索引器
概念:索引器能够让我们的对象,以索引(下标)的形式,便捷地访问类中的集合(数组、泛型集合、键值对)
应用场景:
1、能够便捷地访问类中的集合
2、索引的数据类型、个数、顺序不固定的时候
索引器与数组的比较:
索引器的索引值(index)类型不受限制
索引器与属性的比较:
a、索引器可以被重载,属性不能
b、索引器不能声明为static,属性可以
internal class Program{static void Main(string[] args){Person p = new Person();Console.WriteLine(p[0]);Console.WriteLine(p[1]);p[2] = "张飞";Console.WriteLine(p[2]);Console.WriteLine(p["张三"]);Console.WriteLine(p["李四"]);p["王五"] = 100;Console.WriteLine(p["王五"]); ;Console.ReadKey();Console.ReadKey();}}class Person{//私有字段存储数组private string[] names = { "张三", "李四", "王五", "赵六", "田七" };//键值对private Dictionary<string, int> dic = new Dictionary<string, int>();//在构造函数里给键值对添加数据public Person(){dic.Add("张三", 1);dic.Add("李四", 2);dic.Add("王五", 3);dic.Add("赵六", 4);}//索引器//string:表示通过索引器获取数据的类型//this:表示索引器的名字,必须是this,不能修改//index:索引的类型public string this[int index]{get { return names[index]; }//通过索引取得数组中的值set { names[index] = value; }//给数组中的某个元素赋值}//索引器是可以重载的public int this[string key]{get { return dic[key]; }set { dic[key] = value; }}}索引器案例
internal class Program{//根据员工的姓名、编号,查找员工所在部门。//根据员工的姓名、部门,查找员工的编号。//根据员工的部门、编号,查找员工的姓名。static void Main(string[] args){EmployeeIndexer emps = new EmployeeIndexer();string dep = emps["张三", 1];if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(dep)){Console.WriteLine(dep);}else{Console.WriteLine("查无此人");}int? id = emps["李四", "研发部"];if (id != null){Console.WriteLine(id);}else{Console.WriteLine("查无此人");}Console.ReadKey();}class Employee //员工类{public string Name { get; set; } //员工姓名public int ID { get; set; } //员工编号public string Department { get; set; } //员工部门public Employee(string name, int iD, string department){this.Name = name;this.ID = iD;this.Department = department;}}class EmployeeIndexer //员工的索引类,负责对员工信息进行精确的查询{private List<Employee> listEmps = new List<Employee>();public EmployeeIndexer(){listEmps.Add(new Employee("张三", 1, "行政部"));listEmps.Add(new Employee("李四", 2, "财务部"));listEmps.Add(new Employee("王五", 3, "研发部"));listEmps.Add(new Employee("赵六", 4, "人事部"));}//根据员工的姓名、编号,查找员工所在部门。public string this[string name,int id]{get{for (int i = 0; i < listEmps.Count; i++){if (listEmps[i].Name == name && listEmps[i].ID==id){return listEmps[i].Department;}}return null;}}//根据员工的姓名、部门,查找员工的编号。public int? this[string name, string dep] // int? ? 可空的值类型{get{for (int i = 0; i < listEmps.Count; i++){if (listEmps[i].Name == name && listEmps[i].Department == dep){return listEmps[i].ID;}}return null;}}//根据员工的部门、编号,查找员工的姓名。public string this[int id, string dep]{get{for (int i = 0; i < listEmps.Count; i++){if (listEmps[i].ID == id && listEmps[i].Department == dep){return listEmps[i].Name;}}return null;}}}}foreach的循环原理
1、要被循环的对象,需要实现IEnumerable接口
2、需要给被循环的对象,创建一个遍历的对象,并且要实现IEnumerator接口
3、 Current:返回当前遍历到的数据元素
MoveNext:判断时候可以继续向后循环,并改变index的值
Reset:重置索引
通过代码实现foreachinternal class Program{//foreach的循环原理//只有实现了IEnumerable这个接口的对象才能被foreachstatic void Main(string[] args){Person p = new Person();//获取遍历Person对象的人IEnumerator enumerator = p.GetEnumerator();//开始遍历while (enumerator.MoveNext()){Console.WriteLine(enumerator.Current.ToString());}//IEnumerable :要被遍历的对象必须实现这个接口//IEnumerator: 遍历对象的迭代器对象,要实现Console.ReadKey();//或者可以直接使用foreachforeach (var item in p){Console.WriteLine(item);}Console.ReadKey();}}class Person : IEnumerable{//IEnumerable : 接口,表示可以被foreach遍历的能力//IEnumerator:真正做遍历集合这件事儿的人//GetEnumerator:获取做遍历集合这件事儿的人private string[] names = { "张三", "李四", "王五", "赵六", "田七" };public IEnumerator GetEnumerator(){return new PersonEnumerator(names);}}//枚举/迭代/遍历class PersonEnumerator : IEnumerator{string[] myNames;int index = -1;//构造函数:获取要遍历的真实数据public PersonEnumerator(string[] names){this.myNames = names;}//Current表示返回当前遍历到的元素,object类型public object Current{//索引没有越界的情况get{if (index>=0&&index<this.myNames.Length){return this.myNames[index];}return null;//数组越界了}}//1、索引+1//2、判断是否可以继续向后移动(+1),//如果可以继续向后+1.则索引+1,并且返回true//如果不可以向后+1,返回falsepublic bool MoveNext(){if (index+1<this.myNames.Length){index++;return true;}else{return false;}}//重置索引,让索引回到原始位置public void Reset(){index= -1;}}泛型
概念:在某些情况,我们不想使用特定的数据类型,可以使用泛型
internal class Program{static void Main(string[] args){Person<int> person = new Person<int>();person.SayHi(199);Person<string> person2 = new Person<string>();person2.SayHi("张三");Person<double> person3 = new Person<double>();person3.SayHi_2<string>(3.14, "李四");person3.SayHi_2(3.14);double d = person3.SayHi_3(11.11);Console.WriteLine(d);int n = person3.SayHi_4<int>(3.14, 100);Console.WriteLine(n);int n2 = person3.SayHi_5<int>(3.14);Console.WriteLine(n2);Console.ReadKey();}}//泛型类class Person<T>{public void SayHi(T t){Console.WriteLine(t);}//泛型方法public void SayHi_2<K>(T t, K k){Console.WriteLine(t);Console.WriteLine(k);}//泛型方法也可以重载public void SayHi_2(T t){Console.WriteLine(t);}//返回值类型为T,参数为Tpublic T SayHi_3(T t){return t;}//返回值类型为K,参数为T和Kpublic K SayHi_4<K>(T t, K k){return k;}//返回值类型为K,参数为Kpublic K SayHi_5<K>(K k){return k;}//泛型方法中的返回值如何处理?//1、使用typeof关键字判断泛型的类型//2、使用object作为中间量进行强制转换//3、return defalut。default会返回数据类型的默认值public K SayHi_5<K>(T t){K k;//如果k的类型是intif (typeof(K) == typeof(int)){return (K)(object)100;}else if (typeof(K) == typeof(string)){return (K)(object)"Hello World";}else if (typeof(K) == typeof(double)){return (K)(object)3.14;}else{//返回K类型的默认值return default;}}//泛型接口interface IFlayble<T>{void Fly(T t);}class Plane : IFlayble<string>{public void Fly(string t){throw new NotImplementedException();}}class Bird : IFlayble<int>{public void Fly(int t){throw new NotImplementedException();}}}泛型约束
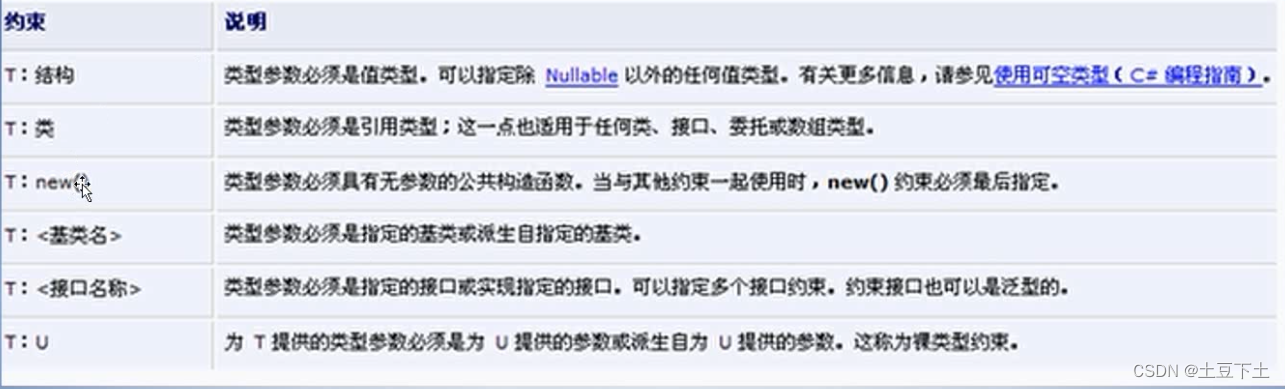
internal class Program{static void Main(string[] args){Person<int> person = new Person<int>();Student<Person<int>> student2 = new Student<Person<int>>();Teacher<Animal> t1 = new Teacher<Animal>();Teacher<Bird> t2 = new Teacher<Bird>();Plane<IFly> plane = new Plane<IFly>();Plane<MaQue> p2 = new Plane<MaQue>();Computer<int, IComparable> cpu = new Computer<int, IComparable>();Computer<FileStream, Stream> cpu2 = new Computer<FileStream, Stream>();}}//泛型约束//where 表示类型要符合的条件class Person<T> where T : struct //值类型约束{}class Student<T> where T : class, new() //引用类型约束{}class Animal { }class Bird : Animal { }interface IFly{void Fly();}class MaQue : IFly{public void Fly(){}}class Teacher<T> where T : Animal { }class Plane<T> where T : IFly { }class Computer<T, U> where T : U { }委托
概念:把方法作为参数,传递给另一个方法
委托,就是一个方法的指针
声明委托:public delegate(委托的关键字) 返回值类型 委托名称(参数列表)
使用委托:创建委托对象,指向某一个跟委托签名一致的方法(签名:参数和返回值)
internal class Program{public delegate void Del();//无参数无返回值的委托public delegate void Del2(string name);//参数为string的委托public delegate int Del3(string name, int age);//有两个参数,返回值为int类型的委托static void Main(string[] args){//虽然在代码层面没有创建委托对象,但是编译器在编译的时候,依然会帮助我们创建一个委托对象//这个委托对象,在内存中指向M1方法Del del = M1;//等同于 Del del = new Del(M1);del(); //对M1方法的直接调用del.Invoke();//对方法的间接调用Del2 del2 = M2;del2("张三");del2.Invoke("李四");Del3 del3 = M3;//委托与他指向的方法签名,必须完全一致,M4的话会报错int res = del3("张三", 18);Console.WriteLine(res);Console.ReadKey();}static void M1(){Console.WriteLine("无参数无返回值的方法");}static void M2(string name){Console.WriteLine("参数string,无返回值的方法");Console.WriteLine(name);}static int M3(string name,int age){Console.WriteLine("两个参数,返回值为int的方法");Console.WriteLine(name);Console.WriteLine(age);return 100;}static int M4(int age,string name){Console.WriteLine("和上面方法的参数类型不同");return 200;}}委托案例
{public delegate string DelProStr(string str);internal class Program{static void Main(string[] args){//处理字符串数组//1、给字符串数组的两边,添加双引号//2、给字符串数组全部转换为大写//3、给字符串数组全部转换为小写string[] names = { "Jay", "James", "green", "blue" };//SYH(names);//StrToUpper(names);//StrToLower(names);ProcessStr(names, StrToSYH);ProcessStr(names, StrToUpper);foreach (var item in names){Console.WriteLine(item);}Console.ReadKey();}static void ProcessStr(string[] names, DelProStr del){for (int i = 0; i < names.Length; i++){names[i] = del(names[i]);}}static string StrToSYH(string str){return "\"" + str + "\"";}static string StrToUpper(string str){return str.ToUpper();}static string StrToLower(string str){return str.ToLower();}把数组中的每一个元素,加双引号//static void SYH(string[] names)//{// for (int i = 0; i < names.Length; i++)// {// names[i] = "\"" + names[i] + "\"";// }//}把数组中的每一个元素,转成大写//static void StrToUpper(string[] names)//{// for (int i = 0; i < names.Length; i++)// {// names[i] = names[i].ToUpper();// }//}把数组中的每一个元素,转成小写//static void StrToLower(string[] names)//{// for (int i = 0; i < names.Length; i++)// {// names[i] = names[i].ToLower();// }//}}
}使用委托计算两个数的最大值
{public delegate int DelCompare<T>(T o1, T o2); //比较o1和o2的值 让o1-o2 > 0internal class Program{static void Main(string[] args){//求数组的最大值 int string Personint[] numbers = { 1, 2, 3, 43, 45 };string[] names = { "ab", "James", "abcdefg" };Person[] pers = { new Person() { Name = "张三", Age = 19 }, new Person() { Name = "李四", Age = 20 }, new Person() { Name = "王五", Age = 22 } };int max = GetMax(numbers, GetIntMax);string max2 = GetMax(names, GetStringMax);Person max3 = GetMax(pers, GetPersonMax);Console.WriteLine(max3.Name);Console.WriteLine(max2);Console.ReadKey();}static T GetMax<T>(T[] nums, DelCompare<T> del) //不同点1:返回值不一样 不同点2:参数不一样 不同点3:比较的方式不一样{T max = nums[0];for (int i = 0; i < nums.Length; i++){//nums[i] > maxif (del(nums[i], max) > 0) //比较的方式,因为要比较的数据类型是不一样的,所以比较的方式也是不一样的。{max = nums[i];}}return max;}static int GetIntMax(int o1, int o2){//值类型---->引用类型:装箱 //int n1 = (int)o1;//int n2 = (int)o2;return o1 - o2;}static int GetStringMax(string o1, string o2){//string s1 = (string)o1;//string s2 = (string)o2;return o1.Length - o2.Length;}static int GetPersonMax(Person o1, Person o2){//Person p1 = (Person)o1;//Person p2 = (Person)o2;return o1.Age - o2.Age;}//求整数类型数组的最大值//static int GetMax(int[] nums) //不同点1:返回值不一样 不同点2:参数不一样 不同点3:比较的方式不一样//{// int max = nums[0];// for (int i = 0; i < nums.Length; i++)// {// if (nums[i] > max)// {// max = nums[i];// }// }// return max;//}求字符串数组的最大值(字符串的长度)//static string GetMax(string[] names)//{// string max = names[0];// for (int i = 0; i < names.Length; i++)// {// if (names[i].Length > max.Length)// {// max = names[i];// }// }// return max;//}求Person数组中,年龄最大的人//static Person GetMax(Person[] pers)//{// Person max = pers[0];// for (int i = 0; i < pers.Length; i++)// {// if (pers[i].Age > max.Age)// {// max = pers[i];// }// }// return max;//}}class Person{public int Age { get; set; }public string Name { get; set; }}
}使用lambda表达式简化上述代码
public delegate int DelCompare<T>(T o1, T o2);//比较o1和o2的值internal class Program{static void Main(string[] args){//求数组的最大值 int string Personint[] numbers = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };string[] names = { "ab", "abc", "avcdsf" };Person[] pers = { new Person() { Name = "张三", Age = 18 }, new Person() { Name = "李四", Age = 20 }, new Person() { Name = "王五", Age = 25 } };//调用泛型方法int intMax = GetMax<int>(numbers, (a, b) => { return a - b; });//lambda表达式:方法的极致的简化写法Console.WriteLine(intMax);string stringMax = GetMax(names, (a, b) => { return a.Length-b.Length; });//如果后面的参数,都是并且只有一个T,则<>可以省略,当你填入第一个参数的时候,所有的T就已经确定了Console.WriteLine(stringMax);Person personMax = GetMax(pers, (a, b) => { return a.Age-b.Age; });Console.WriteLine(personMax.Name);Console.ReadKey();}//写一个泛型方法,用于计算任意类型数组的最大值static T GetMax<T>(T[]nums,DelCompare<T> del){T max = nums[0];for (int i = 0; i < nums.Length; i++){if (del(nums[i],max)>0){max = nums[i];}}return max;}}class Person{public int Age { get; set; }public string Name { get; set;}}