GitHub - milvus-io/milvus-sdk-java: Java SDK for Milvus.
1、安装Standstone 版本
参考:Linux之milvus向量数据库安装_milvus安装-CSDN博客
参考:Install Milvus Standalone with Docker Milvus documentation
一、安装步骤
1、安装docker
docker的安装见博文Linux之docker安装,这里不再赘述。
2、安装fio命令
yum install -y fio
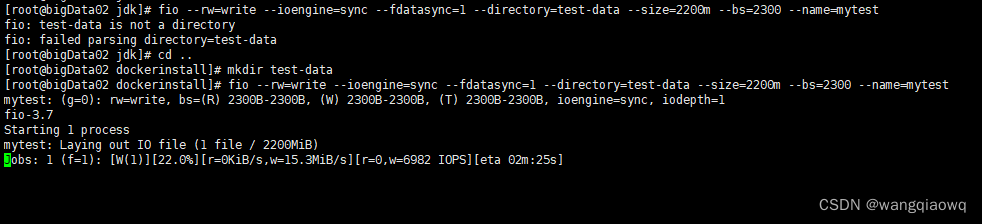
3、磁盘性能测试
fio --rw=write --ioengine=sync --fdatasync=1 --directory=test-data --size=2200m --bs=2300 --name=mytest

4、检查CPU支持的指令集
我们使用lscpu命令可以查看CPU支持的指令集,Flags的参数值就是该服务器支持的CPU指令集
lscpu

5、检查docker版本
根据milvus安装要求,docker版本要求是19.03以上版本,我们这里安装的docker版本为23.0.1,满足要求。

6、安装docker compose组件
根据milvus安装要求,docker compose版本要求是1.25.1以上,我们这里安装的版本是1.29.2,满足要求。
yum -y install python3-pip
pip3 install --upgrade pip
pip install docker-compose

下载
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/milvus-io/milvus/master/scripts/standalone_embed.sh
启动 Start Milvus
bash standalone_embed.sh start

- Stop Milvus
bash standalone_embed.sh stop
- Connect to Milvus
To delete data after stopping Milvus, run:
bash standalone_embed.sh delete
运行
Run Milvus using Python Milvus documentation
安装 PyMilvus

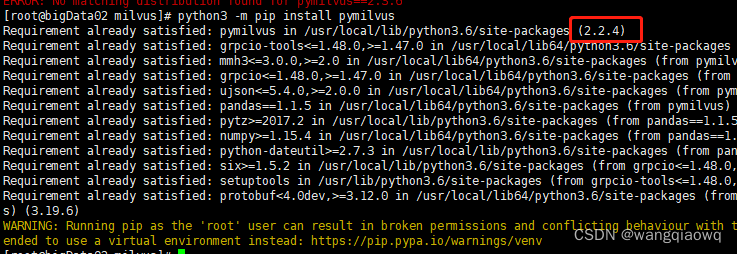
python3 -m pip install pymilvus==2.3.6

python3 -m pip install pymilvus 最新版本是2.2.4
python3 -c "from pymilvus import Collection"
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/milvus-io/pymilvus/master/examples/hello_milvus.py

Run the example code
# hello_milvus.py demonstrates the basic operations of PyMilvus, a Python SDK of Milvus.
# 1. connect to Milvus
# 2. create collection
# 3. insert data
# 4. create index
# 5. search, query, and hybrid search on entities
# 6. delete entities by PK
# 7. drop collection
import timeimport numpy as np
from pymilvus import (connections,utility,FieldSchema, CollectionSchema, DataType,Collection,
)fmt = "\n=== {:30} ===\n"
search_latency_fmt = "search latency = {:.4f}s"
num_entities, dim = 3000, 8#################################################################################
# 1. connect to Milvus
# Add a new connection alias `default` for Milvus server in `localhost:19530`
# Actually the "default" alias is a buildin in PyMilvus.
# If the address of Milvus is the same as `localhost:19530`, you can omit all
# parameters and call the method as: `connections.connect()`.
#
# Note: the `using` parameter of the following methods is default to "default".
print(fmt.format("start connecting to Milvus"))
# connects to a server
connections.connect("default", host="localhost", port="19530")has = utility.has_collection("hello_milvus")
print(f"Does collection hello_milvus exist in Milvus: {has}")#################################################################################
# 2. create collection
# We're going to create a collection with 3 fields.
# +-+------------+------------+------------------+------------------------------+
# | | field name | field type | other attributes | field description |
# +-+------------+------------+------------------+------------------------------+
# |1| "pk" | VarChar | is_primary=True | "primary field" |
# | | | | auto_id=False | |
# +-+------------+------------+------------------+------------------------------+
# |2| "random" | Double | | "a double field" |
# +-+------------+------------+------------------+------------------------------+
# |3|"embeddings"| FloatVector| dim=8 | "float vector with dim 8" |
# +-+------------+------------+------------------+------------------------------+
fields = [FieldSchema(name="pk", dtype=DataType.VARCHAR, is_primary=True, auto_id=False, max_length=100),FieldSchema(name="random", dtype=DataType.DOUBLE),FieldSchema(name="embeddings", dtype=DataType.FLOAT_VECTOR, dim=dim)
]schema = CollectionSchema(fields, "hello_milvus is the simplest demo to introduce the APIs")print(fmt.format("Create collection `hello_milvus`"))
hello_milvus = Collection("hello_milvus", schema, consistency_level="Strong")################################################################################
# 3. insert data
# We are going to insert 3000 rows of data into `hello_milvus`
# Data to be inserted must be organized in fields.
#
# The insert() method returns:
# - either automatically generated primary keys by Milvus if auto_id=True in the schema;
# - or the existing primary key field from the entities if auto_id=False in the schema.
# inserts vectors in the collection
print(fmt.format("Start inserting entities"))
rng = np.random.default_rng(seed=19530)
entities = [# provide the pk field because `auto_id` is set to False[str(i) for i in range(num_entities)],rng.random(num_entities).tolist(), # field random, only supports listrng.random((num_entities, dim)), # field embeddings, supports numpy.ndarray and list
]insert_result = hello_milvus.insert(entities)hello_milvus.flush()
print(f"Number of entities in Milvus: {hello_milvus.num_entities}") # check the num_entities################################################################################
# 4. create index
# We are going to create an IVF_FLAT index for hello_milvus collection.
# create_index() can only be applied to `FloatVector` and `BinaryVector` fields.
# builds indexes on the entities:
print(fmt.format("Start Creating index IVF_FLAT"))
index = {"index_type": "IVF_FLAT","metric_type": "L2","params": {"nlist": 128},
}hello_milvus.create_index("embeddings", index)################################################################################
# 5. search, query, and hybrid search
# After data were inserted into Milvus and indexed, you can perform:
# - search based on vector similarity
# - query based on scalar filtering(boolean, int, etc.)
# - hybrid search based on vector similarity and scalar filtering.
## Before conducting a search or a query, you need to load the data in `hello_milvus` into memory.
# Loads the collection to memory and performs a vector similarity search:
print(fmt.format("Start loading"))
hello_milvus.load()# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# search based on vector similarity
print(fmt.format("Start searching based on vector similarity"))
vectors_to_search = entities[-1][-2:]
search_params = {"metric_type": "L2","params": {"nprobe": 10},
}start_time = time.time()
result = hello_milvus.search(vectors_to_search, "embeddings", search_params, limit=3, output_fields=["random"])
end_time = time.time()for hits in result:for hit in hits:print(f"hit: {hit}, random field: {hit.entity.get('random')}")
print(search_latency_fmt.format(end_time - start_time))# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# query based on scalar filtering(boolean, int, etc.)
print(fmt.format("Start querying with `random > 0.5`"))start_time = time.time()
result = hello_milvus.query(expr="random > 0.5", output_fields=["random", "embeddings"])
end_time = time.time()print(f"query result:\n-{result[0]}")
print(search_latency_fmt.format(end_time - start_time))# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# pagination
r1 = hello_milvus.query(expr="random > 0.5", limit=4, output_fields=["random"])
r2 = hello_milvus.query(expr="random > 0.5", offset=1, limit=3, output_fields=["random"])
print(f"query pagination(limit=4):\n\t{r1}")
print(f"query pagination(offset=1, limit=3):\n\t{r2}")# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# hybrid search
print(fmt.format("Start hybrid searching with `random > 0.5`"))start_time = time.time()
result = hello_milvus.search(vectors_to_search, "embeddings", search_params, limit=3, expr="random > 0.5", output_fields=["random"])
end_time = time.time()for hits in result:for hit in hits:print(f"hit: {hit}, random field: {hit.entity.get('random')}")
print(search_latency_fmt.format(end_time - start_time))###############################################################################
# 6. delete entities by PK
# You can delete entities by their PK values using boolean expressions.
ids = insert_result.primary_keysexpr = f'pk in ["{ids[0]}" , "{ids[1]}"]'
print(fmt.format(f"Start deleting with expr `{expr}`"))result = hello_milvus.query(expr=expr, output_fields=["random", "embeddings"])
print(f"query before delete by expr=`{expr}` -> result: \n-{result[0]}\n-{result[1]}\n")hello_milvus.delete(expr)result = hello_milvus.query(expr=expr, output_fields=["random", "embeddings"])
print(f"query after delete by expr=`{expr}` -> result: {result}\n")###############################################################################
# 7. drop collection
# Finally, drop the hello_milvus collection
print(fmt.format("Drop collection `hello_milvus`"))
utility.drop_collection("hello_milvus")
python3 hello_milvus.py

docker ps

192.168.1.242:9091/api/v1/health
使用浏览器访问连接地址http://ip:9091/api/v1/health,返回{“status”:“ok”}说明milvus数据库服务器运行正常。
docker port milvus-standalone
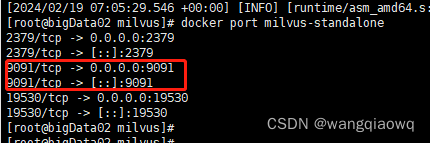
安装Attu
参考:https://github.com/zilliztech/attu/blob/main/doc/zh-CN/attu_install-docker.md
执行:
docker run -p 8000:3000 -e MILVUS_URL=192.168.1.242:19530 zilliz/attu:latest
待参考:kubernetes部署milvus_milvus集群版-CSDN博客

具体使用:
参考:Milvus技术探究 - 知乎 (zhihu.com)