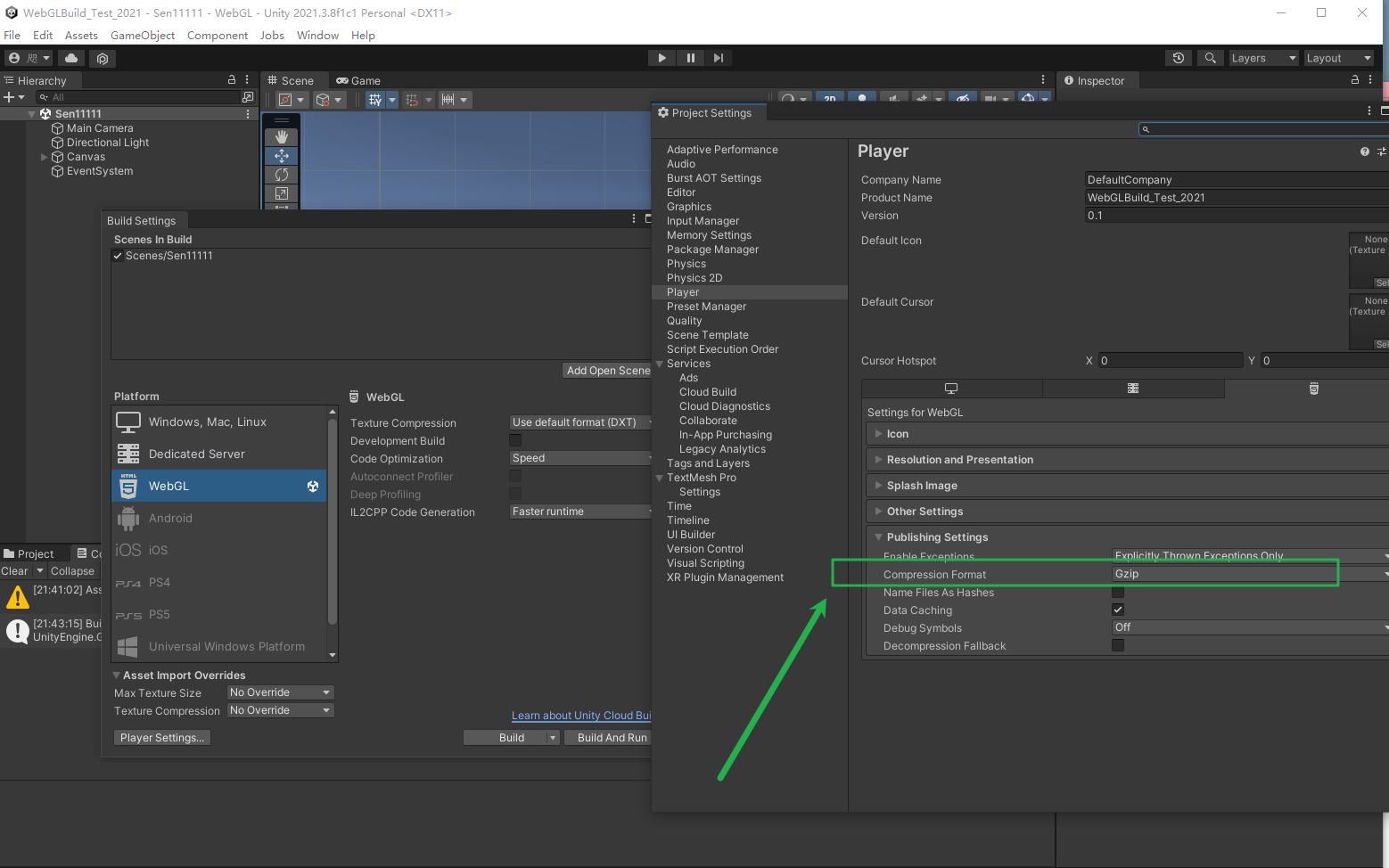
1.文件夹创建,删除,重命名,路径连接,文件打开,关闭读写
#文件夹创建
path = './test'
newpath = "./new"
#判断文件夹是否存在
ret = os.path.exists(path)
if ret:pass
else:#创建文件夹os.mkdir(path)#文件夹重新命名
os.rename(path,newpath)#文件路径连接 #D:new\asc
p = os.path.join('D:',"new","asc")os.rmdir("./new")#删除空文件夹
shutil.rmtree("./new")#删除空或者非空文件夹,利用shutil
#获取当前工作目录,以及打印所有目录文件
print(os.listdir(os.getcwd()))#打开文件,a+表示如果文件存在,移动指针到末尾继续读
file = open("./new/12345.txt",'a+')
file.write('12345')
txt = file.read()
print(txt)
file.close()#创建连续文件夹
path = "./wode/shijie/"
if os.path.exists(path):pass
else:print(os.makedirs(path))2.文件复制,文件夹复制
#复制文件cloudy1.jpg到path = "./wode/shijie/"这个目录"a.jpg"表示重命名为a.jpg文件,如果不写a.jpg,表示直接复制cloudy1.jpg到该目录里面
shutil.copy("E:/test/pythonProject/dataset2/cloudy1.jpg",path+"a.jpg")#文件夹复制
def copy_folder(from_dir_path, to_dir_path):# 文件夹存在则删除if os.path.exists(to_dir_path):shutil.rmtree(to_dir_path)#递归复制文件以及文件夹shutil.copytree(from_dir_path, to_dir_path)#把./dataset2/目录以及里面的文件移动到./setdata/目录里面
shutil.move(path,newpath)#文件或者文件夹移动
path = "./dataset2/"
newpath="./setdata/"
#把./dataset2/目录以及里面的文件移动到./setdata/目录里面
shutil.move(path,newpath)总结:python文件相关操作,主要用 os,os.path,shutil这几个模块就能完成大部分操作。