文章目录
- 问题背景
- pgrep指令
- help文档
- 使用示例
- 1. 列出匹配进程的PID和进程名称(-l)(默认只能从进程名的子集字符串匹配,如果要使用完整进程名的子集字符串匹配,请加-f参数,下同)
- 2. 列出匹配进程的PID和完整的命令行(-a)
- 3. 统计匹配进程的数量(-c)
- 4. 使用完整的进程名称进行匹配(-f)
- 5. 不区分大小写进行匹配(-i)
- 6. 选择最近启动的进程(n)
- 7. 选择最早启动的进程(-o)
- 8. 仅匹配给定父进程的子进程(-P)
- 9. 通过控制终端进行匹配(-t)
- 用途
- 命令
- 测试步骤
- 示例
- 10. 通过有效ID进行匹配(-u)
- 用途
- 命令
- 测试步骤
- 示例
- 11. 通过真实ID进行匹配(-U)
- 命令
- 示例
- 12. 精确匹配命令名称(-x)★★★
- 命令
- 示例
问题背景
按照我之前,在脚本中,获取除脚本自身进程之外与脚本同名进程号的方法:
ps -ef | grep "${SCRIPT_NAME}" | grep -v "grep" | awk '{print $2}' | grep -v "$PID"
这种方法有很大问题,莫名奇妙的,它无法正常过滤掉grep的进程(这里面还有点复杂,我一时半会也搞不明白咋回事,据说是grep会开子进程,并非grep那个子进程,而是开了一个与脚本相同的进程,导致出现问题,具体参考:linux shell脚本执行命令时创建子进程问题(特定的情况,例如后台运行、管道、分支或子shell等,脚本可能会创建子进程执行命令)grep)
后来我改用pgrep指令,用这个命令的好处是,不用使用grep命令了,它直接找出来就是进程号,而且不会带入额外的进程号,下面我们来看下pgrep指令的具体用法。
pgrep指令
pgrep命令用于根据进程的名称或其他属性来查找和列出匹配的进程ID(PID)。它可以根据不同的选项进行灵活的进程查找和过滤。
help文档
root@ubuntu:/ky/boot# pgrep --helpUsage:pgrep [options] <pattern>Options:-d, --delimiter <string> specify output delimiter-l, --list-name list PID and process name-a, --list-full list PID and full command line-v, --inverse negates the matching-w, --lightweight list all TID-c, --count count of matching processes-f, --full use full process name to match-g, --pgroup <PGID,...> match listed process group IDs-G, --group <GID,...> match real group IDs-i, --ignore-case match case insensitively-n, --newest select most recently started-o, --oldest select least recently started-P, --parent <PPID,...> match only child processes of the given parent-s, --session <SID,...> match session IDs-t, --terminal <tty,...> match by controlling terminal-u, --euid <ID,...> match by effective IDs-U, --uid <ID,...> match by real IDs-x, --exact match exactly with the command name-F, --pidfile <file> read PIDs from file-L, --logpidfile fail if PID file is not locked-r, --runstates <state> match runstates [D,S,Z,...]--ns <PID> match the processes that belong to the samenamespace as <pid>--nslist <ns,...> list which namespaces will be considered forthe --ns option.Available namespaces: ipc, mnt, net, pid, user, uts-h, --help display this help and exit-V, --version output version information and exitFor more details see pgrep(1).中文翻译:
root@ubuntu:/ky/boot# pgrep --help用法:pgrep [选项] <模式>选项:-d, --delimiter <字符串> 指定输出分隔符-l, --list-name 列出PID和进程名称-a, --list-full 列出PID和完整命令行-v, --inverse 反转匹配结果-w, --lightweight 列出所有TID-c, --count 统计匹配进程的数量-f, --full 使用完整进程名称进行匹配-g, --pgroup <PGID,...> 匹配指定的进程组ID-G, --group <GID,...> 匹配真实组ID-i, --ignore-case 不区分大小写进行匹配-n, --newest 选择最近启动的进程-o, --oldest 选择最早启动的进程-P, --parent <PPID,...> 仅匹配给定父进程的子进程-s, --session <SID,...> 匹配会话ID-t, --terminal <tty,...> 通过控制终端进行匹配-u, --euid <ID,...> 通过有效ID进行匹配-U, --uid <ID,...> 通过真实ID进行匹配-x, --exact 精确匹配命令名称-F, --pidfile <文件> 从文件中读取PID-L, --logpidfile 如果PID文件未锁定,则失败-r, --runstates <状态> 匹配运行状态 [D,S,Z,...]--ns <PID> 匹配与<pid>相同命名空间的进程--nslist <ns,...> 列出将用于--ns选项的命名空间可用的命名空间:ipc, mnt, net, pid, user, uts-h, --help 显示此帮助信息并退出-V, --version 输出版本信息并退出更多详细信息请参阅pgrep(1)。
请注意,上面的<pattern>是要匹配的进程名称或其他属性的模式。可以根据实际情况替换为具体的值。
使用示例
以下是pgrep命令不同选项的使用示例:
我们在这个容器中测试:
注意:我们首先要学会区分什么是进程的进程名!
进程名就是那个进程的可执行文件,进程名只有一个,除去进程名,其他的都是路径和参数。
比如/bin/bash /usr/local/bin/entrypoint.sh,进程名是bash
root@5940438e0ee6:/build/libevent# echo "=====输出所有进程完整进程信息:"
=====输出所有进程完整进程信息:
root@5940438e0ee6:/build/libevent# ps -ef
UID PID PPID C STIME TTY TIME CMD
root 1 0 0 Jun27 pts/0 00:00:00 /bin/bash /usr/local/bin/entrypoint.sh
root 7 1 0 Jun27 pts/0 00:02:56 ./kyai_rest
root 43 0 0 23:38 pts/1 00:00:00 /bin/bash
root 56 43 0 23:40 pts/1 00:00:00 ps -ef
root@5940438e0ee6:/build/libevent#
root@5940438e0ee6:/build/libevent# echo "输出所有进程进程名:"
=====输出所有进程进程名:
root@5940438e0ee6:/build/libevent# ps -e -o comm=
bash
kyai_rest
bash
ps
root@5940438e0ee6:/build/libevent#
1. 列出匹配进程的PID和进程名称(-l)(默认只能从进程名的子集字符串匹配,如果要使用完整进程名的子集字符串匹配,请加-f参数,下同)
pgrep -l <pattern>
pgrep --list-name <pattern>
示例:
root@5940438e0ee6:/build/libevent#
root@5940438e0ee6:/build/libevent# pgrep -l ky
7 kyai_rest
root@5940438e0ee6:/build/libevent#
root@5940438e0ee6:/build/libevent# pgrep -l ./
root@5940438e0ee6:/build/libevent#
root@5940438e0ee6:/build/libevent# pgrep -l ./ky
root@5940438e0ee6:/build/libevent#
root@5940438e0ee6:/build/libevent# pgrep -l -f ./ky
7 kyai_rest2. 列出匹配进程的PID和完整的命令行(-a)
pgrep -a <pattern>
pgrep --list-full <pattern>
示例:
root@5940438e0ee6:/build/libevent#
root@5940438e0ee6:/build/libevent# pgrep -a ky
7 ./kyai_rest
root@5940438e0ee6:/build/libevent#
root@5940438e0ee6:/build/libevent# pgrep -a ./ky
root@5940438e0ee6:/build/libevent#
root@5940438e0ee6:/build/libevent# pgrep -a -f ./ky
7 ./kyai_rest
root@5940438e0ee6:/build/libevent#
root@5940438e0ee6:/build/libevent# pgrep -af ./ky
7 ./kyai_rest
root@5940438e0ee6:/build/libevent#
root@5940438e0ee6:/build/libevent# pgrep -a bash
1 /bin/bash /usr/local/bin/entrypoint.sh
43 /bin/bash
root@5940438e0ee6:/build/libevent# 3. 统计匹配进程的数量(-c)
pgrep -c <pattern>
pgrep --count <pattern>
示例:
root@5940438e0ee6:/build/libevent#
root@5940438e0ee6:/build/libevent# pgrep -c ky
1
root@5940438e0ee6:/build/libevent#
root@5940438e0ee6:/build/libevent# pgrep -c bash
2
root@5940438e0ee6:/build/libevent#
root@5940438e0ee6:/build/libevent# pgrep -c ./ky
0
root@5940438e0ee6:/build/libevent#
root@5940438e0ee6:/build/libevent# pgrep -c -f ./ky
1
root@5940438e0ee6:/build/libevent# 4. 使用完整的进程名称进行匹配(-f)
pgrep -f <pattern>
pgrep --full <pattern>
示例:
root@5940438e0ee6:/build/libevent#
root@5940438e0ee6:/build/libevent# pgrep -f ky
7
root@5940438e0ee6:/build/libevent#
root@5940438e0ee6:/build/libevent# pgrep -f ./ky
7
root@5940438e0ee6:/build/libevent#
root@5940438e0ee6:/build/libevent# pgrep ./ky
root@5940438e0ee6:/build/libevent#
root@5940438e0ee6:/build/libevent# pgrep /usr/local/bin/entrypoint.sh
root@5940438e0ee6:/build/libevent#
root@5940438e0ee6:/build/libevent# pgrep -f /usr/local/bin/entrypoint.sh
1
root@5940438e0ee6:/build/libevent# 5. 不区分大小写进行匹配(-i)
pgrep -i <pattern>
pgrep --ignore-case <pattern>
示例:
root@5940438e0ee6:/build/libevent#
root@5940438e0ee6:/build/libevent# pgrep -i KyAi
7
root@5940438e0ee6:/build/libevent#
root@5940438e0ee6:/build/libevent# pgrep -i entry
root@5940438e0ee6:/build/libevent#
root@5940438e0ee6:/build/libevent# pgrep -i -f eNtry
1
root@5940438e0ee6:/build/libevent# 6. 选择最近启动的进程(n)
pgrep -n <pattern>
pgrep --newest <pattern>
示例:
root@5940438e0ee6:/build/libevent#
root@5940438e0ee6:/build/libevent# pgrep -a bash
1 /bin/bash /usr/local/bin/entrypoint.sh
43 /bin/bash
root@5940438e0ee6:/build/libevent#
root@5940438e0ee6:/build/libevent# pgrep -a -n bash
43 /bin/bash
root@5940438e0ee6:/build/libevent#
root@5940438e0ee6:/build/libevent# pgrep -n bash
43
root@5940438e0ee6:/build/libevent#
root@5940438e0ee6:/build/libevent# 7. 选择最早启动的进程(-o)
pgrep -o <pattern>
pgrep --oldest <pattern>
示例:
root@5940438e0ee6:/build/libevent#
root@5940438e0ee6:/build/libevent# pgrep -a bash
1 /bin/bash /usr/local/bin/entrypoint.sh
43 /bin/bash
root@5940438e0ee6:/build/libevent#
root@5940438e0ee6:/build/libevent# pgrep -a -o bash
1 /bin/bash /usr/local/bin/entrypoint.sh
root@5940438e0ee6:/build/libevent#
root@5940438e0ee6:/build/libevent# pgrep -o bash
1
root@5940438e0ee6:/build/libevent# 8. 仅匹配给定父进程的子进程(-P)
pgrep -P <PPID> <pattern>
pgrep --parent <PPID> <pattern>
示例:
比如0号进程有1号何2号两个子进程:
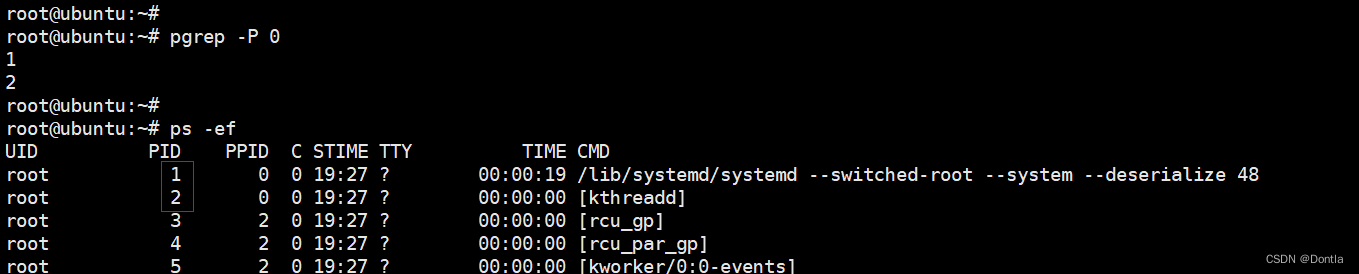
用pgrep -P 0能将0号进程的子进程找出来:
root@ubuntu:~#
root@ubuntu:~# pgrep -P 0
1
2
root@ubuntu:~# 在查找到时对子进程筛选:
root@ubuntu:~#
root@ubuntu:~# pgrep -P 0 "system"
1
root@ubuntu:~#
root@ubuntu:~# pgrep -P 0 "thread"
2
root@ubuntu:~#
root@ubuntu:~# 注意:有时用-f参数从非进程名的字符串段匹配筛选时,注意双引号的使用,以及使用双引号后,仍应注意的问题:
下面测试中:pgrep -f -P 0 --system和pgrep -f -P 0 "--system"都是报错的,只有pgrep -f -P 0 " --system"没出问题。
root@ubuntu:~#
root@ubuntu:~# pgrep -f -P 0 --system
pgrep: unrecognized option '--system'Usage:pgrep [options] <pattern>Options:-d, --delimiter <string> specify output delimiter-l, --list-name list PID and process name-a, --list-full list PID and full command line-v, --inverse negates the matching-w, --lightweight list all TID-c, --count count of matching processes-f, --full use full process name to match-g, --pgroup <PGID,...> match listed process group IDs-G, --group <GID,...> match real group IDs-i, --ignore-case match case insensitively-n, --newest select most recently started-o, --oldest select least recently started-P, --parent <PPID,...> match only child processes of the given parent-s, --session <SID,...> match session IDs-t, --terminal <tty,...> match by controlling terminal-u, --euid <ID,...> match by effective IDs-U, --uid <ID,...> match by real IDs-x, --exact match exactly with the command name-F, --pidfile <file> read PIDs from file-L, --logpidfile fail if PID file is not locked-r, --runstates <state> match runstates [D,S,Z,...]--ns <PID> match the processes that belong to the samenamespace as <pid>--nslist <ns,...> list which namespaces will be considered forthe --ns option.Available namespaces: ipc, mnt, net, pid, user, uts-h, --help display this help and exit-V, --version output version information and exitFor more details see pgrep(1).
root@ubuntu:~#
root@ubuntu:~# pgrep -f -P 0 "--system"
pgrep: unrecognized option '--system'Usage:pgrep [options] <pattern>Options:-d, --delimiter <string> specify output delimiter-l, --list-name list PID and process name-a, --list-full list PID and full command line-v, --inverse negates the matching-w, --lightweight list all TID-c, --count count of matching processes-f, --full use full process name to match-g, --pgroup <PGID,...> match listed process group IDs-G, --group <GID,...> match real group IDs-i, --ignore-case match case insensitively-n, --newest select most recently started-o, --oldest select least recently started-P, --parent <PPID,...> match only child processes of the given parent-s, --session <SID,...> match session IDs-t, --terminal <tty,...> match by controlling terminal-u, --euid <ID,...> match by effective IDs-U, --uid <ID,...> match by real IDs-x, --exact match exactly with the command name-F, --pidfile <file> read PIDs from file-L, --logpidfile fail if PID file is not locked-r, --runstates <state> match runstates [D,S,Z,...]--ns <PID> match the processes that belong to the samenamespace as <pid>--nslist <ns,...> list which namespaces will be considered forthe --ns option.Available namespaces: ipc, mnt, net, pid, user, uts-h, --help display this help and exit-V, --version output version information and exitFor more details see pgrep(1).
root@ubuntu:~#
root@ubuntu:~#
root@ubuntu:~# pgrep -f -P 0 " --system"
1
root@ubuntu:~#
root@ubuntu:~# 9. 通过控制终端进行匹配(-t)
用途
指定特定终端名称进行搜索的用途之一是限定搜索范围。在多用户或多终端环境中,可能会有多个终端同时运行着相同的进程。通过指定终端名称,你可以仅在特定终端中搜索匹配的进程,而不是在所有终端中搜索。
这对于需要在特定终端上执行操作或监控特定终端上的进程非常有用。例如,你可能希望在某个特定的终端上查找正在运行的某个应用程序的进程,或者在某个特定的终端上查找与某个用户相关的进程。
另外,指定终端名称还可以用于在脚本或自动化任务中进行进程管理。通过指定特定的终端,你可以确保只对特定终端上的进程进行操作,而不会影响其他终端上的进程。
总而言之,指定特定终端名称进行搜索可以提供更精确和有针对性的进程查找和管理。
命令
pgrep -t <tty> <pattern>
pgrep --terminal <tty> <pattern>
测试步骤
按照以下步骤进行测试:
- 打开终端。
- 运行
tty命令,获取当前终端的名称。例如,如果终端名称是/dev/tty1,则将<tty>替换为tty1。 - 运行
pgrep -t <tty> <pattern>命令,将<pattern>替换为你想要查找的进程名称或关键字。例如,如果你想要查找所有运行着的bash进程,可以运行pgrep -t tty1 bash。 - 如果命令成功执行,它将输出匹配的进程 ID。
- 你也可以尝试运行
pgrep --terminal <tty> <pattern>命令,它与上述命令的作用相同。
请注意,pgrep 命令用于在进程列表中查找匹配的进程,并输出它们的进程 ID。<tty> 是终端名称,<pattern> 是要查找的进程名称或关键字。你需要根据你的实际情况替换这些参数。
示例
root@ubuntu:~#
root@ubuntu:~# tty
/dev/pts/0
root@ubuntu:~#
root@ubuntu:~#
root@ubuntu:~# pgrep -t /dev/pts/0 bash
root@ubuntu:~#
root@ubuntu:~# pgrep -t /dev/pts/0 sy
root@ubuntu:~#
root@ubuntu:~# pgrep -t /dev/pts/0
root@ubuntu:~#
root@ubuntu:~# pgrep -t "/dev/pts/0"
root@ubuntu:~#
root@ubuntu:~# pgrep -t "/dev/pts/0" bash
root@ubuntu:~#
root@ubuntu:~# 尴尬,我这啥也搜不出来
10. 通过有效ID进行匹配(-u)
用途
pgrep -u <ID> <pattern> 和 pgrep --euid <ID> <pattern> 命令用于在指定用户 ID 或有效用户 ID 下查找匹配的进程。
<ID>参数用于指定用户 ID 或有效用户 ID。你可以使用用户的用户名或用户 ID 来替换<ID>。<pattern>参数用于指定要查找的进程名称或关键字。
命令
pgrep -u <ID> <pattern>
pgrep --euid <ID> <pattern>
测试步骤
- 打开终端。
- 运行
id命令,获取当前用户的用户 ID 和有效用户 ID。例如,如果用户 ID 是1000,有效用户 ID 是1000,则将<ID>替换为1000。 - 运行
pgrep -u <ID> <pattern>命令,将<pattern>替换为你想要查找的进程名称或关键字。例如,如果你想要查找当前用户下所有运行着的bash进程,可以运行pgrep -u 1000 bash。 - 如果命令成功执行,它将输出匹配的进程 ID。
- 你也可以尝试运行
pgrep --euid <ID> <pattern>命令,它与上述命令的作用相同。
请注意,pgrep 命令用于在进程列表中查找匹配的进程,并输出它们的进程 ID。-u 或 --euid 选项用于指定用户 ID 或有效用户 ID。<ID> 是用户 ID 或有效用户 ID,<pattern> 是要查找的进程名称或关键字。你需要根据你的实际情况替换这些参数。
示例
root@ubuntu:~#
root@ubuntu:~# id
uid=0(root) gid=0(root) groups=0(root)
root@ubuntu:~#
root@ubuntu:~#
root@ubuntu:~# pgrep -u 0000 bash
3058
3955
23187
root@ubuntu:~#
root@ubuntu:~# pgrep -u 0 bash
3058
3955
23187
root@ubuntu:~#
root@ubuntu:~# pgrep -u 1000 bash
root@ubuntu:~#
root@ubuntu:~# ps -ef | grep bash
root 1061 1 0 19:27 ? 00:00:00 /bin/bash /etc/systemd/nvmemwarning.sh
root 1260 1 0 19:28 ? 00:00:00 /bin/bash /ky/boot/kyai_nv_server.sh
root 1276 1 0 19:28 ? 00:00:00 /bin/bash /etc/systemd/nvgetty.sh
root 3058 2914 0 19:28 pts/0 00:00:00 /bin/bash /usr/local/bin/entrypoint.sh
root 3955 3915 0 19:28 pts/0 00:00:00 /bin/bash /usr/local/bin/entrypoint.sh
root 23187 23106 0 21:46 pts/0 00:00:00 -bash
root 36607 23187 0 23:39 pts/0 00:00:00 grep --color=auto bash
root@ubuntu:~#
root@ubuntu:~# 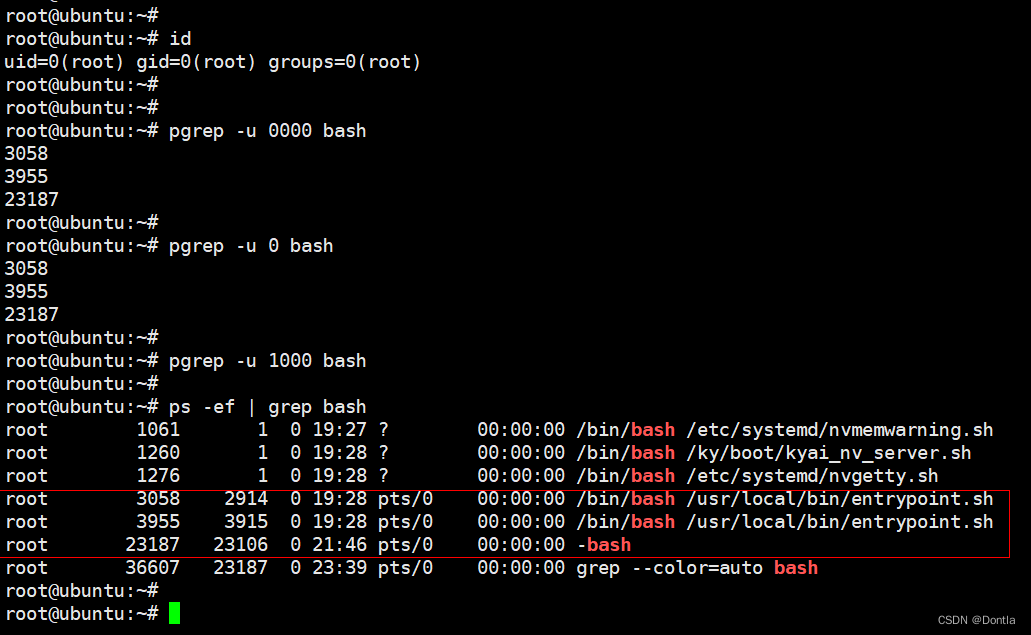
11. 通过真实ID进行匹配(-U)
具体请参见有效id和真实id,我目前还不是很理解。
命令
pgrep -U <ID> <pattern>
pgrep --uid <ID> <pattern>
示例
root@ubuntu:~#
root@ubuntu:~# pgrep -U 0000 bash
3058
3955
23187
root@ubuntu:~#
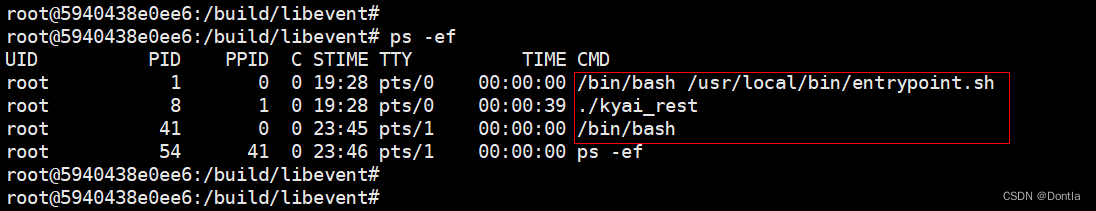
root@ubuntu:~# 12. 精确匹配命令名称(-x)★★★
命令
pgrep -x <pattern>
pgrep --exact <pattern>
示例
root@5940438e0ee6:/build/libevent#
root@5940438e0ee6:/build/libevent#
root@5940438e0ee6:/build/libevent# ps -ef
UID PID PPID C STIME TTY TIME CMD
root 1 0 0 19:28 pts/0 00:00:00 /bin/bash /usr/local/bin/entrypoint.sh
root 8 1 0 19:28 pts/0 00:00:39 ./kyai_rest
root 41 0 0 23:45 pts/1 00:00:00 /bin/bash
root 54 41 0 23:46 pts/1 00:00:00 ps -ef
root@5940438e0ee6:/build/libevent#
root@5940438e0ee6:/build/libevent#
root@5940438e0ee6:/build/libevent# pgrep -x kyai
root@5940438e0ee6:/build/libevent#
root@5940438e0ee6:/build/libevent# pgrep -x kyai_rest
8
root@5940438e0ee6:/build/libevent#
root@5940438e0ee6:/build/libevent# pgrep -x -f kyai_rest
root@5940438e0ee6:/build/libevent#
root@5940438e0ee6:/build/libevent# pgrep -x -f ./kyai_rest
8
root@5940438e0ee6:/build/libevent#
root@5940438e0ee6:/build/libevent# pgrep -x bash
1
41
root@5940438e0ee6:/build/libevent#
root@5940438e0ee6:/build/libevent# pgrep -x -f bash
root@5940438e0ee6:/build/libevent#
root@5940438e0ee6:/build/libevent# pgrep -x -f /bin/bash
41
root@5940438e0ee6:/build/libevent#
root@5940438e0ee6:/build/libevent# pgrep -x -f /bin/bash /usr/local/bin/entrypoint.sh
pgrep: only one pattern can be provided
Try `pgrep --help' for more information.
root@5940438e0ee6:/build/libevent#
root@5940438e0ee6:/build/libevent# pgrep -x -f "/bin/bash /usr/local/bin/entrypoint.sh"
1
root@5940438e0ee6:/build/libevent#
root@5940438e0ee6:/build/libevent# 注意:精准匹配,是包含参数的所有完整匹配