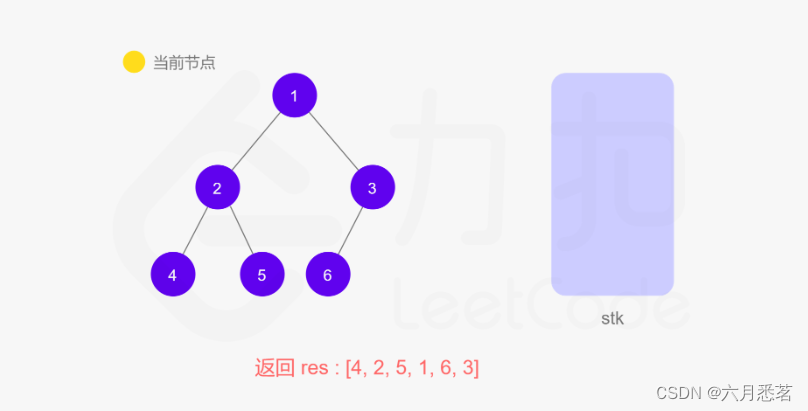
题目描述
给定一个二叉树的根节点 root ,返回 它的 中序 遍历 。

提示:
树中节点数目在范围 [0, 100] 内
-100 <= Node.val <= 100
方法一:递归
思路与算法
首先我们需要了解什么是二叉树的中序遍历:按照访问左子树——根节点——右子树的方式遍历这棵树,而在访问左子树或者右子树的时候我们按照同样的方式遍历,直到遍历完整棵树。因此整个遍历过程天然具有递归的性质,我们可以直接用递归函数来模拟这一过程。
定义 inorder(root) 表示当前遍历到 root 节点的答案,那么按照定义,我们只要递归调用 inorder(root.left) 来遍历 root 节点的左子树,然后将 root 节点的值加入答案,再递归调用inorder(root.right) 来遍历 root 节点的右子树即可,递归终止的条件为碰到空节点。
代码
/*** Definition for a binary tree node.*/
struct TreeNode {int val;struct TreeNode *left;struct TreeNode *right;
};
/*** Note: The returned array must be malloced, assume caller calls free().*//** The inorder function performs an inorder traversal of a binary tree recursively. * It stores the values of the nodes in the result array res and increments the size resSize accordingly. *//** The function "inorder" in the provided code is a recursive function. * When a function calls itself inside its own definition, it is known as recursion. * In this case, the "inorder" function is designed to perform an inorder traversal of a binary tree. * 1. The "inorder" function is called with the root node of the binary tree.* 2. Inside the function, it first checks if the current node is NULL. If it is NULL, the function returns and the recursion stops.* 3. If the current node is not NULL, the function recursively calls itself for the left child of the current node (root->left). This step continues until it reaches a NULL node (i.e., the left subtree is fully traversed).* 4. After traversing the left subtree, the function stores the value of the current node in the result array and increments the size of the result array.* 5. Finally, the function recursively calls itself for the right child of the current node (root->right) to traverse the right subtree.* This recursive process repeats for each node in the binary tree, * effectively performing an inorder traversal by visiting the nodes in the order of left subtree - current node - right subtree. * Each recursive call maintains its own set of variables and execution context, * allowing the function to traverse the entire tree in an ordered manner.*/
void inorder(struct TreeNode* root, int* res, int* resSize) {// Check if the current node is NULLif (!root) {return; // Return if the current node is NULL}// Traverse the left subtree in inorderinorder(root->left, res, resSize);// Store the value of the current node in the result array and increment the sizeres[(*resSize)++] = root->val;// Traverse the right subtree in inorderinorder(root->right, res, resSize);/** `res[(*resSize)++] = root->val;` is not needed here,* because the inorder traversal of a binary tree is structured in such a way that after traversing the left subtree and the current node, * the traversal of the right subtree will naturally continue the process of storing the values in the correct order in the result array `res` .* In an inorder traversal, the sequence of operations ensures that the left subtree is fully explored before visiting the current node, * and then the right subtree is explored after the current node. * Therefore, by the time the function returns from the recursive call `inorder(root->right, res, resSize);` , * the right subtree has been traversed and the values have been stored in the result array in the correct order relative to the current node.* Including `res[(*resSize)++] = root->val;` after the right subtree traversal would result in duplicating the value of the current node in the result array, * which is unnecessary and would disrupt the correct inorder traversal sequence.*/
}
/** The inorderTraversal function initializes the result array, * calls the inorder function to perform the traversal, and then returns the result array. */
int* inorderTraversal(struct TreeNode* root, int* returnSize) {// Allocate memory for the result array// Create an integer array of size 501 dynamically on the heap and assigning the address of the first element of the array to the pointer variable res .int* res = malloc(sizeof(int) * 501);// Initialize the return size to 0*returnSize = 0;// Perform inorder traversal starting from the root nodeinorder(root, res, returnSize);// Return the result array containing the inorder traversal of the binary treereturn res;
}
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:O(n),其中 n 为二叉树节点的个数。二叉树的遍历中每个节点会被访问一次且只会被访问一次。
空间复杂度:O(n)。空间复杂度取决于递归的栈深度,而栈深度在二叉树为一条链的情况下会达到 O(n)的级别。
方法二:迭代
思路与算法
方法一的递归函数我们也可以用迭代的方式实现,两种方式是等价的,区别在于递归的时候隐式地维护了一个栈,而我们在迭代的时候需要显式地将这个栈模拟出来,其他都相同。
代码
/*** Definition for a binary tree node.*/
struct TreeNode {int val;struct TreeNode *left;struct TreeNode *right;
};
/*** An iterative version of the inorder traversal of a binary tree without using recursion.*/
int* inorderTraversal(struct TreeNode* root, int* returnSize) {// Initialize return size to 0*returnSize = 0;// Allocate memory for the result arrayint* res = malloc(sizeof(int) * 501);// Allocate memory for the stack to keep track of nodesstruct TreeNode** stk = malloc(sizeof(struct TreeNode*) * 501);// Initialize top of the stack// variable top to keep track of the top of the stack. int top = 0;// Iterative inorder traversal using a stack// The while loop continues until the current node root is NULL and the stack is empty (indicated by top > 0 ).while (root != NULL || top > 0) {// Traverse left subtree and push nodes onto the stack // a nested while loop to traverse the left subtree of the current node and pushes each node onto the stack. while (root != NULL) {stk[top++] = root;root = root->left;}// Check if the stack is not empty before poppingif (top > 0){// Once the left subtree is fully traversed// Pop a node from the stackroot = stk[--top];// Add the value of the popped node to the result arrayres[(*returnSize)++] = root->val;// Move to the right child of the popped noderoot = root->right;}}// Free the memory allocated for the stackfree(stk);// Return the result array containing inorder traversalreturn res;
}
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:O(n),其中 n 为二叉树节点的个数。二叉树的遍历中每个节点会被访问一次且只会被访问一次。
空间复杂度:O(n)。空间复杂度取决于栈深度,而栈深度在二叉树为一条链的情况下会达到 O(n)的级别。
方法三:Morris 中序遍历
思路与算法
Morris 遍历算法是另一种遍历二叉树的方法,它能将非递归的中序遍历空间复杂度降为 O(1)。
Morris 遍历算法整体步骤如下(假设当前遍历到的节点为 xxx):
- 如果 xxx 无左孩子,先将 xxx 的值加入答案数组,再访问 xxx 的右孩子,即
x=x.right。 - 如果 xxx 有左孩子,则找到 xxx 左子树上最右的节点(即左子树中序遍历的最后一个节点,xxx 在中序遍历中的前驱节点),我们记为 predecessor。根据 predecessor 的右孩子是否为空,进行如下操作。
- 如果 predecessor 的右孩子为空,则将其右孩子指向 xxx,然后访问 xxx 的左孩子,即
x=x.left。 - 如果 predecessor\ 的右孩子不为空,则此时其右孩子指向 xxx,说明我们已经遍历完 xxx 的左子树,我们将 predecessor 的右孩子置空,将 xxx 的值加入答案数组,然后访问 xxx 的右孩子,即
x=x.right。
- 如果 predecessor 的右孩子为空,则将其右孩子指向 xxx,然后访问 xxx 的左孩子,即
- 重复上述操作,直至访问完整棵树。
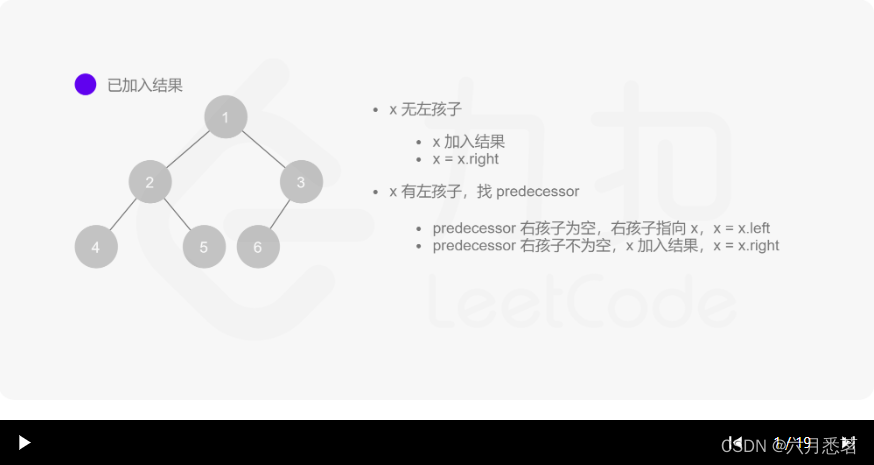
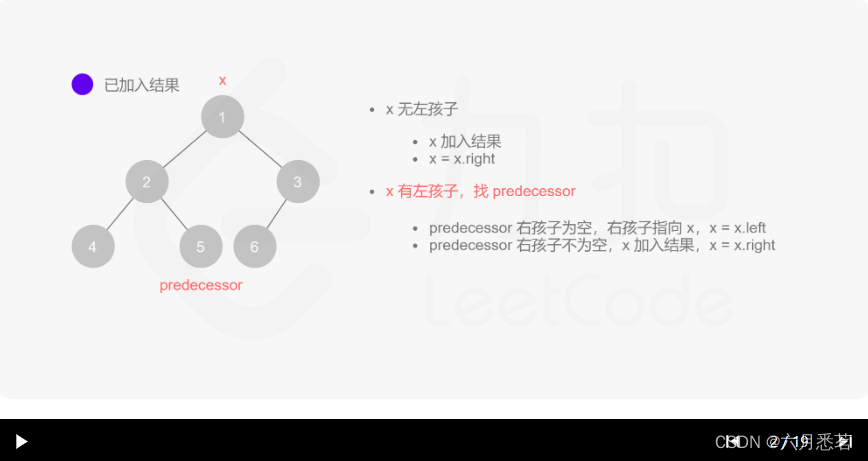
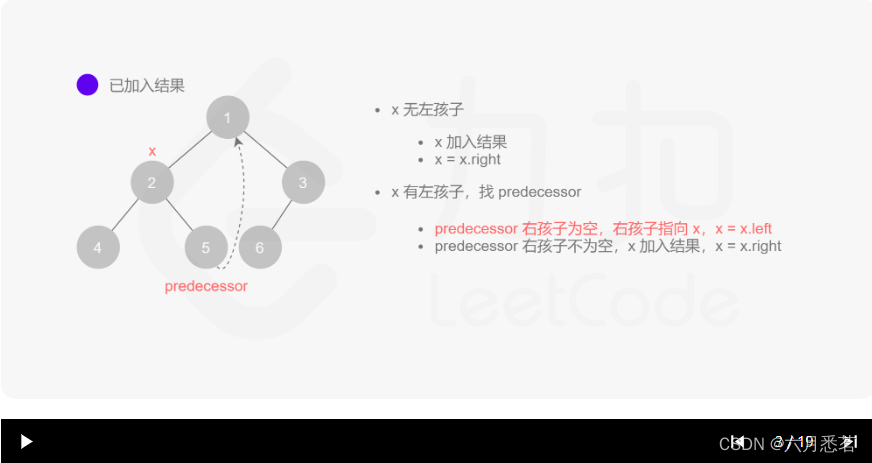
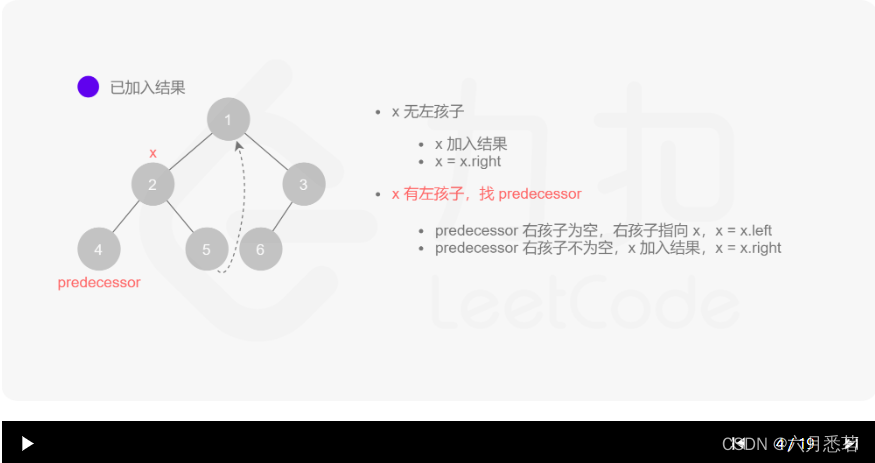
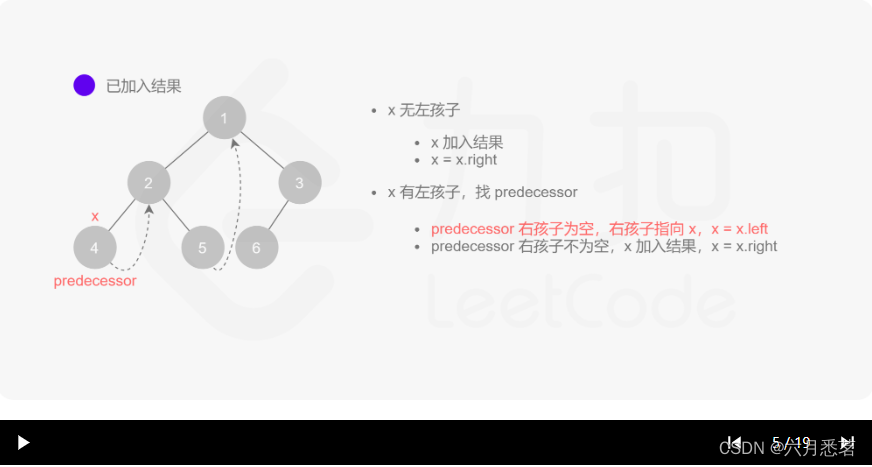
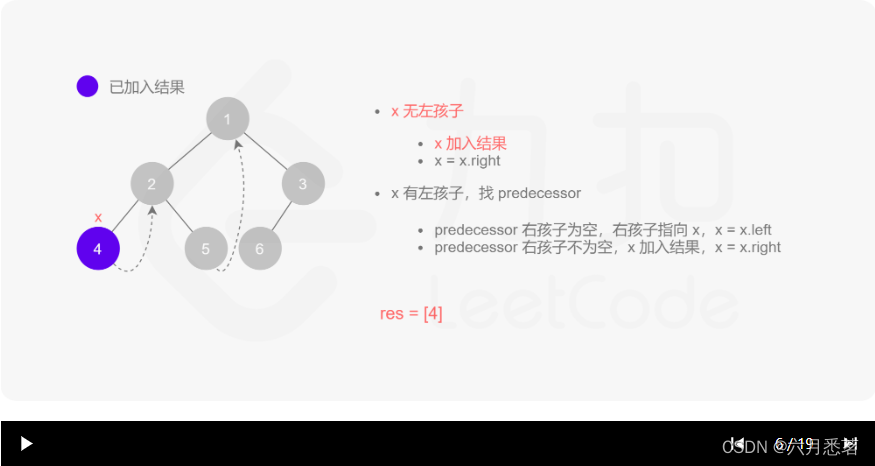
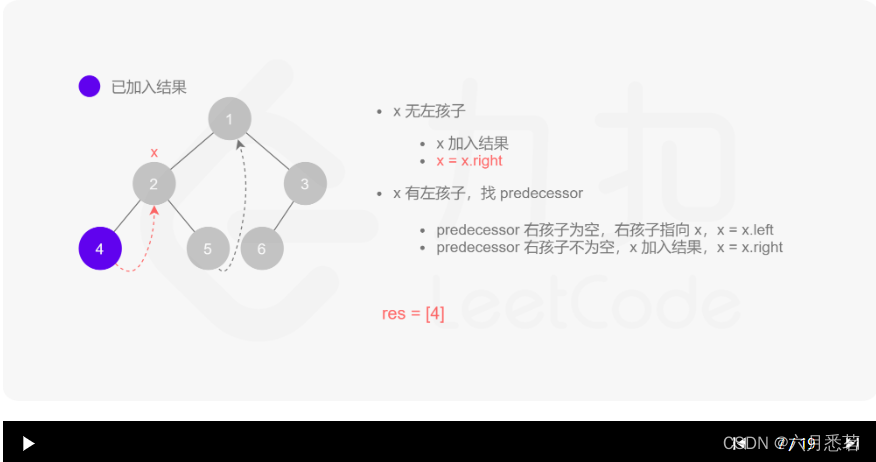
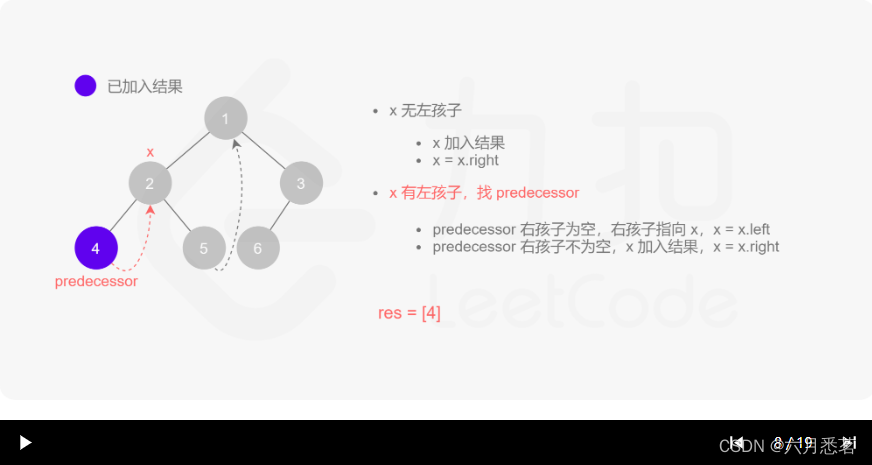
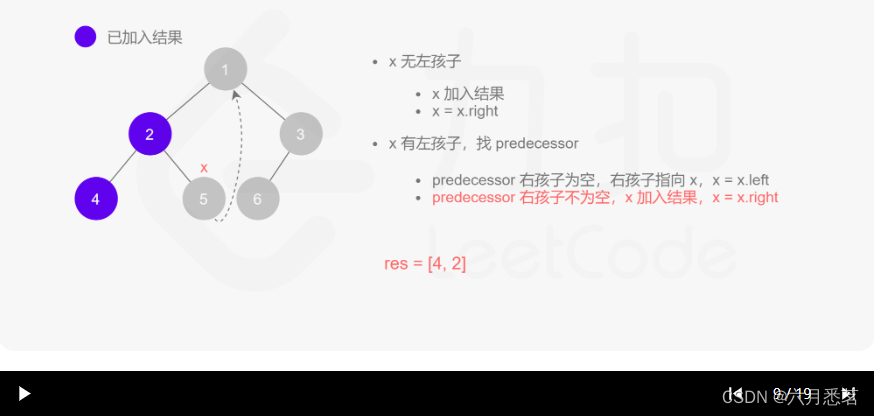
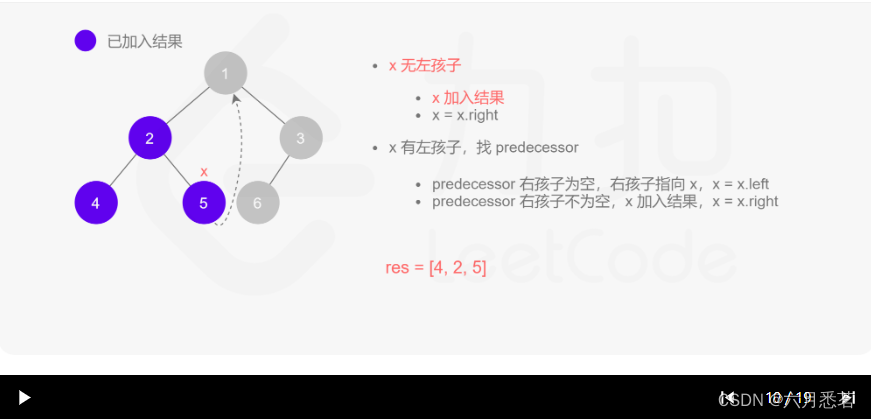
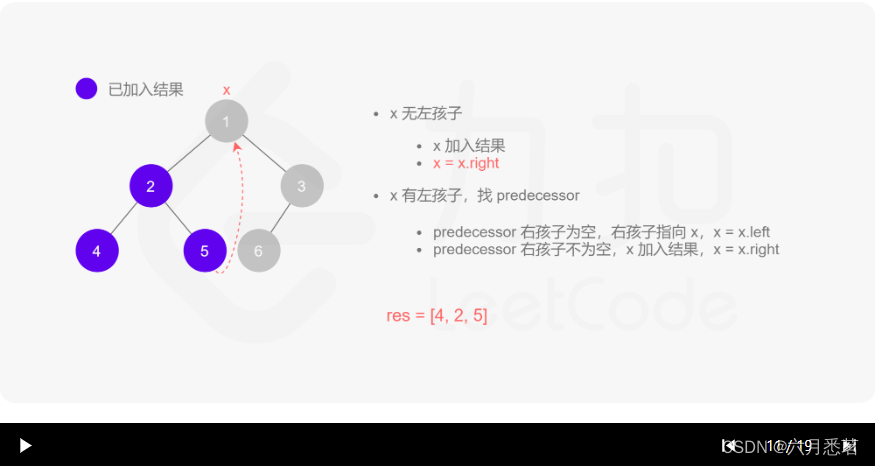
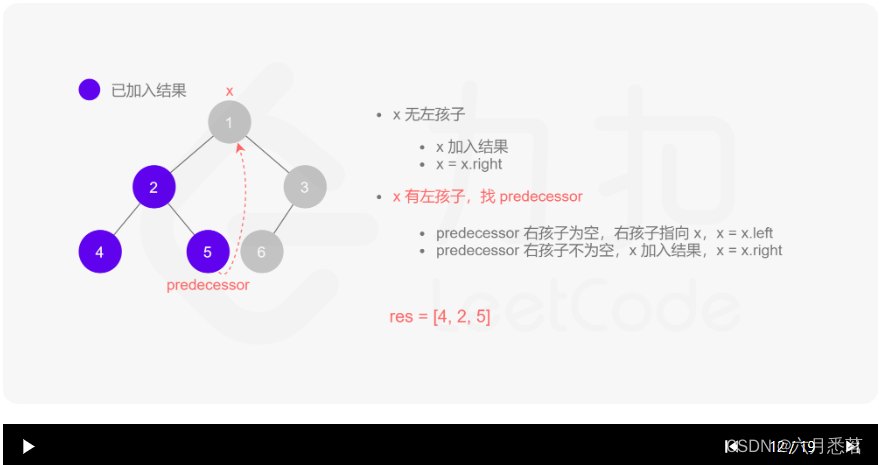
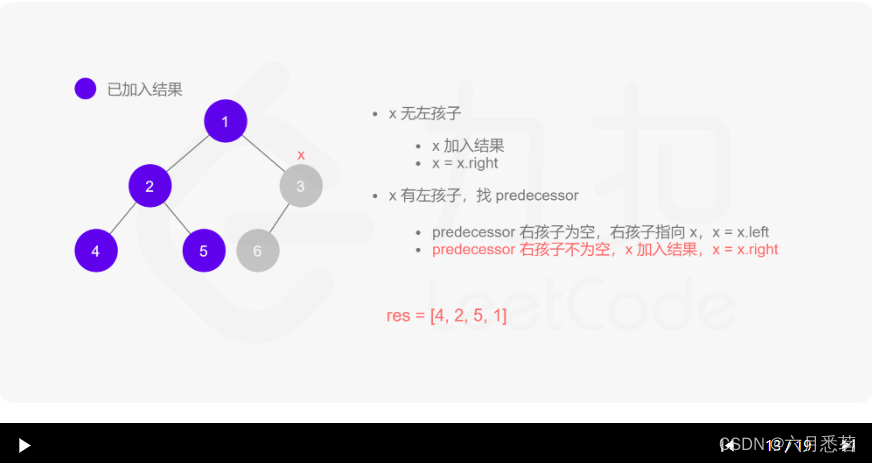
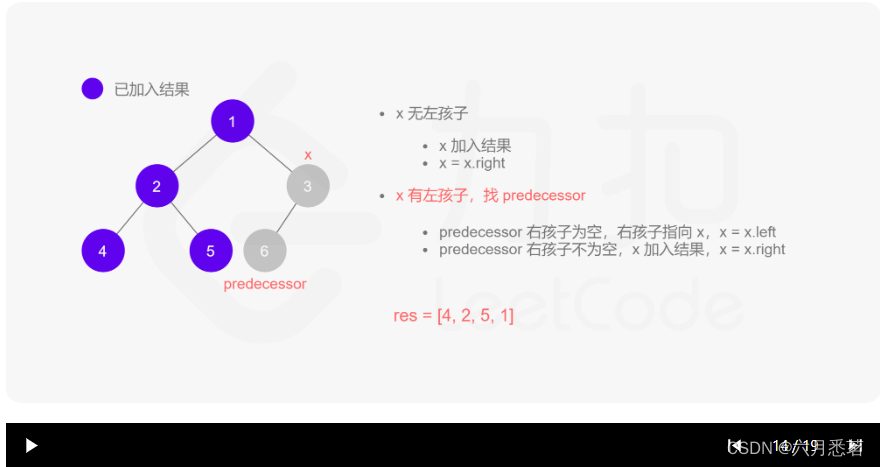
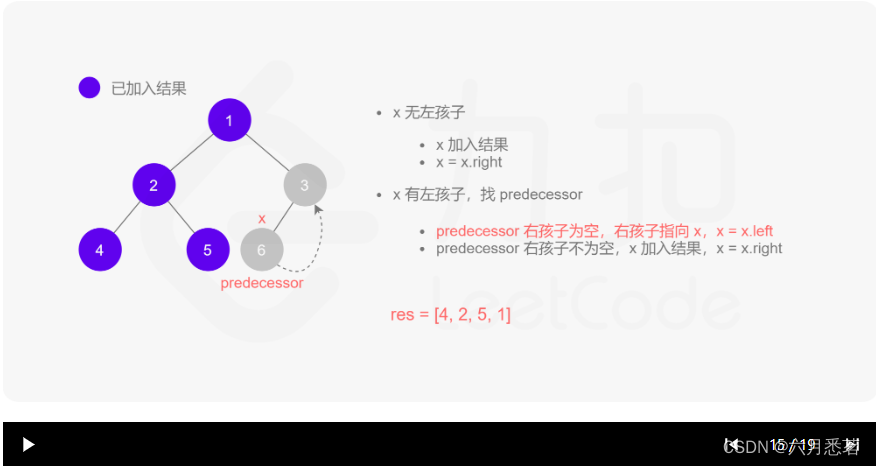
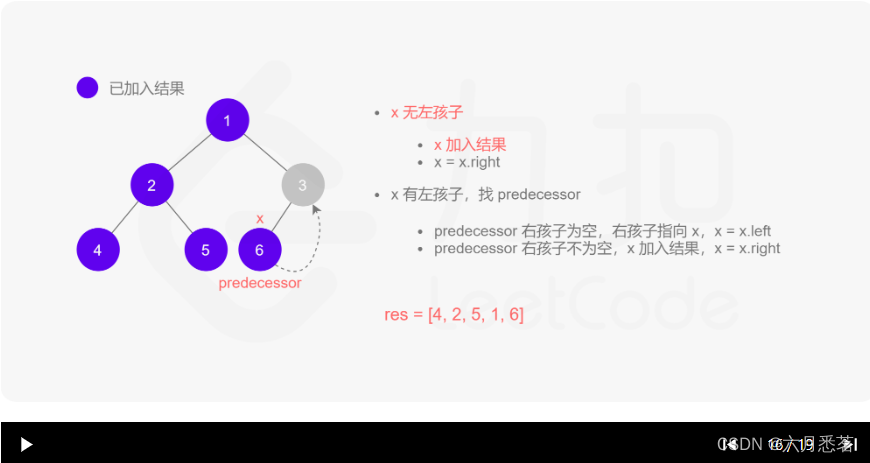
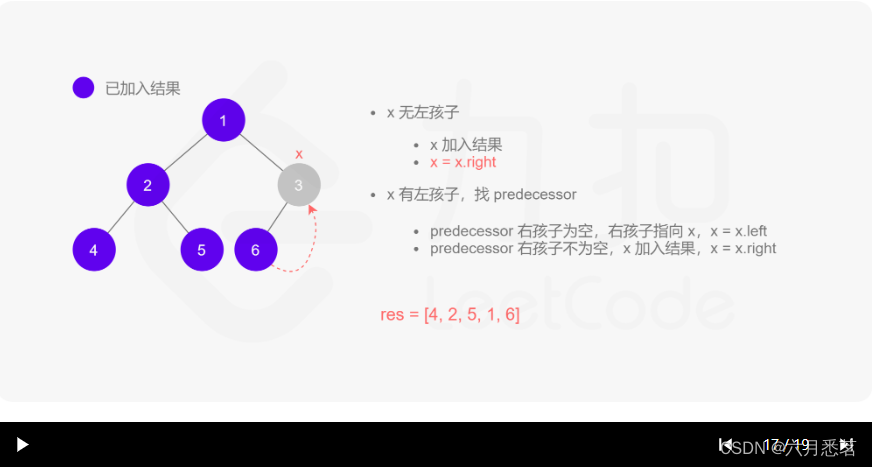
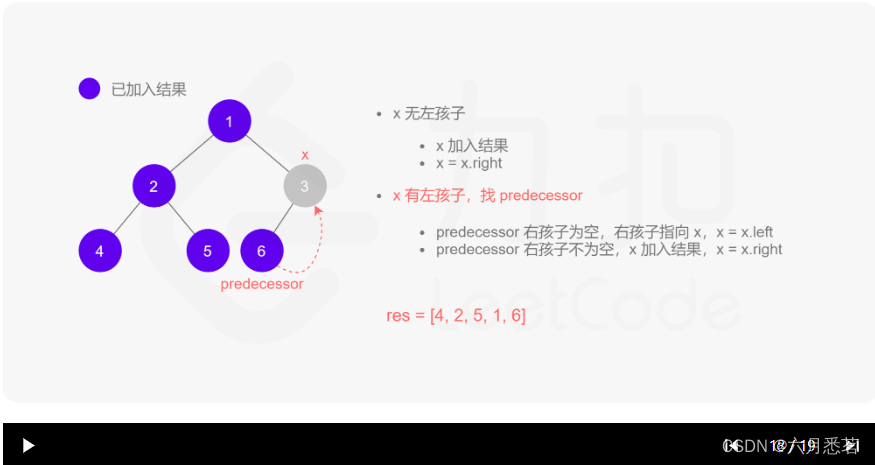
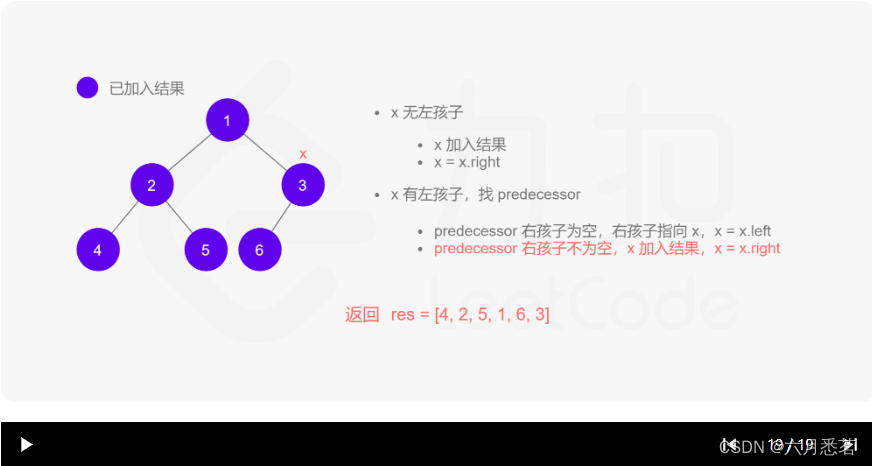
其实整个过程我们就多做一步:假设当前遍历到的节点为 x,将 x 的左子树中最右边的节点的右孩子指向 x,这样在左子树遍历完成后我们通过这个指向走回了 x,且能通过这个指向知晓我们已经遍历完成了左子树,而不用再通过栈来维护,省去了栈的空间复杂度。
代码
/*** Definition for a binary tree node.*/
struct TreeNode {int val;struct TreeNode *left;struct TreeNode *right;
};
/*** The algorithm uses a predecessor node to establish temporary links * between nodes to simulate the recursive call stack * that would be used in a recursive inorder traversal. * This approach allows for an iterative inorder traversal of the binary tree.*/
int* inorderTraversal(struct TreeNode* root, int* returnSize) {// Allocate memory for the result arrayint* res = malloc(sizeof(int) * 501);// Initialize return size to 0*returnSize = 0;// Initialize predecessor node to NULLstruct TreeNode* predecessor = NULL;// Traverse the tree in inorder without using recursionwhile (root != NULL) {// If the current node has a left childif (root->left != NULL) {// Find the predecessor node, which is the rightmost node in the left subtreepredecessor = root->left;while (predecessor->right != NULL && predecessor->right != root) {predecessor = predecessor->right;}// If predecessor's right child is NULL, establish a link and move to the left childif (predecessor->right == NULL) {predecessor->right = root;root = root->left;}// If the left subtree has been visited, disconnect the link and move to the right childelse {res[(*returnSize)++] = root->val;predecessor->right = NULL;root = root->right;}}// If there is no left child, visit the current node and move to the right childelse {res[(*returnSize)++] = root->val;root = root->right;}}// Return the result array containing inorder traversalreturn res;
}
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:O(n),其中 n 为二叉树的节点个数。Morris 遍历中每个节点会被访问两次,因此总时间复杂度为 O(2n)=O(n)。
空间复杂度:O(1)。
作者:力扣官方题解
链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/binary-tree-inorder-traversal/solutions/412886/er-cha-shu-de-zhong-xu-bian-li-by-leetcode-solutio/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。