前言🍭
❤️❤️❤️SSM专栏更新中,各位大佬觉得写得不错,支持一下,感谢了!❤️❤️❤️
Spring + Spring MVC + MyBatis_冷兮雪的博客-CSDN博客
前面我们讲解了MyBatis增删改查基本操作,下面我们来深入了解MyBatis其中不同和需要注意的地方。
一、查询操作🍭
1、单表查询🍉
下面我们来实现⼀下根据用户 id 查询用户信息的功能
UserController 实现代码如下:
//url 路径名直接全部小写即可@RequestMapping("/getuserbyid")public Userinfo geUserById(Integer id){if (id==null)return null;return userService.getUserById(id);}UserMapper 实现代码如下:
/*** 根据用户id查询用户信息* @param id* @return*/Userinfo getUserById(@Param("id") Integer id);UserMapper.xml 实现代码如下:
<select id="getUserById" resultType="com.example.ssmdemo1.entity.Userinfo">select * from userinfo where id=${id}
</select>Ⅰ、参数占位符 #{} 和 ${}🍓
-
#{}:预编译处理。
-
${}:字符直接替换。
预编译处理是指:MyBatis 在处理#{}时,会将 SQL 中的 #{} 替换为?号,使用 PreparedStatement 的 set 方法来赋值。直接替换:是MyBatis 在预处理 ${} 时,就会把 ${} 替换成变量的值。
上面代码我们使用的是${},去传递Integer(整数)类型的参数时,是没有问题的,但如果传递的是String类型的话,程序就会报错。
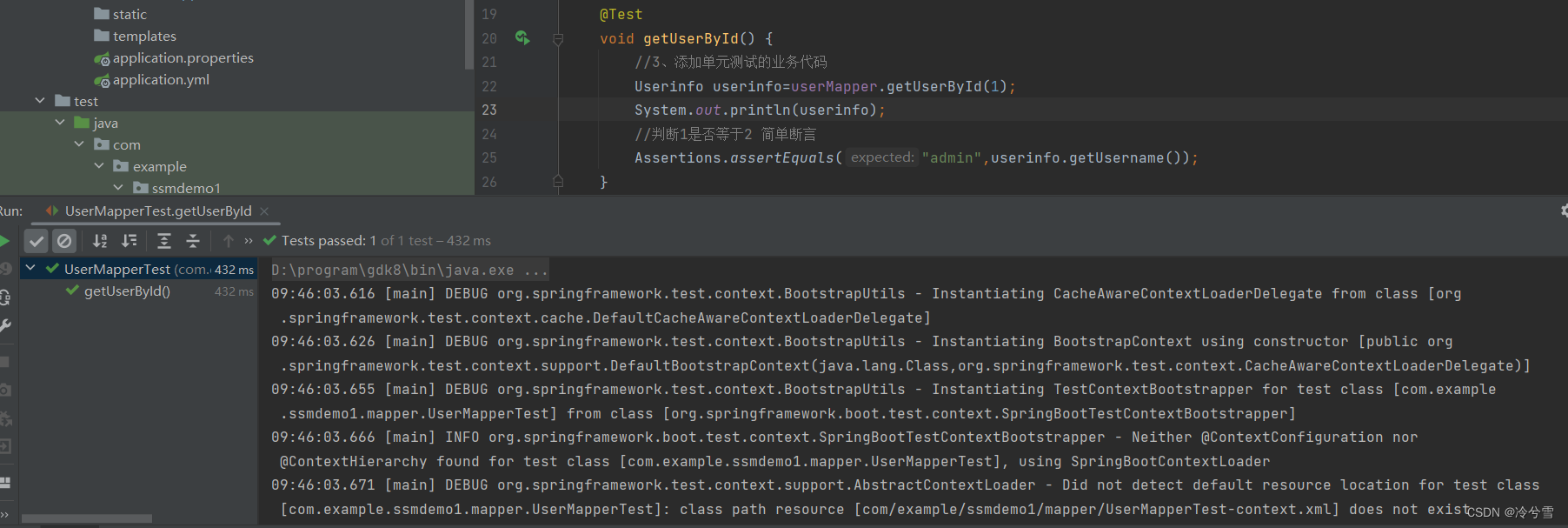
下面我们通过 根据用户名查询用户(getUserByName)来看看
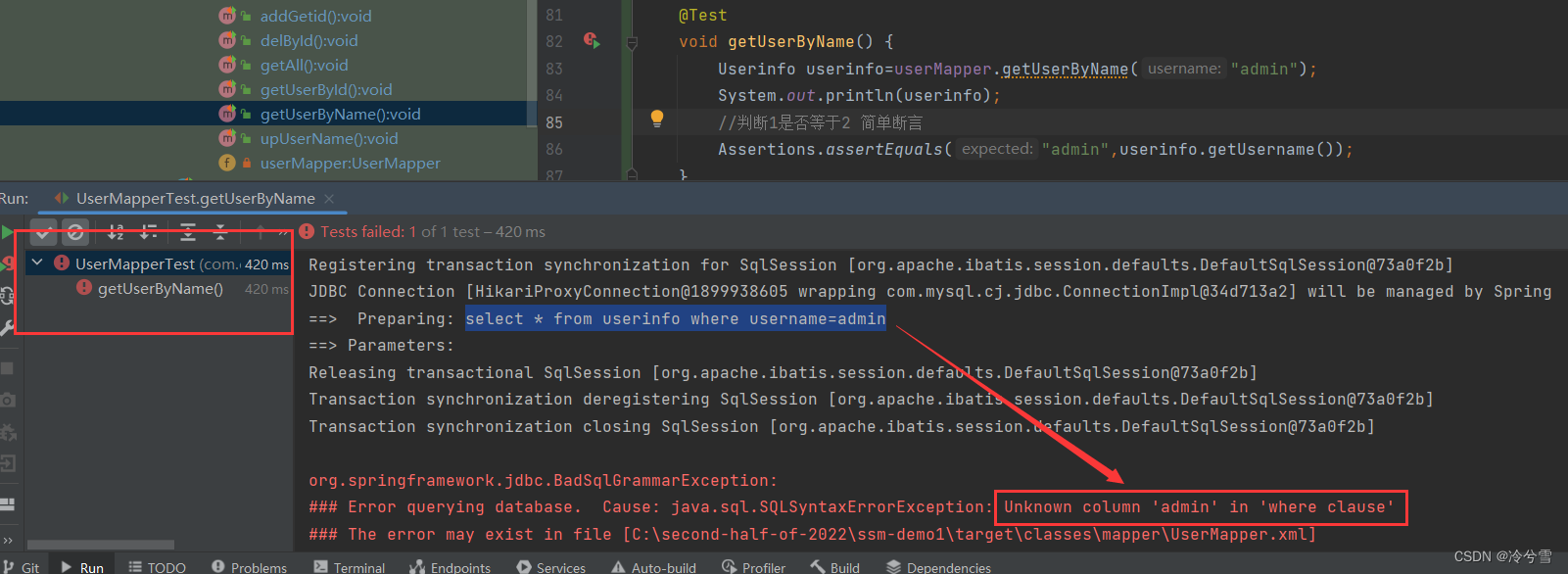
这就直接报错了,说是没有admin这个用户,这是因为${}是直接替换值(不会管你是什么类型,都直接替换),而SQL语句中字符串需要使用单引号,这就会查询不到,报错。
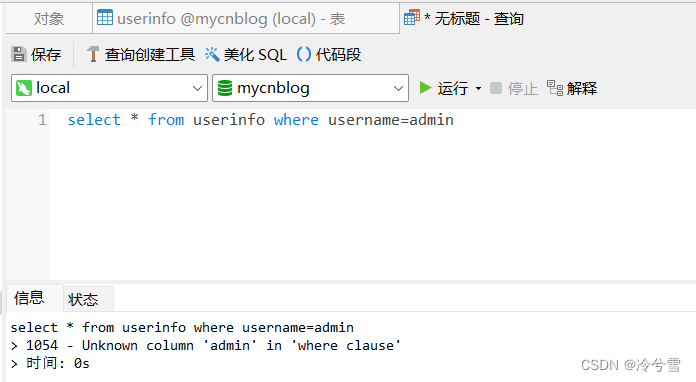
正确SQL:
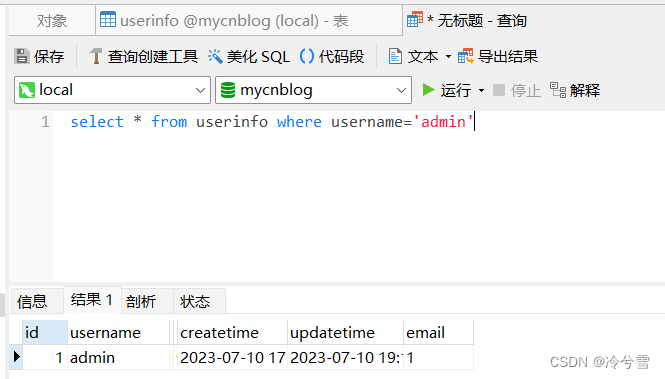
两者区别总结:
1、#{}:安全参数占位符
#{}是MyBatis的预编译语句中的参数占位符,用于传递参数值。它会自动进行参数值的类型转换和防止SQL注入攻击。- 在使用
#{}时,MyBatis会将参数值通过JDBC的PreparedStatement接口进行预编译,参数值会被当做字符串类型处理,然后由JDBC驱动来负责将其转换成对应的数据库类型,这样可以避免SQL注入问题。 - 例子:
SELECT * FROM users WHERE id = #{userId}
2、${}:字符串替换占位符
${}是字符串替换占位符,用于直接将参数的值替换到SQL语句中。在使用${}时,参数值会被直接替换进SQL语句中,不会进行预编译或类型转换。- 由于
${}直接替换参数值到SQL语句中,可能存在SQL注入的风险,因此不建议在动态SQL中使用${}来传递用户输入的参数。 - 例子:
SELECT * FROM users WHERE id = ${userId}
那这为什么还有${}去传递参数呢?全部使用#{}不是更好?
Ⅱ、${}优点🍓
在进行排序时(需要传递关键字时)需要使用到${},而 #{sort} 就不能实现排序查询了,因为使用 #{sort} 查询时, 如果传递的值为 String 则会加单引号,就会导致 sql 错误。
UserMapper接口:
//根据id查询用户 并且进行排序List<Userinfo> getAllByOrder(@Param("order") String order);UserMapper.xml:
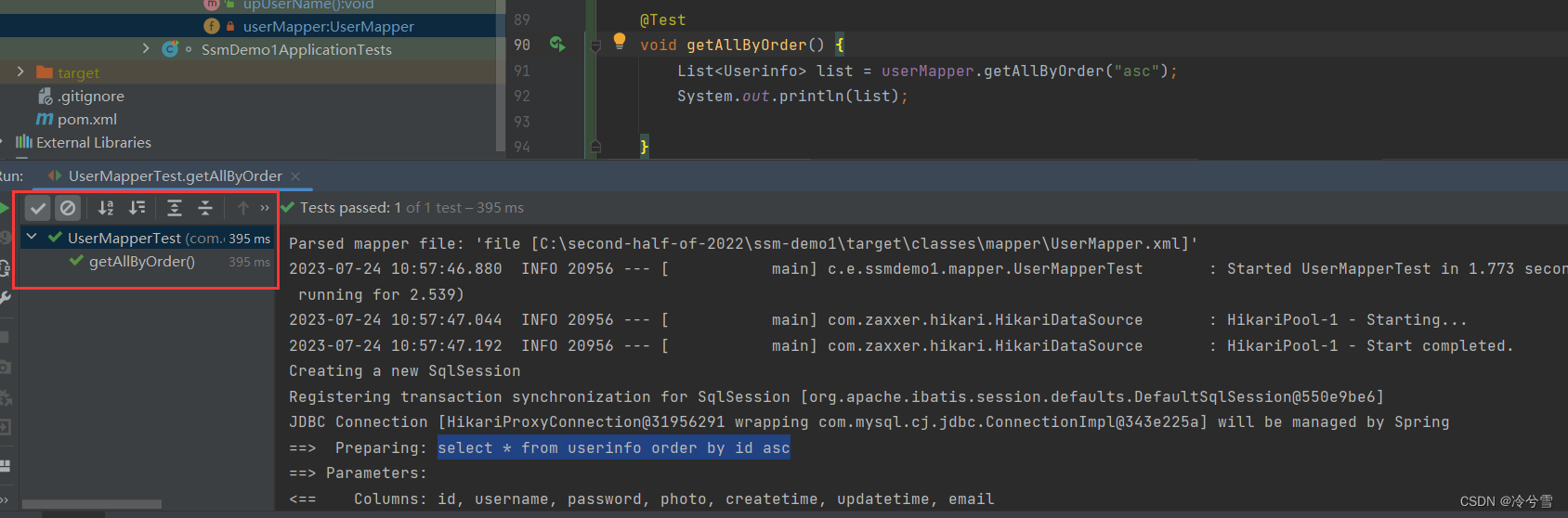
<select id="getAllByOrder" resultType="com.example.ssmdemo1.entity.Userinfo">select * from userinfo order by id ${order}
</select>@Testvoid getAllByOrder() {List<Userinfo> list = userMapper.getAllByOrder("asc");System.out.println(list);}单元测试成功:
Ⅲ、SQL 注入问题 🍓
UserMapper接口:
Userinfo login(@Param("username")String username,@Param("password")String password);UserMapper.xml:
<select id="login" resultType="com.example.ssmdemo1.entity.Userinfo">select *from userinfo where usernaem='${username}' and password='${password}'
</select>因为${}是直接引用,所以我们加上了单引号。 这样就和使用#{}是一样的了
单元测试:
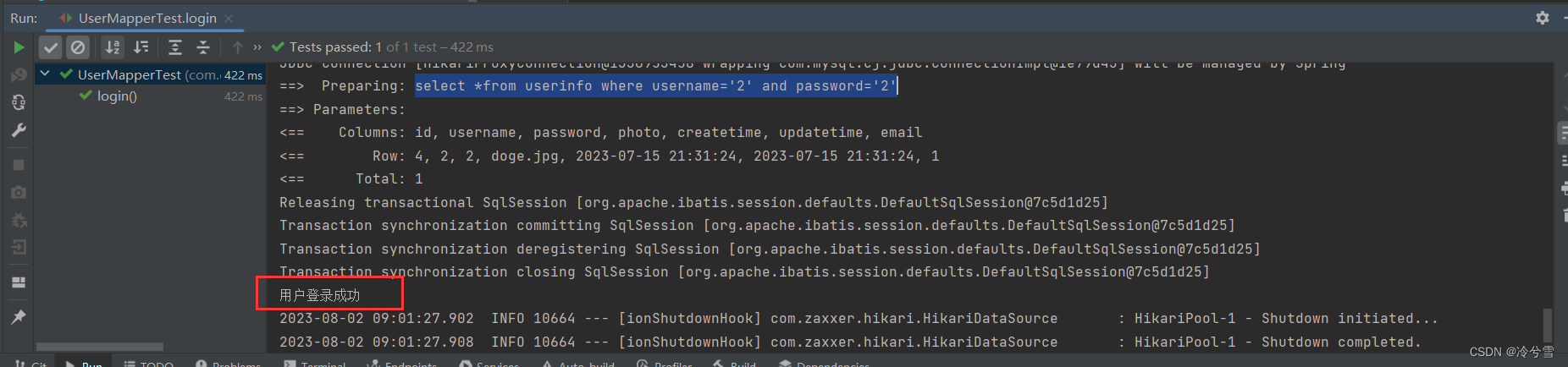
@Testvoid login() {String username="2";String password="2";Userinfo userinfo=userMapper.login(username,password);System.out.println("用户登录"+(userinfo==null?"失败":"成功"));}可以看到此时用户是登录成功的:
但是这样写有SQL注入的风险,我们修改代码如下,然后运行代码
@Testvoid login() {String username="2";String password="'or 1 ='1";Userinfo userinfo=userMapper.login(username,password);System.out.println("用户登录"+(userinfo==null?"失败":"成功"));}单元测试:
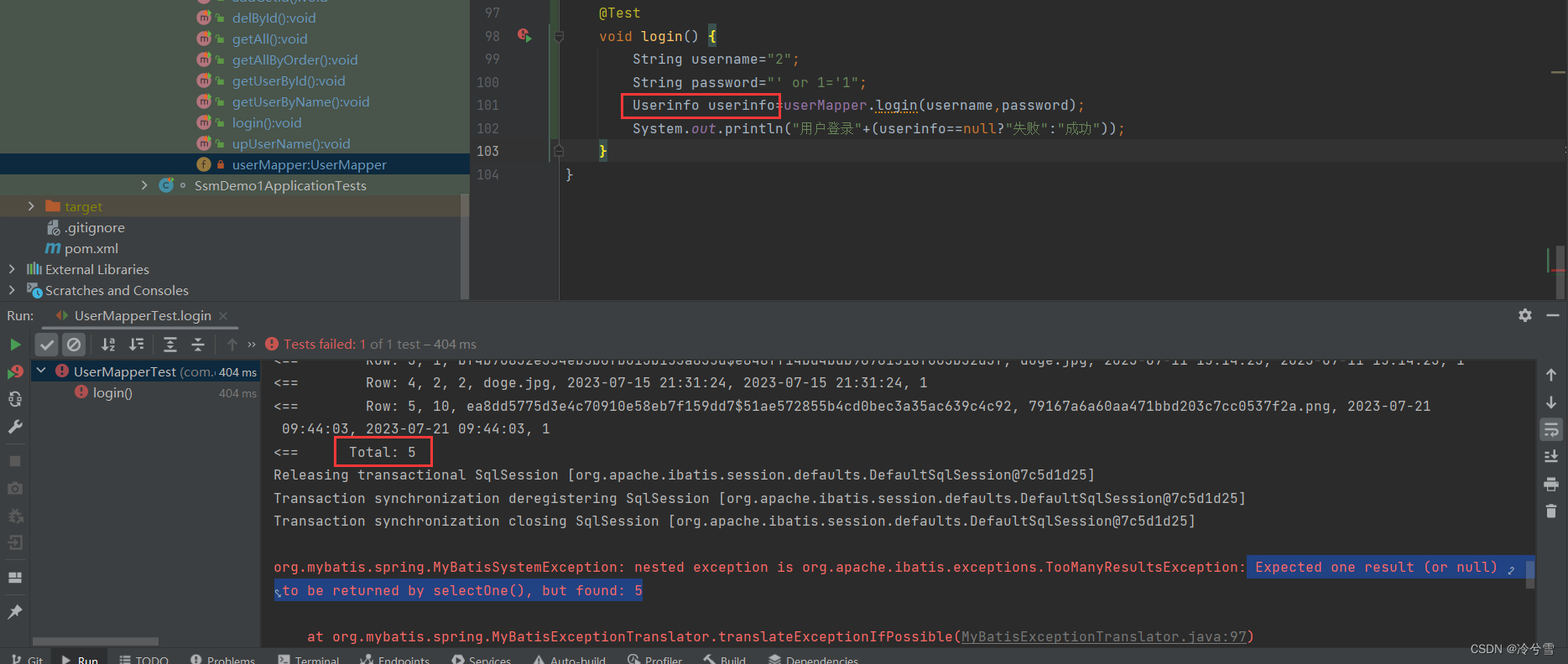
可以看到上面单元测试失败了,但仔细看,是因为返回了5个Userinfo对象,但我只需要接收一个
所以报错了,如果接受的是List<Userinfo>就不会报错了
UserMapper接口:
List<Userinfo> login(@Param("username")String username, @Param("password")String password);单元测试:
@Testvoid login() {String username="2";String password="' or 1='1";List<Userinfo> userinfo=userMapper.login(username,password);System.out.println("用户登录"+(userinfo==null?"失败":"成功"));}单元测试成功:
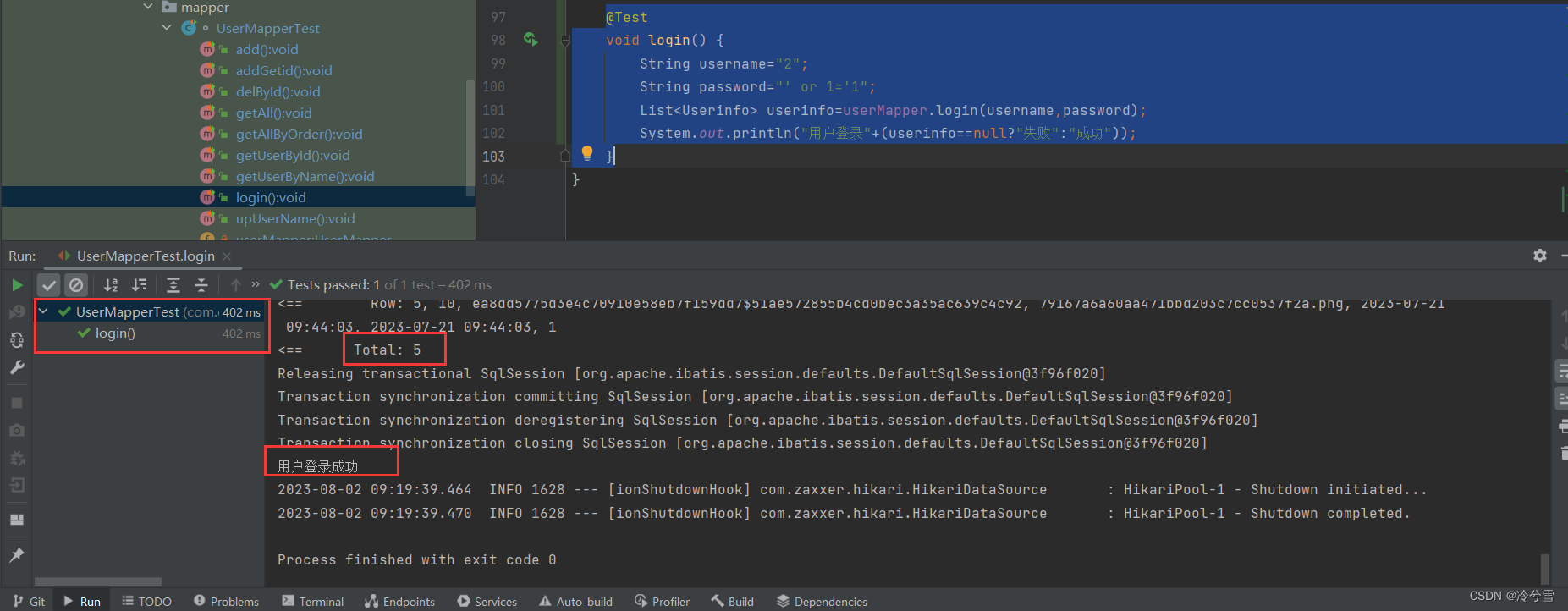
可以看到这是非常可怕的,居然把我所有用户信息返回了(数据库中一共有五个用户),也就是说,你想使用哪个用户登录就可以使用哪个用户登录。
如果使用#{},可能存在这个问题吗?
<select id="login" resultType="com.example.ssmdemo1.entity.Userinfo">select *from userinfo where username=#{username} and password=#{password}
</select>单元测试失败:
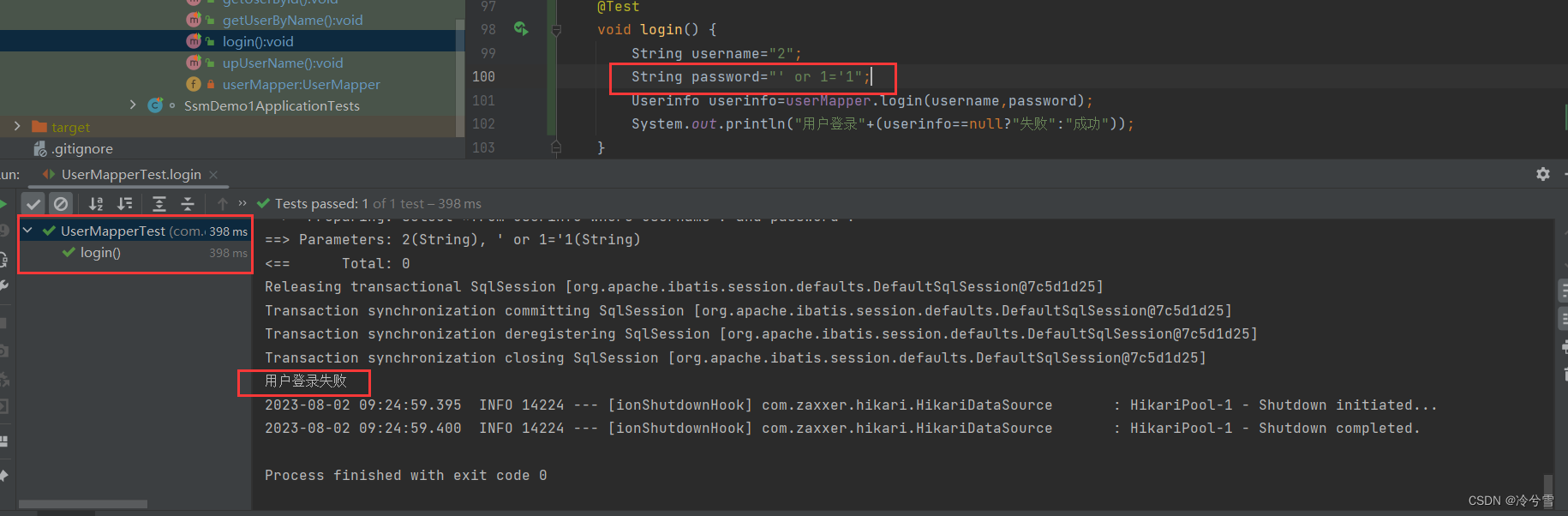
结论:用于查询的字段,尽量使用 #{} 预查询的方式,而需要传递关键字时,使用${}
Ⅳ、like查询🍓
在使用like查询时,使用#{}会报错,下面我们来看看是怎么回事。
UserMapper接口:
List<Userinfo> getListByName(@Param("username")String username);UserMapper.xml:
<select id="getListByName" resultType="com.example.ssmdemo1.entity.Userinfo">select * from userinfo where username like '%#{username}%'
</select>单元测试:
@Testvoid getListByName() {String username="n";List<Userinfo> list=userMapper.getListByName(username);System.out.println("list:"+list);}运行报错:
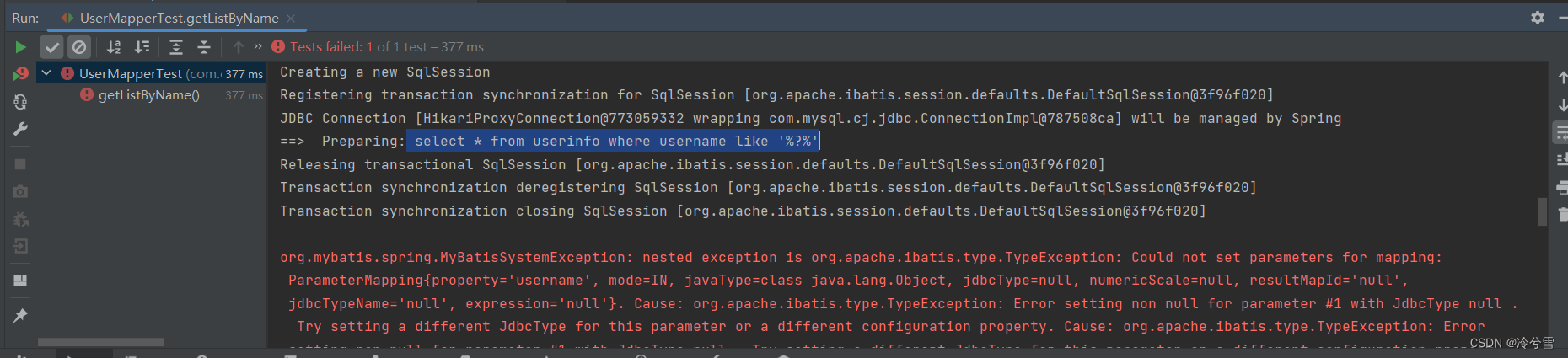
这是因为使用#{}会当作字符串进行替换,就变成下面这样了
select * from userinfo where username like '%'n'%'我们替换${}试试:
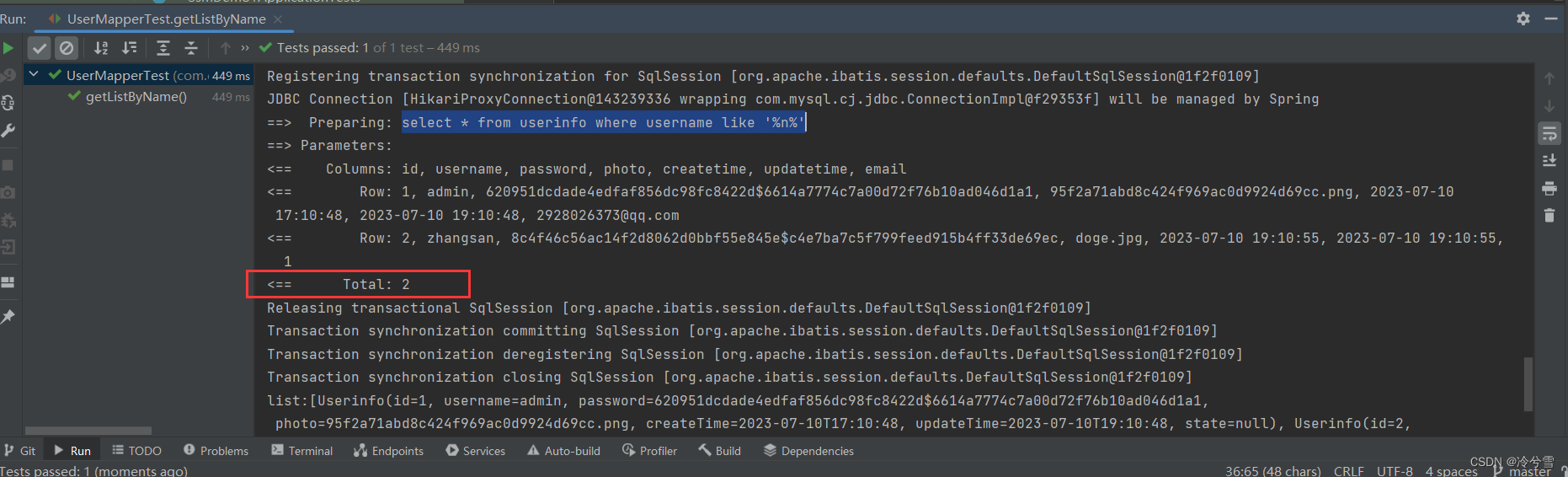
但是前面说了使用${}有SQL注入的风险,所有这是不能直接使用 ${},可以考虑使用 mysql 的内置函数 concat() 来处理,实现代码如下:
<select id="findUserByName3" resultType="com.example.demo.model.User">select * from userinfo where username like concat('%',#{username},'%')
</select>单元测试成功:

在使用like查询时应该搭配concat()函数使用。
2、多表查询🍉
如果是增、删、改返回搜影响的行数,那么在 UserMapper.xml 中是可以不设置返回的类型的,如:
<insert id="add">insert into userinfo(username,password) values(#{username},#{password})</insert><delete id="delById">delete from userinfo where id=#{id}</delete><update id="upUserName">update userinfo set username=#{username} where id=#{id}</update>然而即使是最简单查询用户的名称也要设置返回的类型,否则会出现如下错误:
查询不设置返回类型的错误示例演示:
controller 代码:
@RequestMapping("/getname")
public String getNameById(Integer id) {return userService.getNameById(id);
}<select id="getNameById">select username from userinfo where id=#{id}
</select>访问接口执行结果如下:
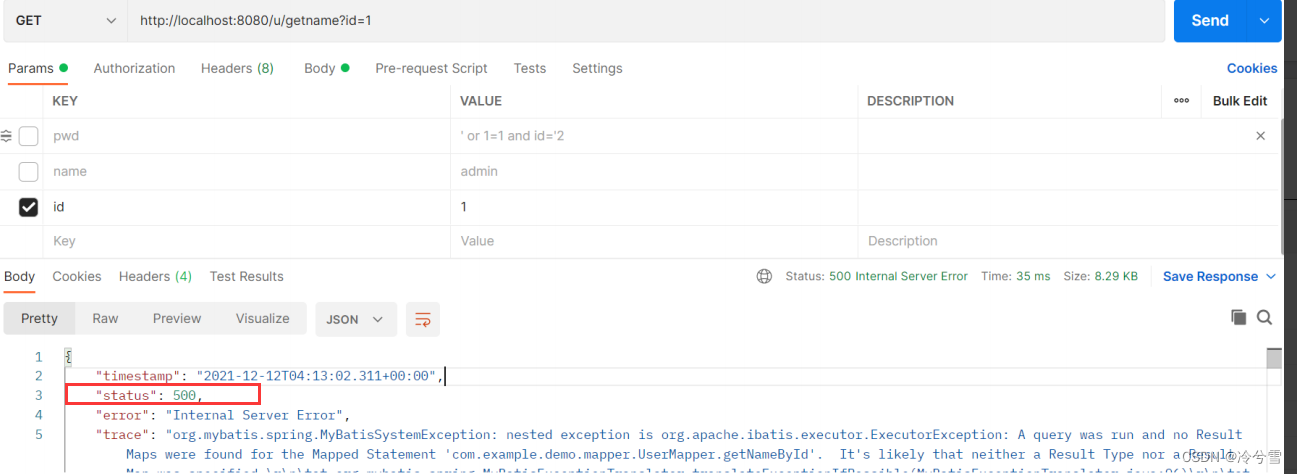
显示运行了⼀个查询但没有找到结果映射,也就是说对于 <select> 查询标签来说至少需要两个属性:
-
id 属性:用于标识实现接口中的那个方法;
-
结果映射属性:结果映射有两种实现标签:<resultMap> 和 <resultType>。
Ⅰ、返回类型:resultType 🍓
绝大数查询场景可以使⽤ resultType 进行返回,如下代码所示:
<select id="getNameById" resultType="java.lang.String">select username from userinfo where id=#{id}
</select>
<select id="getUserByName" resultType="com.example.ssmdemo1.entity.Userinfo">select * from userinfo where username=#{username}
</select>它的优点是使用方便,直接定义到某个实体类即可。
Ⅱ、返回字典映射:resultMap 🍓
-
字段名称和程序中的属性名不同的情况,可使用 resultMap 配置映射;
-
⼀对⼀和⼀对多关系可以使用 resultMap 映射并查询数据。
当程序中的属性值与数据库中的字段名不一样时🍒
@Data
public class Userinfo {private Integer id;private String name;//数据库名为:usernameprivate String password;private String photo;private LocalDateTime createTime;private LocalDateTime updateTime;private Integer state;
}
我们去单元测试,进行用户的查询:
@Testvoid getUserByName() {Userinfo userinfo=userMapper.getUserByName("admin");System.out.println(userinfo);}打印出来就发现,name没有被赋值,为null,这就是因为字段名与属性值不一样的结果。

这个时候就可以使用 resultMap 了,resultMap 的使用如下:
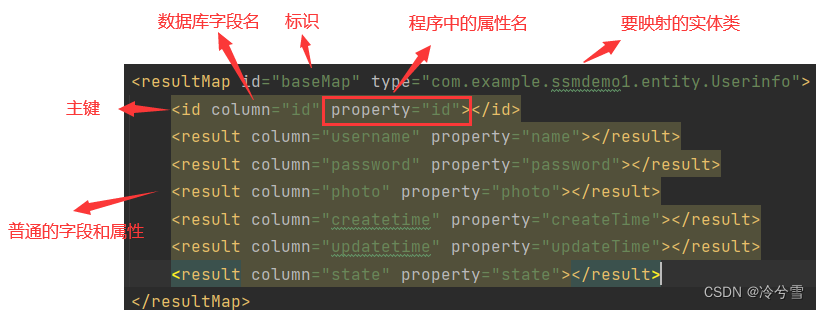
UserMapper.xml:
<resultMap id="baseMap" type="com.example.demo.entity.Userinfo"><id column="id" property="id"></id><result column="username" property="name"></result><result column="password" property="password"></result><result column="photo" property="photo"></result><result column="createtime" property="createtime"></result><result column="updatetime" property="updatetime"></result><result column="state" property="state"></result>
</resultMap>
<select id="getUserByName" resultMap="baseMap">select * from userinfo where username=#{username}
</select>这样查询的结果就有值了,如下图所示:
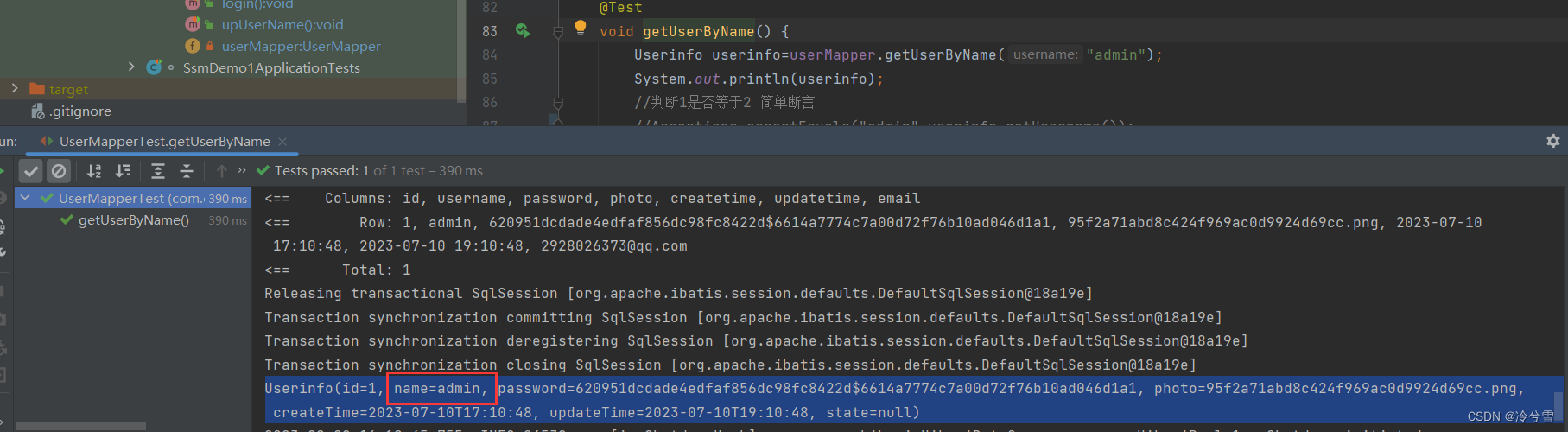
或者使用as关键字(数据库重命名)🍒
如果你一定需要使用resultType,也是可以实现的:
<select id="getUserByName" resultType="com.example.ssmdemo1.entity.Userinfo">select id,username as name,password,photo,createtime,updatetime from userinfo where username=#{username}</select>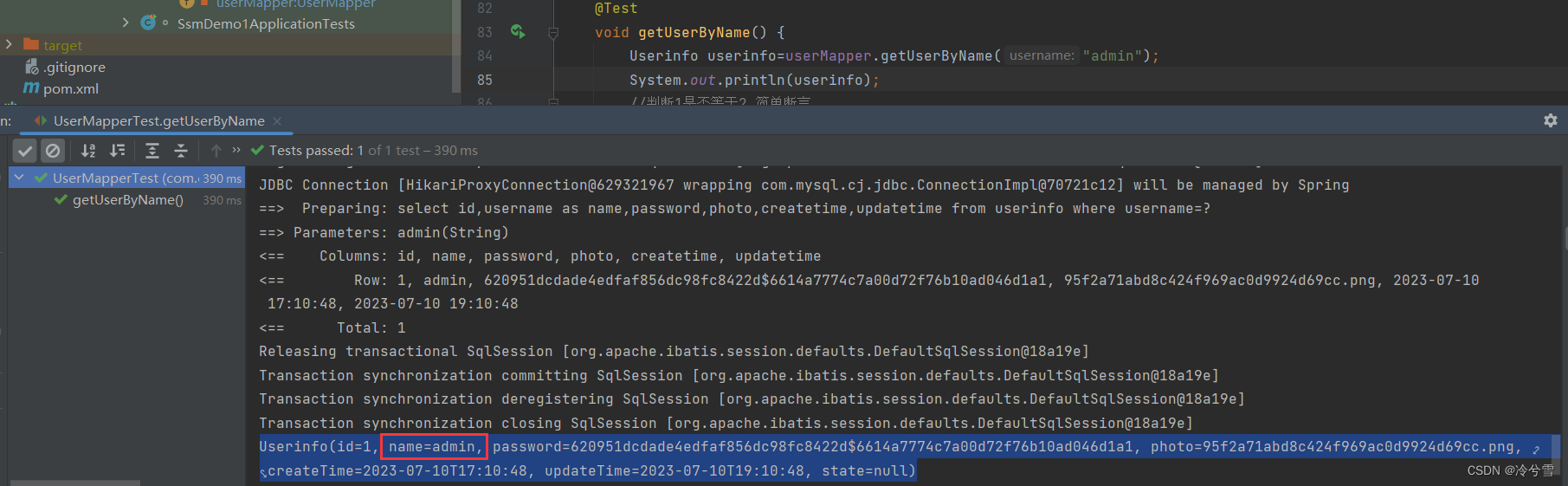
Ⅲ、多表查询🍓
在多表查询时,如果使用 resultType 标签,在⼀个类中包含了另⼀个对象是查询不出来被包含的对象的,比如以下实体类:
@Data
public class ArticleInfo {private Integer id;private String title;private String content;private LocalDateTime createtime;private LocalDateTime updatetime;private Integer rcount;// 包含了 userinfo 对象private UserInfo user;
}程序的执行结果如下图所示:

此时我们就需要使用特殊的手段来实现联表查询了。
通过VO对象🍒
ArticleInfo
package com.example.ssmdemo1.entity;import lombok.Data;import java.time.LocalDateTime;@Data
public class ArticleInfo {private Integer id;private String title;private String content;private LocalDateTime createtime;private LocalDateTime updatetime;private int uid;private Integer rcount;private Integer state;
}VO对象
package com.example.ssmdemo1.entity.vo;import com.example.ssmdemo1.entity.ArticleInfo;public class ArticleInfoVO extends ArticleInfo {private String username;@Overridepublic String toString() {return "ArticleinfoVO{" +"username='" + username + '\'' +"} " + super.toString();}
}ArticleMapper.xml
进行多表程序:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.example.ssmdemo1.mapper.ArticleMapper"><select id="getById" resultType="com.example.ssmdemo1.entity.vo.ArticleInfoVO">select a.*,u.username from articleinfo aleft join userinfo u on u.id=a.uidwhere a.id=#{id}</select>
</mapper>
单元测试:
package com.example.ssmdemo1.mapper;import com.example.ssmdemo1.entity.vo.ArticleInfoVO;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.*;
@SpringBootTest
class ArticleMapperTest {@Autowiredprivate ArticleMapper articleMapper;@Testvoid getById() {ArticleInfoVO articleInfoVO=articleMapper.getById(5);System.out.println(articleInfoVO);}
}单元测试成功,查询到了用户id为5的 文章表的文章信息 和 用户表中的用户名:
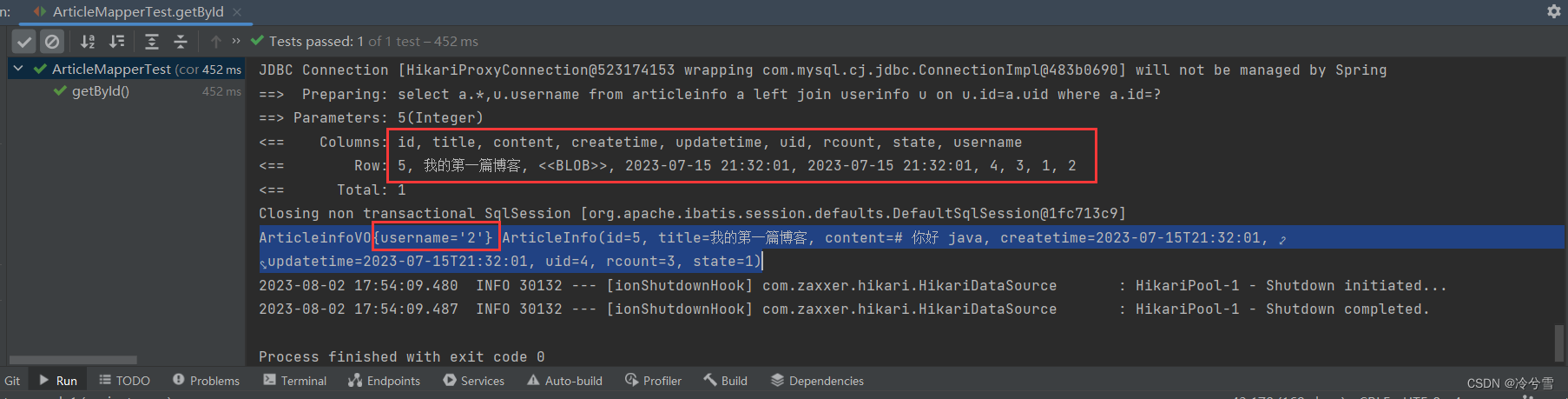
大部分时候多表联查解决方案:
联表查询语句(left join/inner)+xxxVO(新建的实体类)就可以解决