云备份项目
文章目录
- 云备份项目
- 4. 服务端代码设计
- 4.1 服务端工具类实现
- 4.1.1 文件实用工具类设计
- 4.1.2 Json实用工具类设计
- 4.2 服务端配置信息模块实现
- 4.2.1 系统配置信息
- 4.2.2 单例文件配置类设计
- 4.3 服务端数据管理模块实现
- 4.3.1 备份数据类的实现
- 4.3.2 数据管理类的设计
- 4.4 服务端热点管理模块实现
- 4.4.1 热点管理实现思路
- 4.4.2 热点管理类的设计
- 4.5 服务端业务处理模块实现
- 4.5.1 网络通信接口设计
- 4.5.2 业务处理类设计
- <1> upload
- <2> listshow
- <3> download
- **断点续传**
- 4.6 服务端整体模块测试
- 5. 客户端代码设计
- 5.1 客户端文件操作实用类设计
- 5.2 客户端数据管理模块实现
- 5.3 客户端文件备份类设计
- 5.4 客户端服务器功能联调测试
- 6. 项目总结
4. 服务端代码设计
4.1 服务端工具类实现
4.1.1 文件实用工具类设计
不管是客户端还是服务端,文件的传输备份都涉及到文件的读写,包括数据管理信息的持久化也是如此,因此首先设计封装文件操作类,这个类封装完毕之后,则在任意模块中对文件进行操作时都将变的简单化。
文件操作我们使用C++17提供的文件系统更简单:C++17中filesystem手册
此类设计在util.hpp中
#pragma once
#include <string>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include "bundle.h"
#include <experimental/filesystem>
#include <jsoncpp/json/json.h>
#include <memory>namespace fs=std::experimental::filesystem;
namespace yjcloud
{class FileUtil{public:FileUtil(const std::string&filename):_filename(filename){}int64_t file_size() // 获取文件大小{struct stat st;if(stat(_filename.c_str(),&st)<0){std::cout<<"get file size fail"<<std::endl;return -1;}return st.st_size;}time_t last_mtime() // 获取最后一次修改时间{struct stat st;if(stat(_filename.c_str(),&st)<0){std::cout<<"get last modify time fail"<<std::endl;return -1;}return st.st_mtime;}time_t last_atime() // 获取最后一次访问时间{struct stat st;if(stat(_filename.c_str(),&st)<0){std::cout<<"get last modify time fail"<<std::endl;return -1;}return st.st_atime;}std::string file_name() // 获取文件路径中的文件名称 ./abc/a.txt => a.txt{size_t pos=_filename.find_last_of("/");if(pos==std::string::npos)return _filename;return _filename.substr(pos+1);}bool get_pos_len(std::string*body,size_t pos,size_t len) // 获取文件指定位置,指定长度的数据{size_t fsize=this->file_size();if(fsize>len){std::cout<<"get file len is error"<<std::endl;return false;}std::ifstream ifs;ifs.open(_filename,std::ios::binary);if(ifs.is_open()==false){std::cout<<"read open file failed"<<std::endl;return false;}ifs.seekg(pos,std::ios::beg); // 文件跳转到指定位置body->resize(len);ifs.read(&(*body)[0],len);if (ifs.good() == false){std::cout << "read file fail" << std::endl;ifs.close();return false;}ifs.close();return true;}bool get_content(std::string*body) // 获取整个文件内容{return get_pos_len(body,0,file_size());}bool set_content(const std::string&body) // 向文件中写入数据{std::ofstream ofs;ofs.open(_filename, std::ios::binary);if (ofs.is_open() == false){std::cout << "write open file failed" << std::endl;return false;}ofs.write(&body[0], body.size());if (ofs.good() == false){std::cout << "write file fail" << std::endl;ofs.close();return false;}ofs.close();return true;}bool compress(const std::string&packname) // 压缩文件{// 1. 获取源文件数据std::string body;if(this->get_content(&body)==false){std::cout << "compress get file content failed" << std::endl;return false;}// 2. 对数据进行压缩std::string packed=bundle::pack(bundle::LZIP,body);// 3. 将压缩的数据存储到压缩包文件中FileUtil fu(packname);if(fu.set_content(packed)==false){std::cout << "compress write unpacked data failed" << std::endl;return false;}return true;}bool uncompress(const std::string&unpackname) // 解压缩文件{// 1. 将当前压缩包数据读取出来std::string body;if(this->get_content(&body)==false){std::cout << "uncompress get file content failed" << std::endl;return false;}// 2. 对压缩的数据进行解压缩std::string unpacked=bundle::unpack(body);// 3. 将压缩数据写入到新文件FileUtil fu(unpackname);if(fu.set_content(unpacked)==false){std::cout << "uncompress write unpacked data failed" << std::endl;return false;}return true;}bool exists() // 判断文件是否存在{ return fs::exists(_filename);}bool create_directory() // 创建目录{ if(exists())return true;return fs::create_directories(_filename);}bool scan_directory(std::vector<std::string>*array) // 浏览获取目录下所有文件路径名{for(auto&p: fs::directory_iterator(_filename)){// 是目录就跳过if(fs::is_directory(p)==true)continue;// relative_path 带有路径的文件名array->push_back(fs::path(p).relative_path().string());}return true;}private:std::string _filename;};
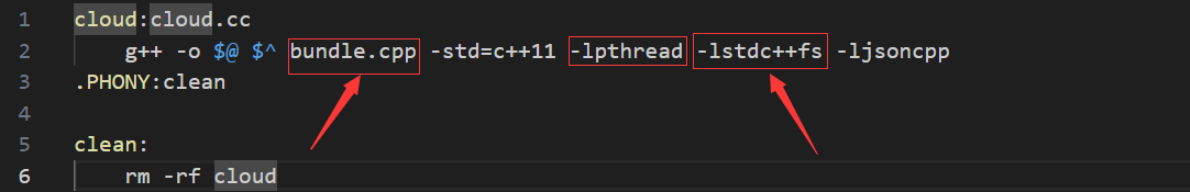
在makefile文件中,我们要链接C++17的文件系统-lstdc++fs,同时压缩解压缩文件时要引入bundle.cpp并链接线程库
几种功能测试:
void FileUtil_test(const std::string&filename)
{// 压缩与解压缩测试std::string packname=filename+".lz";yjcloud::FileUtil file(filename);file.compress(packname);yjcloud::FileUtil nfile(packname);nfile.uncompress("./1.txt");// 目录操作测试yjcloud::FileUtil file(filename);file.create_directory();std::vector<std::string> array;file.scan_directory(&array);for(auto&a:array)std::cout<<a<<std::endl;
}
int main(int argc,char*argv[])
{FileUtil_test(argv[1]);return 0;
}
运行结果:
压缩与解压缩:
目录操作:
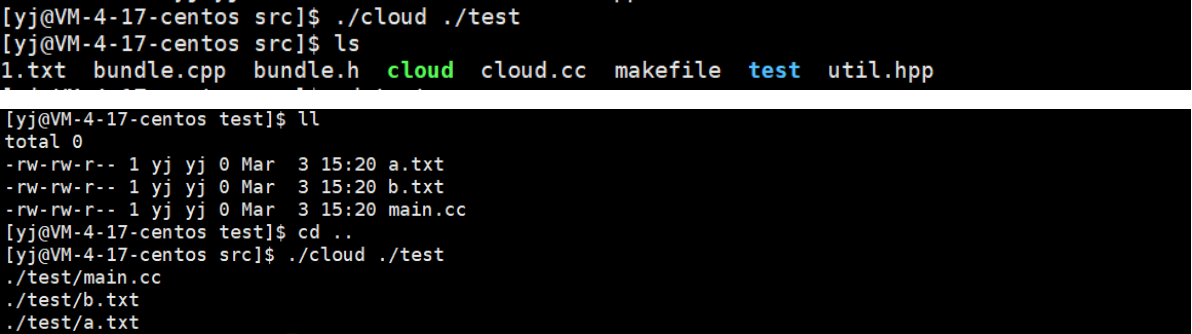
因为链接了bundle库编译速度比较慢,此时将bundle.cpp打包成静态库
g++ -c bundle.cpp -o bundle.o
ar -rc libbundle.a bundle.o
生成libbundle.a的静态库

修改makefile文件
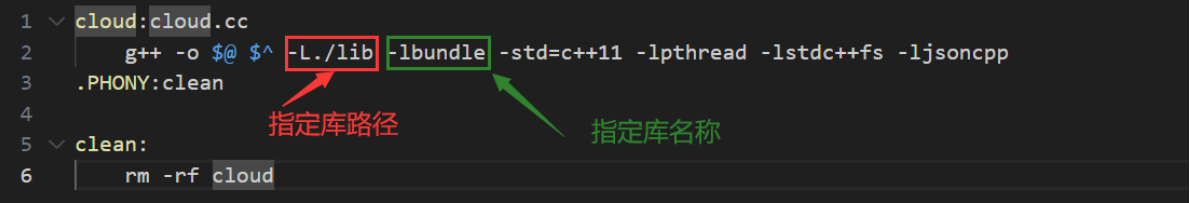
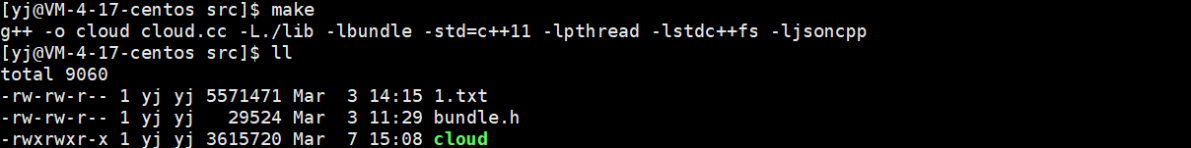
此时编译速度会大大提升
4.1.2 Json实用工具类设计
namespace yjcloud
{class JsonUtil{public:static bool serialize(const Json::Value&val,std::string*str) // 序列化{Json::StreamWriterBuilder swb;std::unique_ptr<Json::StreamWriter> sw(swb.newStreamWriter());std::stringstream ss;if(sw->write(val,&ss)!=0){std::cout << "json write failed!" <<std::endl;return false;}*str=ss.str();return true;}static bool unserialize(std::string&str,Json::Value*val) // 反序列化{Json::CharReaderBuilder cb;std::unique_ptr<Json::CharReader> cr(cb.newCharReader());std::string error;bool ret = cr->parse(str.c_str(), str.c_str() + str.size(), val, &error);if (ret == false){std::cout << "parse error: " << error << std::endl;return false;}return true;}};
}
4.2 服务端配置信息模块实现
服务端采用读取配置文件的方式来获取程序的运行关键信息,使代码运行更加灵活。
关键信息:
-
热点判断时间
- 热点管理:多长时间没有被访问的文件算是非热点文件
-
文件下载的URL前缀路径
-
用于表示客户端请求是一个下载请求
-
比如:当用户发来一个备份列表查看请求
/listshow,我们如何判断这个不是listshow的文件下载请求;可以专门创建一个目录/download,下存放要下载的文件,如/download/listshow
-
-
压缩包后缀名
- 规定的压缩包命名规则,就是在文件原名称之后加上后缀。如
".lz"
- 规定的压缩包命名规则,就是在文件原名称之后加上后缀。如
-
上传文件存放路径
- 决定了文件上传之后实际存储在服务器的哪里
-
压缩包存放路径
- 决定非热点文件压缩后存放的路径
-
服务端备份信息存放文件
- 服务端记录的备份文件信息持久化存储
-
服务器的监听IP地址
- 当程序运行在其他主机上时,不需要直接去修改程序
-
服务器的监听端口
4.2.1 系统配置信息
{"hot_time": 30,"server_port": 8080,"server_ip": "111.231.169.213", "download_prefix": "/download/", "packfile_suffix": ".lz", "pack_dir": "./packdir/", "back_dir": "./backdir/", "backup_file": "./cloud.dat"
}
4.2.2 单例文件配置类设计
使用单例模式管理系统配置信息,能够让配置信息的管理控制更加统一灵活
#pragma once
#include "util.hpp"
#include <mutex>#define CONFIG_FILE "./cloud.conf"namespace yjcloud
{class Config{public:static Config *getinstance(){if (_ins == nullptr){_mtx.lock();if (_ins == nullptr)_ins = new Config;_mtx.unlock();}return _ins;}public:int get_hot_time(){return _hot_time;}std::string get_server_ip(){return _server_ip;}int get_server_port(){return _server_port;}std::string get_dload_pre(){return _download_prefix;}std::string get_pfile_suf(){return _packfile_suffix;}std::string get_pack_dir(){return _pack_dir;}std::string get_back_dir(){return _back_dir;}std::string get_backup_file(){return _backup_file;}private:static std::mutex _mtx;static Config *_ins;Config(){read_config_file();}private:int _hot_time;std::string _server_ip;uint16_t _server_port;std::string _download_prefix; // 文件下载URL前缀路径,如/download/std::string _packfile_suffix; // 压缩包后缀名称,如.lzstd::string _pack_dir; // 压缩文件存放路径std::string _back_dir; // 上传文件存放路径std::string _backup_file; // 服务端备份信息存放文件-->配置文件如 ./cloud.datbool read_config_file(){// 1. 读取文件到字符串body中FileUtil fu(CONFIG_FILE);std::string body;if (fu.get_content(&body) == false){std::cout << "load config file failed" << std::endl;return false;}// 2. 用Json来进行反序列化Json::Value val;if (JsonUtil::unserialize(body, &val) == false){std::cout << "parse config file failed" << std::endl;return false;}_hot_time = val["hot_time"].asInt();_server_port = val["server_port"].asInt();_server_ip = val["server_ip"].asString();_download_prefix = val["download_prefix"].asString();_packfile_suffix = val["packfile_suffix"].asString();_pack_dir = val["pack_dir"].asString();_back_dir = val["back_dir"].asString();_backup_file = val["backup_file"].asString();return true;}};Config *Config::_ins = nullptr;std::mutex Config::_mtx;
}
代码测试:
void Config_test()
{yjcloud::Config*cof=yjcloud::Config::getinstance();std::cout<<cof->get_hot_time()<<std::endl;std::cout<<cof->get_server_port()<<std::endl;std::cout<<cof->get_server_ip()<<std::endl;std::cout<<cof->get_dload_pre()<<std::endl;std::cout<<cof->get_pfile_suf()<<std::endl;std::cout<<cof->get_pack_dir()<<std::endl;std::cout<<cof->get_back_dir()<<std::endl;std::cout<<cof->get_backup_file()<<std::endl;
}
测试结果:

4.3 服务端数据管理模块实现
4.3.1 备份数据类的实现
需要管理的数据:
- 文件实际存储路径
- 当客户端要下载文件时,则从这个文件中读取数据进行响应
- 文件是否压缩标志
- 判断文件是否已经被压缩了
- 压缩包存储路径
- 若此文件是一个非热点文件会被压缩,则这个就是压缩包路径名称。当客户端想要下载文件时,则需要先解压,然后读取解压后的文件数据
- 文件访问URL中资源路径
- 如:
/download/a.txt
- 如:
- 文件最后一次修改时间
- 文件最后一次访问时间
- 文件大小
namespace yjcloud
{struct BackupInfo // 数据信息结构体{bool pack_flag; // 文件是否压缩标志size_t fsize; // 文件大小time_t atime; // 最后一次访问时间time_t mtime; // 最后一次修改时间std::string real_path; // 文件实际存储路径名称std::string pack_path; // 压缩包存储路径名称std::string url_path; // 文件访问URL中资源路径bool new_backup_info(const std::string &realpath, BackupInfo *info){yjcloud::FileUtil fu(realpath);if (fu.exists() == false){std::cout << "file not exists" << std::endl;return false;}yjcloud::Config *conf = Config::getinstance();std::string packdir = conf->get_pack_dir();std::string packsuffix = conf->get_pfile_suf();std::string downprefix = conf->get_dload_pre();pack_flag = false;fsize = fu.file_size();atime = fu.last_atime();mtime = fu.last_mtime();real_path = realpath;// ./backdir/a.txt -> ./packdir/a.txt.lzpack_path = packdir + fu.file_name() + packsuffix;// ./backdir/a.txt -> ./download/a.txturl_path = downprefix + fu.file_name();return true;}};
}
4.3.2 数据管理类的设计
- 内存中以文件访问URL为key,数据信息结构为val,使用哈希表进行管理,查询速度快。使用url作为key是因为往后客户端浏览器下载文件的时候总是以url作为请求。
- 采用文件形式对数据进行持久化存储(序列化方式采用json 格式)
namespace yjcloud
{class DataManger // 数据管理类{public:DataManger(){_backup_file = Config::getinstance()->get_backup_file();pthread_rwlock_init(&_rwlock, nullptr);init_load();}~DataManger(){pthread_rwlock_destroy(&_rwlock);}bool insert(const BackupInfo &info){pthread_rwlock_wrlock(&_rwlock);_hash[info.url_path] = info;pthread_rwlock_unlock(&_rwlock);storage();return true;}bool update(const BackupInfo &info){pthread_rwlock_wrlock(&_rwlock);_hash[info.url_path] = info;pthread_rwlock_unlock(&_rwlock);storage();return true;}// get: 此类接口都是查询数据bool get_one_by_url(const std::string &url, BackupInfo *info) {pthread_rwlock_wrlock(&_rwlock);auto it = _hash.find(url);if (it == _hash.end()){pthread_rwlock_unlock(&_rwlock);return false;}*info = it->second;pthread_rwlock_unlock(&_rwlock);return true;}bool get_one_by_realpath(const std::string &realpath, BackupInfo *info){pthread_rwlock_wrlock(&_rwlock);for (auto &it : _hash){if (it.second.real_path == realpath){*info = it.second;pthread_rwlock_unlock(&_rwlock);return true;}}pthread_rwlock_unlock(&_rwlock);return false;}bool get_all(std::vector<BackupInfo> *array){pthread_rwlock_wrlock(&_rwlock);for (auto &it : _hash){array->push_back(it.second);}pthread_rwlock_unlock(&_rwlock);return true;}bool storage() // 负责数据持久化(在每次新增和更新数据时持久化){// 1. 获取数据std::vector<BackupInfo> array;get_all(&array);// 2. 添加到Json::Value中Json::Value val;for(int i=0;i<array.size();++i){Json::Value item;item["pack_flag"]=array[i].pack_flag;item["fsize"]=(Json::Int64)array[i].fsize;item["atime"]=(Json::Int64)array[i].atime;item["mtime"]=(Json::Int64)array[i].mtime;item["real_path"]=array[i].real_path;item["pack_path"]=array[i].pack_path;item["url_path"]=array[i].url_path;val.append(item); // 添加数组元素}// 3. 对Json::Value序列化std::string body;JsonUtil::serialize(val,&body);// 4. 写文件FileUtil fu(_backup_file);fu.set_content(body);return true;}bool init_load() // 初始化程序运行时从文件读取数据(对象构造后){// 1. 将数据文件中的数据读取出来FileUtil fu(_backup_file);if(fu.exists()==false)return true;std::string body;fu.get_content(&body);// 2. 反序列化Json::Value val;JsonUtil::unserialize(body,&val);// 3. 将反序列化得到的Json::Value中的数据添加到hash中for(int i=0;i<val.size();++i){BackupInfo info;info.pack_flag=val[i]["pack_flag"].asBool();info.fsize=val[i]["fsize"].asInt();info.atime=val[i]["atime"].asInt64();info.mtime=val[i]["mtime"].asInt64();info.real_path=val[i]["real_path"].asString();info.pack_path=val[i]["pack_path"].asString();info.url_path=val[i]["url_path"].asString();insert(info);}return true;}private:std::string _backup_file; // 服务端备份信息存放文件// <文件url, 数据信息结构>std::unordered_map<std::string, yjcloud::BackupInfo> _hash; pthread_rwlock_t _rwlock; // 读写锁, 读共享, 写互斥};
}注意:
- 在数据操纵时采用读写锁
pthread_rwlock_t _rwlock而非互斥锁,因为读写锁:读共享,写互斥。单单读取数据时效率更高。 - 由于测试阶段数据量不大,我们在插入和更新数据时进行持久化存储,初始化程序时我们也要从配置文件中读取数据。
代码测试:
void Data_test(const std::string&filename)
{yjcloud::DataManger data;std::vector<yjcloud::BackupInfo> array;data.get_all(&array);for(auto&a:array){std::cout << a.pack_flag << std::endl;std::cout << a.fsize << std::endl;std::cout << a.atime << std::endl;std::cout << a.mtime << std::endl;std::cout << a.real_path << std::endl;std::cout << a.pack_path << std::endl;std::cout << a.url_path << std::endl;}
}
运行结果:

4.4 服务端热点管理模块实现
4.4.1 热点管理实现思路
-
设计思想
-
对服务器上备份的文件进行检测,哪些文件长时间没有被访问,则认为是非热点文件,进行压缩存储,节省磁盘空间
-
实现思路
-
遍历所有的文件,检测文件的最后一次访问时间,与当前时间进行相减得到差值,此差值如果大于设定好的非热点判断时间则认为是非热点文件,进行压缩存储到压缩路径中,删除源文件
-
遍历所有文件:
-
从数据管理模块中遍历所有的备份文件信息
-
遍历备份文件夹,对所有的文件进行属性获取,最终判断
-
-
选择第二种:遍历备份文件夹,每次获取文件的最新数据进行判断,并且还可以解决数据信息缺漏的问题
-
-
关键点:
-
上传文件有自己的上传存储位置,非热点文件的压缩存储有自己的存储位置
-
流程:
- 遍历备份目录,获取所有文件路径名称
- 逐个文件获取最后一次访问时间与当前系统时间进行比较判断
- 对非热点文件进行压缩处理,删除源文件
- 修改数据管理模块对应的文件信息,即压缩标志置为true
4.4.2 热点管理类的设计
#pragma once
#include"data.hpp"// 因为数据管理要在多个模块中访问的,将其作为全局数据定义,在此处声明使用即可
extern yjcloud::DataManger*_data;
namespace yjcloud
{class HotManger{public:HotManger(){Config*conf=Config::getinstance();_back_dir=conf->get_back_dir();_pack_dir=conf->get_pack_dir();_hot_time=conf->get_hot_time();_pack_suffix=conf->get_pfile_suf();// 创建好两个目录()FileUtil fu1(_back_dir);FileUtil fu2(_pack_dir);fu1.create_directory();fu2.create_directory();}bool run_modle(){while (1){// 1. 遍历备份目录, 获取所有文件名FileUtil fu(_back_dir);std::vector<std::string> array;fu.scan_directory(&array);// 2. 遍历判断文件是否是非热点文件for (auto &a : array){if (hot_judge(a) == true) // 这里的a是文件路径名continue;// 3. 获取文件的备份信息BackupInfo info;if (_data->get_one_by_realpath(a, &info) == false) {// 文件存在, 但是没有备份信息info.new_backup_info(a, &info); // 设置一个新的备份信息}// 4. 对非热点文件进行压缩处理FileUtil tmp(a);tmp.compress(info.pack_path); // 传入压缩后的文件名称// 5. 删除源文件, 修改备份信息tmp.remove_file();info.pack_flag = true; // 修改标志位_data->update(info);}usleep(1000); // 1ms循环一次, 避免空目录循环遍历, 消耗cpu资源过高}return true;}private:bool hot_judge(const std::string&filename) // 非热点文件-返回假; 热点文件-返回真{FileUtil fu(filename);time_t last_time=fu.last_atime();time_t cur_time=time(nullptr);if(cur_time-last_time>_hot_time)return false;return true;}private:std::string _back_dir; // 备份文件路径std::string _pack_dir; // 压缩文件路径std::string _pack_suffix; // 压缩包后缀名int _hot_time; // 热点判断时间};
}
代码测试
void Hot_test()
{_data=new yjcloud::DataManger();yjcloud::HotManger hot;hot.run_modle();
}
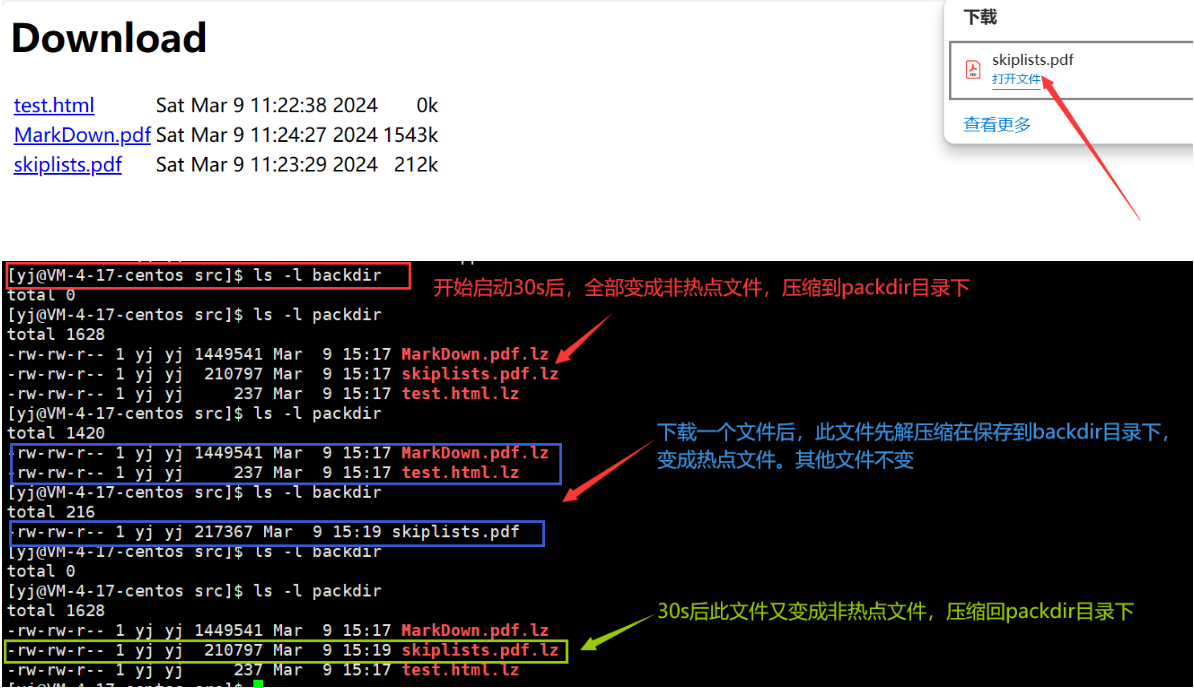
运行结果:此时./cloud运行后会生成两个目录,将文件拷贝到backdir目录中, 30后文件会被视为非热点文件,直接压缩存储到packdir中,同时backdir中没有源文件
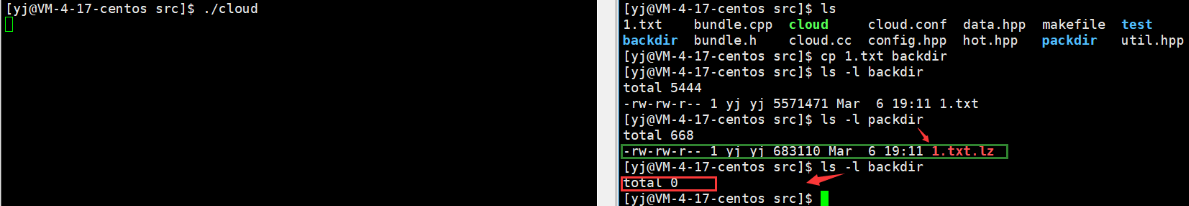
此时生成的cloud.dat中就写入了1.txt文件的相关信息
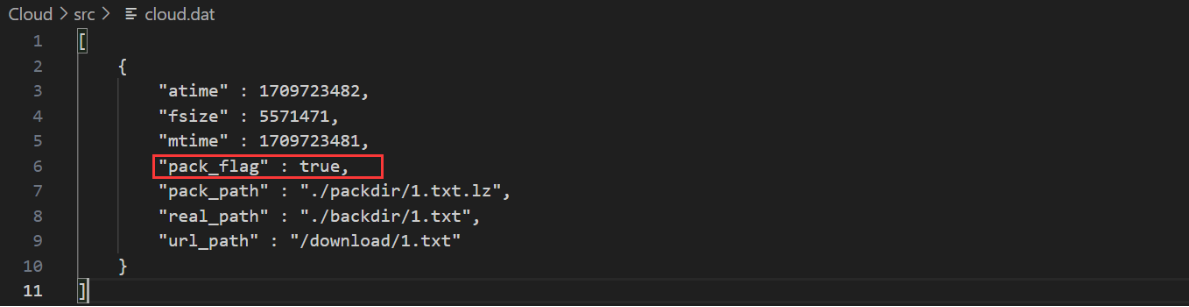
4.5 服务端业务处理模块实现
4.5.1 网络通信接口设计
业务处理模块要对客户端的请求进行处理,那么我们就需要提前定义好客户端与服务端的通信,明确客户端发送什么样的请求,服务端处理后应该给与什么样的响应,而这就是网络通信接口的设计。
请求:文件上传,展示页面,文件下载
HTTP文件上传:
当服务器收到一个POST方法的/upload请求,我们则认为这是一个文件上传请求。解析请求,得到文件数据,将数据写到文件中。
POST /upload HTTP/1.1
Content-Length:11
Content-Type:multipart/form-data;boundary= ----WebKitFormBoundary+16字节随机字符
------WebKitFormBoundary
Content-Disposition:form-data;filename="a.txt";
hello world
------WebKitFormBoundary--
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Content-Length: 0
HTTP展示页面:
GET /listshow HTTP/1.1
Content-Length: 0
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Content-Length:
Content-Type: text/html<html><head><meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8" /><title>Page of Download</title></head><body><h1>Download</h1><table><tr><td><a href="/download/a.txt"> a.txt </a></td><td align="right"> 1994-07-08 03:00 </td><td align="right"> 27K </td></tr></table></body>
</html>
HTTP文件下载:
GET /download/a.txt http/1.1
Content-Length: 0
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Content-Length: 100000
ETags: "filename+fsize+mtime一个能够唯一标识文件的数据"
Accept-Ranges: bytes
文件数据
字段解析:
-
ETag
- 存储了一个资源的唯一标识。客户端第一次下载文件的时候,会收到这个响应;第二次下载,会将这个信息发送给服务器,让服务器根据这个唯一标识判断这个资源是否被修改过,若没有被修改,则直接使用原先缓存的数据,不用重新下载。
- HTTP协议本身对于ETag中是什么数据并不关心,只要服务器能够唯一标识就行。此时我们这里的ETag就用“文件名-文件大小-最后一次修改时间”组成。
- ETag字段不仅仅是缓存用到,下面的断点续传实现也会用到。因为断点续传要保证文件没有被修改过
-
Accept-Ranges: bytes
- 用于告诉客户端服务器支持断点续传,并且数据单位以字节作为单位
-
Content-Type
- 决定了浏览器如何处理响应正文
4.5.2 业务处理类设计
//因为业务处理的回调函数没有传入参数的地方,因此无法直接访问外部的数据管理模块数据
//可以使用lamda表达式解决,但是所有的业务功能都要在一个函数内实现,于功能划分上模块不够清晰
//因此将数据管理模块的对象定义为全局数据,在这里声明一下,就可以在任意位置访问了
extern yjcloud::DataManger*_data;
namespace yjcloud
{class Service{public:Service(){Config*conf=Config::getinstance();_server_port=conf->get_server_port();_server_ip=conf->get_server_ip();_download_prefix=conf->get_dload_pre();}bool run_modle(){_svr.Post("/upload", upload);_svr.Get("/listshow", listshow);_svr.Get("/", listshow);// .* 正则表达式, 表示匹配任意字符任意次std::string download_url = _download_prefix + "(.*)"; _svr.Get(download_url, download);// 云服务器的公网是一个子网共享的,个人的机器是接受从公网ip转发的数据,所以必须绑定0.0.0.0才行_svr.listen("0.0.0.0", _server_port); return true;}private:static void upload(const httplib::Request&req,httplib::Response&resp){}static void listshow(const httplib::Request&req,httplib::Response&resp){}static void download(const httplib::Request&req,httplib::Response&resp){}private:int _server_port;std::string _server_ip;std::string _download_prefix; // 文件下载的前缀路径httplib::Server _svr;};
}
<1> upload
static void upload(const httplib::Request &req, httplib::Response &resp) // 上传请求处理函数
{// post /upload 文件数据在正文中(正文并不全是文件数据)auto res = req.has_file("file"); // 判断有没有上传的文件区域if (res == false){std::cout << "not file upload" << std::endl;resp.status = 400;return;}const auto &file = req.get_file_value("file"); // 获取文件各项数据// file.filename 文件名称 file.content 文件内容std::string back_dir = Config::getinstance()->get_back_dir(); // 备份的文件目录std::string realpath = back_dir + FileUtil((file.filename)).file_name();FileUtil fu(realpath);fu.set_content(file.content); // 将数据写入文件中BackupInfo info;info.new_backup_info(realpath); // 组织备份的文件信息_data->insert(info); // 向数据管理模块添加备份的文件信息return;
}
验证:我们启动服务器
void ServiceTest()
{yjcloud::Service svr;svr.run_modle();
}
进入编写好前端页面的,点击选择文件,选择好后直接上传
这里我上传了test.html文件,上传后出现下面场景
同时backdir目录下出现了上传的文件:

<2> listshow
static void listshow(const httplib::Request &req, httplib::Response &resp)//展示页面获取请求
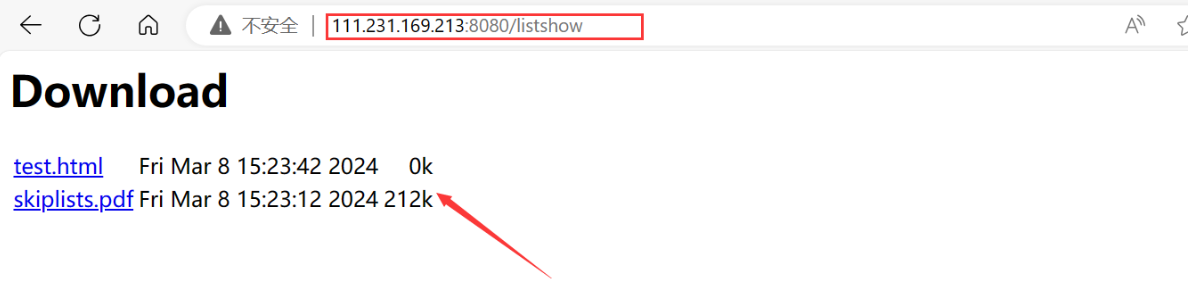
{// 1. 获取所有文件的备份信息std::vector<BackupInfo> arr;_data->get_all(&arr);// 2. 根据所有备份信息, 组织html文件数据std::stringstream ss;ss << "<html><head><title>Download</title></head>";ss << "<body><h1>Download</h1><table>";for (auto &a : arr){ss << "<tr>";std::string filename = FileUtil(a.real_path).file_name();ss << "<td><a href='" << a.url_path << "'>" << filename << "</a></td>";ss << "<td align='right'>" << time_tostr(a.mtime) << "</td>";ss << "<td align='right'>" << a.fsize / 1024 << "k</td>";ss << "</tr>";}ss << "</table></body></html>";resp.body = ss.str();resp.set_header("Content-Type", "text/html");resp.status = 200;
}static const char *time_tostr(time_t t)
{return ctime(&t);
}
验证:
<3> download
static void download(const httplib::Request &req, httplib::Response &resp)//文件下载处理函数
{// 1. 获取客户端请求的资源路径path req.path// 2. 根据资源路径, 获取文件备份信息BackupInfo info;_data->get_one_by_url(req.path, &info);// 3. 判断文件是否被压缩, 如果被压缩, 要先解压缩if (info.pack_flag == true){FileUtil fu(info.pack_path);fu.uncompress(info.real_path); // 文件解压到备份目录下// 4. 删除压缩包, 修改备份信息(已经没有被压缩)fu.remove_file();info.pack_flag = false;_data->update(info);}// 5. 读取文件数据, 放入resp.body中FileUtil fu(info.real_path);fu.get_content(&resp.body);// 6. 设置响应头部字段: Accept-Ranges: bytesresp.set_header("Accept-Ranges", "bytes");resp.set_header("ETag", get_etag(info));resp.set_header("Content-Type", "application/octet-stream"); // octet-stream: 代表二进制数据流(一定要设置)resp.status = 200;
}// 设置一个能够唯一标识文件的数据
static std::string get_etag(const BackupInfo &info) // 文件名-文件大小-文件最近修改时间
{// etag: filename-fsize-mtimeFileUtil fu(info.real_path);std::string etag = fu.file_name();etag += "-";etag += std::to_string(info.fsize);etag += "-";etag += std::to_string(info.mtime);return etag;
}
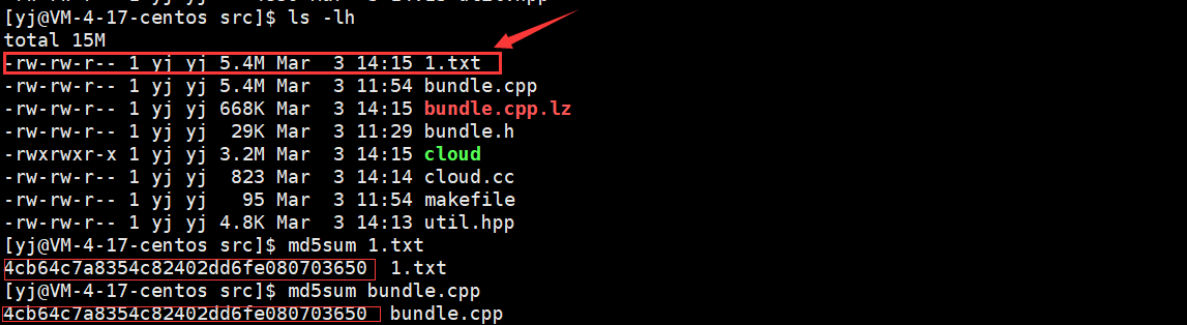
验证:启动服务器后,直接点击蓝色文件名,下载文件
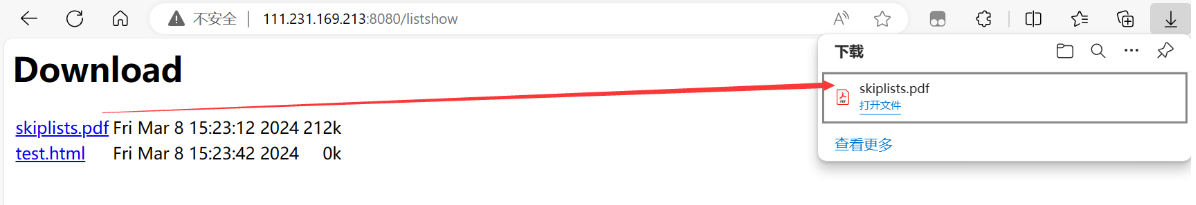
对比两个文件的哈希值,发现完全相同。则证明文件一致
断点续传
功能:当文件下载过程中,因为某种异常而中断,如果再次从头下载,效率较低,因为需要将之前已经传输过的数据再次传输一遍。断点续传就是从上次下载断开的位置,重新下载即可,之前已经传输的数据将不需要再重新传输
目的:提高文件重新传输的效率
实现思想:
- 客户端在下载文件的时候,要每次接收到数据写入文件后记录自己当前下载的数据量。
- 当异常下载中断时,下次断点续传的时候,将要重新下载的数据区间(下载起始位置,结束位置)发送给服务器,服务器收到后,仅仅回传客户端需要的区间数据即可
考虑问题:如果上次下载文件之后,这个文件在服务器上被修改了,则这时候不能重新断点续传,而是应该重新进行文件下载操作
主要关键点:
- 要能够告诉服务器下载区间范围
- 服务器上要能够检测上一次下载之后这个文件是否被修改过
结合协议:
- 客户端
- HTTP请求头部携带
If-Range字段告诉服务器支持断点续传; - HTTP请求头部携带
Range: bytes字段告诉服务器自己需要数据区间的范围。如:Range: bytes=89-999表示需要89-999字节的数据
- HTTP请求头部携带
- 服务器
- HTTP响应头部携带
Accept-Ranges: bytes字段告诉客户端支持断点续传,且数据单位以字节为单位。 - 服务器会根据
Range: bytes数据范围,将数据范围填入响应头部Content-Range,响应正文中就是对应区间的数据。如:Content-Range: bytes 100-表示从100字节开始到文件末尾的数据。 - 最后设置状态码206:表示所请求的区间数据已请求成功。
- HTTP响应头部携带
GET /download/a.txt http/1.1
Content-Length: 0
If-Range: "文件唯一标识"
Range: bytes=89-999
HTTP/1.1 206 Partial Content
Content-Length:
Content-Range: bytes 89-999/100000
Content-Type: application/octet-stream
ETag: "filename+fsize+mtime一个能够唯一标识文件的数据"
Accept-Ranges: bytes
对应文件从89到999字节的数据。
加上断点续传后的下载代码:
static void download(const httplib::Request &req, httplib::Response &resp)//文件下载处理函数
{// 1. 获取客户端请求的资源路径path req.path// 2. 根据资源路径, 获取文件备份信息BackupInfo info;_data->get_one_by_url(req.path, &info);// 3. 判断文件是否被压缩, 如果被压缩, 要先解压缩if (info.pack_flag == true){FileUtil fu(info.pack_path);fu.uncompress(info.real_path); // 文件解压到备份目录下// 4. 删除压缩包, 修改备份信息(已经没有被压缩)fu.remove_file();info.pack_flag = false;_data->update(info);}bool retrans=false;std::string old_etag;if(req.has_header("If-Range")){old_etag=req.get_header_value("If-Range");// 有If-Range字段且, 这个字段的值与请求文件的最新etag一致, 则符合断点续传if(old_etag==get_etag(info)){retrans=true;}}// 5. 读取文件数据, 放入resp.body中FileUtil fu(info.real_path);fu.get_content(&resp.body);// 6. 设置响应头部字段: ETag, Accept-Ranges: bytesif(retrans==false){fu.get_content(&resp.body);resp.set_header("Accept-Ranges", "bytes");resp.set_header("ETag", get_etag(info));resp.set_header("Content-Type", "application/octet-stream"); // octet-resp.status = 200;}else{// httplib内部实现了对于区间请求也就是断点续传请求的处理// 只需要我们用户将文件所有数据读取到rsp.body中, // 它内部会自动根据请求区间, 从body中提取指定区间数据进行响应// std::string range = req.get_header_val("Range"); bytes=start-endfu.get_content(&resp.body);resp.set_header("Accept-Ranges", "bytes");resp.set_header("ETag", get_etag(info));resp.set_header("Content-Type", "application/octet-stream");// resp.set_header("Content-Range", "bytes start-end/fsize");resp.status = 206;}
}// 设置一个能够唯一标识文件的数据
static std::string get_etag(const BackupInfo &info) // 文件名-文件大小-文件最近修改时间
{// etag: filename-fsize-mtimeFileUtil fu(info.real_path);std::string etag = fu.file_name();etag += "-";etag += std::to_string(info.fsize);etag += "-";etag += std::to_string(info.mtime);return etag;
}
验证:我们点击下载后直接断开网络

后重新联网,文件就会从刚才断开的地方继续下载
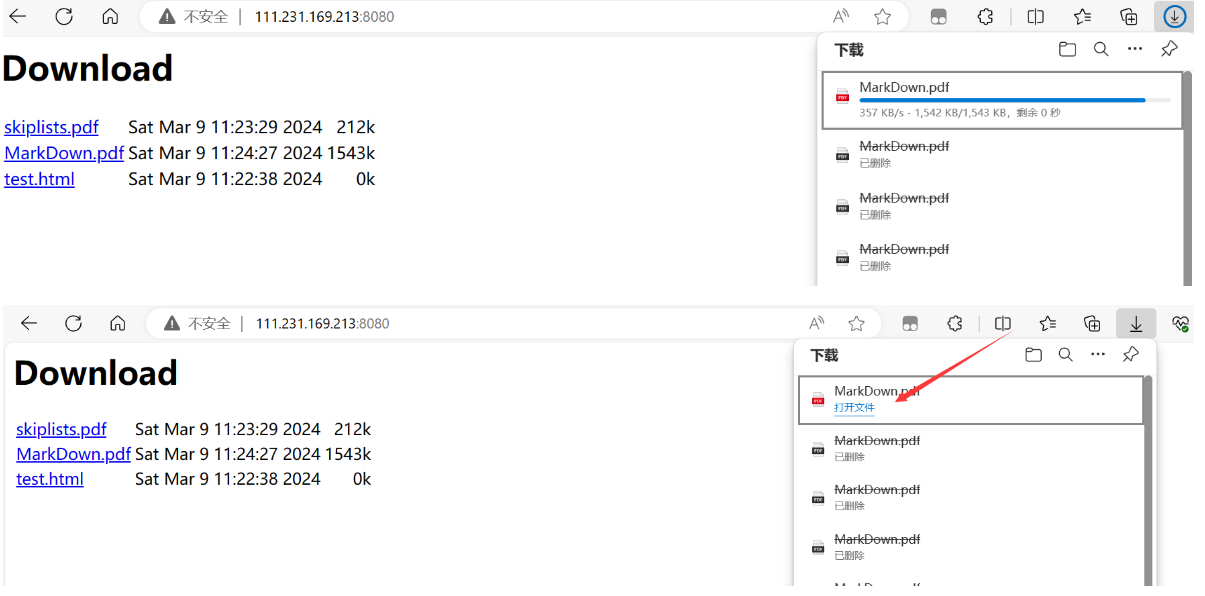
下载完成后,对比两个文件哈希值,发现一致
4.6 服务端整体模块测试
在前面模块的实现业务处理模块与热点管理模块都是死循环,所以我们可以使用多线程来测试这两个模块。
yjcloud::DataManger*_data;
void Hot_test()
{yjcloud::HotManger hot;hot.run_modle();
}
void ServiceTest()
{yjcloud::Service svr;svr.run_modle();
}
int main(int argc,char*argv[])
{// 服务端整体测试_data=new yjcloud::DataManger();std::thread hot_thread(Hot_test);std::thread ser_thread(ServiceTest);hot_thread.join();ser_thread.join();return 0;
}
验证:启动服务器,下载某个文件的前后过程
5. 客户端代码设计
为了让用户体验感更好,客户端我们在Windows下编写。客户端代码设计相比服务端比较简单。
-
功能:自动对指定文件夹中的文件进行备份
-
模块划分:
- 数据管理模块:管理备份的文件信息
- 文件操作模块:获取指定的一些文件信息
- 文件备份模块:将需要备份的文件上传备份到服务器
5.1 客户端文件操作实用类设计
此类设计与服务端雷同,直接拷贝服务端的设计即可
#pragma once
#define _SILENCE_EXPERIMENTAL_FILESYSTEM_DEPRECATION_WARNING
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<fstream>
#include<sys/stat.h>
#include<ctime>
#include<experimental/filesystem>
#include<vector>namespace fs = std::experimental::filesystem;
namespace yjcloud
{class FileUtil{public:FileUtil(const std::string& filename):_filename(filename){}bool remove_file(){if (exists() == false)return true;remove(_filename.c_str());return true;}int64_t file_size() {struct stat st;if (stat(_filename.c_str(), &st) < 0){std::cout << "get file size fail" << std::endl;return -1;}return st.st_size;}time_t last_mtime() {struct stat st;if (stat(_filename.c_str(), &st) < 0){std::cout << "get last modify time fail" << std::endl;return -1;}return st.st_mtime;}time_t last_atime() {struct stat st;if (stat(_filename.c_str(), &st) < 0){std::cout << "get last modify time fail" << std::endl;return -1;}return st.st_atime;}std::string file_name() {size_t pos = _filename.find_last_of("\\"); // "\\"就是原始'\'if (pos == std::string::npos)return _filename;//return fs::path(_filename).filename().string(); // c++17文件系统: 获取纯文件名return _filename.substr(pos + 1);}bool get_pos_len(std::string* body, size_t pos, size_t len) {size_t fsize = this->file_size();if (fsize > len){std::cout << "get file len is error" << std::endl;return false;}std::ifstream ifs;ifs.open(_filename, std::ios::binary);if (ifs.is_open() == false){std::cout << "read open file failed" << std::endl;return false;}ifs.seekg(pos, std::ios::beg); body->resize(len);ifs.read(&(*body)[0], len);if (ifs.good() == false){std::cout << "read file fail" << std::endl;ifs.close();return false;}ifs.close();return true;}bool get_content(std::string* body){return get_pos_len(body, 0, file_size());}bool set_content(const std::string& body){std::ofstream ofs;ofs.open(_filename, std::ios::binary);if (ofs.is_open() == false){std::cout << "write open file failed" << std::endl;return false;}ofs.write(&body[0], body.size());if (ofs.good() == false){std::cout << "write file fail" << std::endl;ofs.close();return false;}ofs.close();return true;}bool exists(){return fs::exists(_filename);}bool create_directory(){if (exists())return true;return fs::create_directories(_filename);}bool scan_directory(std::vector<std::string>* array){for (auto& p : fs::directory_iterator(_filename)){if (fs::is_directory(p) == true)continue;array->push_back(fs::path(p).relative_path().string());}return true;}private:std::string _filename;};
}
5.2 客户端数据管理模块实现
实现思想:
-
内存存储:高访问效率—使用哈希表
-
持久化存储:文件存储
文件存储涉及到数据序列化:由于在VS中安装jsoncpp较为麻烦,这里直接自定义序列格式化
格式: key val\nkey val\n key是文件路径名,val是文件唯一标识。'\n'作为序列化与反序列化时的分隔符。如:./a.txt a.txt-1234-145177\n./b.txt b.txt-1567-18976
#pragma once
#include<unordered_map>
#include<string>
#include<sstream>
#include"util.hpp"namespace yjcloud
{class DataManger{public:DataManger(const std::string &backup_file):_backup_file(backup_file){init_load();}bool storage() // 数据持久化{// 1. 获取所有备份信息std::stringstream ss;for (auto& it : _hash) {// 2. 将所有备份信息进行制定持久化格式的组织(格式: key val\nkey val\n)ss << it.first << " " << it.second << "\n";}// 3. 持久化存储FileUtil fu(_backup_file);fu.set_content(ss.str());return true;}bool init_load() // 初始化加载{// 1. 从文件读取所有数据FileUtil fu(_backup_file);std::string body;fu.get_content(&body);// 2. 进行数据解析, 添加到表中std::vector<std::string> arr;split(body, "\n", &arr); // 分割一个一个文件for (auto& a : arr){// a的格式: b.txt b.txt-1245(文件大小)-14453(最后一次访问时间)std::vector<std::string> tmp;split(a, " ", &tmp); // 分割文件名和文件唯一标识if (tmp.size() != 2) // 分割有问题continue;_hash[tmp[0]] = tmp[1]; // tmp[0]: 文件名 tmp[1]: 文件唯一标识}return true;}bool insert(const std::string&key,const std::string&val){_hash[key] = val;storage();return true;}bool update(const std::string& key, const std::string& val){_hash[key] = val;storage();return true;}bool get_one_by_key(const std::string& key, std::string*val){auto it = _hash.find(key);if (it == _hash.end())return false;*val = it->second;return true;}private:int split(const std::string& str, const std::string& sep, std::vector<std::string>* array){int count = 0;size_t pos = 0, idx = 0; while (1){pos = str.find(sep, idx);if (pos == std::string::npos)break;if (pos == idx){idx = pos + sep.size();continue;}std::string tmp = str.substr(idx, pos - idx);array->push_back(tmp);++count;idx = pos + sep.size();}if (idx < str.size()){array->push_back(str.substr(idx));++count;}return count;}private:std::string _backup_file; // 备份信息的持久化存储文件std::unordered_map<std::string, std::string> _hash; // <路径名, 文件唯一标识>};
}
5.3 客户端文件备份类设计
实现功能:自动将指定文件夹中文件备份到服务器
思路:
- 遍历指定文件夹,获取文件信息
- 逐一判断文件是否需要备份
- 需要备份的文件进行上传备份
#pragma once
#include"data.hpp"
#include"httplib.h"
#include<Windows.h>#define SERVER_ADDR "111.231.169.213"
#define SERVER_PORT 8080namespace yjcloud
{class Backup {public:Backup(const std::string& back_dir, const std::string& back_file):_back_dir(back_dir){_data = new DataManger(back_file);}bool run_module(){while (1){// 1. 遍历获取指定文件夹中所有文件FileUtil fu(_back_dir);std::vector<std::string> arr;fu.scan_directory(&arr);// 2. 逐个判断文件是否需要上传for (auto& a : arr){if (is_need_upload(a) == false)continue;// 3. 如果需要上传则上传文件if (upload(a) == true){_data->insert(a, get_file_identify(a)); // 新增文件备份信息std::cout << a << " upload success!" << std::endl;}}Sleep(1);}return true;}private:bool upload(const std::string& filename){// 1. 获取文件数据FileUtil fu(filename);std::string body;fu.get_content(&body);// 2. 搭建http客户端上传文件数据httplib::Client client(SERVER_ADDR, SERVER_PORT);httplib::MultipartFormData item;item.name = "file"; // 标识字段名(服务端upload用file标识)item.filename = fu.file_name();item.content = body;item.content_type = "application/octet-stream";httplib::MultipartFormDataItems items;items.push_back(item);auto res = client.Post("/upload", items);if (!res || res->status != 200)return false;return true;}bool is_need_upload(const std::string& filename){// 需要上传文件的判断条件: 文件是新增的或文件不是新增但是被修改过// 文件是新增的: 看有没有历史备份信息// 不是新增但是被修改过: 有历史信息, 但是历史的唯一标识与当前最新的唯一标识不一致std::string id;if (_data->get_one_by_key(filename, &id) != false){// 有历史信息std::string new_id = get_file_identify(filename);if (new_id == id)return false; // 不需要被上传-上一次上传后没有被修改过}// 一个文件比较大, 正在徐徐的拷贝到这个目录下。拷贝需要一个过程,// 如果每次遍历则都会判断标识不一致需要上传一个几十G的文件会上传上百次// 因此应该判断一个文件一段时间都没有被修改过了, 则才能上传FileUtil fu(filename);if (time(nullptr) - fu.last_mtime() < 3) // 3秒钟之内刚修改过---认为文件还在修改中return false;std::cout << filename << " need upload!" << std::endl;return true;}std::string get_file_identify(const std::string& filename) // 计算获取文件唯一标识{// b.txt-1234-16792FileUtil fu(filename);std::stringstream ss;ss << fu.file_name() << "-" << fu.file_size() << "-" << fu.last_mtime();return ss.str();}private:std::string _back_dir; // 要监控的文件夹DataManger* _data;};
}
5.4 客户端服务器功能联调测试
客户端:在当前客户端代码路径下自己创建备份目录
将需要备份的文件拷贝至此,运行客户端程序。文件就会备份成功
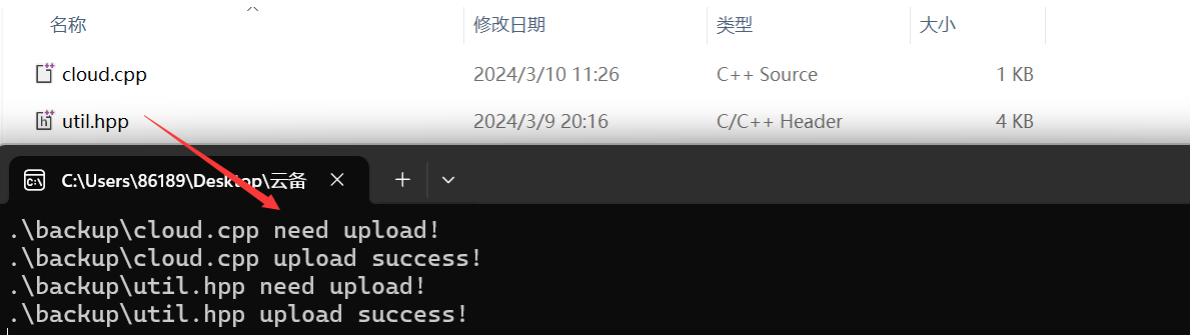
cloud.dat中也写入了对应文件信息

服务器:
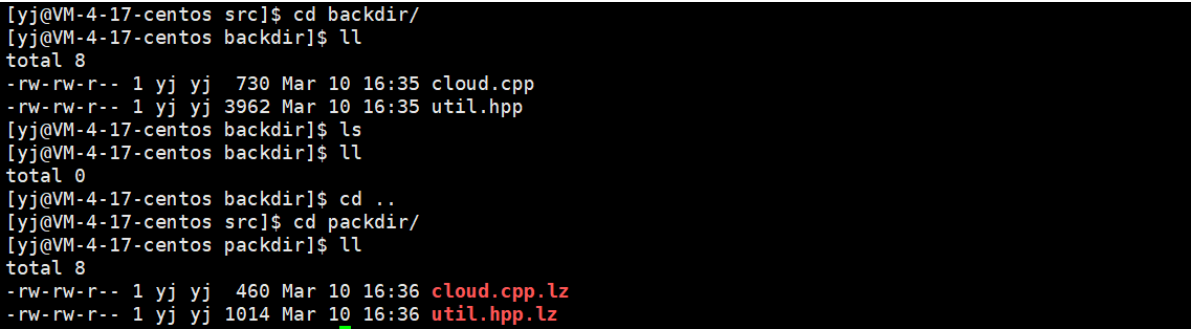
在服务器这端就可以看到对应文件
用浏览器访问,F5刷新页面就可以点击下载文件

6. 项目总结
-
项目名称:云备份系统
-
项目功能:搭建云备份服务器与客户端,客户端程序运行在客户机上自动将指定目录下的文件备份到服务器,并且能够支持浏览器查看与下载,其中下载支持断点续传功能,并且服务器端对备份的文件进行热点管理,将长时间无访问文件进行压缩存储。
-
开发环境:
centos7.6/vim、g++、gdb、makefile以及windows11/vs2019 -
技术特点:
http客户端/服务器搭建,json序列化,文件压缩,热点管理,断点续传,线程池(httplib中),读写锁,单例模式 -
项目模块:
-
服务端:
- 数据管理模块:内存中使用hash表存储提高访问效率,持久化使用文件存储管理备份数据
- 业务处理模块:搭建http 服务器与客户端进行通信处理客户端的上传,下载,查看请求,并支持断点续传
- 热点管理模块:对备份的文件进行热点管理,将长时间无访问文件进行压缩存储,节省磁盘空间。
-
客户端:
- 数据管理模块:内存中使用hash表存储提高访问效率,持久化使用文件存储管理备份数据
- 文件检索模块:基于c++17 文件系统库,遍历获取指定文件夹下所有文件。
- 文件备份模块:搭建http 客户端上传备份文件。
-
-
项目扩展:
- 给客户端开发一个好看的界面,让监控目录可以选择
- 内存中的管理的数据也可以采用热点管理
- 压缩模块也可以使用线程池实现
- 实现用户管理,不同的用户分文件夹存储以及查看
- 实现断点上传
- 客户端限速,收费则放开
![[BJDCTF2020]Cookie is so stable](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/5ef0f77d9edc47219fa053a9025446b0.png)