go限流、计数器固定窗口算法/计数器滑动窗口算法
一、问题
问题1:后端接口只能支撑每10秒1w个请求,要怎么来保护它呢?
问题2:发短信的接口,不超过100次/时,1000次/24小时,要怎么实现?
二、计数器固定窗口算法
所谓固定窗口,就是只设置了一个时间段,给这个时间段加上一个计数器。 常见的就是统计每秒钟的请求量。 这里就是一个QPS计数器。 在这一秒种内的所有请求,只要给这个计数器递增就可以得到当前的并发量了。 用这个方法也就可以解决前面的问题1。可以直接使用系统的当前UNIX时间戳,精确到秒钟。 这个时间戳作为key,设置一个较短的过期时间,比如:10s。
package mainimport ("fmt""time"
)type SlidingWindow struct {WindowSize intWindow []intLastUpdateTime time.TimeWindowDuration time.DurationCurrentIndex intCount intMaxAllowedRequest int
}func NewSlidingWindow(windowSize int, windowDuration time.Duration, maxRequest int) *SlidingWindow {if windowSize <= 0 {panic("windowSize must be greater than 0")}return &SlidingWindow{WindowSize: windowSize,Window: make([]int, windowSize),LastUpdateTime: time.Now(),WindowDuration: windowDuration,CurrentIndex: 0,MaxAllowedRequest: maxRequest,}
}func (sw *SlidingWindow) IncrementCount() {now := time.Now()if now.Sub(sw.LastUpdateTime) >= sw.WindowDuration { //比较时间是否超过限定时间sw.ResetWindow()}sw.Count++sw.Window[sw.CurrentIndex] = sw.Count //窗口总量加1if sw.Count > sw.MaxAllowedRequest { //最好用窗口总量去计算。这里为了显示两种效果fmt.Println("Max allowed request exceeded")}sw.CurrentIndex = (sw.CurrentIndex + 1) % sw.WindowSize //窗口往后移动一个位置
}func (sw *SlidingWindow) ResetWindow() {for i := range sw.Window {//将窗口归零sw.Window[i] = 0}sw.Count = 0sw.LastUpdateTime = time.Now() //记录最后一次更新
}func main2() {windowSize := 5 //窗口粒度,问题1的话可以简化掉。windowDuration := time.Second * 10//十秒的访问量maxRequest := 10000//最大访问量slidingWindow := NewSlidingWindow(windowSize, windowDuration, maxRequest)for i := 0; i < 10; i++ {slidingWindow.IncrementCount()time.Sleep(time.Second)}
}三、计数器滑动窗口算法
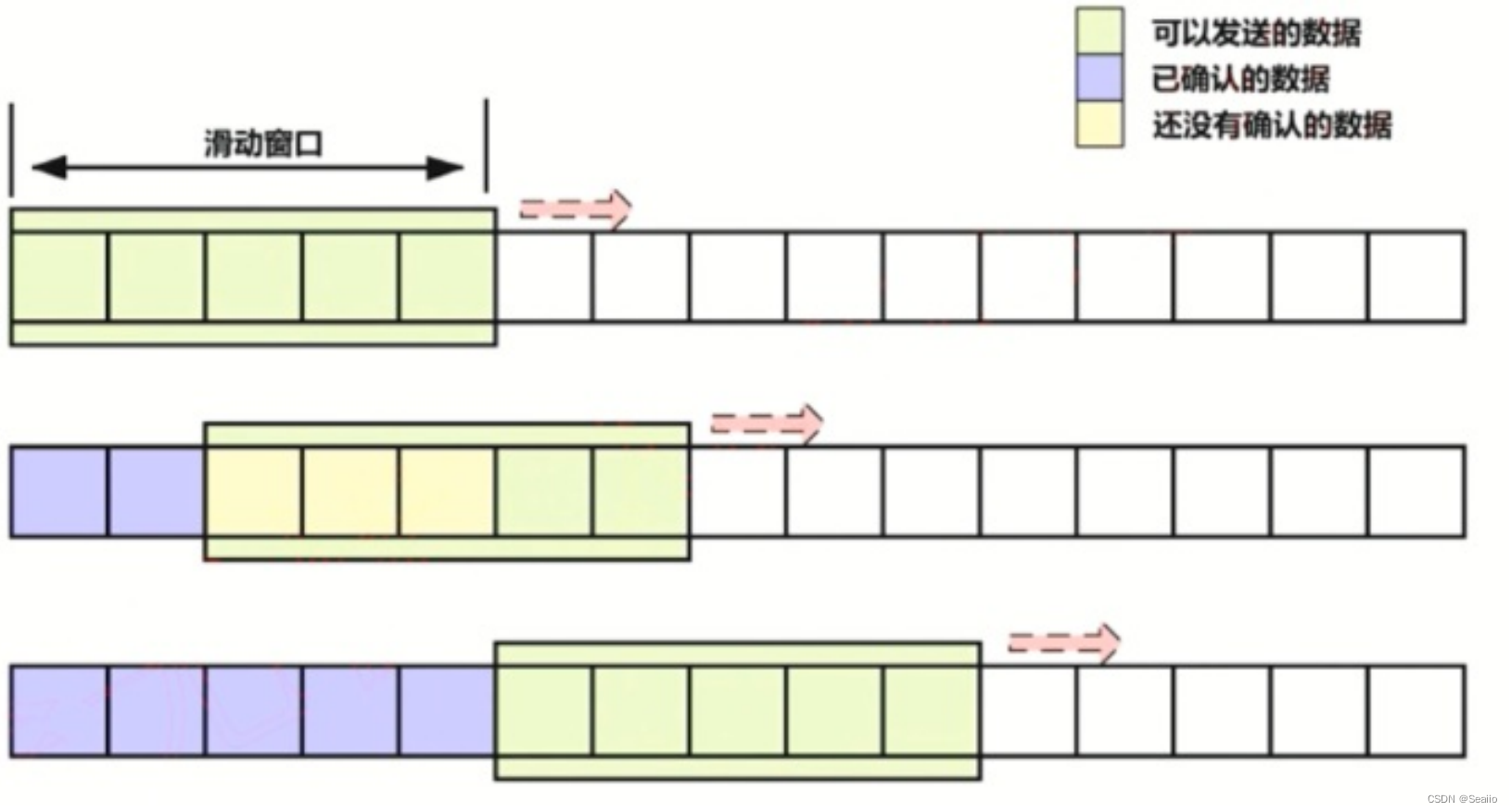
固定窗口就一个计数器,而滑动窗口就需要有多个计数器。 具体需要多少个计数器,要看窗口的范围和粒度来决定窗口大小。 比如:时间窗口的范围是24小时,时间窗口的粒度是1小时,那么窗口大小就是24,需要的计数器也就是24个。 我们再来回顾下前面的问题2。 如果我们用上面的固定窗口算法,需要2个计数器,一个是小时的计数器,一个是24小时,也就是天的计数器。 很明显,天的计数器会有很大的误差。 比如:昨天14点前没有任何请求,然后在14点开始,每小时都有100次请求。 到昨天的23点,刚好用完了1000次全天的额度。 但是这时候,还是每小时有100个请求, 那么从昨天的14点到今天10点,总共20小时就会有2000次请求,远远超过了24小时最多1500次的限制。 所以,这里使用滑动窗口替代固定窗口会更加合适。 如果想要限流控制点更加精准,那么就可以把窗口粒度设计的更细。 而代价就是窗口大小增加,需要的存储和计算量都会增加。 所以,这里也是需要对精准度和成本做平衡和选择,难以兼得。
package mainimport ("fmt""time"
)type RateLimiter struct {perHour intperDay inthourWindow []intdayWindow []intlastHourIdx intlastDayIdx int
}func NewRateLimiter(perHour, perDay int) *RateLimiter {return &RateLimiter{perHour: perHour,perDay: perDay,hourWindow: make([]int, 60),dayWindow: make([]int, 1440),lastHourIdx: 0,lastDayIdx: 0,}
}func (rl *RateLimiter) Allow() bool {now := time.Now()hourIdx := (now.Minute() + now.Hour()*60) % 60 //记录小时的id,dayIdx := now.Hour()*60 + now.Minute() //记录天的idif rl.hourWindow[hourIdx] >= rl.perHour || rl.dayWindow[dayIdx] >= rl.perDay {return false}rl.hourWindow[hourIdx]++rl.dayWindow[dayIdx]++rl.cleanUpOldEntries(hourIdx, dayIdx)return true
}func (rl *RateLimiter) cleanUpOldEntries(hourIdx, dayIdx int) {if hourIdx != rl.lastHourIdx {//如果小时id更新了需要窗口往右移动rl.hourWindow[hourIdx] = 1 //最新小时id的总量为1rl.hourWindow[rl.lastHourIdx] = 0 //窗口往右移动,上一个归零rl.lastHourIdx = hourIdx //记录最新id}if dayIdx != rl.lastDayIdx {rl.dayWindow[dayIdx] = 1rl.dayWindow[rl.lastDayIdx] = 0rl.lastDayIdx = dayIdx}
}func main3() {limiter := NewRateLimiter(100, 1000)for i := 0; i < 1200; i++ {if limiter.Allow() {fmt.Printf("Request %d allowed\n", i+1)} else {fmt.Printf("Request %d blocked\n", i+1)}time.Sleep(time.Second)}
}