wc命令
命令直接执行,输出包含四项,分别代表:行数、字数、字节数、文件。
例子:编译下列代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>int
main(int argc, char *argv[])
{int rc = fork();if (rc < 0) {// fork failed; exitfprintf(stderr, "fork failed\n");exit(1);} else if (rc == 0) {// child: redirect standard output to a fileclose(STDOUT_FILENO); open("./p4.output", O_CREAT|O_WRONLY|O_TRUNC, S_IRWXU);// now exec "wc"...char *myargs[3];myargs[0] = strdup("wc"); // program: "wc" (word count)myargs[1] = strdup("p4.c"); // argument: file to countmyargs[2] = NULL; // marks end of arrayexecvp(myargs[0], myargs); // runs word count} else {// parent goes down this path (original process)int wc = wait(NULL);assert(wc >= 0);}return 0;
}

僵尸进程Zombie和孤儿进程orphan
僵尸进程

运行下列代码

可以看到此时子进程还没有被回收进入僵尸进程

孤儿进程
运行下列代码:

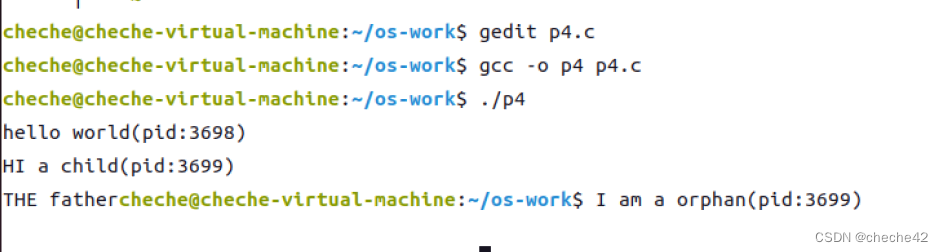
一开始父子进程都运行

而后父进程结束只剩下子进程

结果如下: