TAAD2.2论文概览
- 0.前言
- 1-10
- 1.Bridge the Gap Between CV and NLP! A Gradient-based Textual Adversarial Attack Framework
- a. 背景
- b. 方法
- c. 结果
- d. 论文及代码
- 2.TextHacker: Learning based Hybrid Local Search Algorithm for Text Hard-label Adversarial Attack
- a. 背景
- b. 方法
- c. 结果
- d. 论文及代码
- 3.TextHoaxer: Budgeted Hard-Label Adversarial Attacks on Text
- a. 背景
- b. 方法
- c. 结果
- d. 论文及代码
- 4.Query-Efficient and Scalable Black-Box Adversarial Attacks on Discrete Sequential Data via Bayesian Optimization
- a. 背景
- b. 方法
- c. 结果
- d. 论文及代码
- 5.SemAttack: Natural Textual Attacks on Different Semantic Spaces
- a. 背景
- b. 方法
- c. 结果
- d. 论文及代码
- 6.Gradient-based Adversarial Attacks against Text Transformers
- a. 背景
- b. 方法
- c. 结果
- d. 论文及代码
- 7.A Strong Baseline for Query Efficient Attacks in a Black Box Setting
- a. 背景
- b. 方法
- c. 结果
- d. 论文及代码
- 8.On the Transferability of Adversarial Attacks against Neural Text Classifier
- a. 背景
- b. 方法
- c. 结果
- d. 论文及代码
- 9.Crafting Adversarial Examples for Neural Machine Translation
- a. 背景
- b. 方法
- c. 结果
- d. 论文及代码
- 10.An Empirical Study on Adversarial Attack on NMT: Languages and Positions Matter
- a. 背景
- b. 方法
- c. 结果
- d. 论文及代码
- 11-20
- 11.A Closer Look into the Robustness of Neural Dependency Parsers Using Better Adversarial Examples
- a. 背景
- b. 方法
- c. 结果
- d. 论文及代码
- 12.Contextualized Perturbation for Textual Adversarial Attack
- a. 背景
- b. 方法
- c. 结果
- d. 论文及代码
- 13.Adv-OLM: Generating Textual Adversaries via OLM
- a. 背景
- b. 方法
- c. 结果
- d. 论文及代码
- 14.Adversarial Stylometry in the Wild: Transferable Lexical Substitution Attacks on Author Profiling
- a. 背景
- b. 方法
- c. 结果
- d. 论文及代码
- 15.Generating Natural Language Attacks in a Hard Label Black Box Setting
- a. 背景
- b. 方法
- c. 结果
- d. 论文及代码
- 16.A Geometry-Inspired Attack for Generating Natural Language Adversarial Examples
- a. 背景
- b. 方法
- c. 结果
- d. 论文及代码
- 17.BERT-ATTACK: Adversarial Attack Against BERT Using BERT
- a. 背景
- b. 方法
- c. 结果
- d. 论文及代码
- 18.BAE: BERT-based Adversarial Examples for Text Classification
- a. 背景
- b. 方法
- c. 结果
- d. 论文及代码
- 19.Detecting Word Sense Disambiguation Biases in Machine Translation for Model-Agnostic Adversarial Attacks
- a. 背景
- b. 方法
- c. 结果
- d. 论文及代码
- 20.Imitation Attacks and Defenses for Black-box Machine Translation Systems
- a. 背景
- b. 方法
- c. 结果
- d. 论文及代码
- 21-30
- 21.Robustness to Modification with Shared Words in Paraphrase Identification
- a. 背景
- b. 方法
- c. 结果
- d. 论文及代码
- 22.Word-level Textual Adversarial Attacking as Combinatorial Optimization
- a. 背景
- b. 方法
- c. 结果
- d. 论文及代码
- 23.It's Morphin' Time! Combating Linguistic Discrimination with Inflectional Perturbations
- a. 背景
- b. 方法
- c. 结果
- d. 论文及代码
- 24.On the Robustness of Language Encoders against Grammatical Errors
- a. 背景
- b. 方法
- c. 结果
- d. 论文及代码
- 25.Evaluating and Enhancing the Robustness of Neural Network-based Dependency Parsing Models with Adversarial Examples
- a. 背景
- b. 方法
- c. 结果
- d. 论文及代码
- 26.A Reinforced Generation of Adversarial Examples for Neural Machine Translation
- a. 背景
- b. 方法
- c. 结果
- d. 论文及代码
- 27.Is BERT Really Robust? A Strong Baseline for Natural Language Attack on Text Classification and Entailment
- a. 背景
- b. 方法
- c. 结果
- d. 论文及代码
- 28.Seq2Sick: Evaluating the Robustness of Sequence-to-Sequence Models with Adversarial Examples
- a. 背景
- b. 方法
- c. 结果
- d. 论文及代码
- 29.Greedy Attack and Gumbel Attack: Generating Adversarial Examples for Discrete Data
- a. 背景
- b. 方法
- c. 结果
- d. 论文及代码
- 30.On the Robustness of Self-Attentive Models
- a. 背景
- b. 方法
- c. 结果
- d. 论文及代码
- 31-40
- 31.Generating Natural Language Adversarial Examples through Probability Weighted Word Saliency
- a. 背景
- b. 方法
- c. 结果
- d. 论文及代码
- 32.Generating Fluent Adversarial Examples for Natural Languages
- a. 背景
- b. 方法
- c. 结果
- d. 论文及代码
- 33.Robust Neural Machine Translation with Doubly Adversarial Inputs
- a. 背景
- b. 方法
- c. 结果
- d. 论文及代码
- 34.Universal Adversarial Attacks on Text Classifiers
- a. 背景
- b. 方法
- c. 结果
- d. 论文及代码
- 35.Generating Natural Language Adversarial Examples
- a. 背景
- b. 方法
- c. 结果
- d. 论文及代码
- 36.Breaking NLI Systems with Sentences that Require Simple Lexical Inferences
- a. 背景
- b. 方法
- c. 结果
- d. 论文及代码
- 37.Deep Text Classification Can be Fooled
- a. 背景
- b. 方法
- c. 结果
- d. 论文及代码
- 38.Interpretable Adversarial Perturbation in Input Embedding Space for Text
- a. 背景
- b. 方法
- c. 结果
- d. 论文及代码
- 🔖39.Towards Crafting Text Adversarial Samples
- a. 背景
- b. 方法
- c. 结果
- d. 论文及代码
- 📄40.Crafting Adversarial Input Sequences For Recurrent Neural Networks
- a. 背景(考古2016):
- b. 方法
- c. 结果
- d. 论文及代码
Must-read Papers on Textual Adversarial Attack and Defense (TAAD)
必读的文本对抗性攻击与防御论文(TAAD)系列之2.2 Word-level Attack
2.2 Word-level Attack
0.前言
2024.3.3— 正在编辑
1-10
1.Bridge the Gap Between CV and NLP! A Gradient-based Textual Adversarial Attack Framework
a. 背景
b. 方法
c. 结果
d. 论文及代码
Bridge the Gap Between CV and NLP! A Gradient-based Textual Adversarial Attack Framework. Lifan Yuan, Yichi Zhang, Yangyi Chen, Wei Wei. Findings of ACL 2023. decision[pdf]
论文:[2110.15317] Bridge the Gap Between CV and NLP! A Gradient-based Textual Adversarial Attack Framework (arxiv.org)
代码:https://github.com/Phantivia/T-PGD.
2.TextHacker: Learning based Hybrid Local Search Algorithm for Text Hard-label Adversarial Attack
a. 背景
b. 方法
c. 结果
d. 论文及代码
TextHacker: Learning based Hybrid Local Search Algorithm for Text Hard-label Adversarial Attack. Zhen Yu, Xiaosen Wang, Wanxiang Che, Kun He. Findings of EMNLP 2022. decision[pdf][code]
论文:[2201.08193] TextHacker: Learning based Hybrid Local Search Algorithm for Text Hard-label Adversarial Attack (arxiv.org)
代码:GitHub - JHL-HUST/TextHacker: TextHacker: Learning based Hybrid Local Search Algorithm for Hard-label Text Adversarial Attack
3.TextHoaxer: Budgeted Hard-Label Adversarial Attacks on Text
a. 背景
b. 方法
c. 结果
d. 论文及代码
TextHoaxer: Budgeted Hard-Label Adversarial Attacks on Text. Muchao Ye, Chenglin Miao, Ting Wang, Fenglong Ma. AAAI 2022. decision [pdf] [code]
论文:TextHoaxer: Budgeted Hard-Label Adversarial Attacks on Text | Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence
代码:GitHub - machinelearning4health/TextHoaxer: Implementation Code of TextHoaxer
4.Query-Efficient and Scalable Black-Box Adversarial Attacks on Discrete Sequential Data via Bayesian Optimization
a. 背景
b. 方法
c. 结果
d. 论文及代码
Query-Efficient and Scalable Black-Box Adversarial Attacks on Discrete Sequential Data via Bayesian Optimization. Deokjae Lee, Seungyong Moon, Junhyeok Lee, Hyun Oh Song. ICML 2022. score [pdf][code]
论文:[2206.08575] Query-Efficient and Scalable Black-Box Adversarial Attacks on Discrete Sequential Data via Bayesian Optimization (arxiv.org)
代码:GitHub - snu-mllab/DiscreteBlockBayesAttack: Official PyTorch implementation of “Query-Efficient and Scalable Black-Box Adversarial Attacks on Discrete Sequential Data via Bayesian Optimization” (ICML’22)
5.SemAttack: Natural Textual Attacks on Different Semantic Spaces
a. 背景
b. 方法
c. 结果
d. 论文及代码
SemAttack: Natural Textual Attacks on Different Semantic Spaces. Boxin Wang, Chejian Xu, Xiangyu Liu, Yu Cheng, Bo Li. Findings of NAACL 2022. gradient [pdf] [code]
论文:[2205.01287] SemAttack: Natural Textual Attacks via Different Semantic Spaces (arxiv.org)
代码:github.com
6.Gradient-based Adversarial Attacks against Text Transformers
a. 背景
b. 方法
c. 结果
d. 论文及代码
Gradient-based Adversarial Attacks against Text Transformers. Chuan Guo, Alexandre Sablayrolles, Hervé Jégou, Douwe Kiela. EMNLP 2021. gradient [pdf] [code]
论文:2021.emnlp-main.464.pdf (aclanthology.org)
代码:https://github.com/facebookresearch/text-adversarial-attack
7.A Strong Baseline for Query Efficient Attacks in a Black Box Setting
a. 背景
b. 方法
c. 结果
d. 论文及代码
A Strong Baseline for Query Efficient Attacks in a Black Box Setting. Rishabh Maheswary, Saket Maheshwary, Vikram Pudi. EMNLP 2021. score [pdf] [code]
论文:[2109.04775] A Strong Baseline for Query Efficient Attacks in a Black Box Setting (arxiv.org)
代码:GitHub - RishabhMaheshwary/query-attack: A Query Efficient Natural Language Attack in a Black Box Setting
8.On the Transferability of Adversarial Attacks against Neural Text Classifier
a. 背景
b. 方法
c. 结果
d. 论文及代码
On the Transferability of Adversarial Attacks against Neural Text Classifier. Liping Yuan, Xiaoqing Zheng, Yi Zhou, Cho-Jui Hsieh, Kai-Wei Chang. EMNLP 2021. [pdf]
论文:2011.08558.pdf (arxiv.org)
代码:
9.Crafting Adversarial Examples for Neural Machine Translation
a. 背景
b. 方法
c. 结果
d. 论文及代码
Crafting Adversarial Examples for Neural Machine Translation. Xinze Zhang, Junzhe Zhang, Zhenhua Chen, Kun He. ACL-IJCNLP 2021. score [pdf] [code]
论文:2021.acl-long.153.pdf (aclanthology.org)
代码:GitHub - JHL-HUST/AdvNMT-WSLS: Crafting Adversarial Examples for Neural Machine Translation
10.An Empirical Study on Adversarial Attack on NMT: Languages and Positions Matter
a. 背景
b. 方法
c. 结果
d. 论文及代码
An Empirical Study on Adversarial Attack on NMT: Languages and Positions Matter. Zhiyuan Zeng, Deyi Xiong. ACL-IJCNLP 2021. score [pdf]
论文:2021.acl-short.58.pdf (aclanthology.org)
代码:
11-20
11.A Closer Look into the Robustness of Neural Dependency Parsers Using Better Adversarial Examples
a. 背景
b. 方法
c. 结果
d. 论文及代码
A Closer Look into the Robustness of Neural Dependency Parsers Using Better Adversarial Examples. Yuxuan Wang, Wanxiang Che, Ivan Titov, Shay B. Cohen, Zhilin Lei, Ting Liu. Findings of ACL: ACL-IJCNLP 2021. score [pdf] [code]
论文:2021.findings-acl.207.pdf (aclanthology.org)
代码:github.com
12.Contextualized Perturbation for Textual Adversarial Attack
a. 背景
b. 方法
c. 结果
d. 论文及代码
Contextualized Perturbation for Textual Adversarial Attack. Dianqi Li, Yizhe Zhang, Hao Peng, Liqun Chen, Chris Brockett, Ming-Ting Sun, Bill Dolan. NAACL-HLT 2021. score [pdf] [code]
论文:2021.naacl-main.400.pdf (aclanthology.org)
代码:github.com
13.Adv-OLM: Generating Textual Adversaries via OLM
a. 背景
b. 方法
c. 结果
d. 论文及代码
Adv-OLM: Generating Textual Adversaries via OLM. Vijit Malik, Ashwani Bhat, Ashutosh Modi. EACL 2021. score [pdf] [code]
论文:2021.eacl-main.71.pdf (aclanthology.org)
代码:github.com
14.Adversarial Stylometry in the Wild: Transferable Lexical Substitution Attacks on Author Profiling
a. 背景
b. 方法
c. 结果
d. 论文及代码
Adversarial Stylometry in the Wild: Transferable Lexical Substitution Attacks on Author Profiling. Chris Emmery, Ákos Kádár, Grzegorz Chrupała. EACL 2021. blind [pdf] [code]
论文:2021.eacl-main.203.pdf (aclanthology.org)
代码:github.com
15.Generating Natural Language Attacks in a Hard Label Black Box Setting
a. 背景
b. 方法
c. 结果
d. 论文及代码
Generating Natural Language Attacks in a Hard Label Black Box Setting. Rishabh Maheshwary, Saket Maheshwary, Vikram Pudi. AAAI 2021. decision [pdf] [code]
论文:2012.14956.pdf (arxiv.org)
代码:https://github.com/RishabhMaheshwary/hard-label-attack
16.A Geometry-Inspired Attack for Generating Natural Language Adversarial Examples
a. 背景
b. 方法
c. 结果
d. 论文及代码
A Geometry-Inspired Attack for Generating Natural Language Adversarial Examples. Zhao Meng, Roger Wattenhofer. COLING 2020. gradient [pdf] [code]
论文:2020.coling-main.585.pdf (aclanthology.org)
代码:https://github.com/zhaopku/nlp_geometry_attack
17.BERT-ATTACK: Adversarial Attack Against BERT Using BERT
a. 背景
b. 方法
c. 结果
d. 论文及代码
BERT-ATTACK: Adversarial Attack Against BERT Using BERT. Linyang Li, Ruotian Ma, Qipeng Guo, Xiangyang Xue, Xipeng Qiu. EMNLP 2020. score [pdf] [code]
论文:aclanthology.org/2020.emnlp-main.500.pdf
代码:GitHub - LinyangLee/BERT-Attack: Code for EMNLP2020 long paper: BERT-Attack: Adversarial Attack Against BERT Using BERT
18.BAE: BERT-based Adversarial Examples for Text Classification
a. 背景
b. 方法
c. 结果
d. 论文及代码
BAE: BERT-based Adversarial Examples for Text Classification. Siddhant Garg, Goutham Ramakrishnan. EMNLP 2020. score [pdf] [code]
论文:2020.emnlp-main.498.pdf (aclanthology.org)
代码:TextAttack/textattack/attack_recipes/bae_garg_2019.py at master · QData/TextAttack · GitHub
19.Detecting Word Sense Disambiguation Biases in Machine Translation for Model-Agnostic Adversarial Attacks
a. 背景
b. 方法
c. 结果
d. 论文及代码
Detecting Word Sense Disambiguation Biases in Machine Translation for Model-Agnostic Adversarial Attacks. Denis Emelin, Ivan Titov, Rico Sennrich. EMNLP 2020. blind [pdf] [code]
论文:2020.emnlp-main.616.pdf (aclanthology.org)
代码:GitHub - demelin/detecting_wsd_biases_for_nmt: Repository containing the experimental code for the publication ‘Detecting Word Sense Disambiguation Biases in Machine Translation for Model-Agnostic Adversarial Attacks’ (Emelin, Denis, Ivan Titov, and Rico Sennrich, EMNLP 2020).
20.Imitation Attacks and Defenses for Black-box Machine Translation Systems
a. 背景
b. 方法
c. 结果
d. 论文及代码
Imitation Attacks and Defenses for Black-box Machine Translation Systems. Eric Wallace, Mitchell Stern, Dawn Song. EMNLP 2020. decision [pdf] [code]
论文:aclanthology.org/2020.emnlp-main.446.pdf
代码:GitHub - Eric-Wallace/adversarial-mt: Code for “Imitation Attacks and Defenses for Black-box Machine Translations Systems”
21-30
21.Robustness to Modification with Shared Words in Paraphrase Identification
a. 背景
b. 方法
c. 结果
d. 论文及代码
Robustness to Modification with Shared Words in Paraphrase Identification. Zhouxing Shi, Minlie Huang. Findings of ACL: EMNLP 2020. score [pdf]
论文:aclanthology.org/2020.findings-emnlp.16.pdf
代码:
22.Word-level Textual Adversarial Attacking as Combinatorial Optimization
a. 背景
b. 方法
c. 结果
d. 论文及代码
Word-level Textual Adversarial Attacking as Combinatorial Optimization. Yuan Zang, Fanchao Qi, Chenghao Yang, Zhiyuan Liu, Meng Zhang, Qun Liu, Maosong Sun. ACL 2020. score [pdf] [code]
论文:2020.acl-main.540.pdf (aclanthology.org)
代码:GitHub - thunlp/SememePSO-Attack: Code and data of the ACL 2020 paper “Word-level Textual Adversarial Attacking as Combinatorial Optimization”
23.It’s Morphin’ Time! Combating Linguistic Discrimination with Inflectional Perturbations
a. 背景
b. 方法
c. 结果
d. 论文及代码
It’s Morphin’ Time! Combating Linguistic Discrimination with Inflectional Perturbations. Samson Tan, Shafiq Joty, Min-Yen Kan, Richard Socher. ACL 2020. score [pdf] [code]
论文:2020.acl-main.263.pdf (aclanthology.org)
代码:GitHub - salesforce/morpheus: Code for ACL’20 paper “It’s Morphin’ Time! Combating Linguistic Discrimination with Inflectional Perturbations”
24.On the Robustness of Language Encoders against Grammatical Errors
a. 背景
b. 方法
c. 结果
d. 论文及代码
On the Robustness of Language Encoders against Grammatical Errors. Fan Yin, Quanyu Long, Tao Meng, Kai-Wei Chang. ACL 2020. score [pdf] [code]
论文:2020.acl-main.310.pdf (aclanthology.org)
代码:GitHub - uclanlp/ProbeGrammarRobustness: Source code for ACL2020: On the Robustness of Language Encoders against Grammatical Errors
25.Evaluating and Enhancing the Robustness of Neural Network-based Dependency Parsing Models with Adversarial Examples
a. 背景
b. 方法
c. 结果
d. 论文及代码
Evaluating and Enhancing the Robustness of Neural Network-based Dependency Parsing Models with Adversarial Examples. Xiaoqing Zheng, Jiehang Zeng, Yi Zhou, Cho-Jui Hsieh, Minhao Cheng, Xuanjing Huang. ACL 2020. gradient score [pdf] [code]
论文:2020.acl-main.590.pdf (aclanthology.org)
代码:GitHub - zjiehang/DPAttack: Pytorch implementation for ACL 2020 Paper: “Evaluating and Enhancing the Robustness of Neural Network-based Dependency Parsing Models with Adversarial Examples”
26.A Reinforced Generation of Adversarial Examples for Neural Machine Translation
a. 背景
b. 方法
c. 结果
d. 论文及代码
A Reinforced Generation of Adversarial Examples for Neural Machine Translation. Wei Zou, Shujian Huang, Jun Xie, Xinyu Dai, Jiajun Chen. ACL 2020. decision [pdf]
论文:aclanthology.org/2020.acl-main.319.pdf
代码:
27.Is BERT Really Robust? A Strong Baseline for Natural Language Attack on Text Classification and Entailment
a. 背景
b. 方法
c. 结果
d. 论文及代码
Is BERT Really Robust? A Strong Baseline for Natural Language Attack on Text Classification and Entailment. Di Jin, Zhijing Jin, Joey Tianyi Zhou, Peter Szolovits. AAAI 2020. score [pdf] [code]
论文:1907.11932v4.pdf (arxiv.org)
代码:GitHub - jind11/TextFooler: A Model for Natural Language Attack on Text Classification and Inference
28.Seq2Sick: Evaluating the Robustness of Sequence-to-Sequence Models with Adversarial Examples
a. 背景
b. 方法
c. 结果
d. 论文及代码
Seq2Sick: Evaluating the Robustness of Sequence-to-Sequence Models with Adversarial Examples. Minhao Cheng, Jinfeng Yi, Pin-Yu Chen, Huan Zhang, Cho-Jui Hsieh. AAAI 2020. score [pdf] [code]
论文:1803.01128.pdf (arxiv.org)
代码:GitHub - cmhcbb/Seq2Sick: Adversarial examples for Seq2Seq model in NLP
29.Greedy Attack and Gumbel Attack: Generating Adversarial Examples for Discrete Data
a. 背景
b. 方法
c. 结果
d. 论文及代码
Greedy Attack and Gumbel Attack: Generating Adversarial Examples for Discrete Data. Puyudi Yang, Jianbo Chen, Cho-Jui Hsieh, Jane-LingWang, Michael I. Jordan. JMLR 2020. score [pdf] [code]
论文:19-569.pdf (jmlr.org)
代码:GitHub - Puyudi/Greedy-Attack-and-Gumbel-Attack (Under Construction.)
30.On the Robustness of Self-Attentive Models
a. 背景
b. 方法
c. 结果
d. 论文及代码
On the Robustness of Self-Attentive Models. Yu-Lun Hsieh, Minhao Cheng, Da-Cheng Juan, Wei Wei, Wen-Lian Hsu, Cho-Jui Hsieh. ACL 2019. score [pdf]
论文:P19-1147.pdf (aclanthology.org)
代码:
31-40
31.Generating Natural Language Adversarial Examples through Probability Weighted Word Saliency
a. 背景
b. 方法
c. 结果
d. 论文及代码
Generating Natural Language Adversarial Examples through Probability Weighted Word Saliency. Shuhuai Ren, Yihe Deng, Kun He, Wanxiang Che. ACL 2019. score [pdf] [code]
论文:P19-1103.pdf (aclanthology.org)
代码:[GitHub - JHL-HUST/PWWS: Generating Natural Language Adversarial Examples through Probability Weighted Word Saliency](https://github.com/JHL-HUST/PWWS/)
32.Generating Fluent Adversarial Examples for Natural Languages
a. 背景
b. 方法
c. 结果
d. 论文及代码
Generating Fluent Adversarial Examples for Natural Languages. Huangzhao Zhang, Hao Zhou, Ning Miao, Lei Li. ACL 2019. gradient score [pdf] [code]
论文:Generating Fluent Adversarial Examples for Natural Languages - ACL Anthology
代码:GitHub - LC-John/Metropolis-Hastings-Attacker: “Generating Fluent Adversarial Examples for Natural Languages”
33.Robust Neural Machine Translation with Doubly Adversarial Inputs
a. 背景
b. 方法
c. 结果
d. 论文及代码
Robust Neural Machine Translation with Doubly Adversarial Inputs. Yong Cheng, Lu Jiang, Wolfgang Macherey. ACL 2019. gradient [pdf]
论文:https://aclanthology.org/P19-1425/
代码:
34.Universal Adversarial Attacks on Text Classifiers
a. 背景
b. 方法
c. 结果
d. 论文及代码
Universal Adversarial Attacks on Text Classifiers. Melika Behjati, Seyed-Mohsen Moosavi-Dezfooli, Mahdieh Soleymani Baghshah, Pascal Frossard. ICASSP 2019. gradient [pdf]
论文:Universal Adversarial Attacks on Text Classifiers | IEEE Conference Publication | IEEE Xplore
代码:
35.Generating Natural Language Adversarial Examples
a. 背景
b. 方法
c. 结果
d. 论文及代码
Generating Natural Language Adversarial Examples. Moustafa Alzantot, Yash Sharma, Ahmed Elgohary, Bo-Jhang Ho, Mani Srivastava, Kai-Wei Chang. EMNLP 2018. score [pdf] [code]
论文:Generating Natural Language Adversarial Examples - ACL Anthology
代码:GitHub - nesl/nlp_adversarial_examples: Implementation code for the paper “Generating Natural Language Adversarial Examples”
36.Breaking NLI Systems with Sentences that Require Simple Lexical Inferences
a. 背景
b. 方法
c. 结果
d. 论文及代码
Breaking NLI Systems with Sentences that Require Simple Lexical Inferences. Max Glockner, Vered Shwartz, Yoav Goldberg. ACL 2018. blind [pdf] [dataset]
论文:Breaking NLI Systems with Sentences that Require Simple Lexical Inferences - ACL Anthology
代码:GitHub - BIU-NLP/Breaking_NLI: NLI test set with lexical inferences
37.Deep Text Classification Can be Fooled
a. 背景
b. 方法
c. 结果
d. 论文及代码
Deep Text Classification Can be Fooled. Bin Liang, Hongcheng Li, Miaoqiang Su, Pan Bian, Xirong Li, Wenchang Shi. IJCAI 2018. gradient score [pdf]
论文:1704.08006.pdf (arxiv.org)
代码:
38.Interpretable Adversarial Perturbation in Input Embedding Space for Text
a. 背景
b. 方法
c. 结果
d. 论文及代码
Interpretable Adversarial Perturbation in Input Embedding Space for Text. Sato, Motoki, Jun Suzuki, Hiroyuki Shindo, Yuji Matsumoto. IJCAI 2018. gradient [pdf] [code]
论文:1805.02917.pdf (arxiv.org)
代码:GitHub - aonotas/interpretable-adv: Code for Interpretable Adversarial Perturbation in Input Embedding Space for Text, IJCAI 2018.
——————————————
🔖39.Towards Crafting Text Adversarial Samples
——————————————
a. 背景
提出:对原始文本样本的修改是通过删除或替换文本中的重要或显著单词或者通过在文本样本中引入新单词来完成的。
目标:以最少的修改次数来改变样本的类别标签(使用贪心方法的思想在尽可能少的变化中制作对抗性样本)
展望:在这项工作中,修改所采用的步骤本质上是启发式的,可以进一步改进和自动化以获得更好的结果
——————————————
b. 方法
⭐对原始文本样本的修改是通过:
- 删除(wi是副词)
- 插入(使用FGSM从wi的候选池P中选择一个单词pj. 如果wi是一个形容词,pj是一个副词,通过在wi之前插入pj)新词来完成
- 替换(当wi和pj的词性相同时,才考虑替换它) 文本中重要或突出的单词
⭐具体实现:
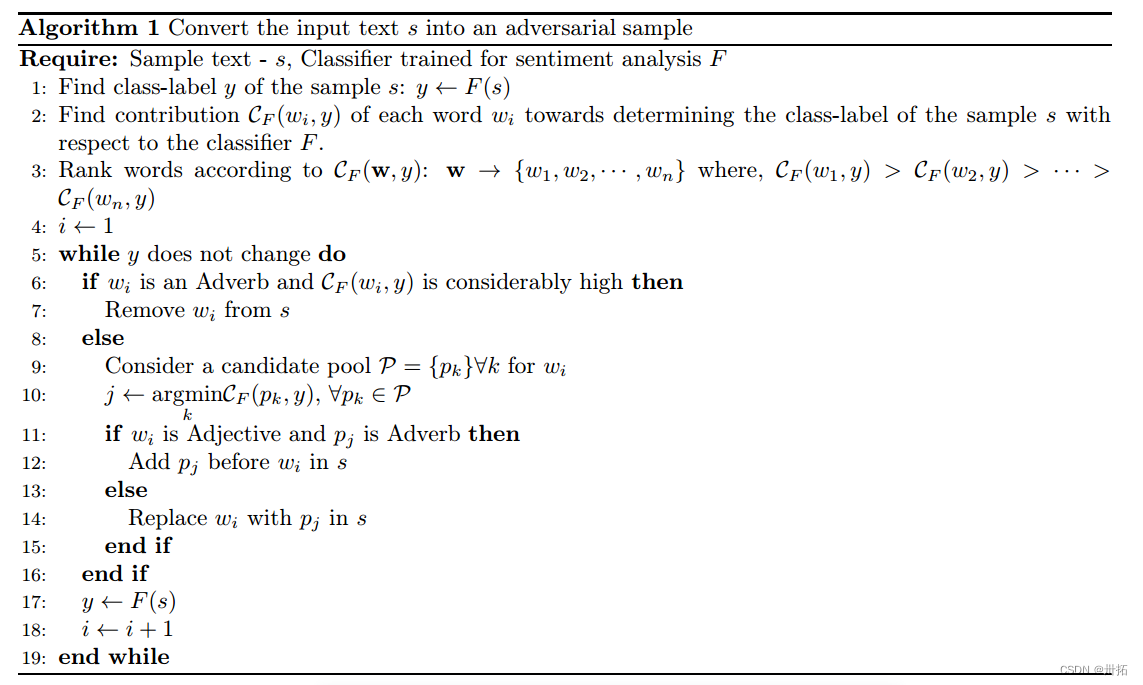
⭐其中,单词wk的贡献CF可以被测量为:
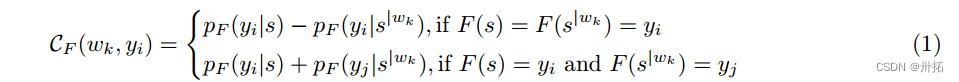
⭐对每个单词计算CF(yi | w)是一个耗时的过程。我们使用FGSM(2)的概念来近似计算单词wk的贡献,其可以计算为:
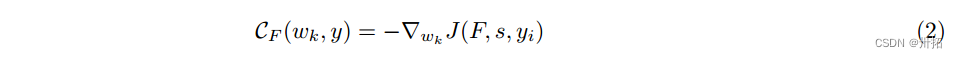
——————————————
c. 结果
数据集:(I)用于情感分析的IMDB电影评论数据集和(ii)用于性别分类的twitter数据集。
- IMDB数据集实验结果

- Twitter数据集实验结果
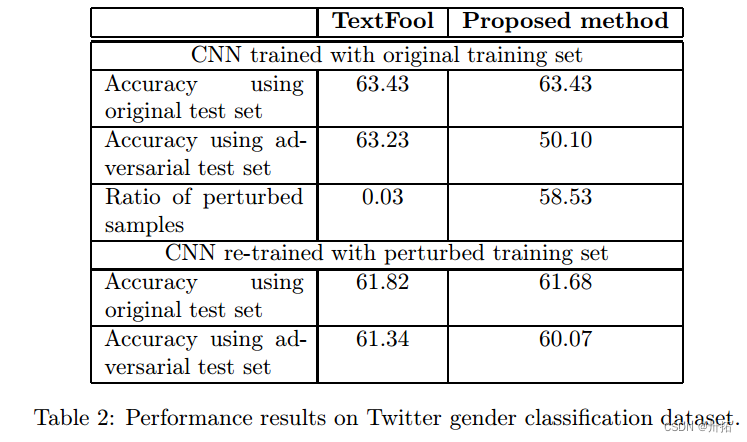
语义相似度使用Spacy工具箱进行度量。
——————————————
d. 论文及代码
Towards Crafting Text Adversarial Samples. Suranjana Samanta, Sameep Mehta. ECIR 2018. gradient [pdf]
论文:1707.02812.pdf (arxiv.org)
代码:
——————————————
📄40.Crafting Adversarial Input Sequences For Recurrent Neural Networks
——————————————
a. 背景(考古2016):
背景:为了选择将神经网络分类器分配的类别更改为不同于合法类别或对手选择的特定目标类别的任何类别的扰动,可以遵循两种方法:快速梯度符号方法(FGSM)和向前导数方法。这些技术主要在为解决图像分类任务而训练的模型上进行评估。
挑战:RNN在其计算图中引入了循环,循环计算的存在潜在地对基于模型区分的现有对立样本算法的适用性提出了挑战,因为循环阻止了通过应用链规则直接计算梯度。
技术:使用一种称为计算图展开的技术,正向导数(即雅可比模型)可以适用于具有循环计算图的神经网络,从而操纵由顺序RNN输出的序列和由分类RNN做出的分类预测。
贡献:
- 形式化了序列数据环境下的对抗性样本优化问题:使用前向导数来调整crafting算法以适应RNNs的特性,这包括展示如何计算循环计算图的向前导数。
- 研究了将对抗性扰动从模型的预处理输入转移到原始输入。
- 使用RNNs进行分类和顺序预测来评估技术的性能。平均来说,在71个单词的电影评论中改变9个单词就足以让分类RNN在对评论进行情感分析时做出100%错误的分类预测。还表明,序列制作使用雅可比扰动第二个RNN的顺序输出。
意义:本文通过研究处理顺序数据的循环神经网络的对抗性输入序列,为对抗性机器学习领域做出了贡献。表明:①之前引入的用于制作由前馈神经网络错误分类的对抗性样本的算法类别可以适用于循环神经网络(RNN)。②对手可以制作对抗序列,误导分类RNN和顺序RNN。
——————————————
b. 方法
⭐RNN计算公式:

⭐对抗样本定义为优化问题:
-
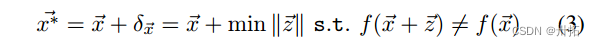
-
找到该优化问题的精确解决方案并不总是可能的,因此,以前的工作引入了一些方法(下面讨论了两种方法)来寻找近似解。方法1:FGSM;方法2:前向梯度。
-
方法1:FGSM
- 快速梯度符号法通过在其输入周围线性化模型的成本函数并使用成本函数相对于输入本身的梯度选择扰动来近似方程(3)中的问题。可以通过遵循训练期间通常用于反向传播的步骤来计算该梯度,但是不是像训练期间通常的情况那样相对于模型参数计算梯度(为了减少预测误差),而是相对于输入计算梯度。这产生以下对抗性样本的公式:
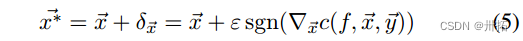
- 只要模型是可微分的,快速梯度符号方法仍然适用——即使在模型的计算图中插入递归连接。
-
方法2:Forward Derivative(前向梯度)
- 【3】中介绍的前向导数是一种制作敌对样本的替代方法。该方法的设计考虑了对手的威胁模型,对手对所选敌对目标中的样本进行错误分类感兴趣。
- 正向导数定义为模型的雅可比矩阵:
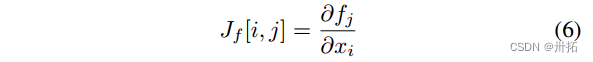
- 利用称为计算图形展开的技术来计算存在循环时的正向导数
- 回头看等式(2),可以观察到,为了计算时间步长t的神经元状态,我们可以递归地应用该公式,同时递减时间步长。这会产生以下结果:

- 这是等式(2)的展开版本。因此,通过展开其递归组件,可以使递归神经网络的计算图成为非循环的。具体实现细节,请阅读论文。
-
⭐对抗序列定义:

- 通过计算模型的雅可比矩阵来找到这个问题的近似解
- 具体计算步骤,看P4左侧栏下方(最后一段)
⭐我们可以用前向导数为两种类型的RNN模型(分类模型和序列模型)制作敌对序列。
——————————————
c. 结果
我们为分类的和顺序的rnn设计对抗序列。
- 分类RNN执行情感分析,将电影评论分为正面或负面。通过改变评论的用词来误导这个分类器。
- 在2000篇评论中,每篇平均修改9.18个单词,平均长度为71.06个单词,我们能够在训练集上实现100%的错误率。
- 第二个RNN被训练来学习合成输入和输出序列之间的映射。基于雅可比的攻击通过识别每个输入序列步骤的贡献来改变模型的输出
- 该模型以103的学习速率训练了400个时期。成本是模型预测和目标之间的均方误差。图4显示了一个示例输入序列和预测的输出序列。
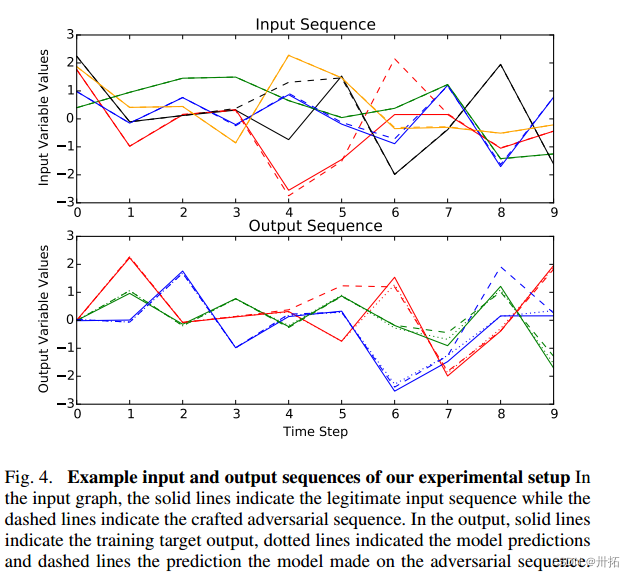
- 由于篇幅有限,完成这些定性结果并进行详细的定量评估是今后的工作。
——————————————
d. 论文及代码
Crafting Adversarial Input Sequences For Recurrent Neural Networks. Nicolas Papernot, Patrick McDaniel, Ananthram Swami, Richard Harang. MILCOM 2016. gradient [pdf]
论文:1604.08275.pdf (arxiv.org)
代码:暂无