在小节里面介绍了二进制信号量,计数信号量,互斥量和递归互斥量等功能,其中二进制信号量和计数信号量(也包括队列)常用于任务和任务之间以及任务和中断之间的同步,她们具有以下属性:
- 当等待的事件没有发生的时候可以让等待的任务进入阻塞状态
- 当等待的事件发生之后可以将因为等待事件发生而进入阻塞状态的任务唤醒,如果有多个任务在等待同一个事件发生的话,那么此时被唤醒的是优先级最高的任务,其它任务依然还是处于阻塞状态。
这里即将要介绍的事件组( E v e n t G r o u p s Event\quad Groups EventGroups)也可以用于任务和任务之间以及任务和中断之间的同步,但是和二进制信号量,计数信号量(也包括队列)不同的是:
- 事件组可以用于等待多个事件的发生而进行同步,而不是像二进制信号量和计数信号量(也包括队列)只能用于等待单一的事件而进行同步
- 当等待的事件中的事件发生的时候可以唤醒多个任务而不是像二进制信号量和计数信号量(也包括队列)只能用于唤醒多个任务中优先级最高的那个任务。
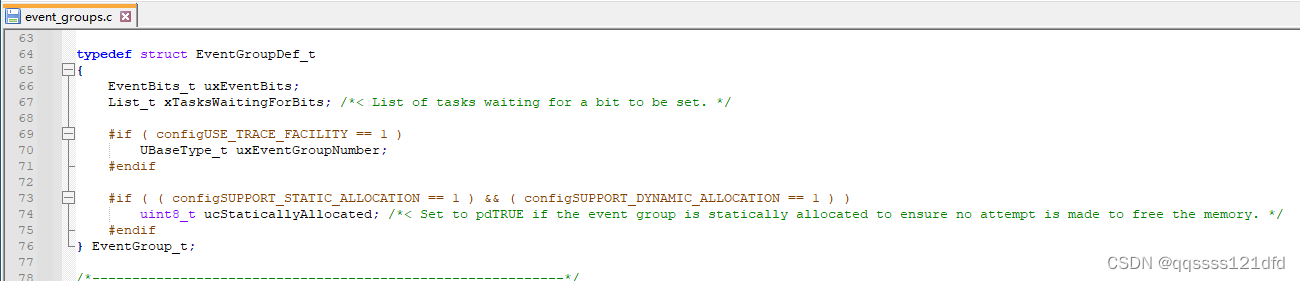
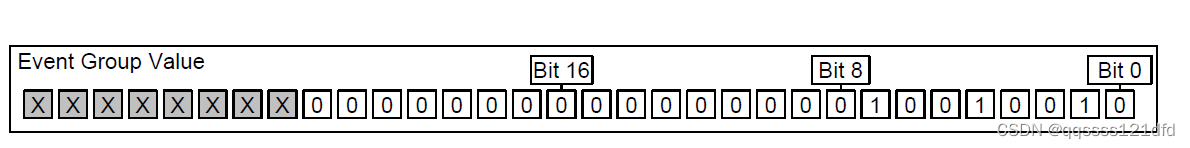
事件组以上的特有属性使得事件组非常适合于多个任务的同步,可以将事件的发生广播给多个任务,也允许一个任务等待一个或多个事件的发生来同步。事件组在 F r e e R T O S FreeRTOS FreeRTOS的源码的 e v e n t g r o u p s . c event_groups.c eventgroups.c文件中用一个结构体来定义,如图1所示。当宏 c o n f i g U S E _ 16 _ B I T _ T I C K S configUSE\_16\_BIT\_TICKS configUSE_16_BIT_TICKS被定义为0的时候,变量 u x E v e n t B i t s uxEventBits uxEventBits的低24位可以用来表示24个事件的状态,如果对应的比特位的值为1则表面对应的事件已经发生,反之对应的事件没有发生,变量 u x E v e n t B i t s uxEventBits uxEventBits的高8位用于特殊用途(对应于图2中的那些宏定义,至于其具体的含义需要通过相应的源码来了解其具体含义)。当宏 c o n f i g U S E _ 16 _ B I T _ T I C K S configUSE\_16\_BIT\_TICKS configUSE_16_BIT_TICKS被定义为1的时候,变量 u x E v e n t B i t s uxEventBits uxEventBits的低8位可以用来表示8个事件的状态,如果对应的比特位的值为1则表面对应的事件已经发生,反之对应的事件没有发生,变量 u x E v e n t B i t s uxEventBits uxEventBits的高8位用于特殊用途(对应于图2中的那些宏定义,至于其具体的含义需要通过相应的源码来了解其具体含义)。
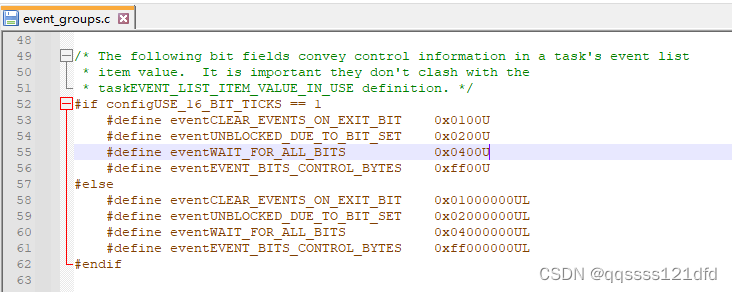
在图3的例子中,这里宏 c o n f i g U S E _ 16 _ B I T _ T I C K S configUSE\_16\_BIT\_TICKS configUSE_16_BIT_TICKS被定义为0,比特位1,4,和7对应的事件已经发生而其它比特位对应的事件还没有发生。事件组可以被多个任务或中断接入,任何任务都有权限对事件组结构体中的变量 u x E v e n t B i t s uxEventBits uxEventBits的低8位或低24位的比特位进行置位,任何任务也都有权限对事件组结构体中的变量 u x E v e n t B i t s uxEventBits uxEventBits进行读取。事件组的结构体的 x T a s k s W a i t i n g F o r B i t s xTasksWaitingForBits xTasksWaitingForBits元素是一个用来记录因为在等待事件组的某个或某些事件而被阻塞的任务。
下面来简单的看几个事件组的 A P I API API接口函数,其它的 A P I API API接口函数可以自己去看看图4所示的文档的详细介绍。
EventBits_t xEventGroupSetBits( EventGroupHandle_t xEventGroup, const EventBits_t uxBitsToSet )
BaseType_t xEventGroupSetBitsFromISR( EventGroupHandle_t xEventGroup,const EventBits_t uxBitsToSet,BaseType_t * pxHigherPriorityTaskWoken ){BaseType_t xReturn;traceEVENT_GROUP_SET_BITS_FROM_ISR( xEventGroup, uxBitsToSet );xReturn = xTimerPendFunctionCallFromISR( vEventGroupSetBitsCallback, ( void * ) xEventGroup, ( uint32_t ) uxBitsToSet, pxHigherPriorityTaskWoken ); /*lint !e9087 Can't avoid cast to void* as a generic callback function not specific to this use case. Callback casts back to original type so safe. */return xReturn;}EventBits_t xEventGroupWaitBits( EventGroupHandle_t xEventGroup,const EventBits_t uxBitsToWaitFor,const BaseType_t xClearOnExit,const BaseType_t xWaitForAllBits,TickType_t xTicksToWait )
接口 x E v e n t G r o u p S e t B i t s xEventGroupSetBits xEventGroupSetBits用来对事件组的结构体里面的变量 u x E v e n t B i t s uxEventBits uxEventBits的低24位或低8位的比特位进行置位,表示对应的比特位表示的事件已经发生,参数 x E v e n t G r o u p xEventGroup xEventGroup表示将要对其进行置位操作的事件组,参数 u x B i t s T o S e t uxBitsToSet uxBitsToSet表示将要对那些比特位进行置位,如果参数 u x B i t s T o S e t uxBitsToSet uxBitsToSet的值为 0 x 00000024 0x00000024 0x00000024且置位操作之前事件组的结构体里面的变量 u x E v e n t B i t s uxEventBits uxEventBits的值为 0 x 00008100 0x00008100 0x00008100,那置位之后事件组的结构体里面的变量 u x E v e n t B i t s uxEventBits uxEventBits的值应该为 0 x 00008124 0x00008124 0x00008124(假设在此期间没有其它任务对这个事件组进行置位或清除操作),也就是说置位操作不会将置位操作以前已经是值1的比特位变成值0,这是因为在进行置位操作的时候进行的是或运算。该接口不能在中断中调用,因为 F r e e R T O S FreeRTOS FreeRTOS的设计理念不允许在中断中进行会产生不确定行行为的操作,这是因为事件组中的事件的发生可以唤醒多个事件,至于具体是几个,我们是无法知道的,因此对事件组的置位操作属于是不确定的操作。该接口对应的中断版本为 x E v e n t G r o u p S e t B i t s F r o m I S R xEventGroupSetBitsFromISR xEventGroupSetBitsFromISR,该接口将事件组的置位操作(其实最后调用的也是接口 x E v e n t G r o u p S e t B i t s xEventGroupSetBits xEventGroupSetBits)转移到 t h e R T O S d a e m o n t a s k the\quad RTOS\quad daemon\quad task theRTOSdaemontask(该点涉及的内容应该是在 S o f t w a r e T i m e r M a n a g e m e n t Software\quad Timer\quad Management SoftwareTimerManagement章节)中进行。我们再来看以下接口 x E v e n t G r o u p W a i t B i t s xEventGroupWaitBits xEventGroupWaitBits,该接口用来等待事件组中的某个单一事件或多个事件的发生,如果等待的事件没有发生则等待参数 x T i c k s T o W a i t xTicksToWait xTicksToWait指定的时间,如果在这个参数指定的时间之内等待的事件发生了,则等待事件的任务会被马上唤醒,如果在这个参数指定的时间之内等待的事件没有发生,也就是等待超时了,等待事件的任务也会离开等待状态。参数 u x B i t s T o W a i t F o r uxBitsToWaitFor uxBitsToWaitFor表示要等待的事件,参数 x W a i t F o r A l l B i t s xWaitForAllBits xWaitForAllBits就很好的体现了事件组的使用可以用来等待多个事件的这个特殊属性,当这个参数的值为pdFALSE的时候,如果参数 u x B i t s T o W a i t F o r uxBitsToWaitFor uxBitsToWaitFor指定了5个事件,那么只要这5个事件中的任何一个发生,等待的任务就会被唤醒,当这个参数的值为pdTRUE的时候,如果参数 u x B i t s T o W a i t F o r uxBitsToWaitFor uxBitsToWaitFor指定了5个事件,那么只有这5个事件全部发生的时候,等待的任务才会被唤醒。
接下来弄了个简单的例子来简单的跑一跑事件组,主要代码如下所示,完整的工程代码在这里,这个例子创建了两个任务,一个任务用来等待事件组中的三个事件的发生,如果这三个事件没有发生的话就一直等待,另一个任务用来对这三个事件在事件组中对应的比特位进行置位,这三个事件分别对应开发板上面的三个按键的一次按下,当开发板上面的三个按键都被按下一次之后,等待事件的任务就会被唤醒。
static EventGroupHandle_t Event_Handle =NULL;/* Definitions for the event bits in the event group. */
#define KEY0_PRESSED_BIT ( 1UL << 0UL ) /* Event bit 0, which is set by a task. */
#define KEY1_PRESSED_BIT ( 1UL << 5UL ) /* Event bit 5, which is set by a task. */
#define KEY_UP_PRESSED_BIT ( 1UL << 9UL ) /* Event bit 9, which is set by a task. */static void vEventBitSettingTask(void* parameter)
{ while (1){if( Key_Scan(1) == KEY0_PRES ) {printf( "KEY 0 has been pressed.\r\n" ); xEventGroupSetBits(Event_Handle,KEY0_PRESSED_BIT); }if( Key_Scan(1) == KEY1_PRES ) {printf( "KEY 1 has been pressed.\r\n" ); xEventGroupSetBits(Event_Handle,KEY1_PRESSED_BIT); }if( Key_Scan(1) == WKUP_PRES ) {printf( "KEY UP has been pressed.\r\n" ); xEventGroupSetBits(Event_Handle,KEY_UP_PRESSED_BIT); } vTaskDelay(pdMS_TO_TICKS(20)); }
}static void vEventBitReadingTask(void* parameter)
{ BaseType_t xReturn = pdTRUE;while (1){xEventGroupWaitBits(Event_Handle, KEY0_PRESSED_BIT | KEY1_PRESSED_BIT | KEY_UP_PRESSED_BIT,pdTRUE, pdTRUE,portMAX_DELAY);printf( "All three keys has been pressed.\r\n" ); }
}int main(void)
{ NVIC_PriorityGroupConfig( NVIC_PriorityGroup_4);KEY_Init();uart_init(115200); printf("Event groups demo start.\r\n");/* Before an event group can be used it must first be created. */Event_Handle = xEventGroupCreate();/* Create the task that sets event bits in the event group. */xTaskCreate( vEventBitSettingTask, "Bit Setter", 1000, NULL, 1, NULL );/* Create the task that waits for event bits to get set in the event group. */xTaskCreate( vEventBitReadingTask, "Bit Reader", 1000, NULL, 2, NULL );/* Start the scheduler so the created tasks start executing. */vTaskStartScheduler(); /* If all is well then main() will never reach here as the scheduler willnow be running the tasks. If main() does reach here then it is likely thatthere was insufficient heap memory available for the idle task to be created.Chapter 2 provides more information on heap memory management. */while(1);
}下面来看一下用接口 x E v e n t G r o u p S e t B i t s xEventGroupSetBits xEventGroupSetBits和接口 x E v e n t G r o u p W a i t B i t s xEventGroupWaitBits xEventGroupWaitBits不太好实现多个任务同步的场景,假设任务 A A A接收到某事件之后需要将和此事件相应的操作分担给任务 B B B,任务 C C C和任务 D D D去执行,在任务 B B B,任务 C C C和任务 D D D完成相应的操作之前,任务 A A A不会再接收事件,因此这4个任务需要相互同步。每一个任务的同步点都是对应的任务已经完成了相应的操作,任务 A A A的同步点就是接收到了事件,任务 B B B,任务 C C C和任务 D D D的同步点都是完成了和任务 A A A接收的事件对应的操作,每一个任务到达自己的同步点之后都不能再继续前进,除非任务 A A A,任务 B B B,任务 C C C和任务 D D D都到达了自己的同步点。此时这种场景可以用接口 x E v e n t G r o u p S y n c xEventGroupSync xEventGroupSync来实现多个任务的同步,这个接口的原型如下所示:
EventBits_t xEventGroupSync( EventGroupHandle_t xEventGroup,const EventBits_t uxBitsToSet,const EventBits_t uxBitsToWaitFor,TickType_t xTicksToWait )
参数 u x B i t s T o S e t uxBitsToSet uxBitsToSet用来对事件组的结构体里面的变量 u x E v e n t B i t s uxEventBits uxEventBits的低24位或低8位的比特位进行置位,对于上面的场景来说就相当于任务 A A A的接收到了事件,任务 B B B,任务 C C C或任务 D D D完成了和任务 A A A接收的事件对应的操作,参数 u x B i t s T o W a i t F o r uxBitsToWaitFor uxBitsToWaitFor用来表示要等待的事件,对于上面的场景来说就相当于任务 A A A,任务 B B B,任务 C C C和任务 D D D都到达了自己的同步点。接下来再弄了个简单的例子来简单的跑一跑接口 x E v e n t G r o u p S y n c xEventGroupSync xEventGroupSync,主要代码如下所示,这个例子模拟了上面的场景,创建了4个任务,其实哲理创建的4个任务的函数都是一样的,根据传入的参数来区别是那一个任务,每一个任务的延时不同,用来模拟所需相应操作的时间。任务 A A A延时1秒,任务 B B B延时2秒,任务 C C C延时5秒,任务 D D D延时10秒,任务 A A A延时最少是因为上面的场景是任务 A A A在接收到事件时候,任务 B B B,任务 C C C和任务 D D D才开始相关操作的执行,至于任务 B B B,任务 C C C和任务 D D D每个任务具体的相关操作的时间都是不固定的。我们从打印中可以看出只有当所有任务的延时都结束之后,任务 A A A,任务 B B B,任务 C C C和任务 D D D才会一同退出同步点。这里任务中在执行打印语句的时候会先进入临界段( C r i t i c a l S e c t i o n s Critical\quad Sections CriticalSections),打印语句执行玩之后再退出临界段,这是因为串口打印是被多个任务共享的,如果有多个任务同时在向串口打印字符的话,会造成打印出的字符顺序混乱。
static EventGroupHandle_t Event_Handle =NULL;/* Definitions for the event bits in the event group. */
#define TASK_A_BIT ( 1UL << 0UL ) /* Event bit 0, which is set by task A. */
#define TASK_B_BIT ( 1UL << 5UL ) /* Event bit 5, which is set by task B. */
#define TASK_C_BIT ( 1UL << 9UL ) /* Event bit 9, which is set by task C. */
#define TASK_D_BIT ( 1UL << 13UL ) /* Event bit 13,which is set by task D. */static void vSyncingTask( void *pvParameters )
{ EventBits_t uxThisTasksSyncBit;const EventBits_t uxAllSyncBits = ( TASK_A_BIT | TASK_B_BIT | TASK_C_BIT | TASK_D_BIT );/* Four instances of this task are created - each task uses a different eventbit in the synchronization. The event bit to use is passed into each taskinstance using the task parameter. Store it in the uxThisTasksSyncBitvariable. */uxThisTasksSyncBit = ( EventBits_t ) pvParameters; while (1){/* Simulate this task taking some time to perform an action by delaying for aperiod of time. Each task's delay time is different.This prevents all four instances of this task reachingthe synchronization point at the same time, and so allows the example's behavior to be observed more easily. */if(uxThisTasksSyncBit==((EventBits_t)(TASK_A_BIT))){vTaskDelay(pdMS_TO_TICKS(1000)); }else if(uxThisTasksSyncBit==((EventBits_t)(TASK_B_BIT))){vTaskDelay(pdMS_TO_TICKS(2000)); } else if(uxThisTasksSyncBit==((EventBits_t)(TASK_C_BIT))){vTaskDelay(pdMS_TO_TICKS(5000)); }else if(uxThisTasksSyncBit==((EventBits_t)(TASK_D_BIT))){vTaskDelay(pdMS_TO_TICKS(10000)); } /* Print out a message to show this task has reached its synchronizationpoint. pcTaskGetTaskName() is an API function that returns the name assignedto the task when the task was created. */taskENTER_CRITICAL(); printf("%s reached sync point\r\n",pcTaskGetTaskName( NULL ));taskEXIT_CRITICAL(); /* Wait for all the tasks to have reached their respective synchronization points. */xEventGroupSync( Event_Handle,/* The event group used to synchronize. */ uxThisTasksSyncBit, /* The bit set by this task to indicate it has reached the synchronization point. */ uxAllSyncBits,/* The bits to wait for, one bit for each task taking part in the synchronization. */portMAX_DELAY /* Wait indefinitely for all three tasks to reach the synchronization point. */);/* Print out a message to show this task has passed its synchronizationpoint. As an indefinite delay was used the following line will only beexecuted after all the tasks reached their respective synchronizationpoints. */ taskENTER_CRITICAL(); printf("%s exited sync point\r\n",pcTaskGetTaskName( NULL ));taskEXIT_CRITICAL();}
}int main(void)
{ NVIC_PriorityGroupConfig( NVIC_PriorityGroup_4);KEY_Init();uart_init(115200); printf("Event groups demo start.\r\n");/* Before an event group can be used it must first be created. */Event_Handle = xEventGroupCreate();/* Create three instances of the task. Each task is given a different name,which is later printed out to give a visual indication of which task isexecuting. The event bit to use when the task reaches its synchronization pointis passed into the task using the task parameter. */xTaskCreate( vSyncingTask, "Task A", 1000, (void * const)(TASK_A_BIT), 1, NULL );xTaskCreate( vSyncingTask, "Task B", 1000, (void * const)(TASK_B_BIT), 1, NULL );xTaskCreate( vSyncingTask, "Task C", 1000, (void * const)(TASK_C_BIT), 1, NULL );xTaskCreate( vSyncingTask, "Task D", 1000, (void * const)(TASK_D_BIT), 1, NULL ); /* Start the scheduler so the created tasks start executing. */vTaskStartScheduler();/* If all is well then main() will never reach here as the scheduler willnow be running the tasks. If main() does reach here then it is likely thatthere was insufficient heap memory available for the idle task to be created.Chapter 2 provides more information on heap memory management. */while(1);
}