一、什么是注解
注解是放在Java源码的类、字段、方法、参数前的一种特殊的“注释”,和普通注释的区别是,普通注释被编译器直接忽略,注解则可以被编译器打包进入Class文件。如下图所示就是lombok中的一些注解。

注解的作用:
从JVM角度看,注解本身对代码逻辑没有任何影响,如何使用注解完全由工具决定。Java的注解可以分为三类:
第一类是由编辑器使用的注解,例如@Override(让编辑器检查该方法是正确的实现了覆写);@SuppressWarnings(告诉编译器忽略此处代码产生的警告)等等,这类注解不会被编译进入.class文件,它们在编译后就被编译器扔掉了。
第二类是由工具处理.class文件使用的注解,比如有些工具会在加载class的时候,对class做动态修改,实现一些特殊的功能。这类注解会被编译进入.class文件,但加载结束后并不会存在于内存中。这类注解只被一些底层库使用,一般我们不必自己处理。
第三类是程序运行期间能够读取的注解,他们加载之后一直存在于JVM中,也是最常用的注解。
二、定义注解
定义一个注解时,还可以定义配置参数,配置参数可以包括所有基本类型、String、枚举或上面三种类型和Class的数组。因为配置参数必须是常量,所以,上述限制保证了注解在定义时就已经确定了每个参数的值。注解的配置参数可以有默认值,缺少某个配置参数时将使用默认值(强烈建议写默认值)。如果在定义的时候只写了注解,相当于全部使用默认值。如果参数名名称是value且只有这一个参数,可以省略参数名称,直接在()里面写值就可以。
Java语言中使用@interface语法来定义注解,格式如下:
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.FIELD)
public @interface Demo13_Annotation {int min() default 0;int max() default 255;
}注解的参数类似于无参数方法,可以使用default设置一个默认值(推荐),最常用的参数应当命名为value。
查看上面代码我们可以发现,在注解的定义中也是用到了一些注解,这些注解就被称为元注解,元注解可以修饰其它注解,Java标准库中已经定义了一些元注解,我们只需要使用即可。

元注解最常用的有两种,分别是@Target和@Retention。
2.1、@Target
使用@Target可以定义注解能够被应用于源码的哪些位置:
1、类或接口:ElementType.TYPE;
2、字段:ElementType.FIELD;
3、方法:ElementType.METHOD;
4、构造方法:ElementType.CONSTRUCTOR;
5、参数方法:ElementType.PARAMETER。
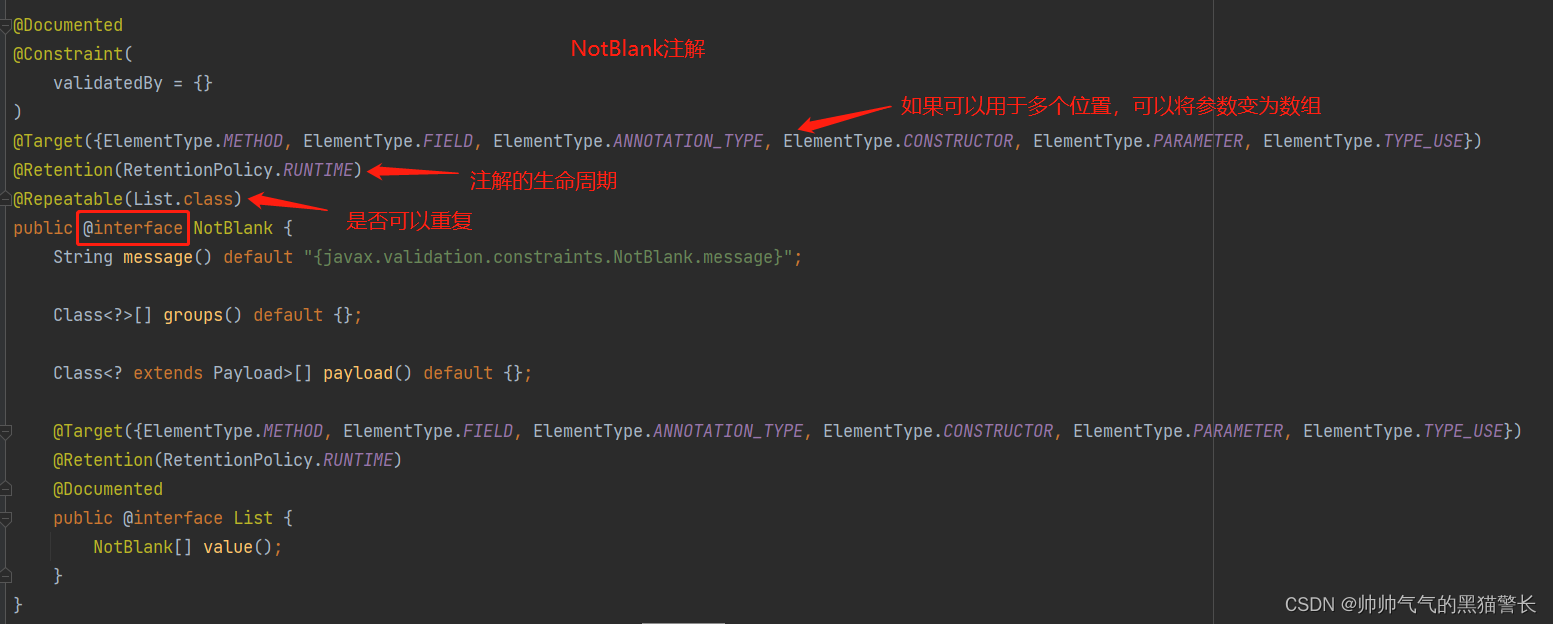
例如上图中我们定义了只能被应用于字段Field。如果可以用于多个位置,可以把@Target的参数变为数组。
2.2、@Retention
使用@Retention可以定义注解的生命周期:
1、仅编译期:RetentionPolicy.SOURCE;
2、仅Class文件:RetentionPolicy.CLASS;
3、运行期:RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME。
如果@Retention不存在,默认是Class。通常我们定义的都是RUNTIME。
2.3、@Repeatable
可以定义注解是否可重复,应用不广泛。
2.4、@Inherited
定义子类是否可以继承父类定义的注解,仅针对@Target(ElementType.TYPE)类型的注解有效。
可以看一下NotBlank的注解:
综上,定义注解的步骤:
1、使用@interface定义注解:
public @interface Demo13_Annotation {
}2、添加参数、默认值:
public @interface Demo13_Annotation {int min() default 0;int max() default 255;
}3、用元注解配置注解:
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.FIELD)
public @interface Demo13_Annotation {int min() default 0;int max() default 255;
}其中必须设置 @Target和@Retention,@Retention一般为RUNTIME。
三、处理注解
Java的注解本身对于代码逻辑没有任何影响,其中SOURCE类型的注解在编译期就被丢掉了;CLASS的注解仅保存在class文件中,不被加载至JVM;RUNTIME类型的注解会被加载至JVM且在运行期可以被程序读取。
如何使用注解完全由工具决定,这里我们只讨论RUNTIME类型的注解。
JAVA提供了使用反射API判断注解是否存在和读取注解的方法:
3.1、判断某个注解是否存在
Class.isAnnotationPresent(Class):是否存在于ClassField.isAnnotationPresent(Class):是否存在于FieldMethod.isAnnotationPresent(Class)Constructor.isAnnotationPresent(Class)
例如判断@Report是否存在于Person类:
Person.class.isAnnotationPresent(Report.class);3.2、利用反射读取注解
Class.getAnnotation(Class)Field.getAnnotation(Class)Method.getAnnotation(Class)Constructor.getAnnotation(Class)
例如获取Person定义的@Report注解:
// 获取Person定义的@Report注解:
Report report = Person.class.getAnnotation(Report.class);
int type = report.type();
String level = report.level();使用反射读取注解有两种方法:
1、先判断是否存在,如果存在,再读取:
Class cls = Person.class;
if (cls.isAnnotationPresent(Report.class)) {Report report = cls.getAnnotation(Report.class);...
}2、直接读取注解,如果注解不存在,返回null:
Class cls = Person.class;
Report report = cls.getAnnotation(Report.class);
if (report != null) {...
}四、使用注解
4.1、声明一个注解
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.FIELD)
public @interface Demo13_Annotation {int min() default 0;int max() default 255;
}4.2、声明一个类使用注解
public class Demo14_UseAnnotation {@Demo13_Annotation(min = 3, max = 25)private String name;@Demo13_Annotation(min = 11, max = 11)private String phone;public Demo14_UseAnnotation(){}public Demo14_UseAnnotation(String name, String phone){this.name = name;this.phone = phone;}}
4.3、定义方法来使用注解
void check(Demo14_UseAnnotation demo14_UseAnnotation) throws IllegalArgumentException, ReflectiveOperationException{for (Field field:demo14_UseAnnotation.getClass().getDeclaredFields()){ // 遍历所有Field(包含私有)field.setAccessible(true); // 如果是私有,设置访问权限if(field.isAnnotationPresent(Demo13_Annotation.class)){ // 判断注解是否存在Demo13_Annotation demo13_Annotation = field.getAnnotation(Demo13_Annotation.class); // 如果存在则读取注解 Object value = field.get(demo14_UseAnnotation); // 通过反射获取该字段值if (value instanceof String){ // 判断是否为StringString s = (String) value;if (s.length() < demo13_Annotation.min() || s.length() > demo13_Annotation.max()){ // 判断是否满足注解的min和maxthrow new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid field: " + field.getName());}}}}}4.4、调用注解方法
import java.lang.reflect.Field;public class Demo15_HandlingAnnotation{public static void main(String[] args) throws IllegalArgumentException, ReflectiveOperationException {Demo15_HandlingAnnotation demo15_HandlingAnnotation = new Demo15_HandlingAnnotation();Demo14_UseAnnotation demo14_UseAnnotation = new Demo14_UseAnnotation("张三", "12345678910");demo15_HandlingAnnotation.check(demo14_UseAnnotation); // 调用注解方法}void check(Demo14_UseAnnotation demo14_UseAnnotation) throws IllegalArgumentException, ReflectiveOperationException{for (Field field:demo14_UseAnnotation.getClass().getDeclaredFields()){ // 遍历所有Field(包含私有)field.setAccessible(true); // 如果是私有,设置访问权限if(field.isAnnotationPresent(Demo13_Annotation.class)){ // 判断注解是否存在Demo13_Annotation demo13_Annotation = field.getAnnotation(Demo13_Annotation.class); // 如果存在则读取注解 Object value = field.get(demo14_UseAnnotation); // 通过反射获取该字段值if (value instanceof String){ // 判断是否为StringString s = (String) value;if (s.length() < demo13_Annotation.min() || s.length() > demo13_Annotation.max()){ // 判断是否满足注解的min和maxthrow new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid field: " + field.getName());}}}}}
}通过上述过程我们就完成了注解的定义和使用。
五、实际应用
使用注解和AOP完成日志记录功能。
5.1、定义日志注解类
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface Log {//模块String value() default "Null";//功能String action() default "Null";}5.2、定义日志切面
@Aspect
@Component
@Slf4j
public class SystemLogAspect {// 定义切点 @Pointcut// 在注解的位置切入代码@Pointcut("@annotation(com....Log)")public void logPointCut(){}// 切面 配置通知@Before("logPointCut()")public void before(JoinPoint joinPoint){//通过反射获取注解MethodSignature signature = (MethodSignature) joinPoint.getSignature();Method method = signature.getMethod();Log actionLog = method.getAnnotation(Log.class);if(actionLog != null){// 获取注解内容String value = actionLog.value();String action = actionLog.action();// 获取HttpServletRequestHttpServletRequest request = ((ServletRequestAttributes) RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes()).getRequest();// 获取请求方法String httpMethod = request.getMethod();// 获取请求路径String requestURL = request.getRequestURI();// 获取用户IPString ip = request.getRemoteAddr();if (ip.equals("0:0:0:0:0:0:0:1")){ip = "127.0.0.1";}// 获取浏览器信息String browser = UserAgent.parseUserAgentString(request.getHeader("User-Agent")).getBrowser().getName();// ......其它需求log.info("action = " + action + ", value = " + value + ", httpMethod = " + httpMethod + ", requestURL = " + requestURL + ", ip = " + ip + ", browser = " + browser );}}
}参考链接:使用注解 - 廖雪峰的官方网站