1:在主函数定义字符数组,在自定义函数中实现字符串比较
4 int my_strcmp(char *a,char *b);5 int main(int argc, const char *argv[])6 {7 //strcmp 函数比叫ascii码值大小8 char a[10]="hello";9 char b[10]="helloo";10 11 int sub= my_strcmp(a,b);12 if(sub>0)13 {14 printf("a>b");15 } 16 else if(sub==0)17 {18 printf("a=b");19 }20 else21 printf("a<b");22 23 return 0;24 }25 int my_strcmp(char *a,char *b)26 { 27 int sub=0;28 int i=0;29 while(*(a+i)==*(b+i))30 {31 if(*(b+i)=='\0')32 break;33 i++;34 }35 sub=*(a+i)-*(b+i);36 return sub;37 }
运行结果:
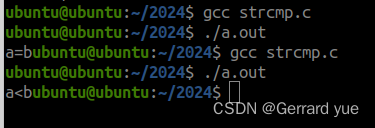
2:在主函数定义字符数组,在自定义函数中实现字符串链接
4 void my_strcat(char *desk,char *src);5 int main(int argc, const char *argv[])6 {7 //strcat 字符串链接 8 char desk[20]="hello";9 char src[20]="world";10 //strcat(desk,src);11 //puts(desk);12 my_strcat(desk,src);13 return 0;14 }15 void my_strcat(char *desk,char *src)16 {17 int i=0;18 while(*(desk+i)!='\0')19 {20 i++;21 }22 for(int j=0;*(src+j)!='\0';j++)23 {24 *(desk+i++)=*(src+j);25 }26 *(desk+i)='\0';27 puts(desk);28 }
运行结果:

3:在主函数定义字符数组,在自定义函数中实现字符串长度
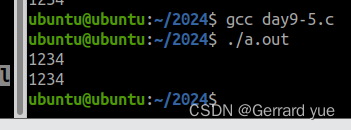
4 int my_strlen(char *a);5 int main(int argc, const char *argv[])6 { 7 char a[20]="hello";8 // strlen(a);9 // printf("%ld\n",strlen(a));10 int count=my_strlen(a);11 printf("%d\n",count);12 return 0;13 }14 int my_strlen(char *a)15 { 16 int count=0;17 for(int i=0;*(a+i)!='\0';i++)18 { 19 count++;20 }21 return count;22 } 运行结果:
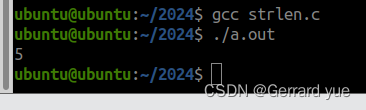
4:在主函数定义字符数组,在自定义函数中实现strcpy
4 void my_strcop(char *a,char *b);5 int main(int argc, const char *argv[])6 {7 //在主函数定义字符数组,在自定义函数中实现字符串拷贝8 char a[20]="hello";9 char b[20]="1234";10 my_strcop(a,b);11 puts(a);12 puts(b);13 14 return 0;15 }16 17 void my_strcop(char *a,char *b)18 { 19 int i=0;20 for(i=0;*(a+i)!='\0';i++)21 { 22 *(a+i)=*(b+i);23 }24 *(a+i)='\0';25 26 }