Tomcat源码系列文章
Tomcat源码解析(一): Tomcat整体架构
Tomcat源码解析(二): Bootstrap和Catalina
目录
- 一、基础组件
- 1、Lifecycle生命周期顶级接口
- 2、组件的默认实现
- 二、启动类Bootstrap
- 1、main
- 2、init
- 3、load与start
- 三、加载Catalina
- 1、load
- 2、start
- 2.1、注册shutdown钩子
- 2.2、监听shutdown命令
- 2.3、停止Tomcat
- 四、总结
一、基础组件
1、Lifecycle生命周期顶级接口
- 由于所有的组件均存在
初始化、启动、停止等生命周期方法,拥有生命周期管理的特性 - 基于生命周期管理抽象成了一个接口
Lifecycle - 组件Server、Service、Container、Executor、Connector组件,都实现生命周期的接口

2、组件的默认实现
先回顾下组件的作用以及之间的关系
Server:表示整个Tomcat Catalina servlet容器,Server中可以有多个ServiceService:表示Connector和Engine的组合,对外提供服务,Service可以包含多个Connector和一个EngineConnector:为Tomcat Engine的连接组件,支持三种协议:HTTP/1.1、HTTP/2.0、AJPEndpoint负责提供字节流给ProcessorProcessor负责提供Tomcat Request对象给AdapterAdapter负责提供ServletRequest对象给容器,实现类只有CoyoteAdapter
Engine:顶级容器,不能被其他容器包含,它接受处理连接器的所有请求,并将响应返回相应的连接器Host:表示一个虚拟主机,包含主机名称和IP地址,这里默认是localhostContext:表示一个 Web 应用程序,是 Servlet、Filter 的父容器Wrapper:表示一个 Servlet,它负责管理 Servlet 的生命周期,并提供了方便的机制使用拦截器

组件默认实现的类图
- 对于Endpoint组件来说,在Tomcat中没有对应的Endpoint接口, 但是有一个抽象类AbstractEndpoint
- Tomcat8.5版本中,默认采用的是
NioEndpoint

- ProtocolHandler:通过封装Endpoint和Processor , 实现针对具体协议的处理功能
- Tomcat按照协议和IO提供了6个实现类
- AJP协议
- AjpNioProtocol :采用NIO的IO模型
- AjpNio2Protocol:采用NIO2的IO模型
- AjpAprProtocol :采用APR的IO模型,需要依赖于APR库
- HTTP协议
Http11NioProtocol :采用NIO的IO模型,默认使用的协议- Http11Nio2Protocol:采用NIO2的IO模型
- Http11AprProtocol :采用APR的IO模型,需要依赖于APR库
- AJP协议

二、启动类Bootstrap
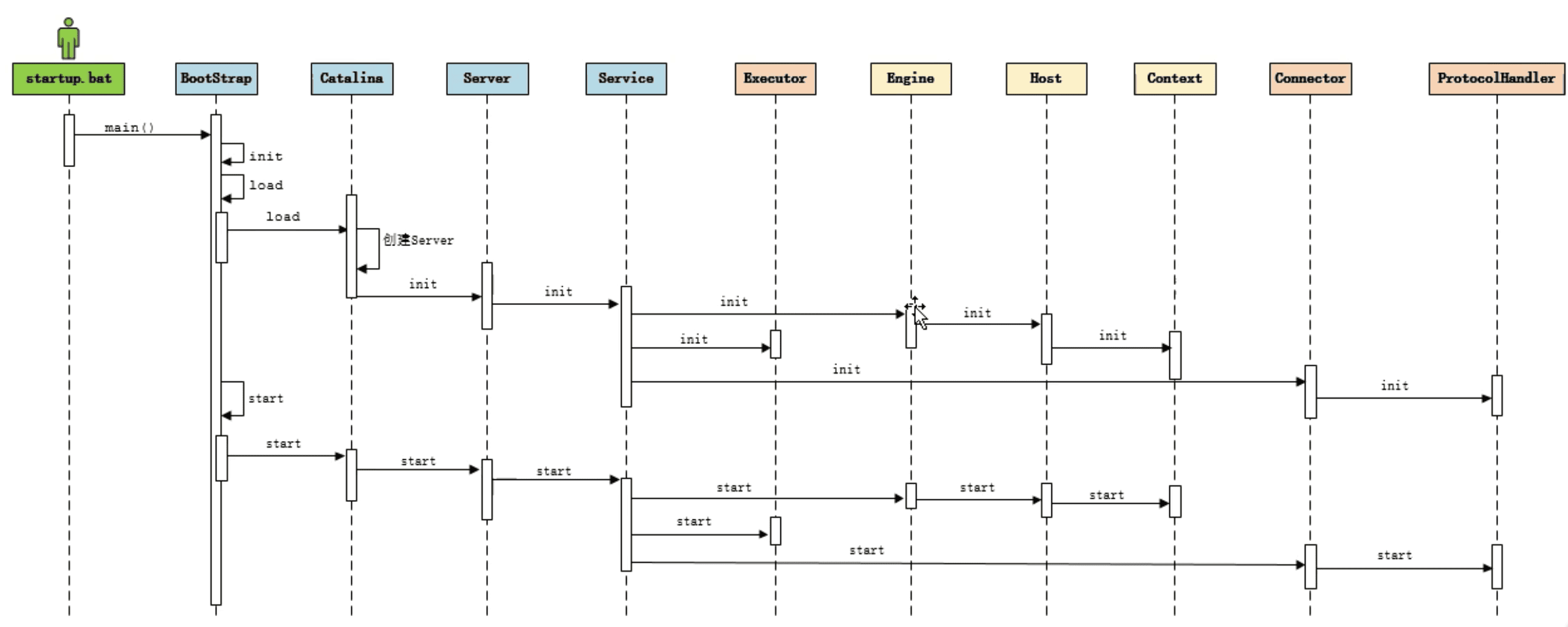
- 首先来看下整个启动过程,我们可以看到
Bootstrap作为启动入口首先进行了初始化方法init然后load方法加载了Catalina
1、main
- Bootstrap的main方法首先会创建一个
Bootstrap对象,调用它的init方法初始化 - 然后根据启动参数,调用Bootstrap对象的不同方法,默认模式为start,该模式下将会先后调用
load与start方法
private static final Object daemonLock = new Object();
private static volatile Bootstrap daemon = null;// Bootstrap类的main方法
public static void main(String args[]) {// 创建一个 Bootstrap 对象synchronized (daemonLock) {if (daemon == null) {Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap();try {// 调用init方法初始化bootstrap.init();} catch (Throwable t) {handleThrowable(t);t.printStackTrace();return;}daemon = bootstrap;} else {Thread.currentThread().setContextClassLoader(daemon.catalinaLoader);}}// 根据启动参数,分别调用 Bootstrap 对象的不同方法try {// 默认参数为startString command = "start"; if (args.length > 0) {command = args[args.length - 1];}if (command.equals("startd")) {...} else if (command.equals("stopd")) {...} else if (command.equals("start")) {daemon.setAwait(true);daemon.load(args);daemon.start();if (null == daemon.getServer()) {System.exit(1);}} else if (command.equals("stop")) {...} else if (command.equals("configtest")) {... } else {log.warn("Bootstrap: command \"" + command + "\" does not exist.");}} catch (Throwable t) {if (t instanceof InvocationTargetException &&t.getCause() != null) {t = t.getCause();}handleThrowable(t);t.printStackTrace();System.exit(1);}
}
2、init
- 本文对类加载器内容不做分析,后续看情况单独讲
- 简单来说init就是
反射实例化Catalina对象
public void init() throws Exception {// 初始化类加载器相关内容initClassLoaders();Thread.currentThread().setContextClassLoader(catalinaLoader);SecurityClassLoad.securityClassLoad(catalinaLoader);// Load our startup class and call its process() methodif (log.isDebugEnabled())log.debug("Loading startup class");// 通过catalinaLoader加载Catalina,反射实例化Catalina对象Class<?> startupClass = catalinaLoader.loadClass("org.apache.catalina.startup.Catalina");Object startupInstance = startupClass.getConstructor().newInstance();// Set the shared extensions class loaderif (log.isDebugEnabled())log.debug("Setting startup class properties");String methodName = "setParentClassLoader";Class<?> paramTypes[] = new Class[1];paramTypes[0] = Class.forName("java.lang.ClassLoader");Object paramValues[] = new Object[1];paramValues[0] = sharedLoader;// 反射将sharedLoader设置为catalinaLoader的父类加载器,本文不做分析Method method =startupInstance.getClass().getMethod(methodName, paramTypes);method.invoke(startupInstance, paramValues);// 将catalina实例引用赋值catalinaDaemon = startupInstance;
}
3、load与start
- load与start都是通过上一步获取到的catalinaDaemon对象反射调用catalina类的
load与start方法 - 这两个过程我们会在下面的Catalina内容中介绍
load方法:
private void load(String[] arguments) throws Exception {String methodName = "load";Object param[];Class<?> paramTypes[];if (arguments==null || arguments.length==0) {paramTypes = null;param = null;} else {paramTypes = new Class[1];paramTypes[0] = arguments.getClass();param = new Object[1];param[0] = arguments;}Method method =catalinaDaemon.getClass().getMethod(methodName, paramTypes); // 反射调用catalina的load方法,参数为nullmethod.invoke(catalinaDaemon, param);
}
start方法:
public void start()throws Exception {if( catalinaDaemon==null ) init();// 反射调用catalina的start方法,参数为nullMethod method = catalinaDaemon.getClass().getMethod("start", (Class [] )null);method.invoke(catalinaDaemon, (Object [])null);}
三、加载Catalina
- 上文中Bootstrap类的load与start方法实质上就是反射调用catalina类的load与start方法
1、load
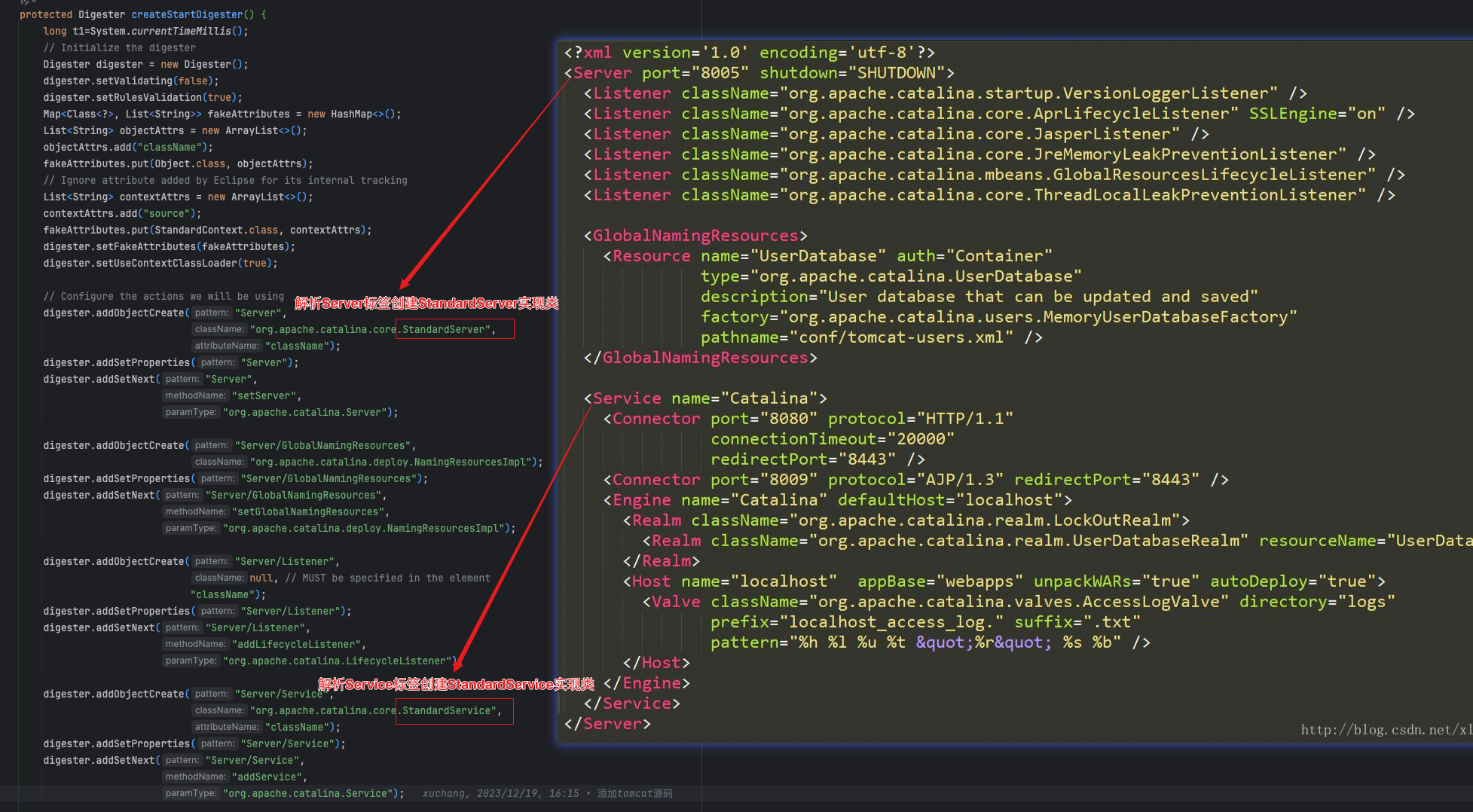
- 创建Digester对象,解析
conf/server.xml文件 - 调用Server实现类
StandardServer的init方法来初始化组件(下篇文章单独讲)
public void load() {// 如果已经加载则退出,默认false,下面会置为trueif (loaded) {return;}loaded = true;initDirs();initNaming();// 创建Digester对象,用来解析server.xml文件Digester digester = createStartDigester();InputSource inputSource = null;InputStream inputStream = null;File file = null;try {// 加载conf目录下的server.xml文件file = configFile();inputStream = new FileInputStream(file);inputSource = new InputSource(file.toURI().toURL().toString());} catch (Exception e) {...}try {inputSource.setByteStream(inputStream);digester.push(this);// 开始解析conf/server.xml文件digester.parse(inputSource);} catch (SAXParseException spe) {...} // server和catalina之间建立关联// Server接口实现类StandardServer是在解析server.xml文件时候创建// 当时StandardServer对象set到Catalina// 此时又将Catalinaset到StandardServer对象中// 形成:你中有我,我中有你getServer().setCatalina(this);getServer().setCatalinaHome(Bootstrap.getCatalinaHomeFile());getServer().setCatalinaBase(Bootstrap.getCatalinaBaseFile());...// 初始化server,后面另开一篇单独讲try {getServer().init();} catch (LifecycleException e) {...}
}
Digester对象解析server.xml文件
2、start
- 再来看下整个启动过程
- Catalina的load方法最后一步getServer().init(),就是Server、Service、Engine等一系列
组件的初始化
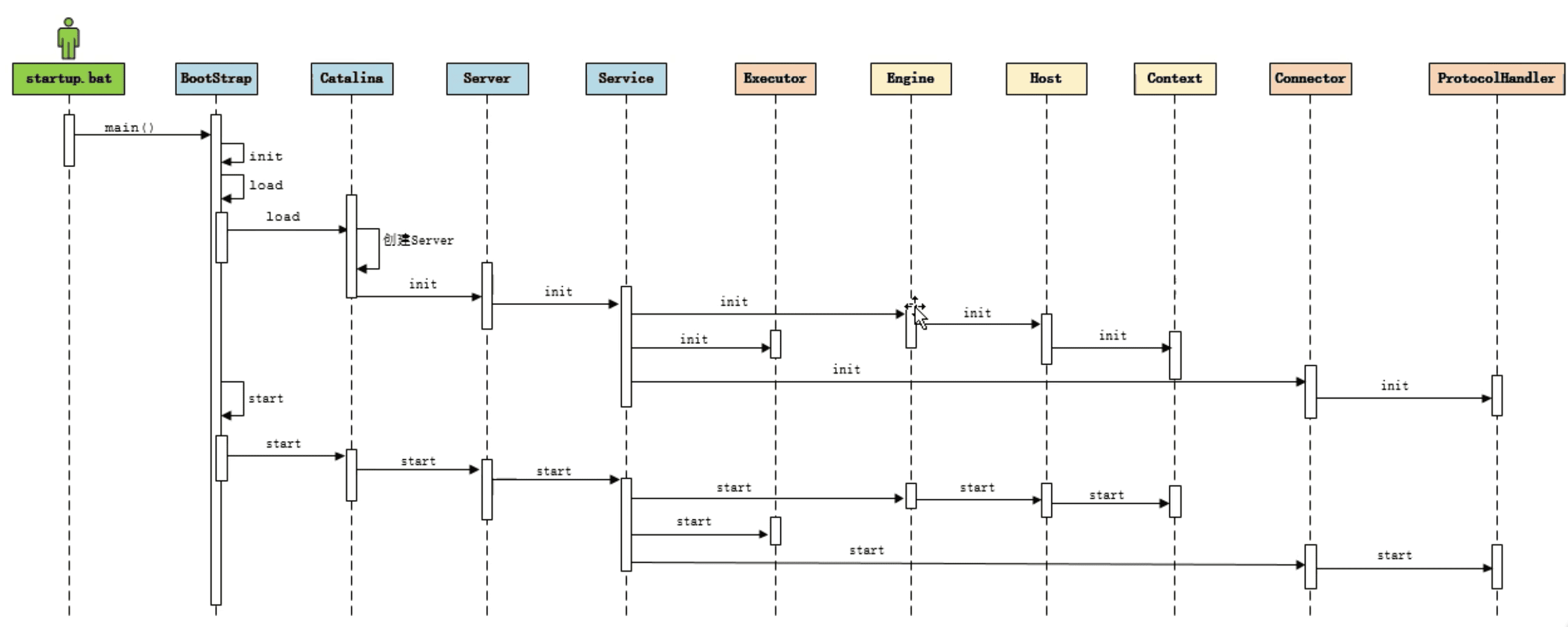
- 调用server实现类
StandardServer的start方法来启动服务器(下篇文章单独讲)
public void start() {if (getServer() == null) {load();}if (getServer() == null) {// 无法启动服务器。未配置服务器实例log.fatal("Cannot start server. Server instance is not configured.");return;}long t1 = System.nanoTime();// 调用server的start方法来启动服务器try {getServer().start();} catch (LifecycleException e) {log.fatal(sm.getString("catalina.serverStartFail"), e);try {getServer().destroy();} catch (LifecycleException e1) {log.debug("destroy() failed for failed Server ", e1);}return;}long t2 = System.nanoTime();if(log.isInfoEnabled()) {log.info("Server startup in " + ((t2 - t1) / 1000000) + " ms");}// 注册关闭钩子if (useShutdownHook) {if (shutdownHook == null) {shutdownHook = new CatalinaShutdownHook();}// 注册shutdown钩子,main结束时调用// 如果server未停止调用stop方法停止Runtime.getRuntime().addShutdownHook(shutdownHook);LogManager logManager = LogManager.getLogManager();if (logManager instanceof ClassLoaderLogManager) {((ClassLoaderLogManager) logManager).setUseShutdownHook(false);}}// 进入等待状态// 启动类Bootstrap默认调start方法设置await=trueif (await) {// main线程等待,等待接收shutdown命令,接受到则跳出阻塞await();// 跳出阻塞,执行Server.stop();stop();}
}
2.1、注册shutdown钩子
- 注册shutdown钩子(CatalinaShutdownHook),即注册一个
线程任务,main结束时调用 - getServer() != null 如果server未停止调用
Catalina的stop方法停止
protected class CatalinaShutdownHook extends Thread {@Overridepublic void run() {try {if (getServer() != null) {Catalina.this.stop();}} catch (Throwable ex) {...}}
}
2.2、监听shutdown命令
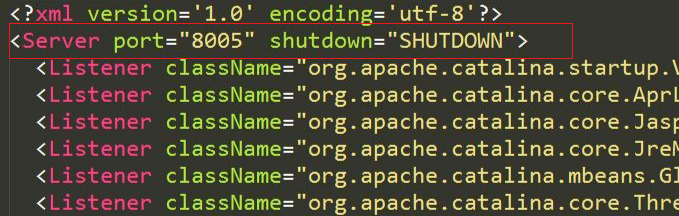
- Socket监听8005端口shutdown命令
- 服务启动后服务器会监听
8005端口,如果这个端口接收到了"SHUTDOWN"这个字符串,那么就会终止Server
server.xml开头内容
- Catalina的await方法实际是调用Server实现类StandardServer的await方法
public void await() {getServer().await();
}
- while循环监听Socket8005端口
- 如果Socket输入流读取到字符串“SHUTDOWN”,跳出while循环
- Catalina的await阻塞方法就通过了
// StandardServer类方法private int port = 8005;private String shutdown = "SHUTDOWN";private volatile ServerSocket awaitSocket = null;@Override
public void await() {// shutdown端口配置为-2,启动完Server直接再终止Serverif( port == -2 ) {return;}// 配置为-1,则不再监听shutdown端口if( port==-1 ) {try {awaitThread = Thread.currentThread();while(!stopAwait) {try {Thread.sleep( 10000 );} catch( InterruptedException ex ) {// continue and check the flag}}} finally {awaitThread = null;}return;}// 开启socket监听server.xml中的shutdown端口// 创建socket服务端try {awaitSocket = new ServerSocket(port, 1,InetAddress.getByName(address));} catch (IOException e) {return;}// 默认false,进入while循环while (!stopAwait) {ServerSocket serverSocket = awaitSocket;if (serverSocket == null) {break;}// Wait for the next connectionSocket socket = null;StringBuilder command = new StringBuilder();InputStream stream;try {// accept阻塞监听端口socket = serverSocket.accept();// 设置阻塞超时时间10秒,如果超时抛异常,catch捕捉到重新进入while循环socket.setSoTimeout(10 * 1000); stream = socket.getInputStream();} catch (SocketTimeoutException ste) {continue;}// 从流中读取字符串...// 如果读取到字符串命令是"SHUTDOWN"则,跳出循环,开始终止服务器// shutdown变量是取server.xml中Server的shutdown属性boolean match = command.toString().equals(shutdown);if (match) {log.info(sm.getString("standardServer.shutdownViaPort"));break;} elselog.warn("StandardServer.await: Invalid command '"+ command.toString() + "' received");}
}
2.3、停止Tomcat
- await方法的作用是
停住主线程,等待用户输入SHUTDOWN命令之后- 停止等待,然后main线程就调用
stop方法来停止Tomcat
- 停止等待,然后main线程就调用
- 最终调用Server的stop和destroy方法(下篇文章单独讲)
public void stop() {try {if (useShutdownHook) {// 移除shutdown钩子,这个stop方法会停止server,不需要钩子再次执行Runtime.getRuntime().removeShutdownHook(shutdownHook);LogManager logManager = LogManager.getLogManager();if (logManager instanceof ClassLoaderLogManager) {((ClassLoaderLogManager) logManager).setUseShutdownHook(true);}}} catch (Throwable t) {ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t);}// 调用Server的stop和destroy方法try {Server s = getServer();LifecycleState state = s.getState();if (LifecycleState.STOPPING_PREP.compareTo(state) <= 0&& LifecycleState.DESTROYED.compareTo(state) >= 0) {// Nothing to do. stop() was already called} else {s.stop();s.destroy();}} catch (LifecycleException e) {log.error("Catalina.stop", e);}
}
四、总结
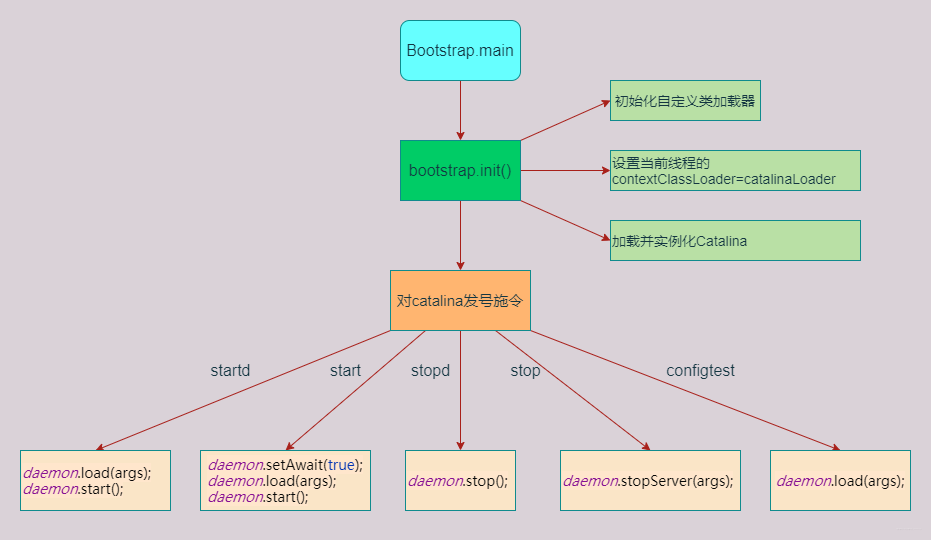
- Bootstrap是一个启动引导类,本身没有太多启动关闭细节的实现
- 而是通过加载Catalina,对Catalina发号施令,调用start、stop等方法
![[LeetCode]143.重排链表](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/7f2d26897f974ab4b5ca2a57ebefe008.png)