本章主要是讲模拟实现list,文章末附上代码。
目录
一、创建思路
二、构造函数
三、迭代器
四、增删
五、代码
一、创建思路
如下方代码,链表是由一块一块不连续的空间组成的,所以这里写了三个模板,一个是节点,一个是迭代器,分别放在struct创建的类,因为这个是可以直接访问,从下方代码可以看出我是在list里面定义了一个head,这个就是哨兵位头节点,然后在list_node里面写的就是节点的初始化,需要使用时直接new一个,_list_iterator这个就是迭代器写的地方了,这里也是直接写了两个一个普通的迭代器,一个const的。
namespace ly
{
template<class T>
struct list_node
{
list_node<T>* _next;
list_node<T>* _prev;
T _data;list_node(const T& x = T())
:_next(nullptr)
, _prev(nullptr)
, _data = x
{}
};template<class T,class Ref,class Ptr>
struct _list_iterator
{
typedef list_node<T> node;
typedef __list_iterator<T, Ref, Ptr> self;node* _node;
node* _node;
_list_iterator(node* n)
:_node(n)
{}};
template<class T>
class list
{
public:
typedef list_node<T> node;
typedef _list_iterator<T, T&, T*> iterator;
typedef _list_iterator<T, const T&, const T*> const_iterator;
private:
node* _head;
};
}
二、构造函数
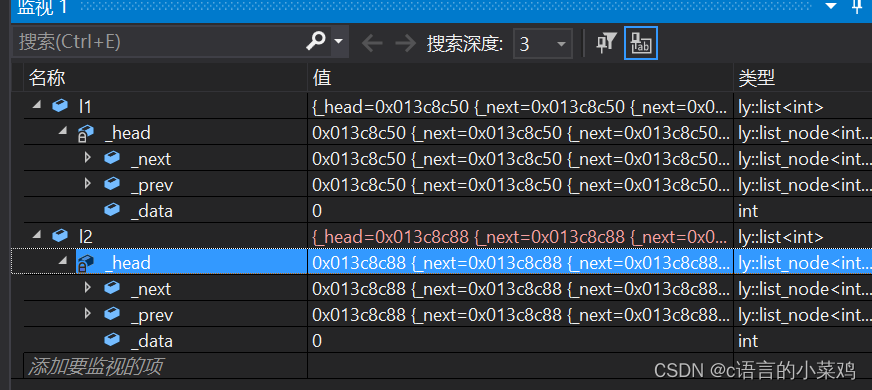
如下方代码所示就是我写的构造函数,因为这个链表是一个双向循环带头链表所以,直接new一个node在把哨兵位的next和prev指向自己,就创建出了一个链表,如下方图片可以看出创造出来了。
list()
{
_head = new node;
_head->_next = _head;
_head->_prev = _head;
}
三、迭代器
这里是把迭代器能用到的都写了,例如解引用,就是利用这个节点指针直接访问就可以了,但是考虑到了可能访问常量指针所以,这里就是利用模板参数进行访问的,第二个就是相当于访问数据了,因为在流输出的时候正常是访问不到,因为迭代器访问的是这个节点的额指针,这时重载了一个->就可以正常访问了,++就是下一个节点的地址,也就是这个节点里面存入的next,前置和后置在之前文章中都说过,这里就不详细介绍了,后置就是价格int以作区分,--也是类似操作,==与!=直接判断节点的地址是否相同就可以了。
Ref operator*()
{
return _node->_data;
}Ptr operator->()
{
return& _node->_data;
}self& operator++()
{
_node = _node->_next;
return *this;
}self operator++(int)
{
self tmp(*this);
_node = _node->_next;
return tmp;
}self& operator--()
{
_node = _node->_prev;
return *this;
}self operator--(int)
{
self tmp(*this);
_node = _node->_prev;
return tmp;
}bool operator==(const self& s)
{
return _node == s._node;
}bool operator!=(const self& s)
{
return _node != s._node;
}
四、增删
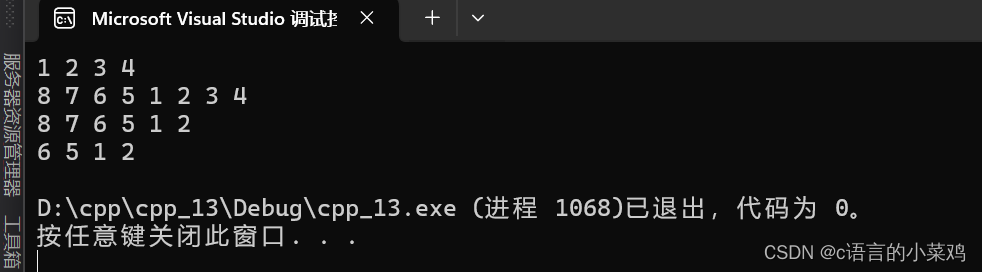
再写数据结构的顺序表的时候就知道了,头插尾插头删尾删是可以直接使用inster的,所以这里是直接写了inster在进行调用的,代码如下,测试代码如下,结果如图,这里是直接调用insert的所以就不测试这个了。
iterator begin()
{
return iterator(_head->_next);
}iterator end()
{
return iterator(_head);
}
const_iterator begin() const
{
return const_iterator(_head->_next);
}const_iterator end() const
{
return const_iterator(_head);
}void push_back(const T& x)
{
insert(end(),x);
}void push_front(const T& x)
{
insert(begin(), x);
}void pop_back()
{
erase(--end());
}void pop_front()
{
erase(begin());
}void insert(iterator pos,const T& x)
{
node* cur = pos._node;
node* prev = cur->_prev;
node* new_node = new node(x);
prev->_next = new_node;
new_node->_prev = prev;
new_node->_next = cur;
cur->_prev = new_node;
}void erase(iterator pos)
{
assert(pos != end());
node* prev = pos._node->_prev;
node* next = pos._node->_next;
prev->_next = next;
next->_prev = prev;
delete pos._node;
}void Test1()
{
list<int> l1;
l1.push_back(1);
l1.push_back(2);
l1.push_back(3);
l1.push_back(4);
print(l1);
l1.push_front(5);
l1.push_front(6);
l1.push_front(7);
l1.push_front(8);
print(l1);
l1.pop_back();
l1.pop_back();
print(l1);
l1.pop_front();
l1.pop_front();
print(l1);
}
五、代码
#pragma once
#include <assert.h>
namespace ly
{template<class T>struct list_node{list_node<T>* _next;list_node<T>* _prev;T _data;list_node(const T& x = T()):_next(nullptr), _prev(nullptr), _data(x){}};template<class T, class Ref, class Ptr>struct _list_iterator{typedef list_node<T> node;typedef _list_iterator<T, Ref, Ptr> self;node* _node;_list_iterator(node* n):_node(n){}Ref operator*(){return _node->_data;}Ptr operator->(){return& _node->_data;}self& operator++(){_node = _node->_next;return *this;}self operator++(int){self tmp(*this);_node = _node->_next;return tmp;}self& operator--(){_node = _node->_prev;return *this;}self operator--(int){self tmp(*this);_node = _node->_prev;return tmp;}bool operator==(const self& s){return _node == s._node;}bool operator!=(const self& s){return _node != s._node;}};template<class T>class list{public:typedef list_node<T> node;typedef _list_iterator<T, T&, T*> iterator;typedef _list_iterator<T, const T&, const T*> const_iterator;list(){_head = new node;_head->_next = _head;_head->_prev = _head;}iterator begin(){return iterator(_head->_next);}iterator end(){return iterator(_head);}const_iterator begin() const{return const_iterator(_head->_next);}const_iterator end() const{return const_iterator(_head);}void push_back(const T& x){insert(end(),x);}void push_front(const T& x){insert(begin(), x);}void pop_back(){erase(--end());}void pop_front(){erase(begin());}void insert(iterator pos,const T& x){node* cur = pos._node;node* prev = cur->_prev;node* new_node = new node(x);prev->_next = new_node;new_node->_prev = prev;new_node->_next = cur;cur->_prev = new_node;}void erase(iterator pos){assert(pos != end());node* prev = pos._node->_prev;node* next = pos._node->_next;prev->_next = next;next->_prev = prev;delete pos._node;}private:node* _head;};void print(list<int> l){list<int>::iterator it = l.begin();while (it != l.end()){cout << *it << ' ';it++;}cout << endl;}void Test1(){list<int> l1;l1.push_back(1);l1.push_back(2);l1.push_back(3);l1.push_back(4);print(l1);l1.push_front(5);l1.push_front(6);l1.push_front(7);l1.push_front(8);print(l1);l1.pop_back();l1.pop_back();print(l1);l1.pop_front();l1.pop_front();print(l1);}
}#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include <iostream>using namespace std;#include "list.h"int main()
{ly::Test1();
}