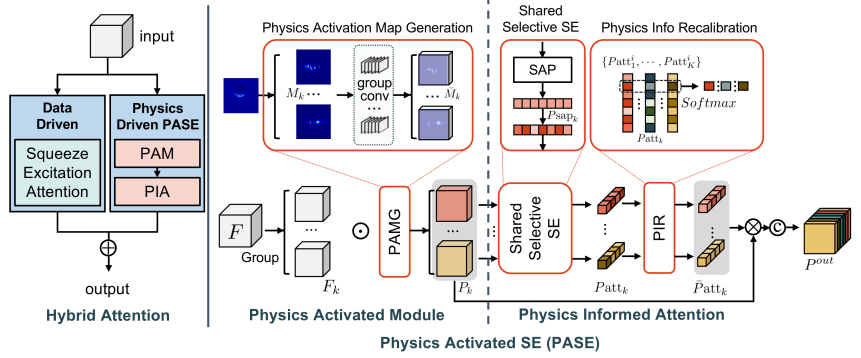
5 种常见的请求类型:
- GET :请求从服务器获取特定资源。举个例子:GET /users(获取所有学生)
- POST :在服务器上创建一个新的资源。举个例子:POST /users(创建学生)
- PUT :更新服务器上的资源(客户端提供更新后的整个资源)。举个例子:PUT /users/12(更新编号为 12 的学生)
- DELETE :从服务器删除特定的资源。举个例子:DELETE /users/12(删除编号为 12 的学生)
- PATCH :更新服务器上的资源(客户端提供更改的属性,可以看做作是部分更新),使用的比较少
GET 请求
@GetMapping("users") 等价于@RequestMapping(value="/users",method=RequestMethod.GET)
@GetMapping("/users")
public ResponseEntity<List<User>> getAllUsers() {return userRepository.findAll();
}POST 请求
@PostMapping("users") 等价于@RequestMapping(value="/users",method=RequestMethod.POST)
关于@RequestBody注解的使用
@PostMapping("/users")
public ResponseEntity<User> createUser(@Valid @RequestBody UserCreateRequest userCreateRequest) {return userRespository.save(user);
}PUT 请求
@PutMapping("/users/{userId}") 等价于@RequestMapping(value="/users/{userId}",method=RequestMethod.PUT)
@PutMapping("/users/{userId}")
public ResponseEntity<User> updateUser(@PathVariable(value = "userId") Long userId,@Valid @RequestBody UserUpdateRequest userUpdateRequest) {......
}DELETE 请求
@DeleteMapping("/users/{userId}")等价于@RequestMapping(value="/users/{userId}",method=RequestMethod.DELETE)
@DeleteMapping("/users/{userId}")
public ResponseEntity deleteUser(@PathVariable(value = "userId") Long userId){......
}PATCH 请求
一般实际项目中,我们都是 PUT 不够用了之后才用 PATCH 请求去更新数据。
@PatchMapping("/profile")public ResponseEntity updateStudent(@RequestBody StudentUpdateRequest studentUpdateRequest) {studentRepository.updateDetail(studentUpdateRequest);return ResponseEntity.ok().build();}