一、基础概念
1. 索引
之前的文章已经写过了,比较细
数据库索引含义,类别,用法,创建方式_表结构加树形id和索引是为什么_马丁•路德•王的博客-CSDN博客
简单概括就是在表的某个列或者多个列或者联合表的时候加个索引,类似图书馆书本的索引编号,查询的时候直接按照索引查询,不用遍历,提高查询效率
2. MySQL 的存储引擎
1. InnoDB 支持事务,外键等
2. Memory 存储引擎将数据存储在内存中,适用于高速读写需求
3. MyISAM 适用于读多写少的场景3. 事务
事务四元素
1. 原子性:一个事件是个事务(例如下单完成之后扣库存,收账)。要么全部成功,要么全部失败回滚
2. 一致性:事务执行前和结束满足预定义的规则,例如所有的约束和完整性规则必须被满足。
一致性确保了数据库的有效状态转换。
3. 隔离性:事务的执行过程互不影响
3. 永久性:事务执行结束后的影响存储在数据库,永久有效4. 事务隔离级别
1. 读未提交:只能读取未提交的数据,可能会读取到脏数据,因为读取的时候其他人会编辑
2. 读已提交:只能读取已经提交的数据,不能读取到提交之前的数据
3. 可重复读:可以重复读取数据,还是会有脏读的case
4. 串行化(读写都隔离):读写分开,同步化innodb默认使用[可重复读]5. 连接池
1. mysql连接池是在程序启动的时候就建立一定的连接数量,当需要使用的时候可以直接用,
而不是每次建立,取消建立的过程,浪费资源
2. 控制连接数可以防止数据库服务器过载,同时提高连接的效率。6. 视图
多表联合/复杂查询后创建的虚拟的表,表的数据是动态更新的。创建后会一直存在,除非主动删除7. 如何优化数据库查询
1. 使用索引
2. 分页查询
3. 避免全表扫描
4. 避免使用 SELECT *,多使用连接8. mysql发生死锁之后怎么处理
innodb_lock_wait_timeout 超时等待时间,默认是50
事务会一直等待,直到结束。
如果发生死锁,会回滚事务,让出资源执行其他操作9. innodb 存储引擎对应的算法锁
1. Record Lock -(行锁),事务读取了某一行的记录,不允许其他事务修改,但可以读取
2. Gap Lock -(间隙锁),锁定某数据的间隙,不包括记录本身
3. Next-Key Lock -(间隙锁+行锁) 锁定一个范围间隙+记录本身添加行锁的方式->使用for update:
但是t这个字段必须已添加索引
select * from tbl where t=1 for update10. 表的优化策略
1. 读写分离:主库负责写数据,从库负责读数据
2. 垂直分区:根据数据属性,对表分离
3. 水平分区:根据数据位置,水平拆分,表的结构不变二、数据库操作
1. Database
create Database RUNOOB;
show Databases;
use RUNOOB;
-- drop database RUNOOB;2. Table
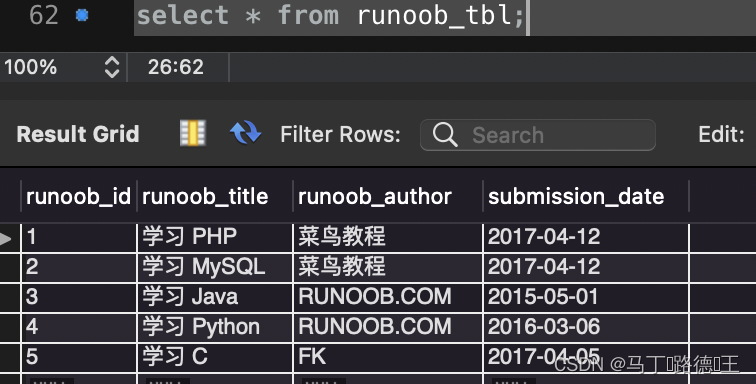
创建表:
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `runoob_tbl`(`runoob_id` INT UNSIGNED AUTO_INCREMENT,`runoob_title` VARCHAR(100) NOT NULL,`runoob_author` VARCHAR(40) NOT NULL,`submission_date` DATE,PRIMARY KEY ( `runoob_id` )
)ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;修改表结构
-- 增加
alter table `runoob_tbl`
add runoob_score DECIMAL(10, 2);-- 修改
alter table `runoob_tbl`
modify runoob_score DECIMAL(10, 2) default 0;-- 删除
alter table `runoob_tbl`
drop runoob_score;
删除表
DROP TABLE table_name ;3. Data
数据结构:
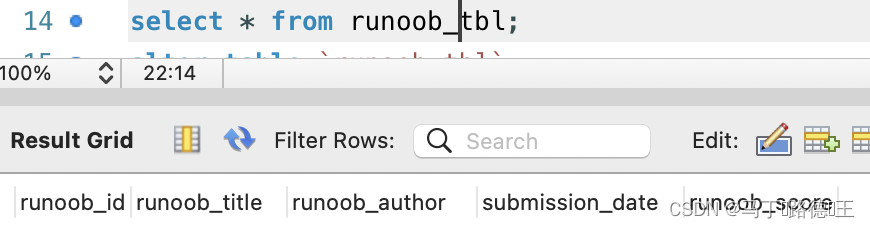
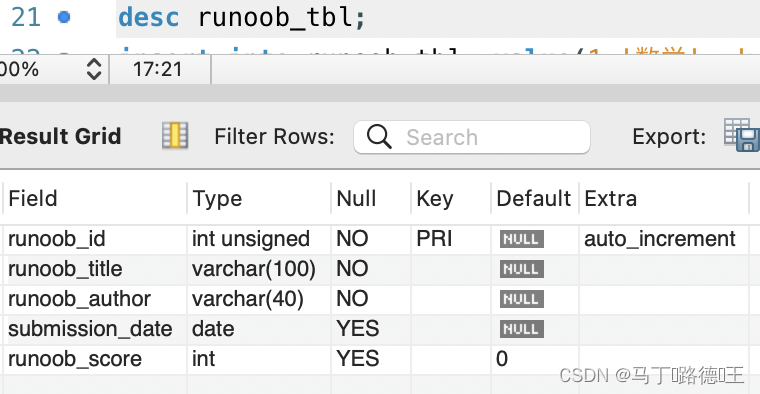
insert
--所有列都输入
insert into runoob_tbl value(1,'数学', 'wanh', sysdate(),20);--只输入可以为空的字段
insert into runoob_tbl (`runoob_title`,`runoob_author`,`submission_date`) values ('语文','wanghao','2023-08-11');select
select * from runoob_tbl;update
-- 注意列名不能带引号
update runoob_tbl set runoob_author='wanghao' where runoob_id = '2';delete
delete from runoob_tbl where runoob_id = '3';4. UNION/ UNION ALL/ DISTINCT
--如果你需要合并多个查询结果,并且不需要去重,可以使用 UNION ALL。
--如果你需要合并多个查询结果,并且需要去重,可以使用 UNION。
--如果你在单个查询中希望去重,可以使用 DISTINCT。select `runoob_title`,`runoob_author` from runoob_tbl
UNION
select `runoob_title`,`runoob_author` from runoob_tbl1;select distinct `runoob_title` from runoob_tbl;select `runoob_title`,`runoob_author` from runoob_tbl
UNION ALL
select `runoob_title`,`runoob_author` from runoob_tbl1;5. order by
select * from runoob_tbl order by runoob_score desc;select * from runoob_tbl order by runoob_score asc;6. group by
--GROUP BY 语句根据一个或多个列对结果集进行分组。--在分组的列上我们可以使用 COUNT, SUM, AVG,等函数。select name,count(*) from employee_tbl group by name;select name,sum(signin) from employee_tbl group by name WITH ROLLUP ;7. or
使用or会使查询放弃索引,使用全表查询。
select * from stu_tbl where num =10 or num=20;--优化为
select * from stu_tbl where num =10
union
select * from stu_tbl where num =20;8. limit
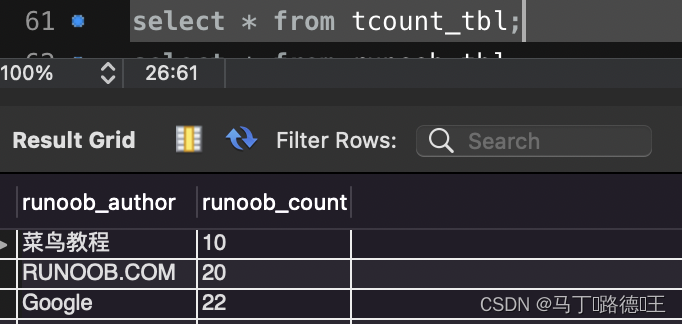
select * from tcount_tbl ;
select * from tcount_tbl limit 10;
select * from tcount_tbl order by runoob_count desc limit 10;
-- 分页:从第6个数据开始查询10条
select * from tcount_tbl order by runoob_count asc limit 10 offset 5;三、连接
1. inner join ... where
select a.runoob_author,a.runoob_count,b.runoob_title
from tcount_tbl a inner join runoob_tbl b
where a.runoob_author = b.runoob_author;
2. left join ... on
select a.runoob_author,a.runoob_count,b.runoob_title
from tcount_tbl a left join runoob_tbl b
on a.runoob_author = b.runoob_author;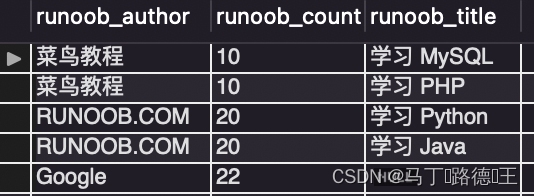
3. right join ... on
select a.runoob_author,a.runoob_count,b.runoob_title
from tcount_tbl a right join runoob_tbl b
on a.runoob_author = b.runoob_author;
四、一些优化及常见问题
1. 优化查询
1. 避免使用or,因为会全局查询,可以使用in或者union
2. 使用索引
3. 避免使用select *
4. 将表分区,然后查询
5. 使用explain查看sql优化
6. 分页查询
7. 使用join代替where
8. 不要用not,不会走索引;例如:not in, not exist, is not null2. 常见查询面试题