C++ 改造红黑树,封装map和set
- 一.前言:已经实现好了的红黑树
- 二.简化STL库里面对于map和set的封装
- 1.STL库中红黑树的简化代码
- 2.STL库中set的简化代码
- 3.STL库中map的简化代码
- 4.封装map和set的第一步
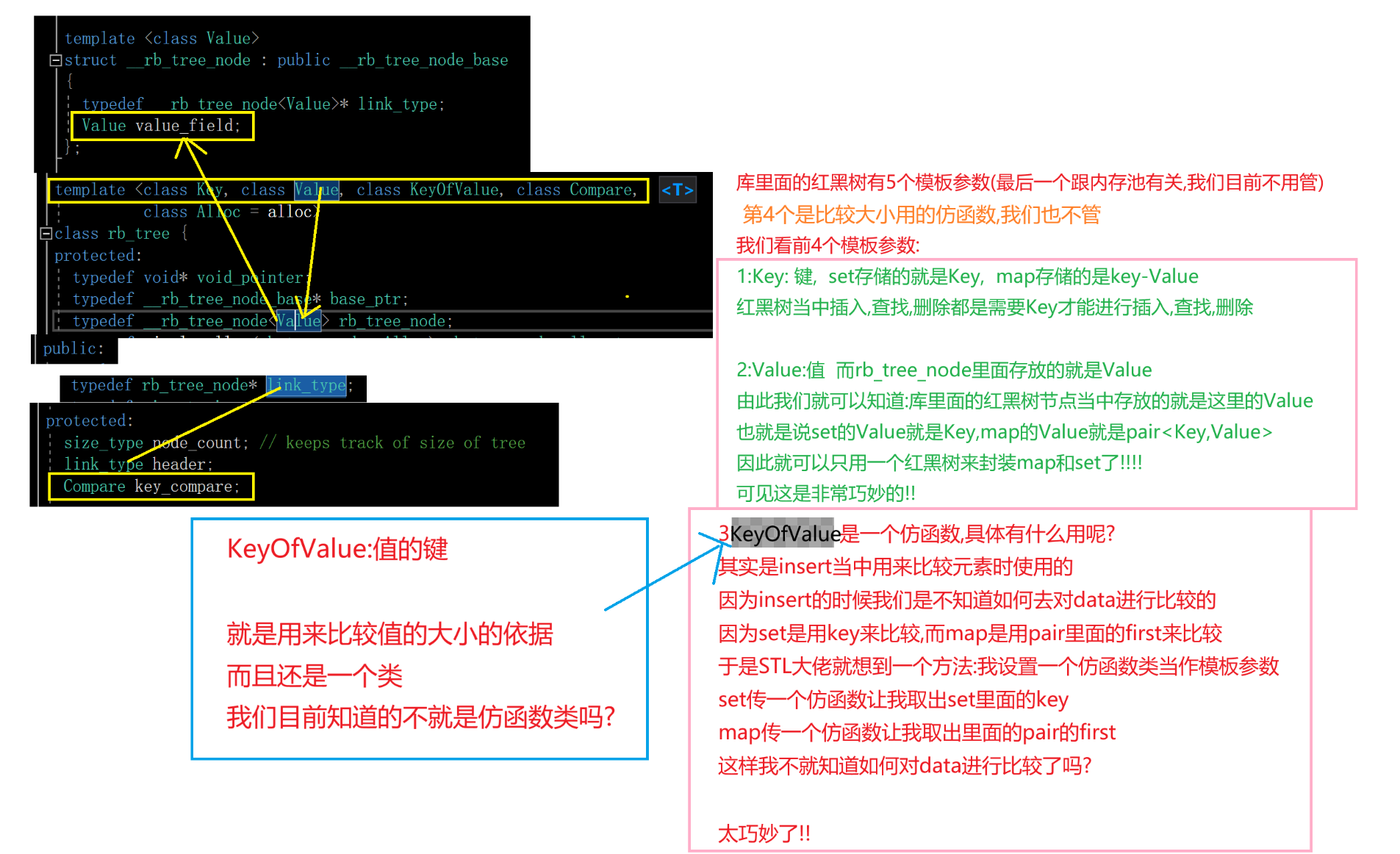
- 5.红黑树第一个模板参数的价值
- 6.红黑树节点的定义
- 三.仿函数
- 1.解除仿函数的误解
- 2.仿函数在这里的价值
- 3.set的仿函数
- 4.map的仿函数
- 5.红黑树的修改
- 6.仿函数小总结
- 四.迭代器
- 1.迭代器类的定义
- 2.解引用,!=,==的实现
- 3.operator++
- 4.给红黑树加上begin和end
- 五.set的实现
- 1.注意
- 1.typename
- 2.set的特性
- 2.set的代码
- 六.map的实现
- 1.operator[]的说明
- 2.map的代码
- 七.改造后的红黑树代码
一.前言:已经实现好了的红黑树
set是Key模型的红黑树
map是Key-Value模型的红黑树
我们之前已经把红黑树实现并测试过了
这是Key-Value模型的红黑树
RBTree.h
#pragma once
enum Color
{RED,BLACK
};template<class K,class V>
struct RBTreeNode
{RBTreeNode<K,V>* _pLeft;RBTreeNode<K,V>* _pRight;RBTreeNode<K,V>* _pParent;Color _color;pair<K,V> _data;//新插入的节点默认是红色RBTreeNode(const pair<K,V>& data):_pLeft(nullptr),_pRight(nullptr),_pParent(nullptr),_color(RED),_data(data){}
};template<class K,class V>
class RBTree
{typedef RBTreeNode<K,V> Node;
public:// 在红黑树中插入值为data的节点,插入成功返回true,否则返回false// 注意:为了简单起见,本次实现红黑树不存储重复性元素bool Insert(const pair<K,V>& data){if (_pRoot == nullptr){_pRoot = new Node(data);//根节点是黑色_pRoot->_color = BLACK;return true;}Node* cur = _pRoot, * parent = nullptr;while (cur){//比我小,往左找if (data.first < cur->_data.first){parent = cur;cur = cur->_pLeft;}//比我大,往右找else if (data.first > cur->_data.first){parent = cur;cur = cur->_pRight;}//有重复元素,插入失败else{return false;}}//找到空位置,开始插入cur = new Node(data);//连接父亲和孩子if (cur->_data.first < parent->_data.first){parent->_pLeft = cur;}else{parent->_pRight = cur;}cur->_pParent = parent;//父亲是黑色,插入成功if (parent->_color == BLACK){return true;}//父亲是红色,需要调整//且此时爷爷一定是黑色//根据叔叔的颜色来调整while (parent && parent->_color == RED){Node* grandParent = parent->_pParent;//爸爸是爷爷的左孩子if (parent == grandParent->_pLeft){Node* uncle = grandParent->_pRight;//根据叔叔的颜色来调整//1.叔叔存在且为红if (uncle && uncle->_color == RED){//修改爸爸,叔叔,爷爷的颜色uncle->_color = parent->_color = BLACK;grandParent->_color = RED;//此时视爷爷为新插入的红色节点继续向上影响cur = grandParent;parent = cur->_pParent;}//2.叔叔不存在或者叔叔是黑else{//1.我是爸爸的左孩子if (parent->_pLeft == cur){//对爷爷进行一次右旋RotateR(grandParent);//把爷爷改成红色,爸爸改成黑色grandParent->_color = RED;parent->_color = BLACK;//此时爸爸是黑色,无需break,当然break也可以,因此爸爸是黑色,下次循环就不会进入了}//2.我是爸爸的右孩子else{//1.对爸爸进行左旋RotateL(parent);//2.对爷爷右旋RotateR(grandParent);//3.孩子改成黑色,爷爷改成红色cur->_color = BLACK;grandParent->_color = RED;//4.一定要break,如果不break的话,因为爸爸是红色,所以循环会继续,此时就乱套了break;}}}//爸爸是爷爷的右孩子else{Node* uncle = grandParent->_pLeft;//1.叔叔存在且为红if (uncle && uncle->_color == RED){uncle->_color = parent->_color = BLACK;grandParent->_color = RED;cur = grandParent;parent = cur->_pParent;}//2.叔叔不存在或者叔叔为黑else{//1.我是爸爸的右孩子if (parent->_pRight == cur){//对爷爷左旋RotateL(grandParent);//爷爷改成红色,爸爸改成黑色grandParent->_color = RED;parent->_color = BLACK;//此时爸爸是黑色,无需break,当然break也可以,因此爸爸是黑色,下次循环就不会进入了}//2.我是爸爸的左孩子else{//1.对爸爸右旋RotateR(parent);//2.对爷爷左旋RotateL(grandParent);//3.把孩子改成黑色,爷爷改成红色cur->_color = BLACK;grandParent->_color = RED;//4.一定要break,如果不break的话,因为爸爸是红色,所以循环会继续,此时就乱套了break;}}}}_pRoot->_color = BLACK;return true;}// 检测红黑树中是否存在关键字为key的节点,存在返回该节点的地址,否则返回nullptrNode* Find(const K& key){Node* cur = _pRoot;while (cur){if (cur->_data.first > key){cur = cur->_pLeft;}else if (cur->_data.second < key){cur = cur->_pRight;}else{return cur;}}return nullptr;}// 检测红黑树是否为有效的红黑树,注意:其内部主要依靠_IsValidRBTRee函数检测bool IsValidRBTRee(){//1.空树是红黑树if (_pRoot == nullptr){return true;}//2.根节点不能为红色if (_pRoot->_color == RED){return false;}//3.为了验证性质: 红黑树的任意一条路径上的黑色节点个数相同 找参考值size_t ReferenceCount = 0;Node* cur = _pRoot;while (cur){if (cur->_color == BLACK){ReferenceCount++;}cur = cur->_pLeft;}return _IsValidRBTRee(_pRoot, 0, ReferenceCount);}void InOrder(){_InOrder(_pRoot);}
private:bool _IsValidRBTRee(Node* pRoot, size_t blackCount, size_t& ReferenceCount){if (pRoot == nullptr){if (blackCount != ReferenceCount){cout << "存在黑色节点数量不相等的路径" << endl;return false;}return true;}//验证性质: 红黑树中不能存在连续的红色节点//如果一个节点是红色,该节点一定不是根节点,因此该节点一定有父亲//只需要保证红色节点的父亲不是红色节点即可if (pRoot->_color == RED){if (pRoot->_pParent->_color == RED){cout << "存在连续的红色节点" << endl;return false;}}else{blackCount++;}return _IsValidRBTRee(pRoot->_pLeft, blackCount, ReferenceCount) && _IsValidRBTRee(pRoot->_pRight, blackCount, ReferenceCount);}// 右单旋void RotateR(Node* pParent){Node* subL = pParent->_pLeft;Node* subLR = subL->_pRight;Node* grandParent = pParent->_pParent;subL->_pRight = pParent;pParent->_pParent = subL;pParent->_pLeft = subLR;if (subLR)subLR->_pParent = pParent;if (grandParent == nullptr){_pRoot = subL;_pRoot->_pParent = nullptr;}else{if (pParent == grandParent->_pLeft){grandParent->_pLeft = subL;}else{grandParent->_pRight = subL;}subL->_pParent = grandParent;}}// 左单旋void RotateL(Node* pParent){Node* subR = pParent->_pRight;Node* subRL = subR->_pLeft;Node* grandParent = pParent->_pParent;pParent->_pParent = subR;subR->_pLeft = pParent;pParent->_pRight = subRL;if (subRL)subRL->_pParent = pParent;//说明此时pParent是_pRootif (grandParent == nullptr){_pRoot = subR;_pRoot->_pParent = nullptr;}//说明此时pParent所在的树是一颗子树,需要跟父亲链接else{if (pParent == grandParent->_pLeft){grandParent->_pLeft = subR;}else{grandParent->_pRight = subR;}subR->_pParent = grandParent;}}void _InOrder(Node* root){if (root == nullptr) return;_InOrder(root->_pLeft);cout << root->_data.first << " " << root->_data.second << " ";_InOrder(root->_pRight);}
private:Node* _pRoot = nullptr;
};
要想用红黑树来封装set和map,我们首先想到的是在搞一份Key模型的红黑树,
然后用Key模型红黑树来封装set,Key-Value模型红黑树封装map
但是STL库中set和map的设计却不是这样的
它们都是只用了一份红黑树,怎么做到的呢?
下面就让我们来探索一下
二.简化STL库里面对于map和set的封装
红黑树的源码:是一个KV模型的红黑树
它是通过传入的Value的值来判断类型,利用模板的技术实现的一棵泛型的红黑树
通过模板的实例化,实现了map和set
1.STL库中红黑树的简化代码
我们挑选出一部分很重要的成员来看看STL库中的红黑树是怎么个泛型法呢?
2.STL库中set的简化代码
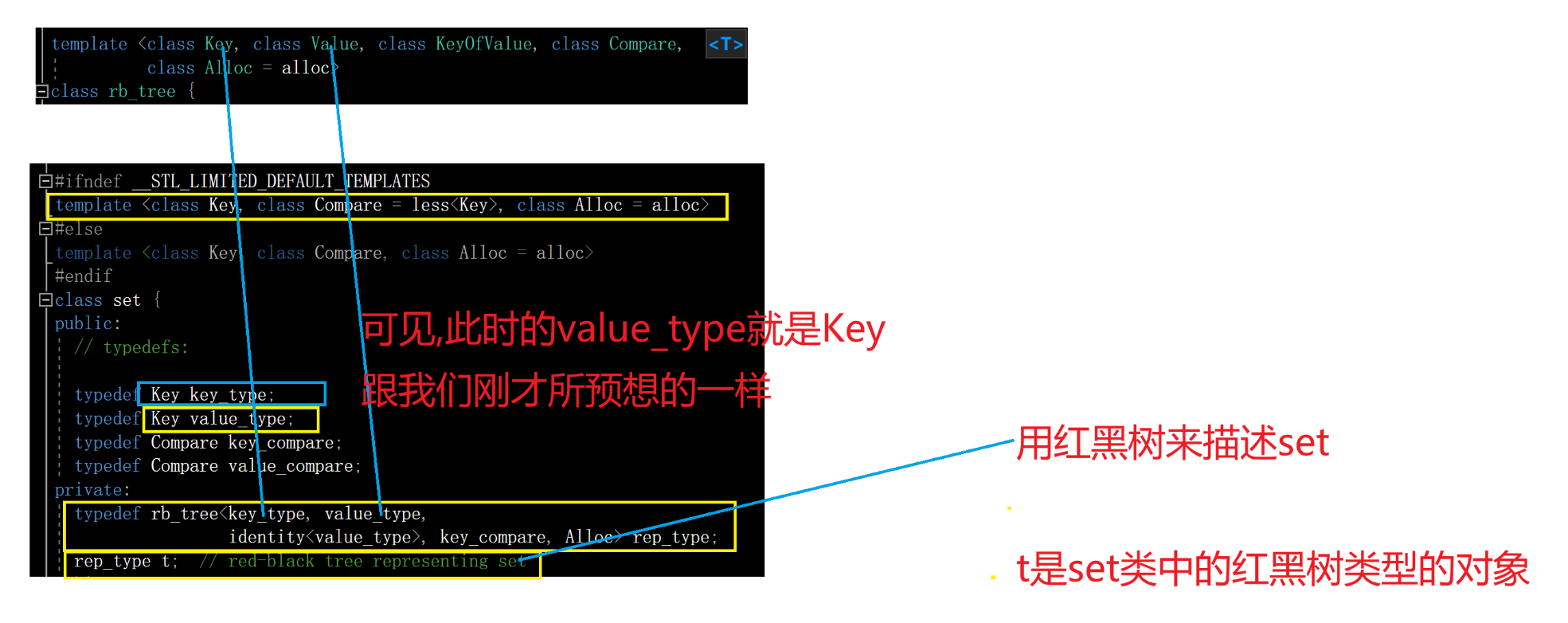
下面我们看一下set
3.STL库中map的简化代码
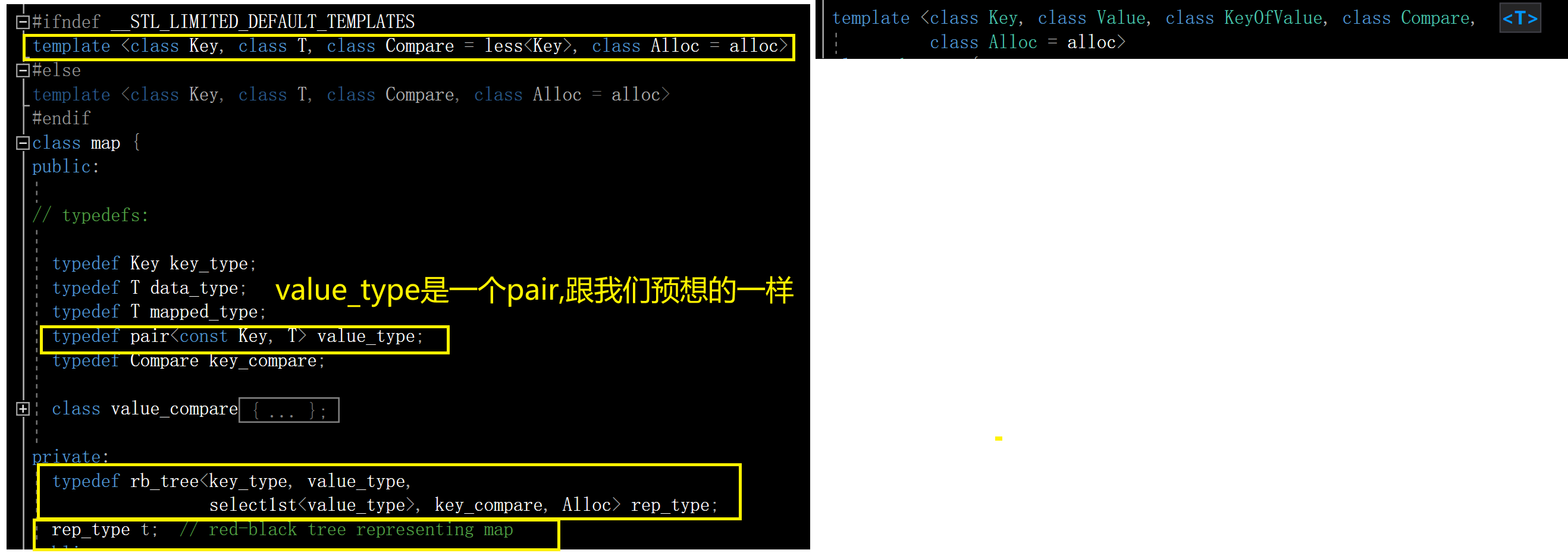
下面我们看一下map
4.封装map和set的第一步

RBTree.h
template<class K, class V>
class RBTree
对于V这个模板参数:
可能是键值Key,也可能是由Key和Value共同组成的键值对pair
MySet.h
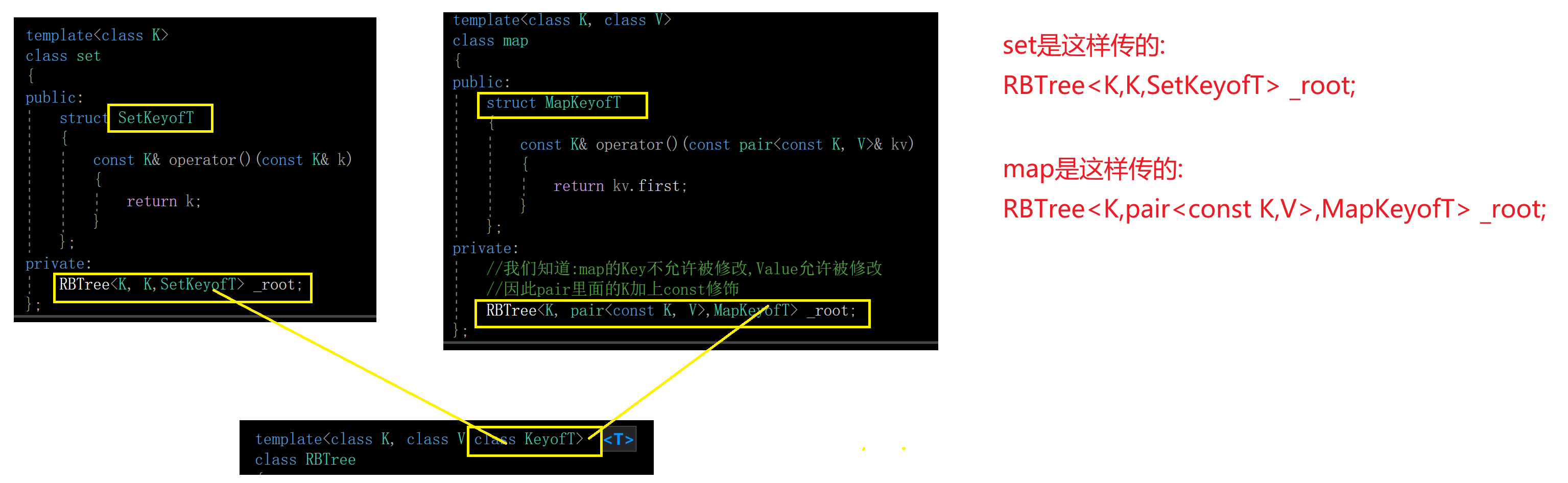
对于set而言,传入底层红黑树的模板参数就是Key和Key
template<class K>
class set
{
private:RBTree<K, K> _root;
};
MyMap.h
对于map而言,传入底层红黑树的模板参数就是Key和pair<const Key,Value>
template<class K, class V>
class map
{
private://我们知道:map的Key不允许被修改,Value允许被修改//因此pair里面的K加上const修饰RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>> _root;
};
5.红黑树第一个模板参数的价值
通过上面的传参,我们可以知道:
只需要对于红黑树的第二个模板参数传入不同的值就可以对set和map进行很好地区分
那么红黑树的第一个模板参数是不是就没有用了呢?
对于insert(const Value& v)来说,是这样的,因为插入的值就是value
set的value是key,map的value是pair
但是对于find(const Key& k)来说,查找的依据是key,对于set是可以的
但是对于map来说,它的value是一个键值对,而我们是需要key来查找的,因此第一个模板参数不能不要
6.红黑树节点的定义

enum Color
{RED,BLACK
};
template<class T>
struct RBTreeNode
{RBTreeNode<T>* _pLeft;RBTreeNode<T>* _pRight;RBTreeNode<T>* _pParent;Color _color;T _data;//新插入的节点默认是红色RBTreeNode(const T& data):_pLeft(nullptr), _pRight(nullptr), _pParent(nullptr), _color(RED), _data(data){}
};
三.仿函数
1.解除仿函数的误解
在学习优先级队列的时候我们遇到了仿函数
当时我们写了一个greater的仿函数,传入greater就能建小堆
传入less就能建大堆
当时我们知道:仿函数是一个类,主要重载operator()
不过仿函数不仅仅可以用于比较大小,这是我们常有的一大误解
2.仿函数在这里的价值
由于红黑树不知道传的是set还是map
因此在insert时进行节点键值的比较时,底层红黑树需要使用仿函数来获取键值key,从而才能进行比较
3.set的仿函数
对set而言,仿函数就是返回Key
template<class K>
class set
{
public:struct SetKeyofT{const K& operator()(const K& k){return k;}};
private:RBTree<K, K,SetKeyofT> _root;
};
4.map的仿函数
对map而言,仿函数就是返回pair的first,也就是Key
template<class K, class V>
class map
{
public:struct MapKeyofT{const K& operator()(const pair<const K, V>& kv){return kv.first;}};
private://我们知道:map的Key不允许被修改,Value允许被修改//因此pair里面的K加上const修饰RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>,MapKeyofT> _root;
};
5.红黑树的修改
修改之后,因为红黑树的代码太长了,所以这里只列出修改的地方
1.类模板
template<class K, class V,class KeyofT>
2.成员变量
private:Node* _pRoot = nullptr;KeyofT _kot;
3.insert插入时的比较逻辑
//1 参数只需要传V即可(也就是红黑树的第二个模板参数)
//对于set而言V就是Key
//对于map而言,V就是pair<K,V>
bool Insert(const V& data)
{if (_pRoot == nullptr){_pRoot = new Node(data);//根节点是黑色_pRoot->_color = BLACK;return true;}Node* cur = _pRoot, * parent = nullptr;while (cur){//比我小,往左找if (_kot(data) < _kot(cur->_data)){parent = cur;cur = cur->_pLeft;}//比我大,往右找else if (_kot(data) > _kot(cur->_data)){parent = cur;cur = cur->_pRight;}//有重复元素,插入失败else{return false;}}//找到空位置,开始插入cur = new Node(data);//连接父亲和孩子if (_kot(cur->_data) < _kot(parent->_data)){parent->_pLeft = cur;}//..旋转变色等其他操作,这些操作都无需进行节点的Key有关比较
}

6.仿函数小总结
四.迭代器
1.迭代器类的定义
跟list类似,红黑树的正向迭代器也是对节点指针进行了一层封装
同样的,为了实现const_iterator,这里传入Ref和Ptr这两个模板参数
不过这里增加了const迭代器和非const迭代器的转化
template<class T, class Ref, class Ptr>
struct __TreeIterator
{typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;typedef __TreeIterator<T, T&, T*> iterator;typedef __TreeIterator<T, Ref, Ptr> Self;Node* _node;__TreeIterator(Node* node):_node(node){}//普通迭代器和const_iterator的转化__TreeIterator(const iterator& it):_node(it._node){}Ref operator*();Ptr operator->();//找中序遍历的下一个节点Self& operator++();bool operator!=(const Self& s);bool operator==(const Self& s);
};
2.解引用,!=,==的实现
Ref operator*()
{return _node->_data;
}Ptr operator->()
{return &_node->_data;
}bool operator!=(const Self& s)
{return _node != s._node;
}bool operator==(const Self& s)
{return _node == s._node;
}
3.operator++
这里的迭代器走的是二叉树的中序遍历,因此++要找到中序遍历的下一个节点
如何找呢?
1.如果节点的右子树不为空,中序的下一个节点就是右子树的最左节点
2.如果节点的右子树为空,那么就需要一直往上找
直到父亲为空或者孩子是父亲的左孩子时,此时的父亲就是中序的下一个节点
//找中序遍历的下一个节点
Self& operator++()
{//1.左子树 根节点 右子树//如果有右孩子,那就是右子树的最左节点//如果没有右孩子,那往上找直到我是父亲的左孩子或者我的父亲是空节点为止,此时我的父亲就是下一个节点Node* cur = _node;if (cur->_pRight){Node* right = cur->_pRight;while (right->_pLeft){right = right->_pLeft;}_node = right;}else{Node* parent = cur->_pParent;while (parent && parent->_pRight == cur){cur = parent;parent = cur->_pParent;}_node = parent;}return *this;
}
4.给红黑树加上begin和end
begin是中序的第一个节点,也就是最左节点
end是中序的最后一个节点的下一个节点,也就是空节点
跟list一样,普通迭代器就是V V& V*
const_iterator就是V const V& const V*
template<class K, class V,class KeyofT>
class RBTree
{typedef RBTreeNode<V> Node;
public:typedef __TreeIterator<V, V&, V*> iterator;typedef __TreeIterator<V,const V&,const V*> const_iterator;iterator begin(){Node* cur = _pRoot;while (cur && cur->_pLeft){cur = cur->_pLeft;}return iterator(cur);}iterator end(){return iterator(nullptr);}const_iterator begin() const{Node* cur = _pRoot;while (cur && cur->_pLeft){cur = cur->_pLeft;}return const_iterator(cur);}const_iterator end() const{return const_iterator(nullptr);}//其他成员....
};
五.set的实现
1.注意
1.typename
直接复用红黑树的接口即可实现set
注意:
typedef typename RBTree<K, K, SetKeyofT>::const_iterator iterator;
typename的作用:因为没有实例化的模板是区分不了静态变量和类型的,因此需要我们使用typename告诉编译器这是类型
2.set的特性
库里面的set是不允许修改里面的值的
也就是说set的普通迭代器和const迭代器其实都是const迭代器
因此都复用红黑树的const_iterator即可
2.set的代码
namespace wzs
{template<class K>class set{public:struct SetKeyofT{const K& operator()(const K& k){return k;}};typedef typename RBTree<K, K, SetKeyofT>::const_iterator iterator;typedef typename RBTree<K, K, SetKeyofT>::const_iterator const_iterator;iterator begin() const{return _root.begin();}iterator end() const{return _root.end();}pair<iterator, bool> insert(const K& k){return _root.Insert(k);}private:RBTree<K, K, SetKeyofT> _root;};
}
六.map的实现
1.operator[]的说明
STL库里面的map容器的方括号[]的作用:
返回值:
插入成功:pair<新插入的key所在的节点的iterator,true>
插入失败:pair<已经存在的key所在的节点的iterator,false>作用:
如果插入成功,那么operator[]相当于insert
如果插入失败,那么operator[]相当于find也就是说operator[]有多重技能
operator[]是map的一个非常重要的函数,可以实现3个功能:插入,查找,修改
这是对源码的一个简化:
operator[]:给一个key,返回这个key所对应的value的引用
简化前:
mapped_type& operator[](const Key_type& k)
{return (*(this->insert(make_pair(k,mapped_type())))).first).second;
}简化后
V& operator(const K& key)
{pair<iterator,bool> ret=insert(key,V());//V():value的默认构造的匿名对象return ret.first->second;
2.map的代码
namespace wzs
{template<class K, class V>class map{public:struct MapKeyofT{const K& operator()(const pair<const K, V>& kv){return kv.first;}};typedef typename RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyofT>::iterator iterator;typedef typename RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyofT>::const_iterator const_iterator;iterator begin(){return _root.begin();}iterator end(){return _root.end();}const_iterator begin() const{return _root.begin();}const_iterator end() const{return _root.end();}pair<iterator, bool> insert(const pair<const K, V>& kv){return _root.Insert(kv);}/*operator[]:给一个key,返回这个key所对应的value的引用简化前:mapped_type& operator[](const Key_type& k){return (*(this->insert(make_pair(k,mapped_type())))).first).second;}简化后V& operator(const K& key){pair<iterator,bool> ret=insert(key,V());//V():value的默认构造的匿名对象return ret.first->second;}*/V& operator[](const K& k){pair<iterator, bool> ret = insert(make_pair(k, V()));return ret.first->second;}private://我们知道:map的Key不允许被修改,Value允许被修改//因此pair里面的K加上const修饰RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyofT> _root;};
}
七.改造后的红黑树代码
#pragma once
namespace wzs
{enum Color{RED,BLACK};template<class T>struct RBTreeNode{RBTreeNode<T>* _pLeft;RBTreeNode<T>* _pRight;RBTreeNode<T>* _pParent;Color _color;T _data;//新插入的节点默认是红色RBTreeNode(const T& data):_pLeft(nullptr), _pRight(nullptr), _pParent(nullptr), _color(RED), _data(data){}};//给红黑树增加迭代器template<class T, class Ref, class Ptr>struct __TreeIterator{typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;typedef __TreeIterator<T, T&, T*> iterator;typedef __TreeIterator<T, Ref, Ptr> Self;Node* _node;__TreeIterator(Node* node):_node(node){}//const迭代器和普通迭代器的转化__TreeIterator(const iterator& it):_node(it._node){}Ref operator*(){return _node->_data;}Ptr operator->(){return &_node->_data;}//找中序遍历的下一个节点Self& operator++(){//1.左子树 根节点 右子树//如果有右孩子,那就是右子树的最左节点//如果没有右孩子,那往上找直到我是父亲的左孩子或者我的父亲是空节点为止,此时我的父亲就是下一个节点Node* cur = _node;if (cur->_pRight){Node* right = cur->_pRight;while (right->_pLeft){right = right->_pLeft;}_node = right;}else{Node* parent = cur->_pParent;while (parent && parent->_pRight == cur){cur = parent;parent = cur->_pParent;}_node = parent;}return *this;}bool operator!=(const Self& s){return _node != s._node;}bool operator==(const Self& s){return _node == s._node;}};template<class K, class V,class KeyofT>class RBTree{typedef RBTreeNode<V> Node;public:typedef __TreeIterator<V, V&, V*> iterator;typedef __TreeIterator<V, const V&, const V*> const_iterator;iterator begin(){Node* cur = _pRoot;while (cur && cur->_pLeft){cur = cur->_pLeft;}return iterator(cur);}iterator end(){return iterator(nullptr);}const_iterator begin() const{Node* cur = _pRoot;while (cur && cur->_pLeft){cur = cur->_pLeft;}return const_iterator(cur);}const_iterator end() const{return const_iterator(nullptr);}//1,参数只需要传V即可(也就是红黑树的第二个模板参数)//对于set而言V就是Key//对于map而言,V就是pair<K,V>pair<iterator, bool> Insert(const V& data){if (_pRoot == nullptr){_pRoot = new Node(data);//根节点是黑色_pRoot->_color = BLACK;return make_pair(iterator(_pRoot), true);}Node* cur = _pRoot, * parent = nullptr;while (cur){//比我小,往左找if (_kot(data) < _kot(cur->_data)){parent = cur;cur = cur->_pLeft;}//比我大,往右找else if (_kot(data) > _kot(cur->_data)){parent = cur;cur = cur->_pRight;}//有重复元素,插入失败else{return make_pair(iterator(cur), false);}}//找到空位置,开始插入cur = new Node(data);Node* newnode = cur;//连接父亲和孩子if (_kot(cur->_data) < _kot(parent->_data)){parent->_pLeft = cur;}else{parent->_pRight = cur;}cur->_pParent = parent;//父亲是黑色,插入成功if (parent->_color == BLACK){return make_pair(iterator(newnode), true);}//父亲是红色,需要调整//且此时爷爷一定是黑色//根据叔叔的颜色来调整while (parent && parent->_color == RED){Node* grandParent = parent->_pParent;//爸爸是爷爷的左孩子if (parent == grandParent->_pLeft){Node* uncle = grandParent->_pRight;//根据叔叔的颜色来调整//1.叔叔存在且为红if (uncle && uncle->_color == RED){//修改爸爸,叔叔,爷爷的颜色uncle->_color = parent->_color = BLACK;grandParent->_color = RED;//此时视爷爷为新插入的红色节点继续向上影响cur = grandParent;parent = cur->_pParent;}//2.叔叔不存在或者叔叔是黑else{//1.我是爸爸的左孩子if (parent->_pLeft == cur){//对爷爷进行一次右旋RotateR(grandParent);//把爷爷改成红色,爸爸改成黑色grandParent->_color = RED;parent->_color = BLACK;//此时爸爸是黑色,无需break,当然break也可以,因此爸爸是黑色,下次循环就不会进入了}//2.我是爸爸的右孩子else{//1.对爸爸进行左旋RotateL(parent);//2.对爷爷右旋RotateR(grandParent);//3.孩子改成黑色,爷爷改成红色cur->_color = BLACK;grandParent->_color = RED;//4.一定要break,如果不break的话,因为爸爸是红色,所以循环会继续,此时就乱套了break;}}}//爸爸是爷爷的右孩子else{Node* uncle = grandParent->_pLeft;//1.叔叔存在且为红if (uncle && uncle->_color == RED){uncle->_color = parent->_color = BLACK;grandParent->_color = RED;cur = grandParent;parent = cur->_pParent;}//2.叔叔不存在或者叔叔为黑else{//1.我是爸爸的右孩子if (parent->_pRight == cur){//对爷爷左旋RotateL(grandParent);//爷爷改成红色,爸爸改成黑色grandParent->_color = RED;parent->_color = BLACK;//此时爸爸是黑色,无需break,当然break也可以,因此爸爸是黑色,下次循环就不会进入了}//2.我是爸爸的左孩子else{//1.对爸爸右旋RotateR(parent);//2.对爷爷左旋RotateL(grandParent);//3.把孩子改成黑色,爷爷改成红色cur->_color = BLACK;grandParent->_color = RED;//4.一定要break,如果不break的话,因为爸爸是红色,所以循环会继续,此时就乱套了break;}}}}_pRoot->_color = BLACK;return make_pair(iterator(newnode), true);}// 检测红黑树中是否存在关键字为key的节点,存在返回该节点的地址,否则返回nullptrNode* Find(const K& key){Node* cur = _pRoot;while (cur){if (cur->_data.first > key){cur = cur->_pLeft;}else if (cur->_data.second < key){cur = cur->_pRight;}else{return cur;}}return nullptr;}// 检测红黑树是否为有效的红黑树,注意:其内部主要依靠_IsValidRBTRee函数检测bool IsValidRBTRee(){//1.空树是红黑树if (_pRoot == nullptr){return true;}//2.根节点不能为红色if (_pRoot->_color == RED){return false;}//3.为了验证性质: 红黑树的任意一条路径上的黑色节点个数相同 找参考值size_t ReferenceCount = 0;Node* cur = _pRoot;while (cur){if (cur->_color == BLACK){ReferenceCount++;}cur = cur->_pLeft;}return _IsValidRBTRee(_pRoot, 0, ReferenceCount);}void InOrder(){_InOrder(_pRoot);}private:bool _IsValidRBTRee(Node* pRoot, size_t blackCount, size_t& ReferenceCount){if (pRoot == nullptr){if (blackCount != ReferenceCount){cout << "存在黑色节点数量不相等的路径" << endl;return false;}return true;}//验证性质: 红黑树中不能存在连续的红色节点//如果一个节点是红色,该节点一定不是根节点,因此该节点一定有父亲//只需要保证红色节点的父亲不是红色节点即可if (pRoot->_color == RED){if (pRoot->_pParent->_color == RED){cout << "存在连续的红色节点" << endl;return false;}}else{blackCount++;}return _IsValidRBTRee(pRoot->_pLeft, blackCount, ReferenceCount) && _IsValidRBTRee(pRoot->_pRight, blackCount, ReferenceCount);}// 右单旋void RotateR(Node* pParent){Node* subL = pParent->_pLeft;Node* subLR = subL->_pRight;Node* grandParent = pParent->_pParent;subL->_pRight = pParent;pParent->_pParent = subL;pParent->_pLeft = subLR;if (subLR)subLR->_pParent = pParent;if (grandParent == nullptr){_pRoot = subL;_pRoot->_pParent = nullptr;}else{if (pParent == grandParent->_pLeft){grandParent->_pLeft = subL;}else{grandParent->_pRight = subL;}subL->_pParent = grandParent;}}// 左单旋void RotateL(Node* pParent){Node* subR = pParent->_pRight;Node* subRL = subR->_pLeft;Node* grandParent = pParent->_pParent;pParent->_pParent = subR;subR->_pLeft = pParent;pParent->_pRight = subRL;if (subRL)subRL->_pParent = pParent;//说明此时pParent是_pRootif (grandParent == nullptr){_pRoot = subR;_pRoot->_pParent = nullptr;}//说明此时pParent所在的树是一颗子树,需要跟父亲链接else{if (pParent == grandParent->_pLeft){grandParent->_pLeft = subR;}else{grandParent->_pRight = subR;}subR->_pParent = grandParent;}}void _InOrder(Node* root){if (root == nullptr) return;_InOrder(root->_pLeft);cout << root->_data.first << " " << root->_data.second << " ";_InOrder(root->_pRight);}private:Node* _pRoot = nullptr;KeyofT _kot;};
}
测试代码:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <vector>
#include "MySet.h"
#include "MyMap.h"
namespace wzs
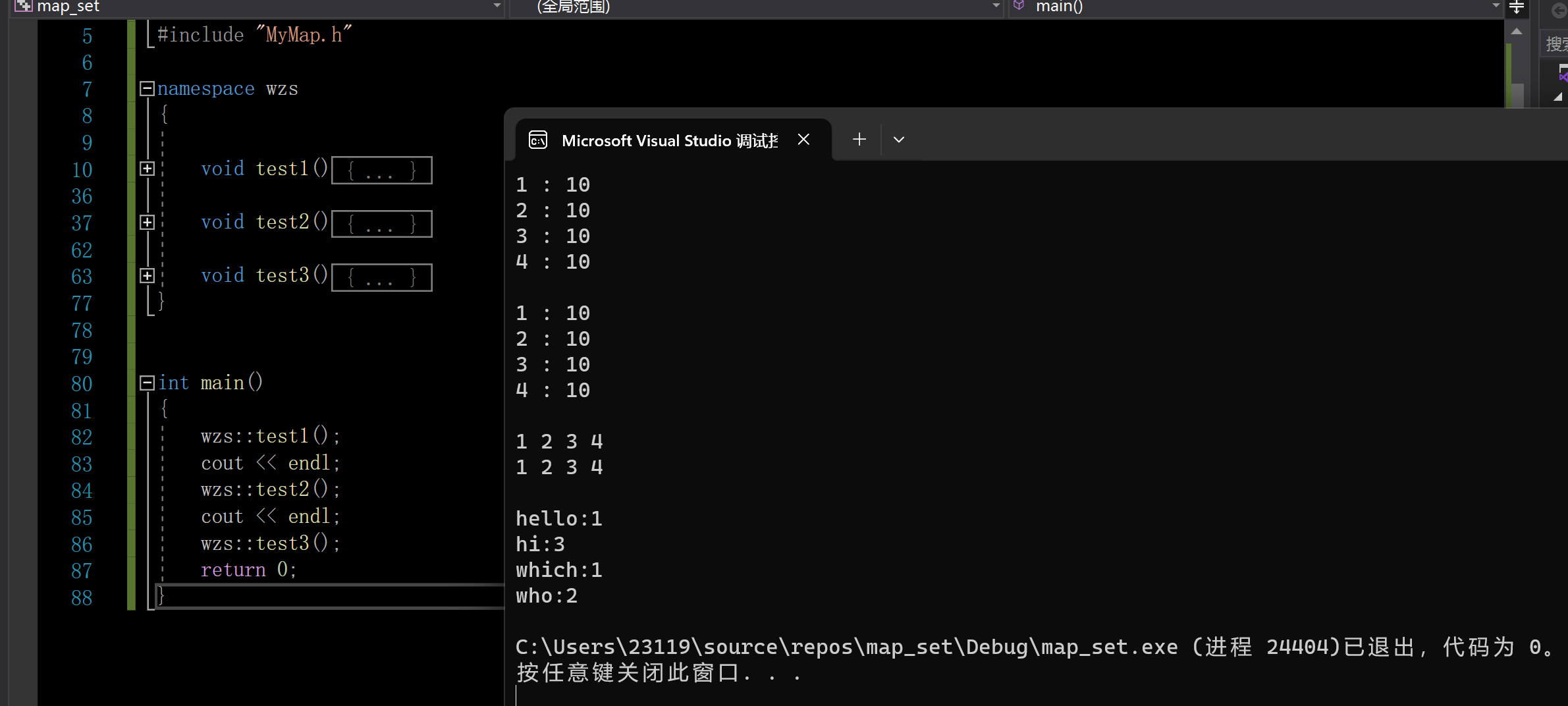
{void test1(){map<int, int> m;m.insert(make_pair(1, 1));m.insert(make_pair(2, 1));m.insert(make_pair(3, 1323));m.insert(make_pair(4, 111));m.insert(make_pair(3, 12));m.insert(make_pair(1, 1));map<int, int>::iterator it = m.begin();while(it != m.end()){it->second = 10;cout << it->first << " : " << it->second << endl;++it;}cout << endl;map<int, int>::const_iterator cit = m.begin();while (cit != m.end()){//it->first = 10;//cit->second = 10;cout << cit->first << " : " << cit->second << endl;++cit;}}void test2(){set<int> s;s.insert(1);s.insert(2);s.insert(3);s.insert(4);set<int>::iterator it = s.begin();while (it != s.end()){//*it += 1;cout << *it << " ";++it;}cout << endl;set<int>::const_iterator cit = s.begin();while (cit != s.end()){//*cit += 1;cout << *cit << " ";++cit;}cout << endl;}void test3(){//统计次数map<string, int> countMap;vector<string> dict = { "hello","hi","who","hi","hi","who","which" };for (auto& e : dict){countMap[e]++;}for (auto& e : countMap){cout << e.first << ":" << e.second << endl;}}
}
int main()
{wzs::test1();cout << endl;wzs::test2();cout << endl;wzs::test3();return 0;
}
以上就是C++ 改造红黑树,封装map和set的全部内容,希望能对大家有所帮助!