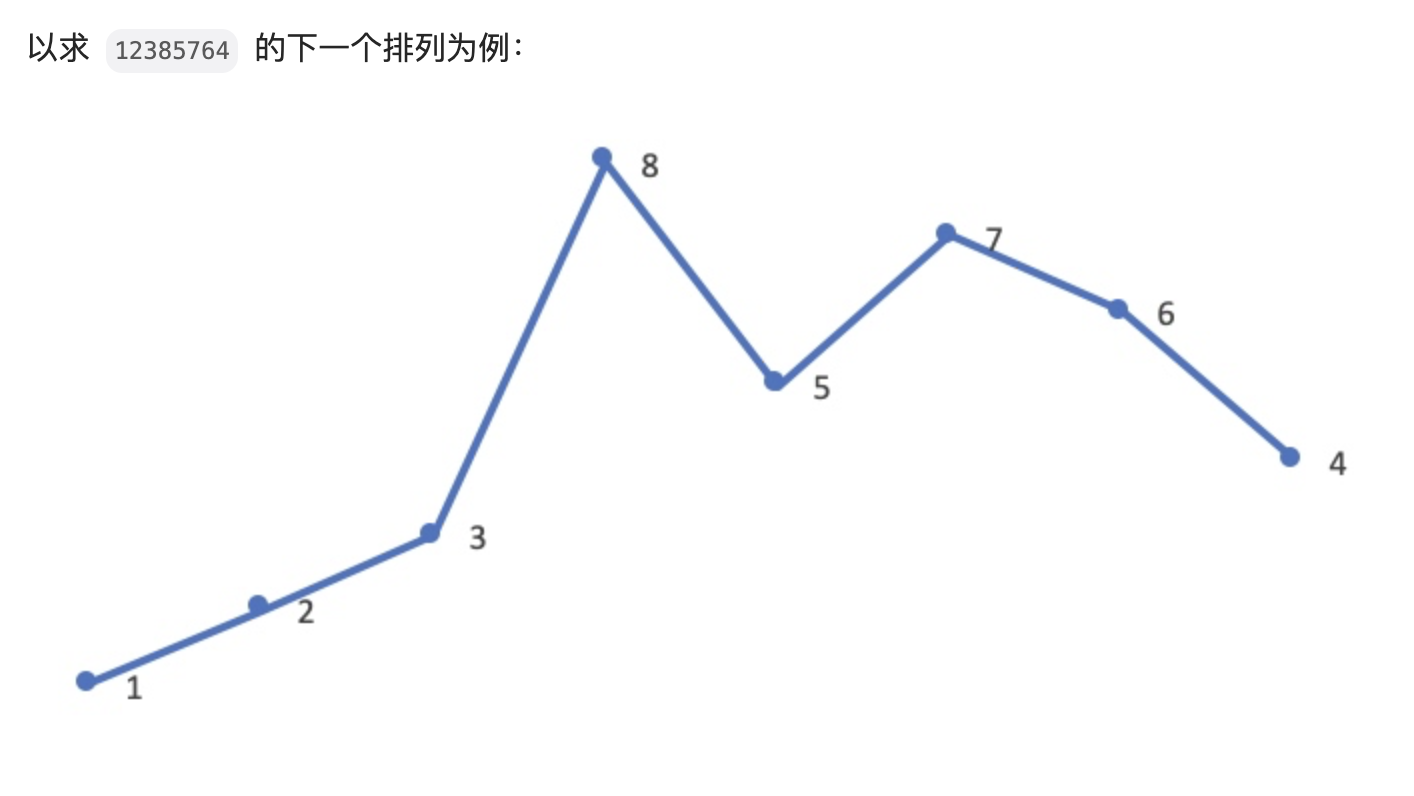
LeetCode 31 下一个排列
整数数组的一个 排列 就是将其所有成员以序列或线性顺序排列。
- 例如,
arr = [1,2,3],以下这些都可以视作arr的排列:[1,2,3]、[1,3,2]、[3,1,2]、[2,3,1]。
整数数组的 下一个排列 是指其整数的下一个字典序更大的排列。更正式地,如果数组的所有排列根据其字典顺序从小到大排列在一个容器中,那么数组的 下一个排列 就是在这个有序容器中排在它后面的那个排列。如果不存在下一个更大的排列,那么这个数组必须重排为字典序最小的排列(即,其元素按升序排列)。
- 例如,
arr = [1,2,3]的下一个排列是[1,3,2]。 - 类似地,
arr = [2,3,1]的下一个排列是[3,1,2]。 - 而
arr = [3,2,1]的下一个排列是[1,2,3],因为[3,2,1]不存在一个字典序更大的排列。
给你一个整数数组 nums ,找出 nums 的下一个排列。
必须原地修改,只允许使用额外常数空间。
示例 1:
输入:nums = [1,2,3]
输出:[1,3,2]
示例 2:
输入:nums = [3,2,1]
输出:[1,2,3]
示例 3:
输入:nums = [1,1,5]
输出:[1,5,1]
提示:
1 <= nums.length <= 1000 <= nums[i] <= 100


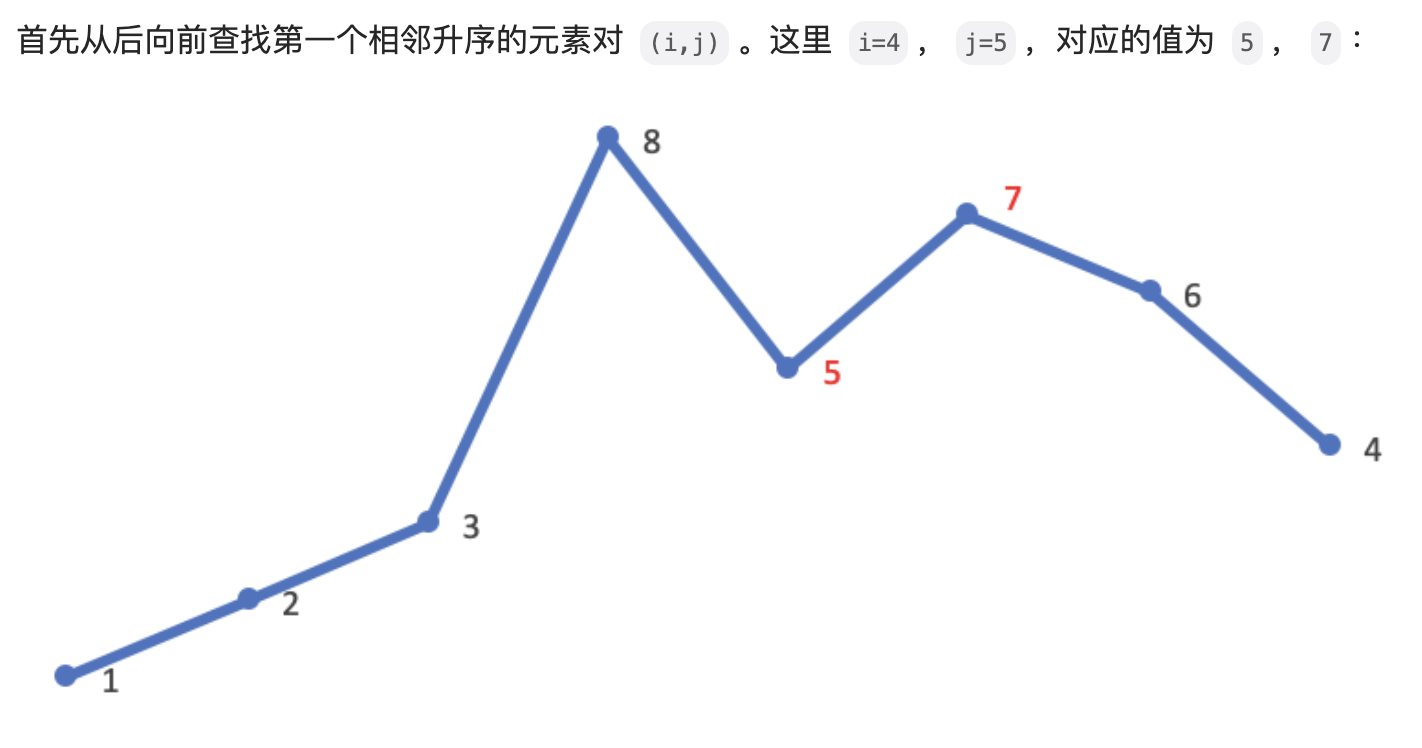
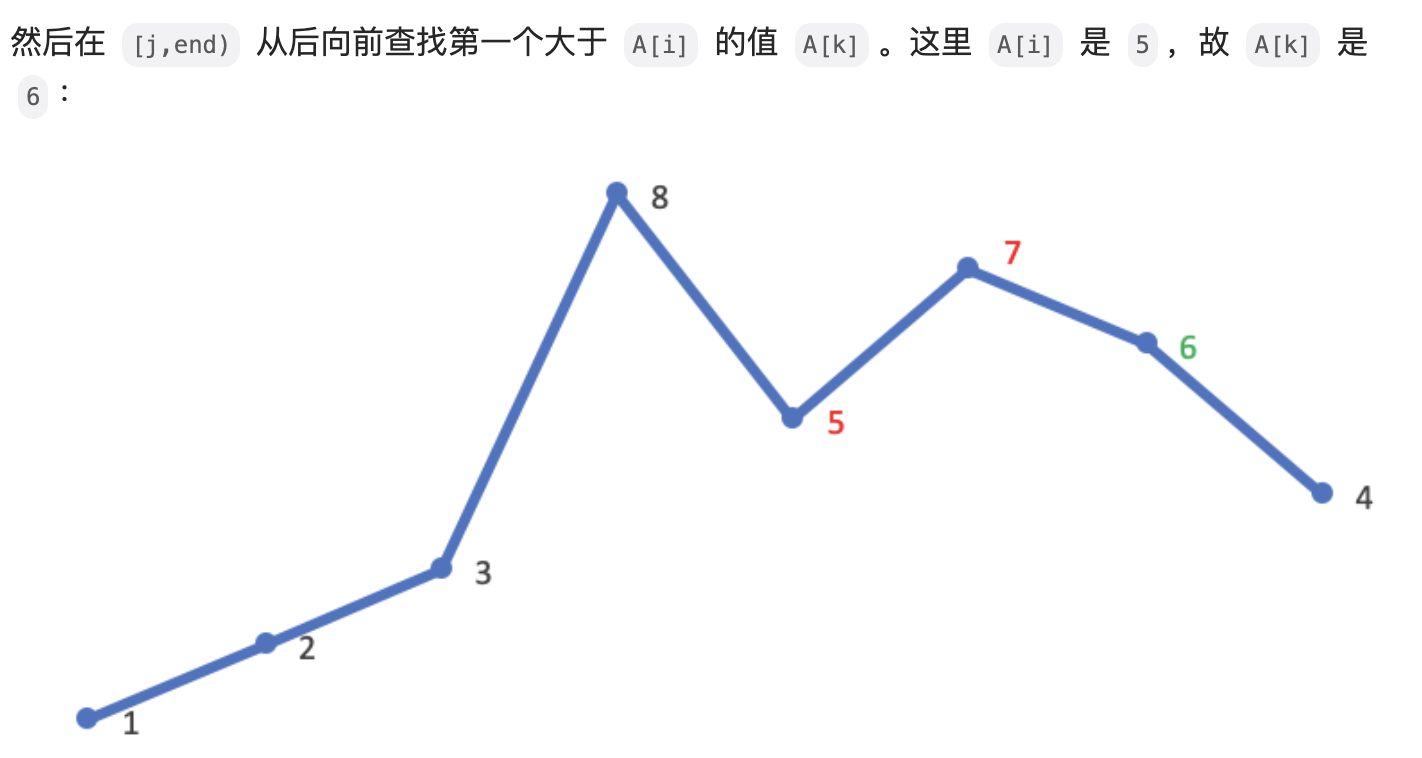
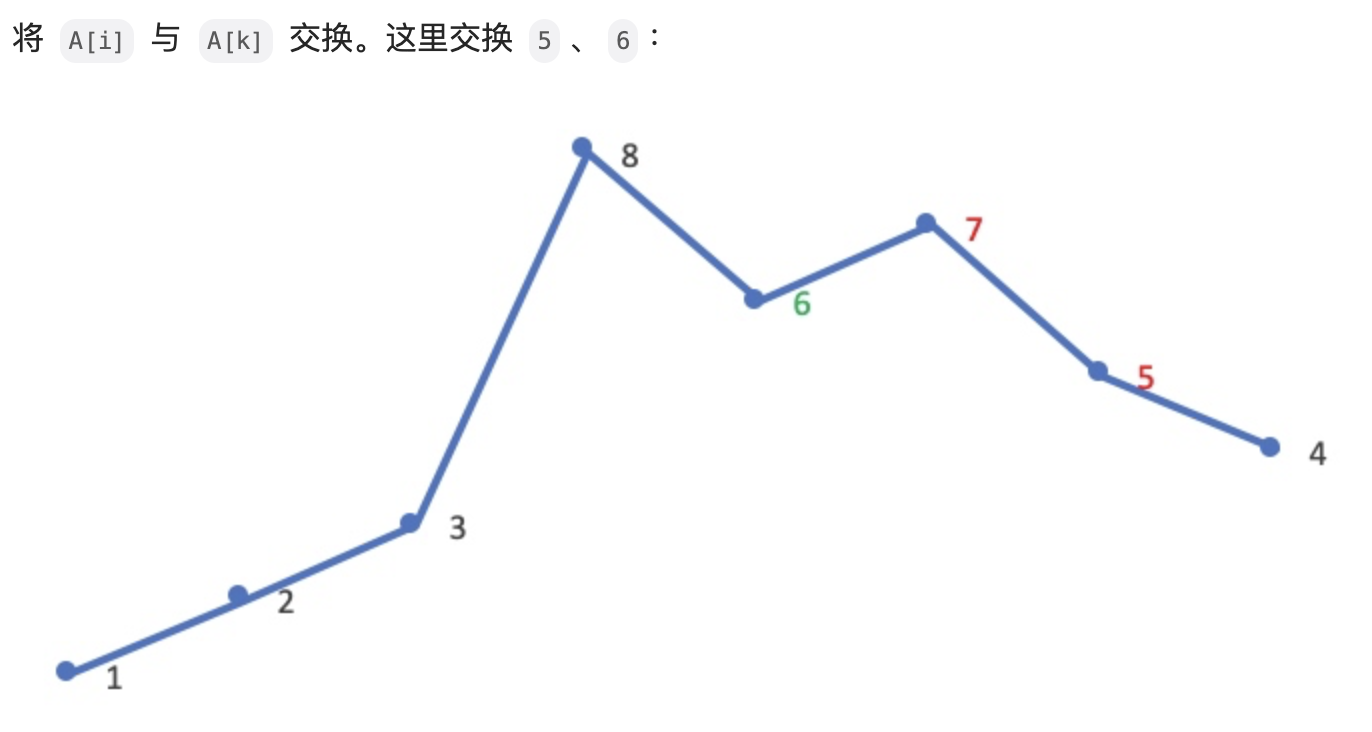
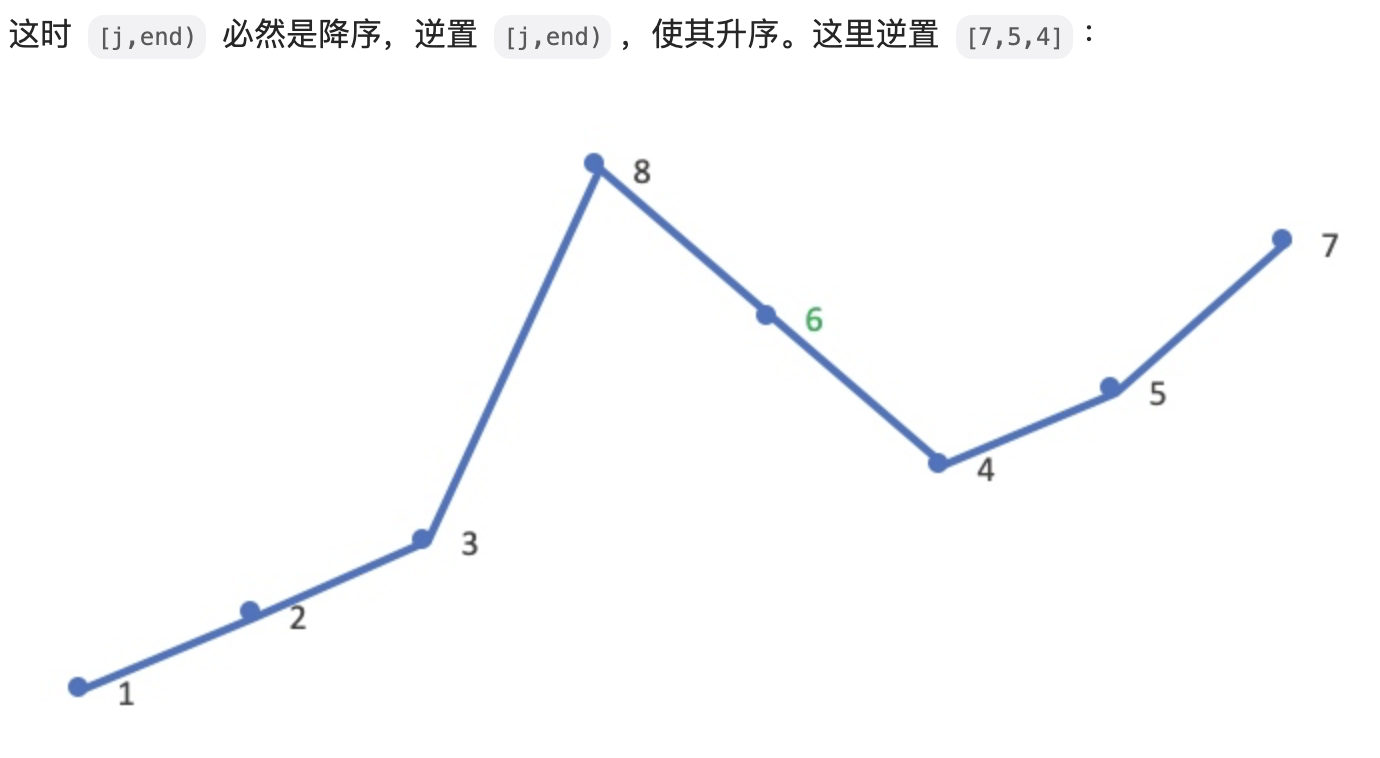
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>using namespace std;//leetcode submit region begin(Prohibit modification and deletion)
class Solution {
public:void nextPermutation(vector<int> &nums) {int l = nums.size();if (l <= 1) {return;}int i = l - 2, j = l - 1, k = l - 1;while (i >= 0 && nums[i] >= nums[j]) {i--;j--;}if (i >= 0) {while (nums[i] >= nums[k]) {k--;}swap(nums[i], nums[k]);}i = j;j = l - 1;while (i < j) {swap(nums[i], nums[j]);i++;j--;}}
};
//leetcode submit region end(Prohibit modification and deletion)