目录
- 一、核心注解
- 二、Spring Bean 相关
- 2.1 @Autowired
- 2.2 @Component, @Repository, @Service, @Controller
- 2.3 @RestController 与 @Controller
- 2.4 @Configuration 与 @Component
- 2.5 @Scope
- 三、处理常见的 HTTP 请求类型
- 3.1 GET 请求
- 3.2 POST 请求
- 3.3 PUT 请求
- 3.4 DELETE 请求
- 3.5 PATCH 请求
- 四、前后端传值
- 4.1 @PathVariable 和 @RequestParam
- 4.2 @RequestBody
- 五、读取配置信息
- 5.1 @Value
- 5.2 @ConfigurationProperties
- 5.3 @PropertySource
- 六、参数校验
- 6.1 常用的字段验证注解
- 6.2 验证请求体(RequestBody)
- 6.3 验证请求参数(Path Variables 和 Request Parameters)
- 七、全局处理 Controller 层异常
- 八、Spring Data JPA 相关
- 8.1 创建数据表
- 8.2 创建主键
- 8.3 设置字段类型
- 8.4 指定不持久化特定字段
- 8.5 声明大字段
- 8.6 创建枚举类型的字段
- 8.7 删除 / 修改数据
- 8.8 增加审计功能
- 8.9 声明关联关系
- 九、事务 @Transactional
- 十、JSON 数据处理
- 10.1 过滤 json 数据
- 10.2 格式化 json 数据
- 10.3 扁平化对象
- 十一、测试相关的注解
在Spring和SpringBoot中,注解是一种非常重要的编程方式,它可以简化代码,提高开发效率。

一、核心注解
@SpringBootApplication是SpringBoot应用程序的核心注解,通常用于主类上。它包含了以下三个注解:
- @Configuration:表示该类是一个配置类,用于定义Spring的配置信息。允许在 Spring 上下文中注册额外的 bean 或导入其他配置类
- @EnableAutoConfiguration:表示启用自动配置,SpringBoot会根据项目中的依赖自动配置相应的组件。
- @ComponentScan:表示启用组件扫描,SpringBoot会自动扫描当前包及其子包下的所有组件。扫描被@Component (@Repository,@Service,@Controller)注解的 bean,注解默认会扫描该类所在的包下所有的类。
这个注解是 Spring Boot 项目的基石,创建 SpringBoot 项目之后会默认在主类加上。
@SpringBootApplication
public class Application {public static void main(String[] args) {SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);}
}
package org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure;
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@SpringBootConfiguration
@EnableAutoConfiguration
@ComponentScan(excludeFilters = {@Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = TypeExcludeFilter.class),@Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter.class) })
public @interface SpringBootApplication {......
}package org.springframework.boot;
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Configuration
public @interface SpringBootConfiguration {......
}
注意事项:
- 主类应放在根包名下,以便能够扫描到所有的组件。
- 如果需要自定义配置,可以在@SpringBootApplication注解中添加属性,例如:exclude用于排除自动配置的类。
二、Spring Bean 相关
2.1 @Autowired
@Autowired是Spring的核心注解之一,用于实现依赖注入。它可以自动装配Bean,无需手动创建和管理对象。被注入进的类同样要被 Spring 容器管理比如:Service 类注入到 Controller 类中。
@RestController
public class UserController {@Autowiredprivate UserService userService;@GetMapping("/users")public List<User> getUsers() {return userService.getUsers();}
}
注意事项:
- 如果有多个实现类,可以使用@Qualifier注解指定Bean的名称。
- 如果允许注入的Bean不存在,可以使用required属性设置为false。
2.2 @Component, @Repository, @Service, @Controller
一般使用 @Autowired 注解让 Spring 容器帮我们自动装配 bean。要想把类标识成可用于 @Autowired 注解自动装配的 bean 的类,可以采用以下注解实现:
@Component:通用的注解,可标注任意类为 Spring 组件。如果一个 Bean 不知道属于哪个层,可以使用@Component 注解标注。@Repository:对应持久层即 Dao 层,主要用于数据库相关操作。@Service:对应服务层,主要涉及一些复杂的逻辑,需要用到 Dao 层。@Controller:对应 Spring MVC 控制层,主要用于接受用户请求并调用 Service 层返回数据给前端页面。
2.3 @RestController 与 @Controller
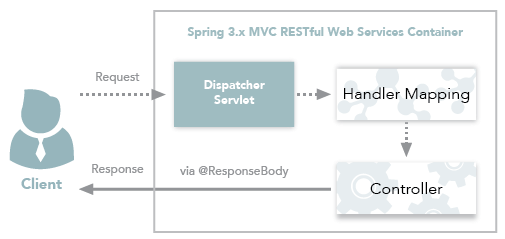
@RestController注解是@Controller和@ResponseBody的合集,表示这是个控制器 bean,并且是将函数的返回值直接填入 HTTP 响应体中,是 REST 风格的控制器。其中,@ResponseBody:表示将方法返回值作为HTTP响应体,而不是视图名称。
在控制器类上添加@RestController注解,然后在方法上添加相应的HTTP请求映射注解,例如:@GetMapping、@PostMapping等。使用方法如下:
@RestController
public class HelloController {@GetMapping("/hello")public String hello() {return "Hello, SpringBoot!";}
}
注意事项:
- 如果需要返回视图,可以使用@Controller注解替换@RestController。
- 如果需要在方法上单独使用@ResponseBody,可以将@RestController替换为@Controller。
@RestController 与 @Controller的区别:
- @Controller 返回一个页面
单独使用 @Controller 不加 @ResponseBody的话一般使用在要返回一个视图的情况,这种情况属于比较传统的Spring MVC 的应用,对应于前后端不分离的情况。

- @RestController 返回JSON 或 XML 形式数据
@RestController只返回对象,对象数据直接以 JSON 或 XML 形式写入 HTTP 响应(Response)中,这种情况属于 RESTful Web服务,这也是目前日常开发所接触的最常用的情况(前后端分离)。

- @Controller +@ResponseBody 返回JSON 或 XML 形式数据
如果需要在Spring4之前开发 RESTful Web服务的话,需要使用@Controller 并结合@ResponseBody注解.也就是说@Controller +@ResponseBody = @RestController(Spring 4 之后新加的注解)。
2.4 @Configuration 与 @Component
@Configuration是Spring的核心注解之一,用于定义配置类。它表示该类是一个Java配置类,可以用来替代XML配置文件。其使用时是在类上添加@Configuration注解,然后在方法上添加@Bean注解定义Bean。
@Configuration
public class AppConfig {@Beanpublic UserService userService() {return new UserService();}
}
注意事项:
- 配置类通常与@ComponentScan、@EnableAutoConfiguration等注解一起使用。
- 如果需要导入其他配置类,可以使用@Import注解。
2.5 @Scope
@Scope用来声明 Spring Bean 的作用域,使用方法:
@Bean
@Scope("singleton")
public Person personSingleton() {return new Person();
}
四种常见的 Spring Bean 的作用域:
- singleton : 唯一 bean 实例,Spring 中的 bean 默认都是单例的。
- prototype : 每次请求都会创建一个新的 bean 实例。
- request : 每一次 HTTP 请求都会产生一个新的 bean,该 bean 仅在当前 HTTP request 内有效。
- session : 每一个 HTTP Session 会产生一个新的 bean,该 bean 仅在当前 HTTP session 内有效。
三、处理常见的 HTTP 请求类型
几种常见的请求类型如下:
GET:请求从服务器获取特定资源。举个例子:GET /users(获取所有用户)POST:在服务器上创建一个新的资源。举个例子:POST /users(创建用户)PUT:更新服务器上的资源(客户端提供更新后的整个资源)。举个例子:PUT /users/1(更新编号为 1 的用户)DELETE:从服务器删除特定的资源。举个例子:DELETE /users/1(删除编号为 1 的用户)PATCH:更新服务器上的资源(客户端提供更改的属性,可以看做作是部分更新),使用的比较少。
3.1 GET 请求
@GetMapping(“users”) 等价于@RequestMapping(value=“/users”,method=RequestMethod.GET)
@GetMapping("/users")
public ResponseEntity<List<User>> getAllUsers() {return userRepository.findAll();
}
@GetMapping("/getUser/{userId}")
public ResponseEntity<User> getUser(@PathVariable(value = "userId") Long userId) {return userRepository.find(userId);
}
3.2 POST 请求
@PostMapping(“users”) 等价于@RequestMapping(value=“/users”,method=RequestMethod.POST)关于@RequestBody注解的使用,在后面的“前后端传值”会解释。
@PostMapping("/users")
public ResponseEntity<User> createUser(@Valid @RequestBody UserCreateRequest userCreateRequest) {return userRespository.save(userCreateRequest);
}
3.3 PUT 请求
@PutMapping(“/users/{userId}”) 等价于@RequestMapping(value=“/users/{userId}”,method=RequestMethod.PUT)
@PutMapping("/users/{userId}")
public ResponseEntity<User> updateUser(@PathVariable(value = "userId") Long userId, @Valid @RequestBody UserUpdateRequest userUpdateRequest) {......
}
3.4 DELETE 请求
@DeleteMapping(“/users/{userId}”)等价于@RequestMapping(value=“/users/{userId}”,method=RequestMethod.DELETE)
@DeleteMapping("/users/{userId}")
public ResponseEntity deleteUser(@PathVariable(value = "userId") Long userId){......
}
3.5 PATCH 请求
一般实际项目中,都是 PUT 不够用了之后才用 PATCH 请求去更新数据。使用PUT请求时,会考虑将整个资源进行替换,适用于需要对整个资源进行更新或替换的情况。这可以确保资源的完整性和一致性。而当只需要对资源的部分属性或字段进行更新时,可以选择使用PATCH请求。PATCH请求更灵活,能够实现部分更新,同时避免了不必要的数据传输和处理,从而提高了效率。
@PatchMapping("/profile")
public ResponseEntity updateStudent(@RequestBody UserUpdateRequest userUpdateRequest) {userRepository.updateDetail(userUpdateRequest);return ResponseEntity.ok().build();}
四、前后端传值
4.1 @PathVariable 和 @RequestParam
@PathVariable用于获取路径参数,@RequestParam用于获取查询参数。
@GetMapping("/user/{userId}")
public List<Teacher> getKlassRelatedTeachers(@PathVariable("userId") Long userId,@RequestParam(value = "type", required = false) String type ) {...
}
如果我们请求的 url 是:/user/123456?type=web,那么服务获取到的数据就是:userId=123456,type=web。
4.2 @RequestBody
用于读取 Request 请求(可能是 POST,PUT,DELETE,GET 请求)的 body 部分并且Content-Type 为 application/json 格式的数据,接收到数据之后会自动将数据绑定到 Java 对象上去。系统会使用HttpMessageConverter或者自定义的HttpMessageConverter将请求的 body 中的 json 字符串转换为 java 对象。
有一个注册的接口:
@PostMapping("/sign-up")
public ResponseEntity signUp(@RequestBody @Valid UserRegisterRequest userRegisterRequest) {userService.save(userRegisterRequest);return ResponseEntity.ok().build();
}
其中,UserRegisterRequest对象:
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class UserRegisterRequest {private String userName;private String password;private String fullName;
}
发送 post 请求到这个接口,并且 body 携带 JSON 数据:
{ "userName": "coder", "fullName": "shuangkou", "password": "123456" }
五、读取配置信息
很多时候我们需要将一些常用的配置信息比如阿里云 oss、发送短信、微信认证的相关配置信息等等放到配置文件中。Spring 为我们提供了哪些方式帮助我们从配置文件中读取这些配置信息。
数据源application.yml内容如下:
myconfig: 我的配置my-profile:name: ltemail: lt@qq.comlibrary:location: 位置books:- name: Javadescription: Java语言。- name: JavaScriptdescription: JavaScript语言。
5.1 @Value
使用 @Value(“${property}”) 读取比较简单的配置信息:
@Value("${myconfig}")
String myconfig;
5.2 @ConfigurationProperties
通过@ConfigurationProperties读取配置信息并与 bean 绑定。可以像使用普通的 Spring bean 一样,将其注入到类中使用。
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "library")
class LibraryProperties {@NotEmptyprivate String location;private List<Book> books;@Data@ToStringstatic class Book {String name;String description;}......
}
5.3 @PropertySource
@PropertySource读取指定 properties 文件
@Component
@PropertySource("classpath:website.properties")class WebSite {@Value("${url}")private String url;
}
六、参数校验
数据的校验在前后端都需要,避免用户绕过浏览器直接通过一些 HTTP 工具直接向后端请求一些违法数据。
JSR(Java Specification Requests)是一套 JavaBean 参数校验的标准,它定义了很多常用的校验注解,可以直接将这些注解加在我JavaBean 的属性上面,这样就可以在校验的时候进行校验了。校验的时候实际用的是 Hibernate Validator 框架。Hibernate Validator 是 Hibernate 团队最初的数据校验框架,SpringBoot 项目的 spring-boot-starter-web( 2.3.11.RELEASE前的版本) 依赖中已经有 hibernate-validator 包,不需要引用相关依赖;但是更新版本的 spring-boot-starter-web 依赖中不再有 hibernate-validator 包,需要自己引入 spring-boot-starter-validation 依赖。
6.1 常用的字段验证注解
- @NotEmpty 被注释的字符串的不能为 null 也不能为空
- @NotBlank 被注释的字符串非 null,并且必须包含一个非空白字符
- @Null 被注释的元素必须为 null
- @NotNull 被注释的元素必须不为 null
- @AssertTrue 被注释的元素必须为 true
- @AssertFalse 被注释的元素必须为 false
- @Pattern(regex=,flag=)被注释的元素必须符合指定的正则表达式
- @Email 被注释的元素必须是 Email 格式。
- @Min(value)被注释的元素必须是一个数字,其值必须大于等于指定的最小值
- @Max(value)被注释的元素必须是一个数字,其值必须小于等于指定的最大值
- @DecimalMin(value)被注释的元素必须是一个数字,其值必须大于等于指定的最小值
- @DecimalMax(value) 被注释的元素必须是一个数字,其值必须小于等于指定的最大值
- @Size(max=, min=)被注释的元素的大小必须在指定的范围内
- @Digits(integer, fraction)被注释的元素必须是一个数字,其值必须在可接受的范围内
- @Past被注释的元素必须是一个过去的日期
- @Future 被注释的元素必须是一个将来的日期
6.2 验证请求体(RequestBody)
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class Person {@NotNull(message = "classId 不能为空")private String classId;@Size(max = 33)@NotNull(message = "name 不能为空")private String name;@Pattern(regexp = "((^Man$|^Woman$|^UGM$))", message = "sex 值不在可选范围")@NotNull(message = "sex 不能为空")private String sex;@Email(message = "email 格式不正确")@NotNull(message = "email 不能为空")private String email;
}
在需要验证的参数上加上了@Valid注解,如果验证失败,它将抛出MethodArgumentNotValidException。
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api")
public class PersonController {@PostMapping("/person")public ResponseEntity<Person> getPerson(@RequestBody @Valid Person person) {return ResponseEntity.ok().body(person);}
}
6.3 验证请求参数(Path Variables 和 Request Parameters)
不要忘记在类上加上 @Valid 注解了,这个参数可以告诉 Spring 去校验方法参数。
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api")
@Validated
public class PersonController {@GetMapping("/person/{id}")public ResponseEntity<Integer> getPersonById(@Valid @PathVariable("id") @Max(value = 5,message = "超过 id 的范围了") Integer id) {return ResponseEntity.ok().body(id);}
}
七、全局处理 Controller 层异常
相关注解:
- @ControllerAdvice : 定义全局异常处理类
- @ExceptionHandler : 声明异常处理方法
如果方法参数不对的话就会抛出MethodArgumentNotValidException,进而处理这个异常。
@ControllerAdvice
@ResponseBody
public class GlobalExceptionHandler {//请求参数异常处理@ExceptionHandler(MethodArgumentNotValidException.class)public ResponseEntity<?> handleMethodArgumentNotValidException(MethodArgumentNotValidException ex, HttpServletRequest request) {......}
}
八、Spring Data JPA 相关
Java Persistence API (JPA) 是一种基于 ORM (Object-Relational Mapping) 技术的 Java EE 规范。它主要用于将 Java 对象映射到关系型数据库中,以便于对数据进行持久化操作。JPA详解可以参考博文:Spring Data JPA 详解
8.1 创建数据表
- @Entity 声明一个类对应一个数据库实体。
- @Table 设置表名
@Entity
@Table(name = "role")
public class Role {@Id@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)private Long id;private String name;private String description;
}8.2 创建主键
- @Id:声明一个字段为主键。
使用@Id声明之后,我们还需要定义主键的生成策略。我们可以使用 @GeneratedValue 指定主键生成策略。
主键生成的两种方法:
-
通过 @GeneratedValue直接使用 JPA 内置提供的四种主键生成策略来指定主键生成策略。
@Id @GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY) private Long id;JPA 使用枚举定义了 4 种常见的主键生成策略,如下:
public enum GenerationType {// 使用一个特定的数据库表格来保存主键,持久化引擎通过关系数据库的一张特定的表格来生成主键TABLE,// 在某些数据库中,不支持主键自增长,比如Oracle、PostgreSQL其提供了一种叫做"序列"的机制生成主键SEQUENCE,// 主键自增长IDENTITY,// 把主键生成策略交给持久化引擎,持久化引擎会根据数据库在以上三种主键生成 策略中选择其中一种AUTO }注意:@GeneratedValue注解默认使用的策略是GenerationType.AUTO。一般使用 MySQL 数据库的话,使用GenerationType.IDENTITY策略比较普遍一点(分布式系统的话需要另外考虑使用分布式 ID)。
-
通过 @GenericGenerator声明一个主键策略,然后 @GeneratedValue使用这个策略
@Id @GeneratedValue(generator = "IdentityIdGenerator") @GenericGenerator(name = "IdentityIdGenerator", strategy = "identity") private Long id;等价于:
@Id @GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY) private Long id;
8.3 设置字段类型
- @Column 声明字段。
示例:
-
设置属性 userName 对应的数据库字段名为 user_name,长度为 20,非空
@Column(name = "user_name", nullable = false, length=20) private String userName; -
设置字段类型并且加默认值。
@Column(columnDefinition = "tinyint(1) default 0") private Boolean enabled;
8.4 指定不持久化特定字段
- @Transient:声明不需要与数据库映射的字段,在保存的时候不需要保存进数据库 。
如果想让secrect 这个字段不被持久化,可以使用 @Transient关键字声明。
@Entity(name="USER")
public class User {@Transientprivate String secrect;
}
除了 @Transient关键字声明, 还可以采用下面几种方法:
static String secrect; // 由于静态而不持久化
final String secrect = "Satish"; // 由于是final而不持久化
transient String secrect; // 由于瞬态而不持久化
8.5 声明大字段
- @Lob:声明某个字段为大字段。
大字段通常是指存储较大数据量的字段,例如文本、二进制数据(如图像或文件)、长字符串等。这些数据通常超过了数据库表的普通列大小限制。
@Lob //声明content为大字段
@Basic(fetch = FetchType.EAGER) //指定Lob类型数据的获取策略, FetchType.EAGER为非延迟加载,FetchType.LAZY为延迟加载
@Column(name = "content", columnDefinition = "LONGTEXT NOT NULL") //columnDefinition 指定数据表对应的 Lob 字段类型
private String content;
8.6 创建枚举类型的字段
- @Enumerated注解修饰枚举字段。
声明定义枚举数据:
public enum Gender {MALE("男性"),FEMALE("女性");private String value;Gender(String str){value=str;}
}
使用方法如下,数据库里面对应存储的是 MALE 或 FEMALE。
@Entity
@Table(name = "role")
public class Role {@Id@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)private Long id;@Enumerated(EnumType.STRING)private Gender gender;
}
8.7 删除 / 修改数据
- @Modifying 注解提示 JPA 该操作是修改操作,注意还要配合@Transactional注解使用。
@Repository
public interface UserRepository extends JpaRepository<User, Integer> {@Modifying@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)void deleteByUserName(String userName);
}
8.8 增加审计功能
- @CreatedDate: 表示该字段为创建时间字段,在这个实体被 insert 的时候,会设置值
- @CreatedBy :表示该字段为创建人,在这个实体被 insert 的时候,会设置值
- @LastModifiedDate、@LastModifiedBy同理。
- @EnableJpaAuditing:开启 JPA 审计功能。
只要继承了 AbstractAuditBase的类都会默认加上下面四个字段:
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
@MappedSuperclass
@EntityListeners(value = AuditingEntityListener.class)
public abstract class AbstractAuditBase {@CreatedDate@Column(updatable = false)@JsonIgnoreprivate Instant createdAt;@LastModifiedDate@JsonIgnoreprivate Instant updatedAt;@CreatedBy@Column(updatable = false)@JsonIgnoreprivate String createdBy;@LastModifiedBy@JsonIgnoreprivate String updatedBy;
}
对应的审计功能对应地配置类可能是下面这样的(Spring Security 项目):
@Configuration
@EnableJpaAuditing
public class AuditSecurityConfiguration {@BeanAuditorAware<String> auditorAware() {return () -> Optional.ofNullable(SecurityContextHolder.getContext()).map(SecurityContext::getAuthentication).filter(Authentication::isAuthenticated).map(Authentication::getName);}
}
8.9 声明关联关系
- @OneToOne 声明一对一关系
- @OneToMany 声明一对多关系
- @ManyToOne 声明多对一关系
- @ManyToMany 声明多对多关系
九、事务 @Transactional
- @Transactional 注解使用在要开启事务的方法上,开启该方法的事务
- @作用于类:Transactional 注解一般可以作用在类或者方法上。作用于类:
- 当把@Transactional 注解放在类上时,表示所有该类的 public 方法都配置相同的事务属性信息。
- 作用于方法:当类配置了@Transactional,方法也配置了@Transactional,方法的事务会覆盖类的事务配置信息。
作用于方法示例如下:
@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)
public void save() {
}
其中, Exception 分为运行时异常 RuntimeException 和非运行时异常。在@Transactional注解中如果不配置rollbackFor属性,那么事务只会在遇到RuntimeException的时候才会回滚,加上rollbackFor=Exception.class,可以让事务在遇到非运行时异常时也回滚。
十、JSON 数据处理
10.1 过滤 json 数据
- @JsonIgnoreProperties 作用在类上用于过滤掉特定字段不返回或者不解析。
//生成json时将userRoles属性过滤 @JsonIgnoreProperties({"userRoles"}) public class User {private String userName;private String password;private List<UserRole> userRoles = new ArrayList<>(); } - @JsonIgnore一般用于类的属性上,作用和上面的@JsonIgnoreProperties 一样。
public class User {private String userName;private String password;//生成json时将userRoles属性过滤@JsonIgnoreprivate List<UserRole> userRoles = new ArrayList<>(); }
10.2 格式化 json 数据
- @JsonFormat一般用来格式化 json 数据。
@JsonFormat(shape=JsonFormat.Shape.STRING, pattern="yyyy-MM-dd'T'", timezone="GMT")
private Date date;
10.3 扁平化对象
- @JsonUnwrapped 扁平化对象
@Data
@ToString
public class Account {private Location location;private PersonInfo personInfo;@Data@ToStringpublic static class Location {private String provinceName;}@Data@ToStringpublic static class PersonInfo {private String userName;}
}
未扁平化之前:
{"location": {"provinceName": "陕西",},"personInfo": {"userName": "lt",}
}
使用@JsonUnwrapped 扁平对象之后:
@Data
@ToString
public class Account {@JsonUnwrappedprivate Location location;@JsonUnwrappedprivate PersonInfo personInfo;......
}
{"provinceName": "陕西","userName": "lt",
}
十一、测试相关的注解
-
@ActiveProfiles 一般作用于测试类上, 用于声明生效的 Spring 配置文件。
@SpringBootTest(webEnvironment = RANDOM_PORT) @ActiveProfiles("test") public abstract class TestBase {...... } -
@Test 声明一个方法为测试方法
-
@Transactional 被声明的测试方法的数据会回滚,避免污染测试数据。
-
@WithMockUser 由Spring Security 提供,用来模拟一个真实用户,并且可以赋予权限。
@Test @Transactional @WithMockUser(username = "lt", authorities = "ROLE_USER") void should_import_user_success() throws Exception {...... }