个人主页:Lei宝啊
愿所有美好如期而遇
前言
前面我们对红黑树进行了模拟实现:
现在我们将使用我们模拟的map和set对我们模拟的红黑树进行封装。
并且,本篇将增加红黑树的迭代器,模拟迭代器++(这里理解原理即可,--反过来就可以,唯一不同在于end()位置--,我们单独判断即可),然后建立我们自己的map和set对红黑树进行封装,同时为map重载operator[],添加map和set迭代器,insert方法。
红黑树代码
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;enum Color
{RED,BLACK
};template<class K, class T>
struct RBTreeNode
{struct RBTreeNode* _left;struct RBTreeNode* _right;struct RBTreeNode* _parent;pair<K, T> _p;int _color;RBTreeNode(const K& key, const T& val): _left(nullptr), _right(nullptr), _parent(nullptr), _color(RED), _p(key, val){}
};template<class K, class T>
class RBTree
{typedef RBTreeNode<K, T> Node;
public:bool Insert(const K& key, const T& val){Node* newnode = new Node(key, val);if (_root == nullptr){_root = newnode;_root->_color = BLACK;return true;}Node* cur = _root;Node* par = nullptr;while (cur){par = cur;if (cur->_p.first == key) return false;else if (cur->_p.first < key) cur = cur->_right;else cur = cur->_left;}if (par->_p.first > key) par->_left = newnode;else par->_right = newnode;newnode->_parent = par;cur = newnode;while (par && par->_color == RED){Node* grandfather = par->_parent;if (grandfather->_left == par){Node* uncle = grandfather->_right;//情况一:鼠鼠存在且为红色if (uncle && uncle->_color == RED){par->_color = BLACK;uncle->_color = BLACK;grandfather->_color = RED;cur = grandfather;par = cur->_parent;}//情况二:鼠鼠不存在或者鼠鼠为黑色(可以一同处理)else{//左左,右单旋if (cur == par->_left){RotateR(grandfather);grandfather->_color = RED;par->_color = BLACK;}//左右,左右双旋else{RotateL(par);RotateR(grandfather);cur->_color = BLACK;grandfather->_color = RED;}break;}}else{Node* uncle = grandfather->_left;//情况一:鼠鼠存在且为红色if (uncle && uncle->_color == RED){par->_color = BLACK;uncle->_color = BLACK;grandfather->_color = RED;cur = grandfather;par = cur->_parent;}//情况二:鼠鼠不存在或者鼠鼠为黑色(可以一同处理)else{//右右,左单旋if (cur == par->_right){RotateL(grandfather);grandfather->_color = RED;par->_color = BLACK;}//右左,右左双旋else{RotateR(par);RotateL(grandfather);cur->_color = BLACK;grandfather->_color = RED;}break;}} }_root->_color = BLACK;return true;}bool IsBlance(){if (_root && _root->_color == RED)return false;int standard_black_num = 0;Node* cur = _root;while (cur){if (cur->_color == BLACK)standard_black_num++;cur = cur->_left;}return _IsBlance(_root, 0, standard_black_num);}void Inorder(){return _Inorder(_root);}private:// 检查这棵树是否是红黑树// 1、遵守根节点为黑色// 2、遵守不能有连续的红色节点// 3、每条路径黑色节点数量相同// // 遵守最长路径不超过最短路径的两倍,最长路径为一黑一红,最短路径为全黑。bool _IsBlance(Node *root, int real_black_num, int standard_black_num){if (root == nullptr){if (real_black_num != standard_black_num)return false;return true;}if (root != _root && root->_color == RED && root->_parent->_color == RED)return false;if (root->_color == BLACK)real_black_num++;return _IsBlance(root->_left, real_black_num, standard_black_num)&& _IsBlance(root->_right, real_black_num, standard_black_num);}void _Inorder(Node* root){if (root == nullptr)return;_Inorder(root->_left);cout << root->_p.first << " : " << root->_p.second << endl;_Inorder(root->_right);}//左单旋void RotateL(Node* par){Node* subR = par->_right;Node* subRL = subR->_left;par->_right = subRL;if (subRL)subRL->_parent = par;Node* p_par = par->_parent;subR->_left = par;par->_parent = subR;if (p_par == nullptr){_root = subR;subR->_parent = nullptr;}else{if (p_par->_left == par){p_par->_left = subR;subR->_parent = p_par;}else{p_par->_right = subR;subR->_parent = p_par;}}}//右单旋void RotateR(Node* par){Node* subL = par->_left;Node* subLR = subL->_right;par->_left = subLR;if (subLR)subLR->_parent = par;Node* p_par = par->_parent;subL->_right = par;par->_parent = subL;if (p_par == nullptr){_root = subL;subL->_parent = nullptr;}else{if (p_par->_left == par){p_par->_left = subL;subL->_parent = p_par;}else{p_par->_right = subL;subL->_parent = p_par;}}}Node* _root = nullptr;};map类结构
这是我们最终的结果,可以先大致看一下,我们后面会对每一个细节和结构进行讲解。
#pragma once
#include "Map_Set_use_RBTree.h"template<class K, class T>
class my_map
{struct MapKeyOftypedef typename
RBTree<K, pair<const K, T>, MapKeyOf>::iterator iterator;
typedef typename
RBTree<K, pair<const K, const T>, MapKeyOf>::const_iterator const_iterator;public:T& operator[](const K& key)iterator begin()iterator end()const_iterator begin()constconst_iterator end()constpair<iterator, bool> insert(const pair<const K, T>& data)private:RBTree<K, pair<const K, T>, MapKeyOf> _t;
};
set类结构
这是我们最终的结果,可以先大致看一下,我们后面会对每一个细节和结构进行讲解。
#pragma once
#include "Map_Set_use_RBTree.h"template<class T>
class my_set
{//仿函数,提取key值,底层的红黑树进行比较struct SetKeyOftypedef typename
RBTree<T, const T, SetKeyOf>::iterator iterator;
typedef typename
RBTree<T, const T, SetKeyOf>::const_iterator const_iterator;public:bool Insert(const T& data)iterator begin()iterator end()const_iterator begin()constconst_iterator end()constpair<iterator, bool> insert(const T& data)private:RBTree<T, const T, SetKeyOf> _t;};红黑树迭代器
从这里开始,我们将详细说明map、set的封装细节以及迭代器的实现和封装。
首先是红黑树的迭代器,我们的迭代器首先应该是指向红黑树节点的,之后我们的迭代器++和--按照中序遍历的顺序迭代,而我们红黑树的节点直接++是无法到达下一个节点的,同时我们在创建红黑树对象后,使用红黑树的begin()和end()获得迭代器,返回值是迭代器对象,而这个迭代器是指向红黑树节点的,我们不可能获得一个函数类型的返回值,所以我们不在红黑树的类里去实现红黑树的迭代器。
我们写一个迭代器类:RBTreeIterator,这个类的大致结构是这样的:
template <class T, class Ptr, class Ref>
struct RBTreeIterator
{typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;RBTreeIterator(Node* node): _node(node){}Ptr operator->();Ref operator *(); bool operator==(const RBTreeIterator& s); bool operator!=(const RBTreeIterator& s);RBTreeIterator& operator++();RBTreeIterator& operator--();Node* _node;
};_node是我们通过红黑树类的方法构建这个类的对象而进行初始化的,而这个节点++或--就是我们要实现的。
我们先来实现operator++的运算符重载,返回类型当然还是我们这个类的对象,现在我们给出一个图,思考如何按照中序找到一个节点的下一个节点。
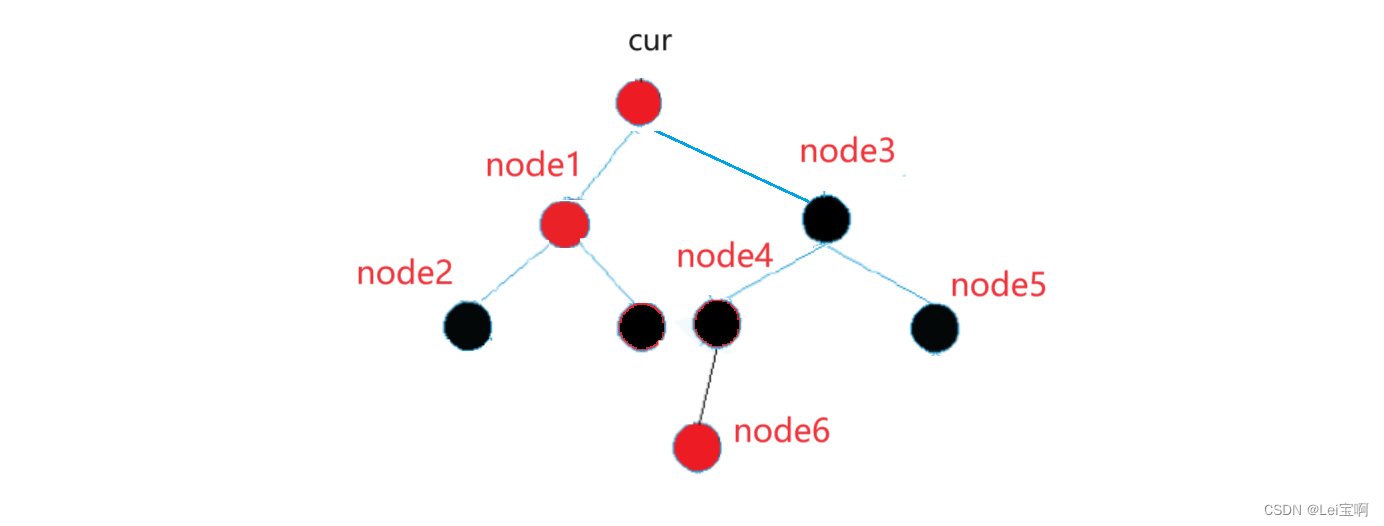 我们现在想要找出cur节点的下一个节点,也就是node6节点,如何得到node6节点呢?
我们现在想要找出cur节点的下一个节点,也就是node6节点,如何得到node6节点呢?
如果我们想要node2的下一个节点,也就是node1节点,又如何得到node1节点呢?
首先我们先来看node2节点,他的右节点是空的,所以直接返回到上一个节点,也就到了node1节点,而如果是node3节点,他的右节点不为空,就到了node5节点,而node5节点的左是空的,那么我们也就得到了node3节点。
也就是说,如果当前节点的右为空,那么就会返回去找未走过的祖先(这里我们指出,就是孩子节点为父节点左孩子的祖先节点),如果右不为空,那么就会走右子树的最左节点。
所以node6节点是cur节点右树的最左节点,也就是我们要的节点。
所以我们这样实现这个operator++:
RBTreeIterator& operator++(){if (_node->_right){Node* subRL = _node->_right;while (subRL->_left){subRL = subRL->_left;}_node = subRL;}else{Node* cur = _node;Node* parent = cur->_parent;while (parent && parent->_left != cur){cur = parent;parent = parent->_parent;}_node = parent;}return *this;} operator--就是逻辑反一下,并且加上一个特殊判断,当节点位于end()位置,也就是空位置时,我们对节点--应该是到最大的那个节点,也就是右树的最右节点,我们单独作处理即可,这里不多做解释和实现。
现在,我们给出完整的迭代器类:
这里我们解释一下Ptr参数和Ref参数,Ptr参数我们将来可以传T*或者const T*,Ref参数将来可以传T&或者const T&。
template <class T, class Ptr, class Ref>
struct RBTreeIterator
{typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;RBTreeIterator(Node* node): _node(node){}Ptr operator->(){return &_node->_data;}Ref operator *(){return _node->_data;}bool operator==(const RBTreeIterator& s){return _node == s._node;}bool operator!=(const RBTreeIterator& s){return _node != s._node;}//前置++//寻找节点的右子树不为空的最左节点,否则寻找孩子为父亲左孩子的祖先节点 RBTreeIterator& operator++(){if (_node->_right){Node* subRL = _node->_right;while (subRL->_left){subRL = subRL->_left;}_node = subRL;}else{Node* cur = _node;Node* parent = cur->_parent;while (parent && parent->_left != cur){cur = parent;parent = parent->_parent;}_node = parent;}return *this;} Node* _node;
};
现在我们来为红黑树类添加迭代器:
以下代码新增于红黑树类内,
typedef RBTreeIterator<T, T*, T&> iterator;typedef RBTreeIterator<T, const T*, const T&> const_iterator;iterator begin(){Node* cur = _root;while (cur && cur->_left){cur = cur->_left;}return iterator(cur);}iterator end(){return iterator(nullptr);}const_iterator begin() const{Node* cur = _root;while (cur && cur->_left){cur = cur->_left;}return const_iterator(cur);}const_iterator end() const{return const_iterator(nullptr);}此时如果我们定义一个红黑树对象a,并定义RBTree<省略>::iterator it = a.begin(); a.begin()返回一个RBTreeIterator类型的迭代器对象,当我们it++时,调用的就是it这个对象的operator++。
map、set迭代器
接下来我们要为map和set的迭代器做准备,首先先对红黑树进行一些改变,首先是参数:
template<class K, class T, class KeyOf>我们多了一个参数,KeyOf,这个参数我们将来当做仿函数使用,是为了insert方法做出的改变,我们希望这个仿函数能够提取出节点的key值,方便我们map节点pair<>中的key进行比较。
这里我们的T参数,将来传值可能是set的key,或者是map的pair<>,而K这个参数将在find和erase方法中用到,insert方法的返回值我们参照库里修改为pair<itreator,bool>,这里面的Iterator指的是指向红黑树节点的迭代器,bool是指是否插入成功。
首先我们来看修改后的insert方法:
pair<iterator, bool> Insert(const T& data){KeyOf compare;Node* newnode = new Node(data);if (_root == nullptr){_root = newnode;_root->_color = BLACK;return make_pair(iterator(newnode), true);}Node* cur = _root;Node* par = nullptr;while (cur){par = cur;if (compare(data) < compare(cur->_data)) cur = cur->_left;else if (compare(cur->_data) < compare(data)) cur = cur->_right;else return make_pair(iterator(cur), false);}if (compare(data) < compare(par->_data)) par->_left = newnode;else par->_right = newnode;newnode->_parent = par;cur = newnode;Node* renode = newnode;while (par && par->_color == RED){Node* grandfather = par->_parent;if (grandfather->_left == par){Node* uncle = grandfather->_right;//情况一:鼠鼠存在且为红色if (uncle && uncle->_color == RED){par->_color = BLACK;uncle->_color = BLACK;grandfather->_color = RED;cur = grandfather;par = cur->_parent;}//情况二:鼠鼠不存在或者鼠鼠为黑色(可以一同处理)else{//左左,右单旋if (cur == par->_left){RotateR(grandfather);grandfather->_color = RED;par->_color = BLACK;}//左右,左右双旋else{RotateL(par);RotateR(grandfather);cur->_color = BLACK;grandfather->_color = RED;}break;}}else{Node* uncle = grandfather->_left;//情况一:鼠鼠存在且为红色if (uncle && uncle->_color == RED){par->_color = BLACK;uncle->_color = BLACK;grandfather->_color = RED;cur = grandfather;par = cur->_parent;}//情况二:鼠鼠不存在或者鼠鼠为黑色(可以一同处理)else{//右右,左单旋if (cur == par->_right){RotateL(grandfather);grandfather->_color = RED;par->_color = BLACK;}//右左,右左双旋else{RotateR(par);RotateL(grandfather);cur->_color = BLACK;grandfather->_color = RED;}break;}}}_root->_color = BLACK;return make_pair(iterator(renode), true);}接下来就是map和set的迭代器:
map:
这里我们对迭代器进行解释,RBTree<K, pair<const K, T>, MapKeyOf>::iterator 这里的一堆参数是传给RBTree类的,我们这里的Iterator本质是RBTree的Iterator,而RBTree的Iterator本质是RBTreeIterator的,也就是说,实际上,我们在创建好一个map对象后,当我们调用迭代器时,实际是这样的:
map<string, int> m;
map<string,int>::iterator it = m.begin(); 这个begin()的返回值是RBTree<>::iterator,也就是RBTreeIterator的对象,我们将来it++,实际上就是这个对象调用他类里的operator++。
而我们底层用的当然是红黑树,所以也就创建红黑树对象,当我们想要插入值等等操作,直接调用红黑树里的方法即可,事实上,我们这个类除了仿函数,仅仅只是对红黑树的方法做了一层封装。
set也是同样的道理。
template<class K, class T>
class my_map
{struct MapKeyOf{const K& operator()(const pair<const K, T>& data){return data.first;}};typedef typename
RBTree<K, pair<const K, T>, MapKeyOf>::iterator iterator;
typedef typename
RBTree<K, pair<const K, const T>, MapKeyOf>::const_iterator const_iterator;public:iterator begin(){return _t.begin();}iterator end(){return _t.end();}const_iterator begin()const{return _t.begin();}const_iterator end()const{return _t.end();}pair<iterator, bool> insert(const pair<const K, T>& data){return _t.Insert(data);}private:RBTree<K, pair<const K, T>, MapKeyOf> _t;
};set:
template<class T>
class my_set
{//仿函数,提取key值,底层的红黑树进行比较struct SetKeyOf{const T& operator()(const T& key){return key;}};typedef typename
RBTree<T, const T, SetKeyOf>::iterator iterator;
typedef typename
RBTree<T, const T, SetKeyOf>::const_iterator const_iterator;public:bool Insert(const T& data){return _t.Insert(data);}iterator begin(){return _t.begin();}iterator end(){return _t.end();}const_iterator begin()const{return _t.begin();}const_iterator end()const{return _t.end();}pair<iterator, bool> insert(const T& data){return _t.Insert(data);}private:RBTree<T, const T, SetKeyOf> _t;};map的operator[]重载
T& operator[](const K& key){//iterator是map中pair的地址pair<iterator, bool> it = insert(make_pair(key, T()));return it.first->second;}我们使用map时也就是做插入、查找以及修改value这么些操作,那么它的返回值理所当然是T&,这里的T和RBTRee的T是不一样的,这里的T类型是value的类型,而RETree的T是pair<K,T>类型的。
我们知道insert返回值是pair<iterator,bool>,这里的Iterator就是RBTreeIterator的对象,bool就是是否插入成功,我们返回值是这样的,it.first是取到这个迭代器,这个迭代器是指向一个RBTreeIterator的对象,并且这个对象的类里重载了->()方法,假设这个对象叫做a,我们这样使用:a.operator->()就是取到了pair<>节点的地址,再这样: a.operator->()->second,也就取出了T&的值,但是这样写比较长,我们正常情况应该是这样:a->->second,但是编译器省略了一个,也就是这样:a->second,多写反而是错的。
整体代码
#pragma once
#include "Map_Set_use_RBTree.h"template<class T>
class my_set
{//仿函数,提取key值,底层的红黑树进行比较struct SetKeyOf{const T& operator()(const T& key){return key;}};typedef typename RBTree<T, const T, SetKeyOf>::iterator iterator;typedef typename RBTree<T, const T, SetKeyOf>::const_iterator const_iterator;public:bool Insert(const T& data){return _t.Insert(data);}iterator begin(){return _t.begin();}iterator end(){return _t.end();}const_iterator begin()const{return _t.begin();}const_iterator end()const{return _t.end();}pair<iterator, bool> insert(const T& data){return _t.Insert(data);}private:RBTree<T, const T, SetKeyOf> _t;};#pragma once
#include "Map_Set_use_RBTree.h"template<class K, class T>
class my_map
{struct MapKeyOf{const K& operator()(const pair<const K, T>& data){return data.first;}};typedef typename RBTree<K, pair<const K, T>, MapKeyOf>::iterator iterator;typedef typename RBTree<K, pair<const K, const T>, MapKeyOf>::const_iterator const_iterator;public:T& operator[](const K& key){//iterator是map中pair的地址pair<iterator, bool> it = insert(make_pair(key, T()));return it.first->second;}iterator begin(){return _t.begin();}iterator end(){return _t.end();}const_iterator begin()const{return _t.begin();}const_iterator end()const{return _t.end();}pair<iterator, bool> insert(const pair<const K, T>& data){return _t.Insert(data);}private:RBTree<K, pair<const K, T>, MapKeyOf> _t;
};#pragma once
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;enum Color
{RED,BLACK
};//树的节点,作为RBTree的成员变量。
template<class T>
struct RBTreeNode
{struct RBTreeNode* _left;struct RBTreeNode* _right;struct RBTreeNode* _parent;T _data;Color _color;RBTreeNode(const T& data): _left(nullptr), _right(nullptr), _parent(nullptr), _color(RED), _data(data){}
};//作为RBTree的迭代器,在RBTree内使用,接收来自RBTree内的Node节点
template <class T, class Ptr, class Ref>
struct RBTreeIterator
{typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;RBTreeIterator(Node* node): _node(node){}Ptr operator->(){return &_node->_data;}Ref operator *(){return _node->_data;}bool operator==(const RBTreeIterator& s){return _node == s._node;}bool operator!=(const RBTreeIterator& s){return _node != s._node;}//前置++//寻找节点的右子树不为空的最左节点,否则寻找孩子为父亲左孩子的祖先节点 RBTreeIterator& operator++(){if (_node->_right){Node* subRL = _node->_right;while (subRL->_left){subRL = subRL->_left;}_node = subRL;}else{Node* cur = _node;Node* parent = cur->_parent;while (parent && parent->_left != cur){cur = parent;parent = parent->_parent;}_node = parent;}return *this;} /*** @param null* 前置--* 寻找孩子的左子树不为空的最右节点,否则寻找孩子为父亲右孩子的祖先节点*/RBTreeIterator& operator--(){if (_node->_left){Node* cur = _node->_left;while (cur->_right){cur = cur->_right;}_node = cur;}else{Node* cur = _node;Node* parent = cur->_parent;while (parent && cur != parent->_right){cur = parent;parent = parent->_parent;}_node = cur;}return *this;}Node* _node;
};//红黑树的实现
template<class K, class T, class KeyOf>
class RBTree
{public:typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;typedef RBTreeIterator<T, T*, T&> iterator;typedef RBTreeIterator<T, const T*, const T&> const_iterator;iterator begin(){Node* cur = _root;while (cur && cur->_left){cur = cur->_left;}return iterator(cur);}iterator end(){return iterator(nullptr);}const_iterator begin() const{Node* cur = _root;while (cur && cur->_left){cur = cur->_left;}return const_iterator(cur);}const_iterator end() const{return const_iterator(nullptr);}pair<iterator, bool> Insert(const T& data){KeyOf compare;Node* newnode = new Node(data);if (_root == nullptr){_root = newnode;_root->_color = BLACK;return make_pair(iterator(newnode), true);}Node* cur = _root;Node* par = nullptr;while (cur){par = cur;if (compare(data) < compare(cur->_data)) cur = cur->_left;else if (compare(cur->_data) < compare(data)) cur = cur->_right;else return make_pair(iterator(cur), false);}if (compare(data) < compare(par->_data)) par->_left = newnode;else par->_right = newnode;newnode->_parent = par;cur = newnode;Node* renode = newnode;while (par && par->_color == RED){Node* grandfather = par->_parent;if (grandfather->_left == par){Node* uncle = grandfather->_right;//情况一:鼠鼠存在且为红色if (uncle && uncle->_color == RED){par->_color = BLACK;uncle->_color = BLACK;grandfather->_color = RED;cur = grandfather;par = cur->_parent;}//情况二:鼠鼠不存在或者鼠鼠为黑色(可以一同处理)else{//左左,右单旋if (cur == par->_left){RotateR(grandfather);grandfather->_color = RED;par->_color = BLACK;}//左右,左右双旋else{RotateL(par);RotateR(grandfather);cur->_color = BLACK;grandfather->_color = RED;}break;}}else{Node* uncle = grandfather->_left;//情况一:鼠鼠存在且为红色if (uncle && uncle->_color == RED){par->_color = BLACK;uncle->_color = BLACK;grandfather->_color = RED;cur = grandfather;par = cur->_parent;}//情况二:鼠鼠不存在或者鼠鼠为黑色(可以一同处理)else{//右右,左单旋if (cur == par->_right){RotateL(grandfather);grandfather->_color = RED;par->_color = BLACK;}//右左,右左双旋else{RotateR(par);RotateL(grandfather);cur->_color = BLACK;grandfather->_color = RED;}break;}}}_root->_color = BLACK;return make_pair(iterator(renode), true);}bool IsBlance(){if (_root && _root->_color == RED)return false;int standard_black_num = 0;Node* cur = _root;while (cur){if (cur->_color == BLACK)standard_black_num++;cur = cur->_left;}return _IsBlance(_root, 0, standard_black_num);}void Inorder(){return _Inorder(_root);}private:// 检查这棵树是否是红黑树// 1、遵守根节点为黑色// 2、遵守不能有连续的红色节点// 3、每条路径黑色节点数量相同// // 遵守最长路径不超过最短路径的两倍,最长路径为一黑一红,最短路径为全黑。bool _IsBlance(Node* root, int real_black_num, int standard_black_num){if (root == nullptr){if (real_black_num != standard_black_num)return false;return true;}if (root != _root && root->_color == RED && root->_parent->_color == RED)return false;if (root->_color == BLACK)real_black_num++;return _IsBlance(root->_left, real_black_num, standard_black_num)&& _IsBlance(root->_right, real_black_num, standard_black_num);}void _Inorder(Node* root){if (root == nullptr)return;_Inorder(root->_left);cout << root->_p.first << " : " << root->_p.second << endl;_Inorder(root->_right);}//左单旋void RotateL(Node* par){Node* subR = par->_right;Node* subRL = subR->_left;par->_right = subRL;if (subRL)subRL->_parent = par;Node* p_par = par->_parent;subR->_left = par;par->_parent = subR;if (p_par == nullptr){_root = subR;subR->_parent = nullptr;}else{if (p_par->_left == par){p_par->_left = subR;subR->_parent = p_par;}else{p_par->_right = subR;subR->_parent = p_par;}}}//右单旋void RotateR(Node* par){Node* subL = par->_left;Node* subLR = subL->_right;par->_left = subLR;if (subLR)subLR->_parent = par;Node* p_par = par->_parent;subL->_right = par;par->_parent = subL;if (p_par == nullptr){_root = subL;subL->_parent = nullptr;}else{if (p_par->_left == par){p_par->_left = subL;subL->_parent = p_par;}else{p_par->_right = subL;subL->_parent = p_par;}}}Node* _root = nullptr;};需要注意的点和容易犯错的点

这里需要注意到的是迭代器是RBTree里的迭代器,因为红黑树需要我们提供一种提取key的方法,所以才有了第三个参数。

const迭代器并不是改了返回值就是const类型的方法了,需要this指针也是const类型。

明确自己的类里定义的成员变量,以及要传的参数。
 这里需要实现,范围for需要这个方法,同时,参数是本类的类型。
这里需要实现,范围for需要这个方法,同时,参数是本类的类型。

_node和_right写对,不要少了_。
 这些只是重命名,:: 前的是类的类型,后面才是迭代器,表示某个类里的迭代器,这么一层层下去,实际上用的一直都是RBTreeIterator的对象。
这些只是重命名,:: 前的是类的类型,后面才是迭代器,表示某个类里的迭代器,这么一层层下去,实际上用的一直都是RBTreeIterator的对象。