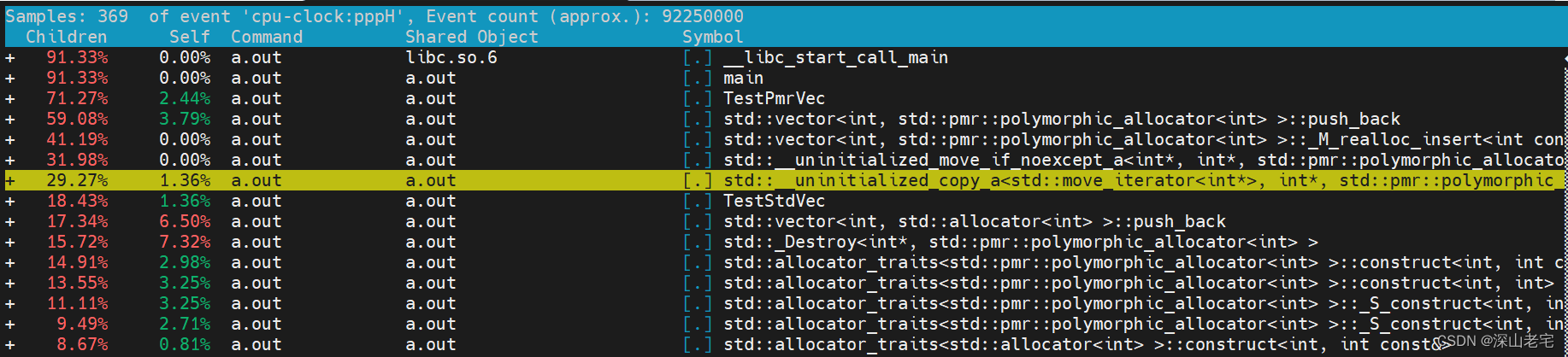
找到__uninitialized_copy_a的实现,我的机器在目录/usr/include/c++/11/bits/stl_uninitialized.h中:
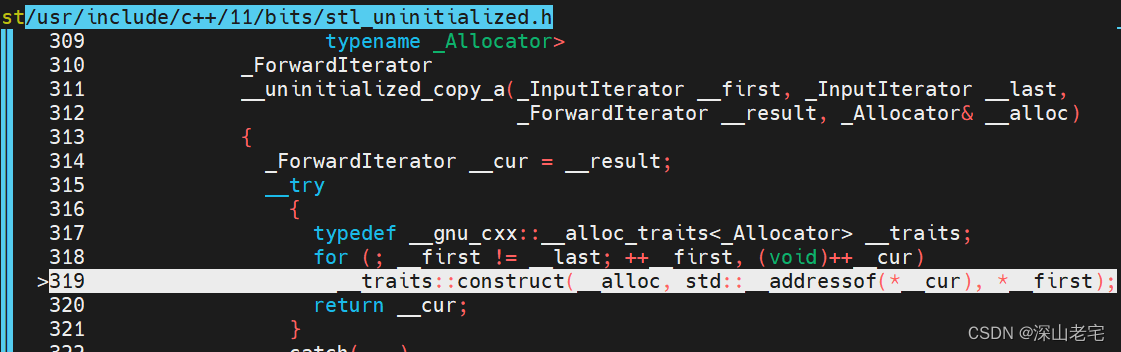
从perf report能隐约看出调用栈,__uninitialized_copy_a是从push_back -> _M_realloc_insert 调过来的,从名字猜也能猜到是vector旧的分配的空间不够了需要reallocate, 分配完新的空间后需要调用__uninitialized_copy_a把旧的数据copy或move过来,但是重点是:这里竟然是for循环,是一个个copy或move过来的!
4. std::allocator快的原因
作为对比,我们查下std::vector 空间不够是怎么做的?
读者可自行调试TestStdVec,我这里直接上代码:
#0 std::__relocate_a_1<int, int> (__first=0x41b2e8, __last=0x41b2e8, __result=0x41b2cc) at /usr/include/c++/11/bits/stl_uninitialized.h:1012
#1 0x000000000040451f in std::__relocate_a<int*, int*, std::allocator<int> > (__first=0x41b2e8, __last=0x41b2e8, __result=0x41b2cc, __alloc=...)at /usr/include/c++/11/bits/stl_uninitialized.h:1046
#2 0x000000000040423f in std::vector<int, std::allocator<int> >::_S_do_relocate (__first=0x41b2e8, __last=0x41b2e8, __result=0x41b2cc, __alloc=...)at /usr/include/c++/11/bits/stl_vector.h:456
#3 0x0000000000403e5d in std::vector<int, std::allocator<int> >::_S_relocate (__first=0x41b2e8, __last=0x41b2e8, __result=0x41b2cc, __alloc=...)at /usr/include/c++/11/bits/stl_vector.h:469
#4 0x000000000040376a in std::vector<int, std::allocator<int> >::_M_realloc_insert<int const&> (this=0x7fffffffdb70, __position=0)at /usr/include/c++/11/bits/vector.tcc:468
#5 0x0000000000402f24 in std::vector<int, std::allocator<int> >::push_back (this=0x7fffffffdb70, __x=@0x7fffffffdb3c: 2)
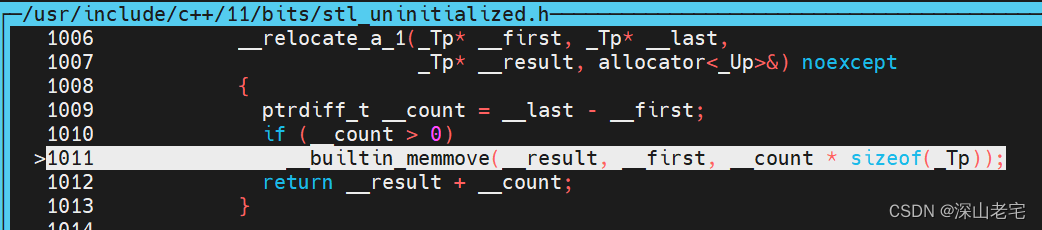
直接调用__builtin_memmove把旧数据一股脑memmove过去,能不快吗?!
可能有读者有一点点疑问:想__builtin_memmove真的调用memmove吗?简单看下汇编就知道啦。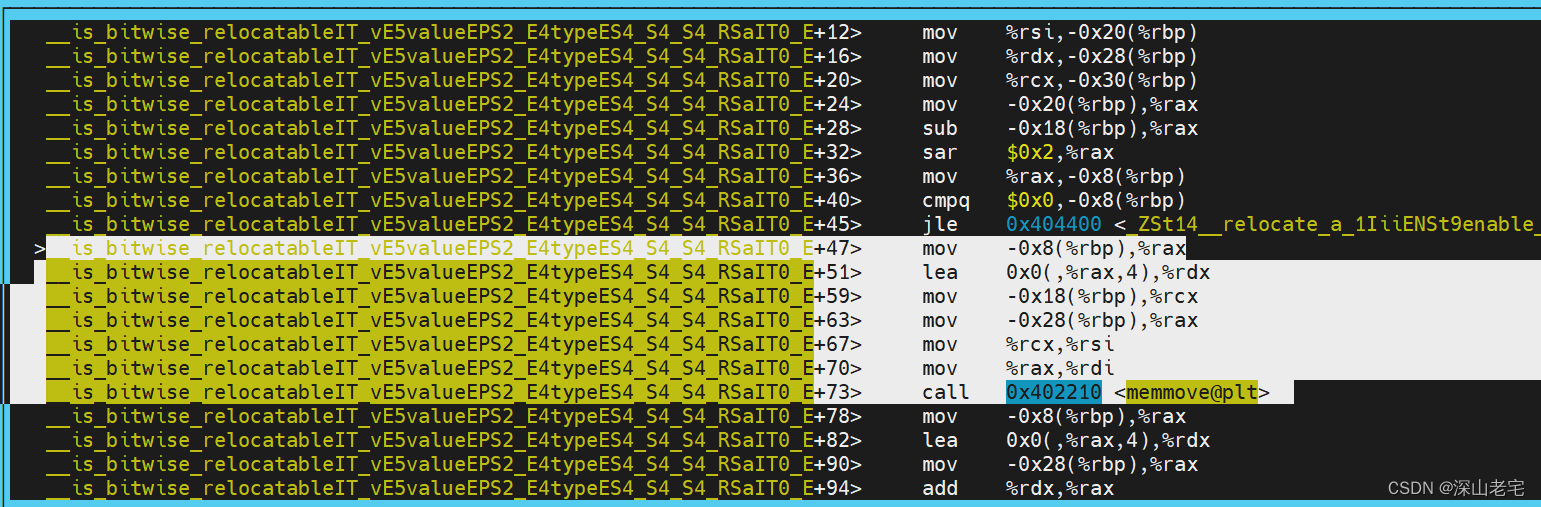
何时调用memmove何时调用for循环
通过上面的分析,我们现在知道了pmr慢而普通allocator快的原因了,接着新的问题来了:为什么pmr不走memmove? 什么条件下走memmove哪?
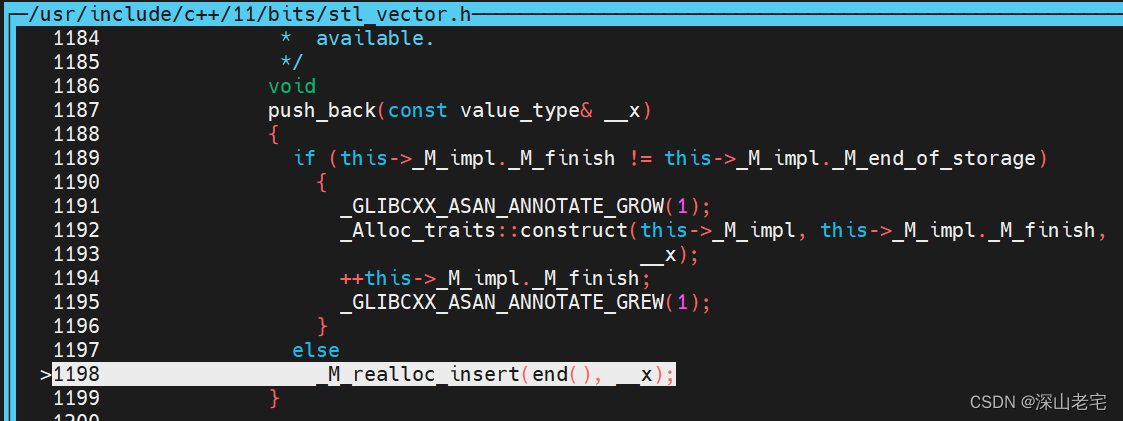
/usr/include/c++/11/bits/vector.tcc
423 template<typename _Tp, typename _Alloc>424 template<typename... _Args>425 void426 vector<_Tp, _Alloc>::427 _M_realloc_insert(iterator __position, _Args&&... __args)434 {458 #if __cplusplus >= 201103L459 if _GLIBCXX17_CONSTEXPR (_S_use_relocate())460 {461 __new_finish = _S_relocate(__old_start, __position.base(),462 __new_start, _M_get_Tp_allocator());463464 ++__new_finish;465466 __new_finish = _S_relocate(__position.base(), __old_finish,467 __new_finish, _M_get_Tp_allocator());468 }469 else470 #endif471 {472 __new_finish473 = std::__uninitialized_move_if_noexcept_a474 (__old_start, __position.base(),475 __new_start, _M_get_Tp_allocator());476477 ++__new_finish;478479 __new_finish480 = std::__uninitialized_move_if_noexcept_a481 (__position.base(), __old_finish,482 __new_finish, _M_get_Tp_allocator());483 }
关键点在_S_use_relocate()的值,此函数的定义如下:
/usr/include/c++/11/bits/stl_vector.h430 static constexpr bool431 _S_nothrow_relocate(true_type)432 {433 return noexcept(std::__relocate_a(std::declval<pointer>(),434 std::declval<pointer>(),435 std::declval<pointer>(),436 std::declval<_Tp_alloc_type&>()));437 }438439 static constexpr bool440 _S_nothrow_relocate(false_type)441 { return false; }442443 static constexpr bool444 _S_use_relocate()445 {446 // Instantiating std::__relocate_a might cause an error outside the447 // immediate context (in __relocate_object_a's noexcept-specifier),448 // so only do it if we know the type can be move-inserted into *this.449 return _S_nothrow_relocate(__is_move_insertable<_Tp_alloc_type>{});450 }
- 首先看__is_move_insertable<_Tp_alloc_type>{},无论_Tp_alloc_type是std::allocator 还是std::pmr::polymorphic_allocator,结果是true.
785 template<typename _Alloc>
786 struct __is_move_insertable
787 : __is_alloc_insertable_impl<_Alloc, typename _Alloc::value_type>::type
788 { };
789
790 // std::allocator<_Tp> just requires MoveConstructible
791 template<typename _Tp>
792 struct __is_move_insertable<allocator<_Tp>>
793 : is_move_constructible<_Tp>
794 { };
std::allocator匹配后者(791行),is_move_constructible为true;
pmr匹配前者(785行), 匹配下面的两者之一。
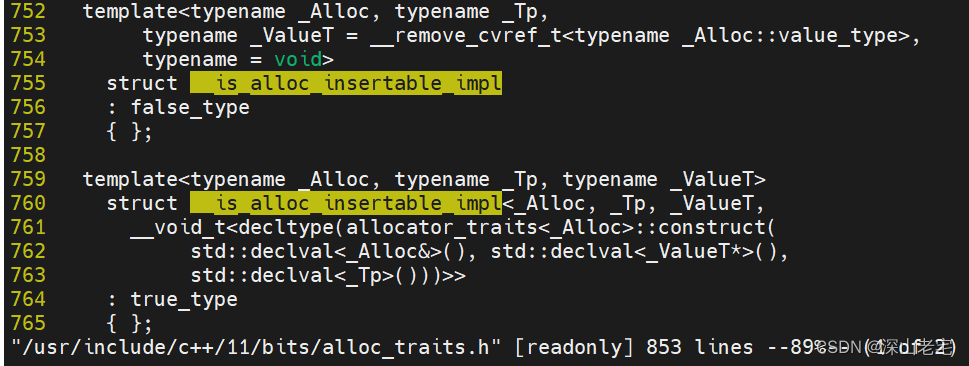 此处用了SFINAE思想,如果_Alloc能用_Tp做参数类型构造一个_ValueT*对象,则匹配true的这个模板,否则false, 分别对应__is_move_insertable的结果。std::allocator及polymorphic_allocator都有construct函数,构造int对象没问题。
此处用了SFINAE思想,如果_Alloc能用_Tp做参数类型构造一个_ValueT*对象,则匹配true的这个模板,否则false, 分别对应__is_move_insertable的结果。std::allocator及polymorphic_allocator都有construct函数,构造int对象没问题。
2. 看std::__relocate_a是否抛出异常,__relocate_a会看__relocate_a_1是否抛出异常,而__relocate_a_1会看__relocate_object_a是否抛出异常,__relocate_object_a是否抛出异常取决于:
984 template<typename _Tp, typename _Up, typename _Allocator>985 inline void986 __relocate_object_a(_Tp* __restrict __dest, _Up* __restrict __orig,987 _Allocator& __alloc)988 noexcept(noexcept(std::allocator_traits<_Allocator>::construct(__alloc,989 __dest, std::move(*__orig)))990 && noexcept(std::allocator_traits<_Allocator>::destroy(991 __alloc, std::__addressof(*__orig))))
std::allocator_traits<_Allocator>::construct 取决于 std::is_nothrow_constructible<_Up, _Args…>::value
std::allocator_traits<_Allocator>::destroy 取决于 is_nothrow_destructible<_Up>::value
以上仅当所有情况都是noexcept为true才会走_S_relocate的分支(不走__uninitialized_move_if_noexcept_a)。
不过除此之外__relocate_a_1还有一个特例:
1000 template<typename _Tp, typename = void>
1001 struct __is_bitwise_relocatable
1002 : is_trivial<_Tp> { };
1003
1004 template <typename _Tp, typename _Up>
1005 inline __enable_if_t<std::__is_bitwise_relocatable<_Tp>::value, _Tp*>
1006 __relocate_a_1(_Tp* __first, _Tp* __last,
1007 _Tp* __result, allocator<_Up>&) noexcept
1008 {
1009 ptrdiff_t __count = __last - __first;
1010 if (__count > 0)
1011 __builtin_memmove(__result, __first, __count * sizeof(_Tp));
1012 return __result + __count;
1013 }
如果_Tp(我的例子里是int)是trivial的 且 分配器是std::allocator,则__relocate_a_1是noexcept的,则走_S_relocate的分支(不走__uninitialized_move_if_noexcept_a)
草草的画了一个流程图(大家凑合看):
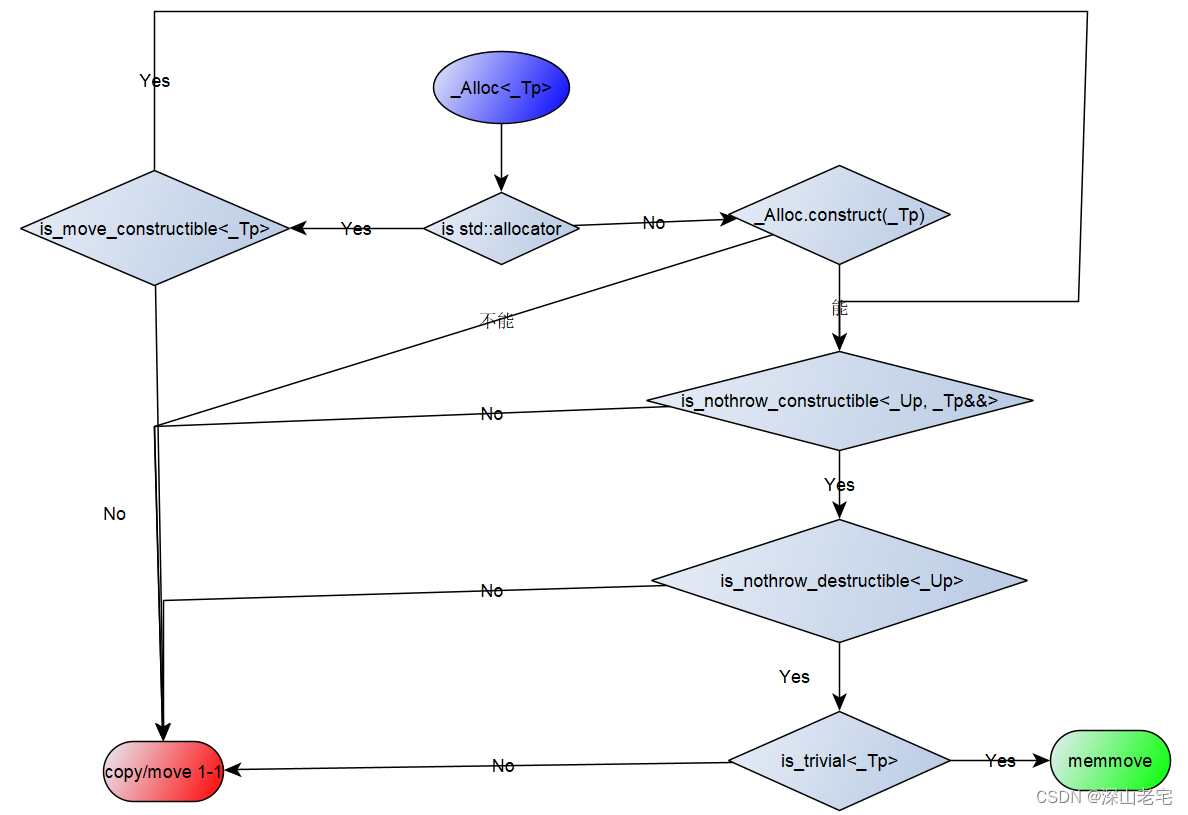
上面两条捋了一遍_S_use_relocate()的结果, 但并不是它是true就一定用memmove,
/usr/include/c++/11/bits/stl_vector.h452 static pointer453 _S_do_relocate(pointer __first, pointer __last, pointer __result,454 _Tp_alloc_type& __alloc, true_type) noexcept455 {456 return std::__relocate_a(__first, __last, __result, __alloc);457 }458459 static pointer460 _S_do_relocate(pointer, pointer, pointer __result,461 _Tp_alloc_type&, false_type) noexcept462 { return __result; }463464 static pointer465 _S_relocate(pointer __first, pointer __last, pointer __result,466 _Tp_alloc_type& __alloc) noexcept467 {468 using __do_it = __bool_constant<_S_use_relocate()>;469 return _S_do_relocate(__first, __last, __result, __alloc, __do_it{});470 }
459行永远也走不到,因为_S_use_relocate()位true才会调用到这,而其值为true则一定匹配452行的函数特化版本。
__relocate_a最终调用到__relocate_a_1,上面提到过它有两个版本:
只有_Tp是trivial 且 用std::allocator 才会调用memmove。
1004 template <typename _Tp, typename _Up>
1005 inline __enable_if_t<std::__is_bitwise_relocatable<_Tp>::value, _Tp*>
1006 __relocate_a_1(_Tp* __first, _Tp* __last,
1007 _Tp* __result, allocator<_Up>&) noexcept
1008 {
1009 ptrdiff_t __count = __last - __first;
1010 if (__count > 0)
1011 __builtin_memmove(__result, __first, __count * sizeof(_Tp));
1012 return __result + __count;
1013 }
1014
1015 template <typename _InputIterator, typename _ForwardIterator,
1016 typename _Allocator>
1017 inline _ForwardIterator
1018 __relocate_a_1(_InputIterator __first, _InputIterator __last,
1019 _ForwardIterator __result, _Allocator& __alloc)
1020 noexcept(noexcept(std::__relocate_object_a(std::addressof(*__result),
1021 std::addressof(*__first),
1022 __alloc)))
1023 {
1024 typedef typename iterator_traits<_InputIterator>::value_type
1025 _ValueType;
1026 typedef typename iterator_traits<_ForwardIterator>::value_type
1027 _ValueType2;
1028 static_assert(std::is_same<_ValueType, _ValueType2>::value,
1029 "relocation is only possible for values of the same type");
1030 _ForwardIterator __cur = __result;
1031 for (; __first != __last; ++__first, (void)++__cur)
5. 看一个简单的class的例子
上面我用的是int,下面用一个简单的类看看,验证下上面的流程图。
我就不分析了,大家执行代码看结果来理解吧。
#include<iostream>
#include<memory_resource>
#include<vector>
#include "../PerfSum.hpp"
using namespace std;struct MyClass{MyClass(int _i):i(_i) {}int i;
};void TestPmrVec(){char buffer[1000000*4] = {0};std::pmr::monotonic_buffer_resource pool{std::data(buffer), std::size(buffer)};std::pmr::vector<MyClass> vec{&pool};PerfSum t;for(int i=0;i<1000000;i++){vec.push_back(MyClass{i});}std::cout<<"End"<<std::endl;}void TestStdVec(){std::vector<MyClass> vec ;PerfSum t;for(int i=0;i<1000000;i++){vec.push_back(MyClass{i});}std::cout<<"End"<<std::endl;}int main() {std::cout<<"is_move_constructible<MyClass>: "<<std::is_move_constructible_v<MyClass><<std::endl;std::cout<<"is_nothrow_constructible<MyClass>: "<<std::is_nothrow_constructible_v<MyClass,MyClass&&><<std::endl;std::cout<<"is_nothrow_destructible<MyClass>: "<<std::is_nothrow_destructible_v<MyClass><<std::endl;std::cout<<"trivail<MyClass>: "<<std::is_trivial_v<MyClass><<std::endl;std::cout<<"std vector cost:"<<std::endl;TestStdVec();std::cout<<"pmr vector cost:"<<std::endl;TestPmrVec();
}