输入数据
-
模型使用absmax 量化方法进行b比特量化,将输入量化到 [ − Q b , Q b ] ( Q b = 2 b − 1 ) \left[-Q_{b},Q_{b}\right](Q_{b}=2^{b-1}) [−Qb,Qb](Qb=2b−1)
x ~ = Q u a n t ( x ) = C l i p ( x × Q b γ , − Q b + ϵ , Q b − ϵ ) , Clip ( x , a , b ) = max ( a , min ( b , x ) ) , γ = ∣ ∣ x ∣ ∣ ∞ , \widetilde{x}=\mathrm{Quant}(x)=\mathrm{Clip}(x\times\frac{Q_b}{\gamma},-Q_b+\epsilon,Q_b-\epsilon),\\ \operatorname{Clip}(x,a,b)=\max(a,\min(b,x)),\quad\gamma=||x||_\infty, x =Quant(x)=Clip(x×γQb,−Qb+ϵ,Qb−ϵ),Clip(x,a,b)=max(a,min(b,x)),γ=∣∣x∣∣∞, -
其中 ε 是一个小的浮点数,可防止在执行截断时溢出。
// https://github.com/kyegomez/BitNet/blob/main/bitnet/bitbnet_b158.py
def absmean_quantize_weights(weights):"""Quantizes the weights to -1, 0, or +1 using an absmean quantization function.Parameters:- weights (Tensor): The weights of a neural network layer.Returns:- Tensor: The quantized weights."""# Calculate the average absolute value (γ) of the weightsgamma = torch.mean(torch.abs(weights))# Scale weights by γ and round to the nearest integer among {-1, 0, +1}quantized_weights = torch.clamp(torch.round(weights / gamma), min=-1, max=1)return quantized_weights
权重
- 权重 W 的二值化可以公式化为:
α = 1 n m ∑ i j W i j W ~ = S i g n ( W − α ) , Sign ( W i j ) = { + 1 , if W i j > 0 , − 1 , if W i j ≤ 0 , \\ \alpha=\frac1{nm}\sum_{ij}W_{ij} \\ \widetilde{W}=\mathrm{Sign}(W-\alpha),\\ \left.\operatorname{Sign}(W_{ij})=\left\{\begin{array}{ll}+1,&\quad\text{if}W_{ij}>0,\\-1,&\quad\text{if}W_{ij}\leq0,\end{array}\right.\right. α=nm1ij∑WijW =Sign(W−α),Sign(Wij)={+1,−1,ifWij>0,ifWij≤0,
矩阵乘法
- 使用上述量化方程,矩阵乘法可以写成:
y = W ~ x ~ y=\widetilde W\widetilde{x} y=W x
- 为了保持量化后的方差,我们在激活量化之前引入了一个 LayerNorm函数。这样,输出 y 的方差就估计为 1
y = W ~ x ~ = W ~ Quant ( LN ( x ) ) × β γ Q b y=\widetilde{W}\widetilde{x}=\widetilde{W}\text{Quant}(\text{LN}(x))\times\frac{\beta\gamma}{Q_b} y=W x =W Quant(LN(x))×Qbβγ
L N ( x ) = x − E ( x ) V a r ( x ) + ϵ , β = 1 n m ∥ W ∥ 1 \mathrm{LN}(x)=\frac{x-E(x)}{\sqrt{\mathrm{Var}(x)+\epsilon}},\quad\beta=\frac1{nm}\|W\|_1 LN(x)=Var(x)+ϵx−E(x),β=nm1∥W∥1

// https://github.com/kyegomez/BitNet/blob/main/bitnet/bitlinear.py
import torch
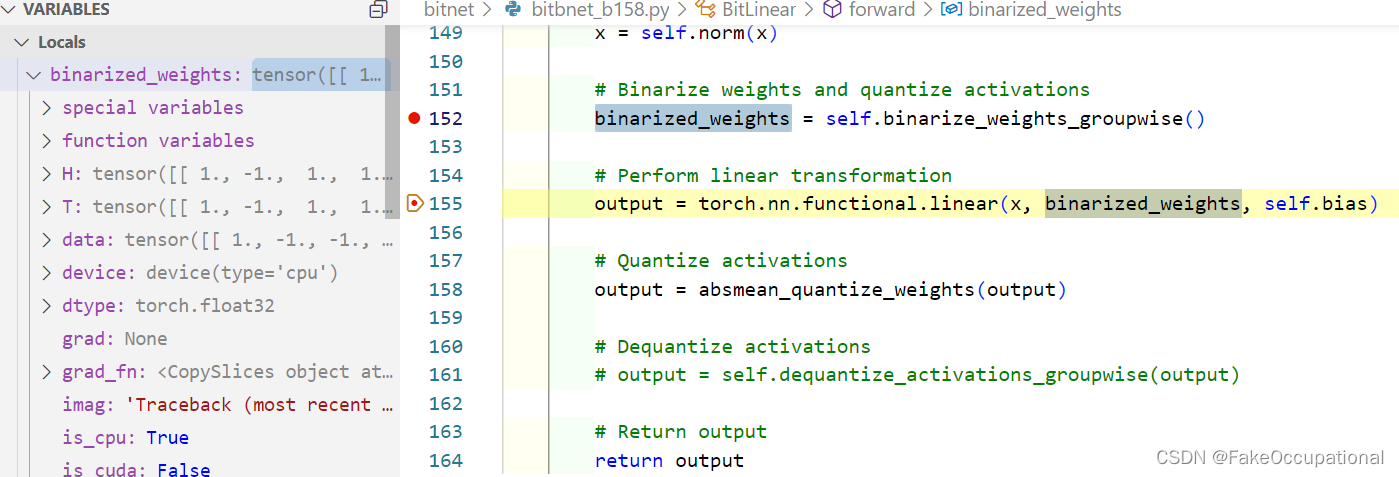
from torch import Tensor, nnclass BitLinear(nn.Linear):"""BitLinear is a custom linear layer that performs binarization of weights and quantization of activationsin a group-wise manner.Args:in_features (int): Number of input features.out_features (int): Number of output features.bias (bool, optional): If set to False, the layer will not learn an additive bias. Default is True.num_groups (int, optional): Number of groups to divide the weights and activations into. Default is 1."""def __init__(self,in_features: int,out_features: int,bias: bool = True,num_groups: int = 1,b: int = 8,):super().__init__(in_features, out_features, bias)self.in_features = in_featuresself.out_features = out_featuresself.b = bself.num_groups = num_groupsself.eps = 1e-5self.norm = nn.LayerNorm(in_features)def ste(self, x):"""Applies the sign function for binarization and uses Straight-Through Estimator (STE) during backward pass.Args:x (Tensor): Input tensor.Returns:Tensor: Binarized tensor."""binarized_x = torch.sign(x)binarized_x = (binarized_x - x).detach() + xreturn binarized_xdef binarize_weights_groupwise(self):"""Binarizes the weights of the layer in a group-wise manner using STE.Returns:Tensor: Binarized weights tensor."""group_size = self.weight.shape[0] // self.num_groupsbinarized_weights = torch.zeros_like(self.weight)for g in range(self.num_groups):start_idx = g * group_sizeend_idx = (g + 1) * group_sizeweight_group = self.weight[start_idx:end_idx]alpha_g = weight_group.mean()binarized_weights[start_idx:end_idx] = self.ste(weight_group - alpha_g)return binarized_weightsdef quantize_activations_groupwise(self, x):"""Quantizes the activations of the layer in a group-wise manner.Args:x (Tensor): Input tensor.b (int, optional): Number of bits for quantization. Default is 8.Returns:Tensor: Quantized activations tensor."""Q_b = 2 ** (self.b - 1)group_size = x.shape[0] // self.num_groupsquantized_x = torch.zeros_like(x)for g in range(self.num_groups):start_idx = g * group_sizeend_idx = (g + 1) * group_sizeactivation_group = x[start_idx:end_idx]gamma_g = activation_group.abs().max()quantized_x[start_idx:end_idx] = torch.clamp(activation_group * Q_b / (gamma_g + self.eps),-Q_b + self.eps,Q_b - self.eps,)return quantized_xdef dequantize_activations_groupwise(self, x):"""Dequantizes the activations of the layer in a group-wise manner.Args:x (Tensor): Quantized input tensor.b (int, optional): Number of bits used during the quantization. Default is 8.Returns:Tensor: Dequantized activations tensor."""Q_b = 2 ** (self.b - 1)dequantized_x = torch.zeros_like(x)for g in range(self.num_groups):start_idx = g * x.shape[0] // self.num_groupsend_idx = (g + 1) * x.shape[0] // self.num_groupsquantized_group = x[start_idx:end_idx]gamma_g = quantized_group.abs().max()dequantized_x[start_idx:end_idx] = quantized_group * gamma_g / Q_breturn dequantized_xdef forward(self, x: Tensor) -> Tensor:"""Forward pass of the BitLinear layer.Args:x (Tensor): Input tensor.Returns:Tensor: Output tensor."""# Normalize inputx = self.norm(x)# Binarize weights and quantize activationsbinarized_weights = self.binarize_weights_groupwise()# Perform linear transformationoutput = torch.nn.functional.linear(x, binarized_weights, self.bias)# Quantize activationsoutput = self.quantize_activations_groupwise(output)# Dequantize activationsoutput = self.dequantize_activations_groupwise(output)# Return outputreturn output# Example usage
bitlinear = BitLinear(10, 5, num_groups=2, b=8)
input_tensor = torch.randn(5, 10) # Example input tensor
output = bitlinear(input_tensor)
print(output) # Example output tensor
CG
-
【自然语言处理】【大模型】BitNet:用1-bit Transformer训练LLM
-
BitNet: Scaling 1-bit Transformers for Large Language Models
-
The Era of 1-bit LLMs: All Large Language Models are in 1.58 Bits
-
Implementation of “BitNet: Scaling 1-bit Transformers for Large Language Models” in pytorch
-
DB-LLM: Accurate Dual-Binarization for Efficient LLMs
-
如何看待微软提出的BitNet b1.58?