最近比赛需要,所以特出一期建立知识图谱和相关知识问答的教程
整个过程需要用到工具Neo4j,这在我以前的博客中讲到怎么部署详情请看:
Neo4j部署教程
如果想快速入门Neo4j请点击这里:
Neo4j快速入门
此项目的github地址
参考的刘焕勇项目地址
一. 构建数据集
最终的数据格式:
{"name":"八阵图","author":"杜甫","dynasty":"唐","category":"五言绝句","content":"功盖三分国,名成八阵图。(名成 一作:名高)江流石不转,遗恨失吞吴。","trans":"三国鼎立你建立了盖世功绩,创八阵图你成就了永久声名。任凭江流冲击,石头却依然如故,遗憾的是刘备不听诸葛亮之言吞吴失策。","annotation":"八阵图:由八种阵势组成的图形,用来操练军队或作战。盖:超过。三分国:指三国时魏、蜀、吴三国。石不转:指涨水时,八阵图的石块仍然不动。失吞吴:是吞吴失策的意思。","background":"杜甫在公元766年(唐代宗大历元年)夏迁居夔州,夔州有武侯庙,江边有八阵图,传说为三国时诸葛亮在夔州江滩所设。向来景仰诸葛亮的杜甫用了许多笔墨记咏古迹抒发情怀。《八阵图》便是其中一首。","appreciation":"这是作者初到夔州(治今重庆奉节)时的一首咏怀诸葛亮的诗,写于大历元年(766)。“八阵图”,指由天、地、风、云、龙、虎、鸟、蛇八种阵势所组成的军事操练和作战的阵图,由诸葛亮创制而成,反映了他卓越的军事才能。“功盖三分国,名成八阵图。”这首小诗的前两句是说,三国鼎立你建立了盖世功绩,创八阵图你成就了永久声名。这两句赞颂了诸葛亮的丰功伟绩。第一句是从总的方面来写,说诸葛亮在确立魏蜀吴三分天下、鼎足而立的局势的过程中,功绩最为卓绝。三国并存局面的形成,固然有许多因素,而诸葛亮辅助刘备从无到有的创建蜀国基业,应该说是重要原因之一。杜甫这一高度概括的赞语,客观地反映了三国时代的历史真实。第二句是从具体的方面来说,诸葛亮创制的八阵图使他声名卓著。对这一点古人曾屡加称颂,而杜甫的这句诗则是更集中、更凝练的赞颂了诸葛亮的军事业绩。这两句诗在写法上用的是对仗句,“三分国”对“八阵图”,以全局性的业绩对军事上的贡献,显得精巧工整,自然妥帖。在结构上,前句劈头提起,开门见山;后句点出诗题,进一步赞颂功绩,同时又为下面凭吊遗迹做了铺垫。“江流石不转,遗恨失吞吴。”这两句就“八阵图”的遗址抒发感慨。“八阵图”遗址在夔州西南永安宫前平沙上。据《荆州图副》和刘禹锡《嘉话录》记载,这里的八阵图聚细石成堆,高五尺,六十围,纵横棋布,排列为六十四堆,始终保持原来的样子不变,即使被夏天大水冲击淹没,等到冬季水落平川,万物都失故态,唯独八阵图的石堆却依然如旧,六百年来岿然不动。前一句极精炼地写出了遗迹这一富有神奇色彩的特征。“石不转”,化用了《诗经·国风·邶风·柏舟》中的诗句“我心匪石,不可转也”。在作者看来,这种神奇色彩和诸葛亮的精神心志有内在的联系:他对蜀汉政权和统一大业忠贞不二,矢志不移,如磐石之不可动摇。同时,这散而复聚、长年不变的八阵图石堆的存在,似乎又是诸葛亮对自己赍志以殁表示惋惜、遗憾的象征,所以杜甫紧接着写的最后一句是“遗恨失吞吴”,说刘备吞吴失计,破坏了诸葛亮联吴抗曹的根本策略,以致统一大业中途夭折,而成了千古遗恨。当然,这首诗与其说是在写诸葛亮的“遗恨”,无宁说是杜甫在为诸葛亮惋惜,并在这种惋惜之中渗透了杜甫“伤己垂暮无成”(黄生语)的抑郁情怀。这首怀古绝句,具有融议论入诗的特点。但这种议论并不空洞抽象,而是语言生动形象,抒情色彩浓郁。诗人把怀古和述怀融为一体,浑然不分,给人一种此恨绵绵、余意不尽的感觉。"}
要想做到这一点,爬虫是必不可少的!
爬虫代码如下:
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoupdef fetch_html(url):try:response = requests.get(url)response.raise_for_status()return response.textexcept requests.RequestException as e:print(f"Error fetching HTML content: {e}")return Nonedef extract_poem_urls(html_content):soup = BeautifulSoup(html_content, 'html.parser')poem_urls = []for a_tag in soup.find_all('a', href=True):href = a_tag['href']if href.startswith("/shiwenv_"):full_url = f"https://so.gushiwen.cn{href}"poem_urls.append(full_url)return poem_urlsdef fetch_poem_details(url):poem_details = {"name": "","author": "","dynasty": "","content": "","trans": "","annotation": "","appreciation": "","background": ""}response = requests.get(url)if response.status_code == 200:soup = BeautifulSoup(response.text, 'html.parser')title_tag = soup.find('h1')if title_tag:poem_details["name"] = title_tag.text.strip().replace("\n", "")source_tag = soup.find('p', class_='source')if source_tag:source_info = source_tag.find_all('a')if len(source_info) > 0:poem_details["author"] = source_info[0].text.strip().replace("\n", "")poem_details["dynasty"] = source_info[1].text.strip().replace("\n", "").replace("〔", "").replace("〕","")content_tag = soup.find('div', class_='contson')if content_tag:poem_details["content"] = content_tag.get_text().strip().replace("\n", "")# 提取译文和注释trans_annotation_tag = soup.find('div', class_='contyishang')if trans_annotation_tag:p_tags = trans_annotation_tag.find_all('p')for p_tag in p_tags:if '译文' in p_tag.text:poem_details["trans"] = p_tag.get_text().strip().replace("译文", "").replace("展开阅读全文 ∨", "")elif '注释' in p_tag.text:poem_details["annotation"] = p_tag.get_text().strip().replace("注释", "").replace("展开阅读全文 ∨", "")appreciation_divs = soup.find_all('div', class_='contyishang')for div in appreciation_divs:if div.find('h2') and ('赏析' in div.find('h2').text or '鉴赏' in div.find('h2').text):appreciation_paragraphs = div.find_all('p')appreciation_text = "".join(p.get_text().strip() for p in appreciation_paragraphs).replace("\n", "").replace("展开阅读全文 ∨", "")poem_details["appreciation"] += "。"+appreciation_text# 提取创作背景background_divs = soup.find_all('div', class_='contyishang')for div in background_divs:if div.find('h2') and '创作背景' in div.find('h2').text:background_paragraphs = div.find_all('p')background_text = "".join(p.get_text().strip() for p in background_paragraphs).replace("\n", "").replace("展开阅读全文 ∨", "")poem_details["background"] = background_textreturn poem_detailsif __name__ == "__main__":urls = ["https://so.gushiwen.cn/gushi/tangshi.aspx","https://so.gushiwen.cn/gushi/sanbai.aspx","https://so.gushiwen.cn/gushi/songsan.aspx"]poem_urls = []for url in urls:html_content = fetch_html(url)if html_content:poem_urls.extend(extract_poem_urls(html_content))else:print("Failed to fetch or parse HTML content.")for url in poem_urls:details = fetch_poem_details(url)print(details)
整理成上面描述的json格式后我们便可以进行下一步。
二. 代码设计
2.1 构建知识图谱
该项功能由build_graph.py来实现,具体代码如下:
import os
from py2neo import Graph,Node
import jsonclass KL_Graph():#初始化def __init__(self):cur_dir = '/'.join(os.path.abspath(__file__).split('/')[:-1])self.data_path=os.path.join(cur_dir,'data/kownledge.json')self.g = Graph("http://localhost:7474", auth=("neo4j", "jiayuang123"),name="neo4j")#读取文件def read_nodes(self):#构建实体节点poem=[]#诗词author=[]#作者dynasty=[]#朝代category=[]#种类#theme=[]#主题poem_infos=[]#诗词信息#构建节点实体关系rel_create=[]#创作关系rel_dynasty=[]#朝代归属关系rel_belongC=[]#分类关系rel_birth=[]#作者与朝代关系count=0for data in open(self.data_path,encoding='utf-8'):poem_dict={}count+=1print(count)data_json=json.loads(data)poem_name=data_json['name']#print(poem_name)poem_dict['name']=poem_namepoem.append(poem_name)poem_dict['content']=''poem_dict['trans']=''poem_dict['annotation']=''poem_dict['appreciation']=''poem_dict['background']=''if 'dynasty' in data_json:dynasty.append(data_json['dynasty'])rel_dynasty.append([poem_name,data_json['dynasty']])if 'author' in data_json:author.append(data_json['author'])print(author)rel_create.append([poem_name,data_json['author']])if 'category' in data_json:category.append(data_json['category'])rel_belongC.append([poem_name,data_json['category']])if 'author' in data_json and 'dynasty' in data_json:rel_birth.append([data_json['author'],data_json['dynasty']])if 'content' in data_json:poem_dict['content']=data_json['content']if 'trans' in data_json:poem_dict['trans']=data_json['trans']if 'annotation' in data_json:poem_dict['annotation']=data_json['annotation']if 'appreciation' in data_json:poem_dict['appreciation']=data_json['appreciation']if 'background' in data_json:poem_dict['background']=data_json['background']poem_infos.append(poem_dict)return set(poem),set(author),set(dynasty),set(category),poem_infos,\rel_create,rel_dynasty,rel_belongC,rel_birth#创建普通节点def create_node(self,label,nodes):""":param label: 节点标签(即名称):param nodes: 具体节点:return: None"""count=0for node_name in nodes:node=Node(label,name=node_name)self.g.create(node)count+=1print(count,len(nodes))return#创建poem中心结点def create_poem_nodes(self,poem_infos):""":param poem_infos: 诗歌节点具体信息:return: None"""count=0for poem_dict in poem_infos:node=Node("Poem",name=poem_dict['name'],content=poem_dict['content'],trans=poem_dict['trans'],annotation=poem_dict['annotation'],appreciation=poem_dict['appreciation'],background=poem_dict['background'])self.g.create(node)count+=1print(count)return#创建指示图谱的实体节点def create_graphnodes(self):poem, author, dynasty, category, poem_infos, rel_create, rel_dynasty, rel_belongC,rel_birth=self.read_nodes()self.create_poem_nodes(poem_infos)#创建古诗详细信息self.create_node('Dynasty',dynasty)#创建朝代节点self.create_node('Author',author)#创建作者节点self.create_node('Category',category)#创建种类节点returndef create_relationship(self,start_node,end_node,edges,rel_type,rel_name):""":param start_node: 起始节点:param end_node: 终点节点:param edges: 边:param rel_type: 关系类型:param rel_name: 关系名字:return: None"""count=0#去重处理set_edges=[]for edge in edges:set_edges.append('###'.join(edge))#使用###作为不同关系之间分隔的标志all=len(set(set_edges))for edge in set(set_edges):edge=edge.split('###')p=edge[0]q=edge[1]query="match(p:%s),(q:%s) where p.name='%s' and q.name='%s' create (p)-[rel:%s{name:'%s'}]->(q)"%(start_node,end_node,p,q,rel_type,rel_name)#match语法,p,q分别为标签,rel_type表示关系类别,rel_name 关系名字try:self.g.run(query)count+=1print(rel_type,count,all)except Exception as e:print(e)return#创建实体关系边def create_graphrels(self):poem, author, dynasty, category, poem_infos, rel_create, rel_dynasty, rel_belongC,rel_birth = self.read_nodes()self.create_relationship('Poem','Author',rel_create,'created_by','被创作')self.create_relationship('Poem','Dynasty',rel_dynasty,'created_during','创作于')self.create_relationship('Poem','Category',rel_belongC,'belongs_to','属于')self.create_relationship('Author','Dynasty',rel_birth,'born in','生于')def export_data(self):poem, author, dynasty, category, poem_infos, rel_create, rel_dynasty, rel_belongC,rel_birth = self.read_nodes()f_poem=open('poem.txt','w+')f_author=open('author.txt','w+')f_dynasty = open('dynasty.txt', 'w+')f_category = open('category.txt', 'w+')f_poem.write('\n'.join(list(poem)))f_author.write('\n'.join(list(author)))f_dynasty.write('\n'.join(list(dynasty)))f_category.write('\n'.join(list(category)))f_poem.close()f_author.close()f_dynasty.close()f_category.close()return
if __name__ == '__main__':handler=KL_Graph()#创建图数据库handler.export_data()handler.create_graphnodes()handler.create_graphrels()
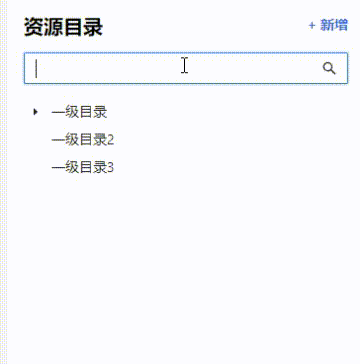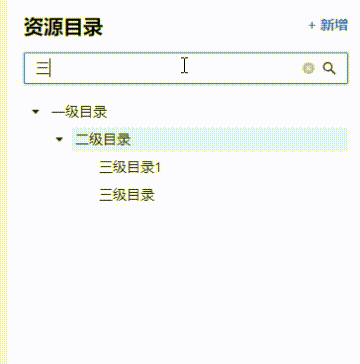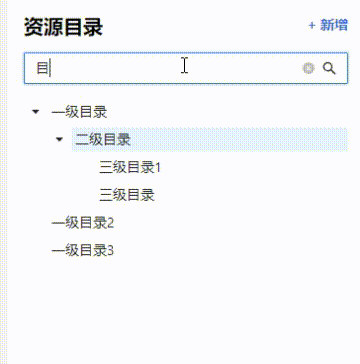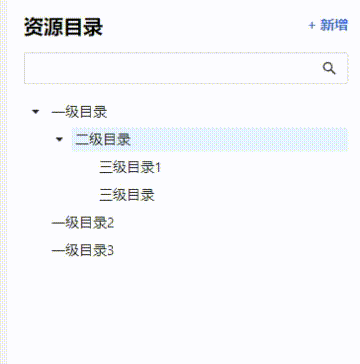
构建好的知识图谱长这样:
(当然我只是做个演示,所以只加了三条数据,真正的图谱要比这个复杂得多)
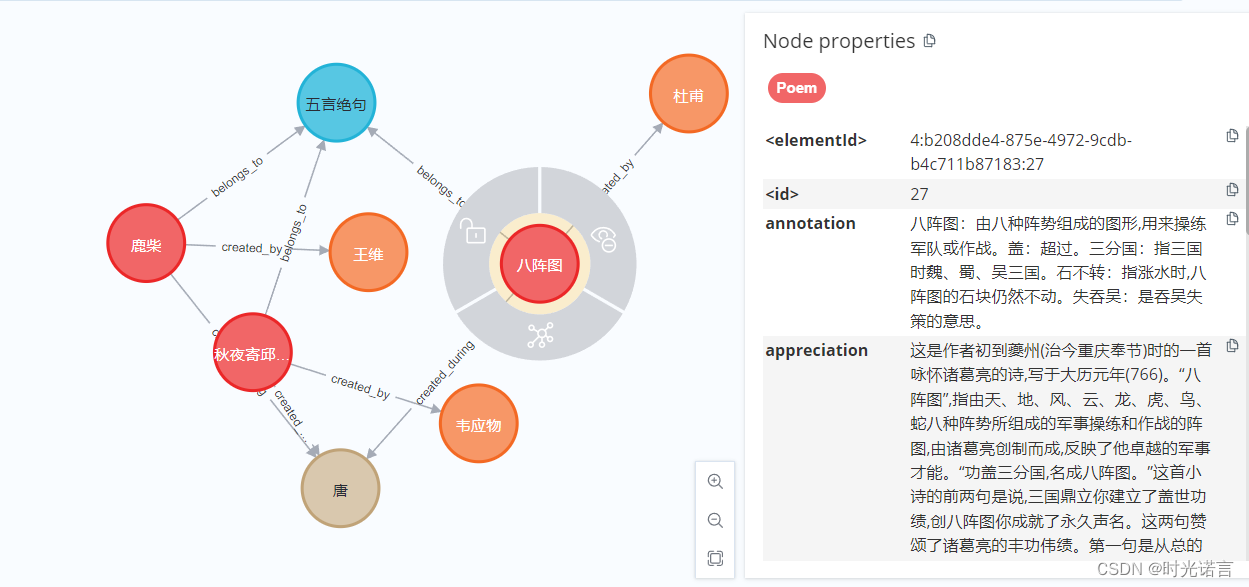
2.2 人机交互
知识图谱建立成功后,相当于我们背靠强大的数据系统,需要完成一些前端的(最起码是shell面板上)的一些人机交互来完善整个系统。
2.2.1 安装pyahocorasick库
pyahocorasick是一个Python库,提供了高效的Aho-Corasick自动机实现。Aho-Corasick算法是一种字符串搜索算法,用于在一个或多个较长的文本中快速查找一个或多个较短字符串的出现位置。这种算法特别适用于需要在大量文本中搜索大量模式(例如,敏感词过滤、生物信息学中的基因序列搜索等)的情况。
有兴趣的伙伴请看:
pyahocorasick讲解
当然大部分人只要会用即可
pyahocorasick安装命令:
pip install pyahocorasick -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple
2.2.2 实现问题分类
在提问时,系统需要根据问题中的关键词找准定位,从而提炼出相关的节点和边。
此功能基于下列代码实现:
# -*- coding: gbk -*-
import ahocorasick
import os
class QuestionClassifier():def __init__(self):cur_dir = '/'.join(os.path.abspath(__file__).split('/')[:-1])#特征词路径self.poem_path=os.path.join(cur_dir,'dictionary/poem.txt')self.dynasty_path=os.path.join(cur_dir,'dictionary/dynasty.txt')self.category_path=os.path.join(cur_dir,'dictionary/category.txt')self.author_path=os.path.join(cur_dir,'dictionary/author.txt')#加载特征词self.poem_wds=[i.strip() for i in open(self.poem_path,encoding="gbk") if i.strip()]self.dynasty_wds=[i.strip() for i in open(self.dynasty_path,encoding="gbk") if i.strip()]self.category_wds=[i.strip() for i in open(self.category_path,encoding="gbk") if i.strip()]self.author_wds=[i.strip() for i in open(self.author_path,encoding="gbk") if i.strip()]self.field_words=set(self.poem_wds+self.dynasty_wds+self.category_wds+self.author_wds)#构建领域actree,可以将文本流输入自动机,自动机会在文本中寻找所有预先定义的关键词,并且能够告诉你每个关键词的出现位置。这种方法比逐一查找每个关键词要高效得多,特别是在关键词集合很大或文本很长的情况下。self.field_tree=self.build_actree(list(self.field_words))#构建词典self.wdtype_dict=self.build_wdtype_dict()#问句疑问句self.author_qwd=['作者','谁写的','诗人','词人','出自谁笔']self.dynasty_qwd=['朝代','年代','哪个时期']self.content_qwd=['内容是什么','怎么写的','咋写的','怎么背','请你背写','默写','补全']self.category_qwd=['体裁','形式']self.appreciation_qwd=['赏析','鉴赏','品鉴','分析','解析','意义','目的是']self.background_qwd=['历史背景','创作背景','背景是','历史环境','当时','那时','写作缘由','写作原因']self.trans_qwd=['翻译','这首诗的解释','通俗','释义','人话','解释']self.annotation_qwd=['注释','关键知识点','常见词语','知识点']#print('model init finished ......')return#分类主函数def classify(self,question):data={}poem_dict=self.check_poems(question)#过滤一下问题if not poem_dict:#如果为空return {}data['args']=poem_dict#收集问题当中的实体类型types=[]for type_ in poem_dict.values():types+=type_question_type='others'#无意义question_types=[]if self.check_words(self.author_qwd,question) and ('poem' in types):#这首诗的作者是谁question_type='poem_author'question_types.append(question_type)if self.check_words(self.dynasty_qwd,question) and 'poem' in types:#这首诗的朝代是什么question_type='poem_dynasty'question_types.append(question_type)if self.check_words(self.dynasty_qwd,question) and 'author' in types:#作者朝代是什么question_type='author_dynasty'question_types.append(question_type)if self.check_words(self.content_qwd,question) and 'poem' in types:#这首诗的内容是什么?question_type='poem_content'question_types.append(question_type)if self.check_words(self.category_qwd,question) and 'poem' in types:#这首诗的体裁是什么question_type='poem_category'question_types.append(question_type)if self.check_words(self.trans_qwd,question) and 'poem' in types:#这首诗的翻译是什么question_type='poem_trans'question_types.append(question_type)if self.check_words(self.annotation_qwd,question) and 'poem' in types:#这首诗的常见注释是什么question_type='poem_annotation'question_types.append(question_type)if self.check_words(self.appreciation_qwd,question): #鉴赏是什么question_type='appreciation'question_types.append(question_type)if self.check_words(self.background_qwd,question): #背景是什么question_type='background'question_types.append(question_type)data['question_types']=question_typesreturn data#构建actree加速过滤def build_actree(self,wordlist):actree=ahocorasick.Automaton()for index,word in enumerate(wordlist):actree.add_word(word,(index,word))actree.make_automaton()return actreedef build_wdtype_dict(self):#构造词类型wd_dict=dict()for wd in self.field_words:#找到用户输入的词是什么范围的wd_dict[wd]=[]if wd in self.poem_wds:wd_dict[wd].append('poem')if wd in self.author_wds:wd_dict[wd].append('author')if wd in self.dynasty_wds:wd_dict[wd].append('dynasty')if wd in self.category_wds:wd_dict[wd].append('category')return wd_dict#问句过滤def check_poems(self,question):field_wds=[]for i in self.field_tree.iter(question):# ahocorasick库 匹配问题 iter返回一个元组,i的形式如(3, (23192, '杜甫'))wd=i[1][1]#匹配到的词field_wds.append(wd)stop_wds=[]for wd1 in field_wds:for wd2 in field_wds:if wd1 in wd2 and wd1 != wd2:stop_wds.append(wd1) #stopword取重复且较短的词语final_wds = [i for i in field_wds if i not in stop_wds] # final_wds取长词,也就是最后返回的是长词final_dict= {i:self.wdtype_dict.get(i) for i in final_wds}#来自于构造词典,# 获取词和词所对应的实体类型return final_dict#基于特征词进行分类def check_words(self,wds,sent):for wd in wds:if wd in sent:return Truereturn Falseif __name__ == '__main__':handler=QuestionClassifier()while True:question=input('请输入您的问题:')data = handler.classify(question)print(data)
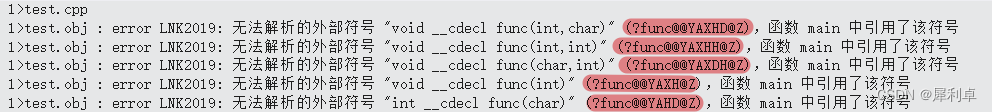
此代码实现的效果图:

2.2.3 将问题解析到知识图谱中
上面我们只是把问题在格式上解析成了args和question_types的形式,但是仍然未涉及到利用我们已经建立好的的知识图谱,下面就是具体实现与知识图谱串联起来的代码:
class QuestionParser:# 创建实体节点,构造了以关系为键,节点为值的字典def build_entity(self,args):entity_dict={}for arg,types in args.items():for type in types:if type not in entity_dict:entity_dict[type]=[arg]else:entity_dict[type].append(arg)return entity_dict#解析主函数,res_classify就是conversation_graph.py中的datadef parser_main(self,res_classify):args=res_classify['args']entity_dict=self.build_entity(args)question_types=res_classify['question_types']sqls=[]for question_type in question_types:sq={}sq['question_type']=question_typesql=[]if question_type=='poem_author':sql=self.sql_transfer(question_type,entity_dict.get('poem'))elif question_type=='poem_dynasty':sql=self.sql_transfer(question_type,entity_dict.get('poem'))elif question_type=='author_dynasty':sql=self.sql_transfer(question_type,entity_dict.get('author'))elif question_type=='poem_category':sql=self.sql_transfer(question_type,entity_dict.get('poem'))elif question_type=='poem_content':sql=self.sql_transfer(question_type,entity_dict.get('poem'))elif question_type=='poem_trans':sql=self.sql_transfer(question_type,entity_dict.get('poem'))elif question_type=='appreciation':sql=self.sql_transfer(question_type,entity_dict.get('poem'))elif question_type=='annotation':sql=self.sql_transfer(question_type,entity_dict.get('poem'))elif question_type == 'background':sql = self.sql_transfer(question_type, entity_dict.get('poem'))if sql:sq['sql']=sqlsqls.append(sq)return sqls #返回sql查询语句供图谱查询(可以是多条)def sql_transfer(self,question_type,entities):#针对不同的问题进行转换if not entities:return []#查询语句sql=[]#查询if question_type=='poem_author':sql=["MATCH (m:Poem)-[r:created_by]->(n:Author) where m.name = '{0}' return m.name,r.name,n.name".format(i) for i in entities]elif question_type=='poem_dynasty':sql=["MATCH (m:Poem)-[r:created_during]->(n:Dynasty) where m.name = '{0}' return m.name, r.name, n.name".format(i) for i in entities]elif question_type=='author_dynasty':sql=["MATCH (m:Poem)-[r:born in]->(n:Dynasty) where m.name = '{0}' return m.name, r.name, n.name".format(i) for i in entities]elif question_type=='poem_category':sql=["MATCH (m:Poem)-[r:belongs_to]->(n:Category) where m.name = '{0}' return m.name, r.name, n.name".format(i) for i in entities]elif question_type=='poem_content':sql = ["MATCH (m:Poem) where m.name = '{0}' return m.name, m.content".format(i) for i in entities]elif question_type=='poem_trans':sql=["MATCH (m:Poem) where m.name = '{0}' return m.name, m.trans".format(i) for i in entities]elif question_type=='appreciation':sql=["MATCH (m:Poem) where m.name = '{0}' return m.name, m.appreciation".format(i) for i in entities]elif question_type=='annotation':sql=["MATCH (m:Poem) where m.name = '{0}' return m.name, m.annotation".format(i) for i in entities]elif question_type=='background':sql=["MATCH (m:Poem) where m.name = '{0}' return m.name, m.background".format(i) for i in entities]return sqlif __name__ == '__main__':handler=QuestionParser()
2.2.4 找寻最终答案
此模块的功能在于读图谱,也就是在得到上述sql语句的后续查找过程
代码如下:
# -*- coding: gbk -*-
from py2neo import Graph
class AnswerSearcher:def __init__(self):#调用数据库进行查询self.g = Graph("http://localhost:7474", auth=("neo4j", "jiayuang123"),name="neo4j")self.num_limit=5 #答案种类的限制数目#执行cypher查询并返回相应结果def search_main(self,sqls):final_answers=[]for sq in sqls:question_type=sq['question_type']queries=sq['sql']answers=[]for query in queries:res=self.g.run(query).data()answers+=resfinal_answer=self.answer_prettify(question_type,answers)if final_answer:final_answers.append(final_answer)return final_answersdef answer_prettify(self,question_type,answers):final_answer=[]if not answers:return ''if question_type=='poem_author':desc=[i ['n.name'] for i in answers]subject=answers[0]['m.name']final_answer='{0}的作者是{1}'.format(subject,';'.join(list(set(desc))[:self.num_limit]))elif question_type=='poem_dynasty':desc=[i ['n.name'] for i in answers]subject=answers[0]['m.name']final_answer='{0}这首经典作于{1}'.format(subject,';'.join(list(set(desc))[:self.num_limit]))elif question_type=='author_dynasty':desc=[i ['n.name'] for i in answers]subject=answers[0]['m.name']final_answer='{0}生活的朝代是{1}'.format(subject,';'.join(list(set(desc))[:self.num_limit]))elif question_type=='poem_category':desc=[i ['m.category'] for i in answers]subject=answers[0]['m.name']final_answer = '{0}的体裁是{1}'.format(subject, ';'.join(list(set(desc))[:self.num_limit]))elif question_type=='poem_content':desc = [i['m.content'] for i in answers]subject = answers[0]['m.name']final_answer = '{0}的具体内容是{1}'.format(subject, ';'.join(list(set(desc))[:self.num_limit]))elif question_type=='poem_trans':desc = [i['m.trans'] for i in answers]subject = answers[0]['m.name']final_answer = '{0}的具体翻译是{1}'.format(subject, ';'.join(list(set(desc))[:self.num_limit]))elif question_type=='appreciation':desc = [i['m.appreciation'] for i in answers]subject = answers[0]['m.name']final_answer = '{0}的详细赏析如下{1}'.format(subject, ';'.join(list(set(desc))[:self.num_limit]))elif question_type=='annotation':desc = [i['m.annotation'] for i in answers]subject = answers[0]['m.name']final_answer = '{0}的常见知识点和注释如下{1}'.format(subject, ';'.join(list(set(desc))[:self.num_limit]))elif question_type=='background':desc = [i['m.background'] for i in answers]subject = answers[0]['m.name']final_answer = '{0}的创作背景是{1}'.format(subject, ';'.join(list(set(desc))[:self.num_limit]))return final_answerif __name__ == '__main__':seacher=AnswerSearcher()
三.汇总
现在我们将以上三个子模块复用在一个类中实现最后的问答功能:
# -*- coding: gbk -*-
from question_parser import *
from conversation_graph import *
from answer_search import *class ChatPoemGraph:def __init__(self):self.classifier=QuestionClassifier()self.parser=QuestionParser()self.seacher=AnswerSearcher()def chat_main(self,sent):answer='很抱歉没能理解你的问题,您也许可以换个问法再问一次'res_classify=self.classifier.classify(sent)#对问题进行分类if not res_classify:#如果没有找到合适的分类就返回初始answerreturn answerres_sql=self.parser.parser_main(res_classify)final_answers=self.seacher.search_main(res_sql)if not final_answers: #最终未找到合适的答案return answerelse:return '\n'.join(final_answers)
if __name__ == '__main__':handler=ChatPoemGraph()while True:question=input('请输入您的问题:')answer=handler.chat_main(question)print('小星的回答:',answer)效果图:

下一步肯定是强化UI了,开学再做叭,码字不易还请多多支持




![[更新]ARCGIS之土地耕地占补平衡、进出平衡系统报备坐标txt格式批量导出工具(定制开发版)](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/456dc85e991d42f685c026ca693dde49.png)