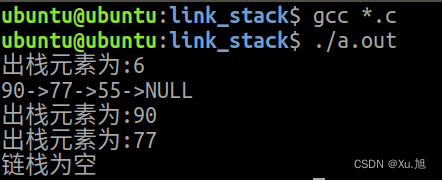
1.整理链栈的代码
//link_stack.c#include"link_stack.h"
//申请栈顶指针
top_p create_top()
{top_p top=(top_p)malloc(sizeof(top_t));if(top==NULL){printf("空间申请失败\n");return NULL;}top->len = 0;top->ptop = NULL; //刚申请栈指针时没有指向元素return top;
}//申请结点的函数
link_p create_node(int data)
{link_p new=(link_p)malloc(sizeof(link_stack));if(new==NULL){printf("申请空间失败\n");return NULL;}new->data=data;return new;
}//入栈/压栈
void push_stack(top_p T,int data)
{if(T==NULL){printf("入参为空\n");return;}link_p new = create_node(data);//入栈new->next = T->ptop;T->ptop = new;T->len++;
}//判空
int empty(top_p T)
{if(T==NULL){printf("入参为空\n");return -1;}return T->ptop==NULL?1:0;
}//出栈/弹栈
void pop_stack(top_p T)
{if(T==NULL){printf("入参为空\n");return;}if(empty(T)){printf("链栈为空\n");return;}link_p del=T->ptop;T->ptop=T->ptop->next;printf("出栈元素为:%d\n",del->data);free(del);T->len--;
}//遍历
void show_stack(top_p T)
{if(T==NULL){printf("入参为空\n");return;}if(empty(T)){printf("链栈为空\n");return;}link_p p=T->ptop;while(p!=NULL){printf("%d->",p->data);p=p->next;}printf("NULL\n");
}//销毁
void free_stack(top_p T)
{if(T==NULL){printf("入参为空\n");return;}if(empty(T)){printf("链栈为空\n");return;}link_p p=T->ptop;while(p!=NULL){pop_stack(T);p=p->next;}T->ptop=NULL;
}
//link_stack.h#ifndef __LINK_STACK_H__
#define __LINK_STACK_H__
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef struct link_stack
{int data;struct link_stack *next;
}link_stack,*link_p;//栈顶指针的类型
//栈顶指针应该独立于栈存在,为了和栈中元素不同
typedef struct top_t
{int len;link_p ptop;
}top_t,*top_p;//申请栈顶指针
top_p create_top();
//申请结点的函数
link_p create_node(int data);
//入栈/压栈
void push_stack(top_p T,int data);
//判空
int empty(top_p T);
//出栈/弹栈
void pop_stack(top_p T);
//遍历
void show_stack(top_p T);
//销毁
void free_stack(top_p T);#endif
//main.c#include"link_stack.h"
int main()
{top_p T=create_top();push_stack(T,55);push_stack(T,77);push_stack(T,90);push_stack(T,6);pop_stack(T);show_stack(T);free_stack(T);show_stack(T);return 0;
}
![[设计模式Java实现附plantuml源码~行为型]算法的封装与切换——策略模式](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/c3f715fd4cc24ea48cdb328b8abe5436.png)