参考
Binary Search Tree Visualization (usfca.edu)
一、构建排序二叉树
注意引用 tree
/*** 构造二叉排序树* @param tree* @param x*/
void buildTree(BSTree &tree,ElementType &x){if (tree==NULL){tree=(BSTree) calloc(1, sizeof(BSTNode));tree->data=x;//注意return;}if (x>tree->data){buildTree(tree->rchild,x);}if (x<tree->data){buildTree(tree->lchild,x);}if (x==tree->data){return;}
}二、查询排序二叉树的目标节点
注意引用 tree
//查找
int getPosition(BSTree &tree,int postion,ElementType x){if (tree!=NULL&&x==tree->data){return tree->data;}if (x>tree->data){return getPosition(tree->rchild,0,x);} else{return getPosition(tree->lchild,0,x);}
}三、删除二叉排序树的节点
注意引用
注意左子树右子树都不为空的情况 删除的时候递归删除 因为我们不知道它的父亲节点
注意记得删除前改变被删除的位置的地址
//删除节点
void delTNode(BSTree &tree,ElementType x){if (tree==NULL){return;}BSTNode *temp=tree;if (x>temp->data){delTNode(tree->rchild,x);}if (x<temp->data){delTNode(tree->lchild,x);}if (x==temp->data){if (temp->lchild==NULL&&temp->rchild!=NULL){//注意记得改变此时被删除的位置的地址tree=temp->rchild;free(temp);}if (temp->rchild==NULL&&temp->lchild!=NULL){//注意记得改变此时被删除的位置的地址tree=temp->lchild;free(temp);}if (temp->lchild==NULL&&temp->rchild==NULL){//注意记得改变此时被删除的位置的地址tree=NULL;free(temp);}if (temp->lchild!=NULL&&temp->rchild!=NULL){//左右子树都不为空//找左子树的左右边//或者找右子树的最左边来代替temp=temp->lchild;while (temp->rchild!=NULL){temp=temp->rchild;}tree->data=temp->data;//因为这时候有俩个一样的值了 我们要确认我们要删除的是哪个值//因此这里应该删除这个节点的左子树上那个替死鬼delTNode(tree->lchild,temp->data);}}
}四、完整代码
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>typedef int ElementType;typedef struct BSTNode{ElementType data;BSTNode *rchild;BSTNode *lchild;
}BSTNode,*BSTree;/*** 构造二叉排序树* @param tree* @param x*/
void buildTree(BSTree &tree,ElementType &x){if (tree==NULL){tree=(BSTree) calloc(1, sizeof(BSTNode));tree->data=x;//注意return;}if (x>tree->data){buildTree(tree->rchild,x);}if (x<tree->data){buildTree(tree->lchild,x);}if (x==tree->data){return;}
}//查找
int getPosition(BSTree &tree,int postion,ElementType x){if (tree!=NULL&&x==tree->data){return tree->data;}if (x>tree->data){return getPosition(tree->rchild,0,x);} else{return getPosition(tree->lchild,0,x);}
}//删除节点
void delTNode(BSTree &tree,ElementType x){if (tree==NULL){return;}BSTNode *temp=tree;if (x>temp->data){delTNode(tree->rchild,x);}if (x<temp->data){delTNode(tree->lchild,x);}if (x==temp->data){if (temp->lchild==NULL&&temp->rchild!=NULL){//注意记得改变此时被删除的位置的地址tree=temp->rchild;free(temp);}if (temp->rchild==NULL&&temp->lchild!=NULL){//注意记得改变此时被删除的位置的地址tree=temp->lchild;free(temp);}if (temp->lchild==NULL&&temp->rchild==NULL){//注意记得改变此时被删除的位置的地址tree=NULL;free(temp);}if (temp->lchild!=NULL&&temp->rchild!=NULL){//左右子树都不为空//找左子树的左右边//或者找右子树的最左边来代替temp=temp->lchild;while (temp->rchild!=NULL){temp=temp->rchild;}tree->data=temp->data;//因为这时候有俩个一样的值了 我们要确认我们要删除的是哪个值//因此这里应该删除这个节点的左子树上那个替死鬼delTNode(tree->lchild,temp->data);}}
}//中序遍历 对于二叉排序树来说中序遍历就是从小到大依次排序
void inOrder(BSTree tree){if (tree==NULL){return;}inOrder(tree->lchild);printf("%3d",tree->data);inOrder(tree->rchild);
}int main() {BSTree tree;ElementType str[7]={56,20,30,1,3,78,9};//注意tree=(BSTree) calloc(1, sizeof(BSTNode));tree->data=56;for (int i = 1; i < 7; ++i) {buildTree(tree,str[i]);}ElementType x;x=getPosition(tree,0,1);printf("%d\n",x);delTNode(tree,1);inOrder(tree);return 0;
}
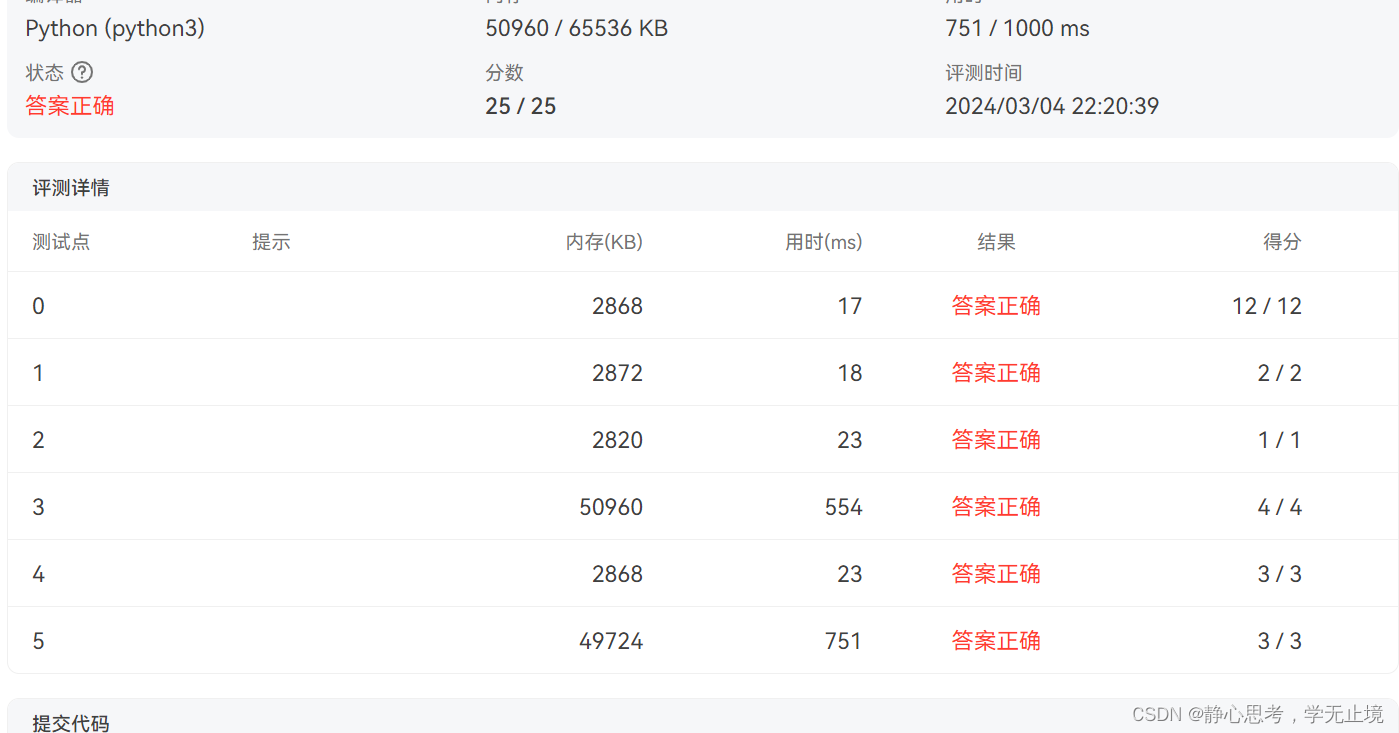
五、折半查找OJ练习
读取10个元素 87 7 60 80 59 34 86 99 21 3,然后建立二叉查找树, 中序遍历输出3 7 21 34 59 60 80 86 87 99, 针对有序后的元素,存入一个长度为10的数组中,通过折半查找找到21的下标(下标为2), 然后输出2
//折半查找
int getPosition(ElementType A[],ElementType x,int low,int high){if (low>=high){return -1;}int mid=(low+high)/2;if (A[mid]==x){return mid;}if (x>A[mid]){return getPosition(A,x,mid+1,high);} else{return getPosition(A,x,low,mid-1);}
}完整代码
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>/*** 读取10个元素 87 7 60 80 59 34 86 99 21 3,然后建立二叉查找树,* 中序遍历输出3 7 21 34 59 60 80 86 87 99,* 针对有序后的元素,存入一个长度为10的数组中,通过折半查找找到21的下标(下标为2),然后输出2*/typedef int ElementType;typedef struct BSTNode{ElementType data;BSTNode *rchild;BSTNode *lchild;
}BSTNode,*BSTree;/*** 构造二叉排序树* @param tree* @param x*/
void buildTree(BSTree &tree,ElementType &x){if (tree==NULL){tree=(BSTree) calloc(1, sizeof(BSTNode));tree->data=x;//注意return;}if (x>tree->data){buildTree(tree->rchild,x);}if (x<tree->data){buildTree(tree->lchild,x);}if (x==tree->data){return;}
}//查找
int getPosition(BSTree &tree,int postion,ElementType x){if (tree!=NULL&&x==tree->data){return tree->data;}if (x>tree->data){return getPosition(tree->rchild,0,x);} else{return getPosition(tree->lchild,0,x);}
}//删除节点
void delTNode(BSTree &tree,ElementType x){if (tree==NULL){return;}BSTNode *temp=tree;if (x>temp->data){delTNode(tree->rchild,x);}if (x<temp->data){delTNode(tree->lchild,x);}if (x==temp->data){if (temp->lchild==NULL&&temp->rchild!=NULL){//注意记得改变此时被删除的位置的地址tree=temp->rchild;free(temp);}if (temp->rchild==NULL&&temp->lchild!=NULL){//注意记得改变此时被删除的位置的地址tree=temp->lchild;free(temp);}if (temp->lchild==NULL&&temp->rchild==NULL){//注意记得改变此时被删除的位置的地址tree=NULL;free(temp);}if (temp->lchild!=NULL&&temp->rchild!=NULL){//左右子树都不为空//找左子树的左右边//或者找右子树的最左边来代替temp=temp->lchild;while (temp->rchild!=NULL){temp=temp->rchild;}tree->data=temp->data;//因为这时候有俩个一样的值了 我们要确认我们要删除的是哪个值//因此这里应该删除这个节点的左子树上那个替死鬼delTNode(tree->lchild,temp->data);}}
}//中序遍历 对于二叉排序树来说中序遍历就是从小到大依次排序
void inOrder(BSTree tree){if (tree==NULL){return;}inOrder(tree->lchild);printf("%3d",tree->data);inOrder(tree->rchild);
}int i=0;//中序遍历 对于二叉排序树来说中序遍历就是从小到大依次排序
void inOrderI(BSTree tree,ElementType A[]){if (tree==NULL){return;}inOrderI(tree->lchild,A);A[i++]=tree->data;printf("%3d",tree->data);inOrderI(tree->rchild,A);
}//折半查找
int getPosition(ElementType A[],ElementType x,int low,int high){if (low>=high){return -1;}int mid=(low+high)/2;if (A[mid]==x){return mid;}if (x>A[mid]){return getPosition(A,x,mid+1,high);} else{return getPosition(A,x,low,mid-1);}
}int main() {BSTree tree;//注意tree=(BSTree) calloc(1, sizeof(BSTNode));ElementType x;scanf("%d",&x);tree->data=x;for (int i = 1; i <= 9; ++i) {scanf("%d",&x);buildTree(tree,x);}ElementType A[10];inOrderI(tree,A);printf("\n");int position=getPosition(A,21,0,9);printf("%d\n", position);return 0;
}
六、折半查找 (真题)中位数应用
注意最后是s / d 的位置的值
注意移动的时候数组长度是变化的
1. 判断哪个中位数小
保证消掉的元素个数是相等的
奇数个长度 消掉小的前面的所有元素 大的后面的所有元素
偶数个长度 消掉小的前面的所有元素及其它本身 大的后面的所有元素
2.退出循环的条件是 s1!=d1|| s2!=d2 --直到俩个数组中就s1d1都指向一个元素 s2d2同理


#include <stdio.h>void NarrowScope(int n, int m1, int m2, int &s2, int &d1);//不合并查找中位数--去掉数 --就是移动下标
int getMidA_B(int A[],int B[],int n){//分别为 A B的 首尾 中位数 所在下标位置int s1,s2,d1,d2,m1,m2;s1=s2=0;d1=d2=n-1;m1=(s1+d1)/2;m2=(s2+d2)/2;if (A[m1]==B[m2]){return A[m1];}//去掉小哪个中位数之前的数 注意分奇偶//去掉大的那个中位数之后的数 注意分奇偶//循环判断哪个中位数大--缩小范围--直到俩个数组中都只剩下一个数s1=d1 s2=d2时 小的那个即为中位数while (s1!=d1||s2!=d2){m1=(s1+d1)/2;m2=(s2+d2)/2;if (A[m1]==B[m2]){return A[m1];}if (A[m1]>B[m2]){if ((s1+d1)%2==0){//奇数个//去掉大的之后的所有数d1=m1;//去掉小的之前的所有数s2=m2;} else{//偶数个//去掉大的 之后的所有数d1=m1;//去掉小的 中位数及之前的所有数s2=m2+1;}}if (A[m1]<B[m2]){if ((s1+d1)%2==0){//奇数个//去掉大的之后的所有数d2=m2;//去掉小的之前的所有数s1=m1;} else{//偶数个//去掉大的 之后的所有数d2=m2;//去掉小的 中位数及之前的所有数s1=m1+1;}}}//注意这里 要的是s / d 而不是m 因为最终s 与d会重合return A[s1]>B[s2]?B[s2]:A[s1];
}int main() {int A[]={11,13,15,17,19};int B[]={2,4,6,8,20};int n=5;int mid=getMidA_B(A,B,n);printf("%d\n",mid);return 0;
}