1. Promise介绍和基本应用
1.1 Promise是什么
1.1.1 理解
| 抽象表达 | 1. 新的技术,ES6规范 |
|---|---|
| 2. JS进行异步编程的新解决方案(旧方案是单纯使用回调函数) | |
| 具体表达 | 1. 语法:Promise是一个构造函数 |
| 2. 功能:promise对象用来封装一个异步操作并可以获取其成功/失败的结果值 |
异步编程有哪些:
- fs文件操作
// 回调函数形式 require('fs').readFile('./index.html',(err,data)=>{if(err) throw err;console.log(data.toString()); })// Promise形式let promise = new Promise((resolve,reject)=>{fs.readFile('./html',(err,data)=>{if(err) reject(err);resolve(data);}) })promise.then((value) => {console.log(value.toString()); }, (err) => {console.log(err); })
- 数据库操作
- AJAX
const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest(); xhr.open('GET','http://api.apiopen.top/getJob'); xhr.send(); xhr.onreadystatechange = function(){if(xhr.readyState === 4){if(xhr.status >= 200 && xhr.status < 300){console.log(xhr.response);}else{console.log(xhr.status)}} }// Promise形式 const promise = new Promise((resolve,reject) => {const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();xhr.open('GET','http://api.apiopen.top/getJob');xhr.send();xhr.onreadystatechange = function(){if(xhr.readyState === 4){if(xhr.status >= 200 && xhr.status < 300){resolve(xhr.response)}else{reject(xhr.status)}}} })promise.then((value) => {console.log(value) }, (err) => {console.warn(err); })
- 定时器
setTimeout(()=>{},2000)
1.2 为什么要使用Promise
1.2.1 指定回调函数的方式更加灵活
| 旧的方法 | Promise方法 |
|---|---|
| 必须在启动异步任务前指定 | 1. 启动异步任务; 2. 返回Promise对象; 3. 给Promise对象绑定回调函数; (可以在异步任务结束后指定多个) |
1.2.2 支持链式调用,可解决回调地狱问题
1. 什么是回调地狱
- 回调地狱嵌套调用,外部回调函数异步执行的结果是内部嵌套的回调函数执行的条件
asyncFunc1(opt,(...args1)=>{asyncFunc2(opt,(...args2)=>{asyncFunc3(opt,(...args3)=>{asyncFunc4(opt,(...args4)=>{// 一些操作}); });}); });
2. 回调地狱缺点
- 可读性差
- 不便于异常处理
3. 解决方案
- Promise链式调用
1.3 Promise的状态改变
- pending未决定的
- resolved / fulfilled 成功
- rejected 失败
注意只有这两种改变方法,每个promise对象只能改变一次。
- pending --> resolved / fulfilled
- pending --> rejected
无论是成功还是失败,都会有一个结果数据(value / reason)
1.4 Promise基本流程
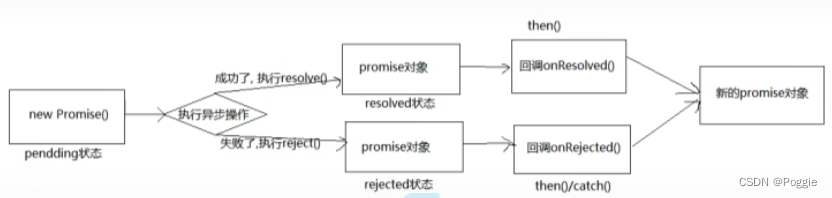
2. Promise API
2.1 Promise构造函数 Promise( (executor) { } )
2.1.1 excutor函数
执行器:(resolve,reject)=> { }
executor会在Promise内部立即同步调用,异步操作在执行器中执行
new Promise((resolve,reject)=>{console.log('111'); // 同步调用
})
console.log('222');// 打印
// 111
// 2222.1.2 resolve函数
内部定义成功时调用 (value) => { }
2.1.3 reject函数
内部定义失败时调用(reason)=> { }
2.2 Promise.prototype.then((value) => {},(reason) => {})
指定用于得到成功value的成功回调和失败reason的失败回调
返回一个新的promise对象
在不同回调函数里返回的promise对象是怎样的?
2.2.1 onResolved函数
成功的回调函数(value)=> { }
2.2.3 onRejected函数
失败的回调函数(reason)=> { }
2.3 Promise.prototype.catch((reason) => {})
2.3.1 onRejected函数
失败的回调函数(reason)=> { }
2.4 Promise.resolve((value) => {})
| 形参 | 非Promise对象 | Promise对象 |
| 返回的promise对象 | 成功promise对象 | 取决于传入对象的结果 |
2.5 Promise.reject((reason) => {})
| 形参 | 任何数据 |
| 返回的promise对象 | 失败的promise对象 |
2.6 Promise.all((promises) => {})
| 形参 | [ 所有promise对象都是成功的 ] | [ 存在失败的promise对象 ] |
| 返回的Promise对象 | state: 成功 | state: 失败 |
| result:[ 所有promise对象的结果 ] | result:失败对象的结果 |
2.7 Promise.race((promises) => {})
| 形参 | [ 多个promise对象 ] |
| 返回的promise对象 | state:首个执行完的promise状态 |
| result:首个执行完的promise结果 |
3. Promise关键问题
1. 如何改变promise的状态?
- 执行resolve():pending --> resolved
- 执行reject():pending --> reject
- throw : pending --> reject
2. 一个promise执行多个成功/失败回调函数,都会调用吗?
- 当promise对象状态改变为相应状态时,通过then执行多个回调函数
- 状态必须改变
3. 改变promise状态和指定回调函数,谁先谁后?
- 都可能
- 正常情况:先指定回调再改变状态
- 如何先改变状态再执行回调
- 在执行器中直接调用resolve()/ reject()
- 延迟更长时间才调用then()
- 什么时候才得到数据
- 先指定回调时
- 状态改变时调用回调函数 --> 得到数据
- 先改变状态时
- 指定回调时调用回调函数 --> 得到数据
4. promise.then( )返回的新promise的结果状态由什么决定?
- 若抛出异常:新promise的state为reject,result为抛出的异常
- 若返回非promise的任意值:新promise的state为resolved,result为返回的值
- undefined | 其他指定值
- 若返回另一个promise,新promise的结果为该promise的结果
5. promise如何串联多个操作任务
- 通过then()进行链式调用,串联多个同步/异步任务
6. promise异常穿透
- 使用promise的then链式调用时,可在最后指定失败的回调
- 前面任何操作出了异常,都会传到最后失败的回调中处理
7. 中断promise链
- 当使用promise的then链式调用时,在中间中断,不在调用后面的回调函数
- 在回调函数中返回一个pending状态的Promise对象
4. Promise自定义封装
5. 异步之宏队列与微队列
5.1 原理图
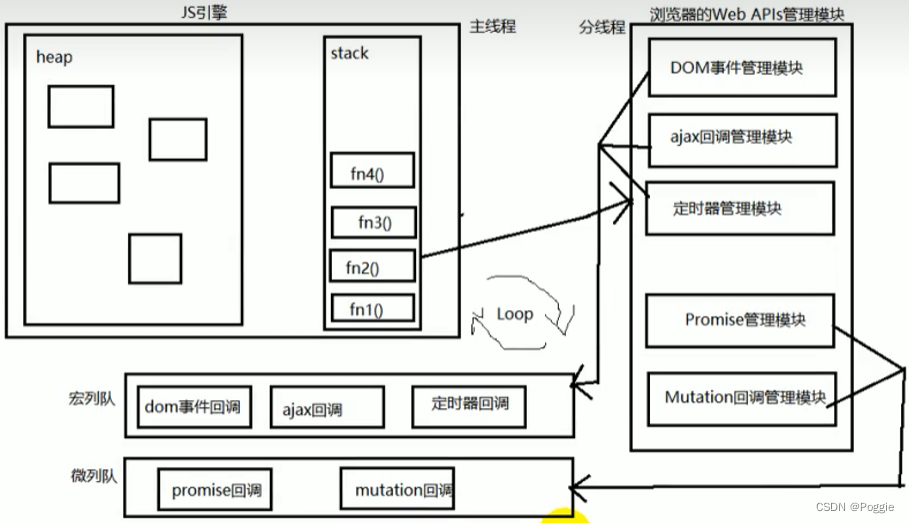
5.2 说明
- JS有两种不同队列来存储待执行回调函数
- 宏队列:保存待执行的宏任务
- 定时器回调
- DOM事件回调
- AJAX回调
- 微队列:保存待执行的微任务
- Promise回调
- MutationObserver回调
- 如何按顺序执行
- JS引擎首先必须先执行所有的初始化同步任务代码
- JS每次执行第一个宏任务前,都要将微队列中的微任务执行完毕
- 先执行微队列里的所有微任务
- 当该执行宏队列里的宏任务,宏任务里存在微任务时
- 将其中的微任务放入微队列
- 在执行下一个宏任务前,执行完微队列里的微任务
console.log('同步任务1');setTimeout(() => {Promise.resolve(1).then(value=>{console.log('定时器宏任务1里的微任务1');}) });setTimeout(() => {console.log('定时器宏任务2'); },1000);console.log('同步任务2');setTimeout(() => {console.log('定时器宏任务3'); });console.log('同步任务3');setTimeout(() => {Promise.resolve(1).then(value=>{console.log('定时器宏任务4里的微任务1');}) });console.log('同步任务4');Promise.resolve(2).then(value=>{console.log('Promise微任务1');}) console.log('同步任务5');new Promise((resolve,reject)=>{console.log('Promise微任务2里的Executor同步任务6');resolve();}).then(value=>{console.log('Promise微任务2');}) console.log('同步任务7');// 打印: // 同步任务1 // 同步任务2 // 同步任务3 // 同步任务4 // 同步任务5 // Promise微任务2里的Executor同步任务6 // 同步任务7 // Promise微任务1 // Promise微任务2 // 定时器宏任务1里的微任务1 // 定时器宏任务3 // 定时器宏任务4里的微任务1 // 定时器宏任务2
- 同步任务
- executor函数
- 同步任务executor在微任务new Promise里容易混淆
// 按顺序执行,将同步任务输出,处理异步函数:微任务-->宏任务const first=()=>(new Promise((resolve,reject)=>{console.log(3); // 微任务1 同步任务1let p= new Promise((resolve,reject)=>{console.log(7); // 微任务1-1 Executor同步任务1setTimeout(() => { // 微任务1-1 宏任务1console.log(5); // 微任务1-1 宏任务1里的同步任务1resolve(6) // 不执行了,已经resolve(1)}, 0);resolve(1); // 微任务1-1 同步任务2 // Promise{<fulfilled>:1}})resolve(2); // 微任务1 同步任务2 // Promise{<fulfilled>:2}p.then((arg)=>{console.log(arg); // 微任务1-2 输出1})}))first().then((arg)=>{console.log(arg); // 微任务2 输出2})console.log(4); // 同步任务1// 打印顺序 3 7 4 1 2 5
- 可以试着模拟两个队列的进出
setTimeout(() => {console.log(0); // 宏任务1 }, 0);new Promise((resolve,reject)=>{console.log(1); // 微任务1 Executor同步任务1resolve();}).then(()=>{console.log(2); // 微任务2new Promise((resolve,reject)=>{console.log(3); // 微任务3 Executor同步任务1resolve();}).then(()=>{console.log(4); // 微任务4 }).then(()=>{console.log(5); // 微任务5})}).then(()=>{console.log(6); // 微任务6})new Promise((resolve,reject)=>{ console.log(7); // 微任务7 Executor同步任务1resolve();}).then(()=>{console.log(8); // 微任务8 })//打印 1 7 2 3 8 4 6 5 0
- 这块有部分执行顺序不太理解
// 宏队列 【】 // 微队列 【】 // 打印 1 7 2 3 9 8 4 6 5 0setTimeout(() => {console.log(0); // 宏任务1 }, 0);new Promise((resolve,reject)=>{console.log(1); // 微任务1 Executor同步任务1resolve();}).then(()=>{console.log(2); // 微任务2new Promise((resolve,reject)=>{console.log(3); // 微任务3 Executor同步任务1resolve();}).then(()=>{console.log(4); // 微任务4 }).then(()=>{console.log(5); // 微任务5})console.log(9);// 这部分执行后到6}).then(()=>{console.log(6); // 微任务6})new Promise((resolve,reject)=>{ console.log(7); // 微任务7 Executor同步任务1resolve();}).then(()=>{console.log(8); // 微任务8 })
6. Promise语法糖
6.1 async 函数
- 函数返回值为 Promise 对象
- promsie对象的结果由 async函数执行结果 决定
// async的返回结果类似于then方法
async function testAsync(){// return '123'; // Promise {<fulfilled> : '123'}return new Promise((resolve,reject)=>{resolve('456'); // Promise {<fulfilled> : '456'}// reject('sorry') // Promise {<rejected> : 'sorry'}// throw 'bad' // Promise {<rejected> : 'bad'}})// throw 'error' // Promise {<rejected> : 'error'}
}let result = testAsync();
console.log(result);6.2 await表达式
- await 右侧表达式
- 若为Promise对象,await 返回的是Promise成功的值
- 若为其他值,await直接返回该值
async function testAsync(){let a = await '123'; // 123let b = await new Promise((resolve,reject)=>{resolve('456'); // 456reject('sorry') // Uncaught (in promise) sorrythrow 'bad' // Uncaught (in promise) bad})console.log('a',a);console.log('b',b);
}
6.3 注意
- await必须写在async中
- async中可以没有await
- 如果await的promise失败,会抛出异常,需要try..catch处理
async function testAsync(){let a = await '123'; // 123console.log('a',a);try { let b = await new Promise((resolve,reject)=>{// resolve('456'); // 456reject('sorry') // sorry// throw 'bad' // bad}) console.log('b',b);} catch (error) {console.log(error);} }
7. 实例
7.1 文件读写
案例:拼接多个文件的内容
- 回调函数方法
fs.readFile('./resource/1.html',(err,data1) => {if(err) throw err;fs.readFile('./resource/2.html',(err,data2) => {if(err) throw err;fs.readFile('./resource/3.html',(err,data3) => {if(err) throw err;console.log(data1 + data2 + data3)});});
});- async await方法
async function read(){try{let data1 = await mineReadFile('./resource/1.html');let data2 = await mineReadFile('./resource/2.html');let data3 = await mineReadFile('./resource/3.html');console.log(data1 + data2 + data3)}catch(e){console.log(e)}
}