💞💞 前言
hello hello~ ,这里是大耳朵土土垚~💖💖 ,欢迎大家点赞🥳🥳关注💥💥收藏🌹🌹🌹
💥个人主页:大耳朵土土垚的博客
💥 所属专栏:C++入门至进阶
这里将会不定期更新有关C++的内容,希望大家多多点赞关注收藏💖💖
目录
- 💞💞 前言
- 1.日期类Date的构造
- 2.日期类Date的实现
- 2.1获取某年某月的天数
- 2.2默认成员函数的实现
- 2.2.1全缺省的构造函数
- 2.2.2拷贝构造函数
- 2.2.3赋值运算符重载
- 2.2.4析构函数
- 2.3日期计算类函数
- 2.3.1日期+=天数
- 2.3.2日期+天数
- 2.3.3日期-=天数
- 2.3.4日期-天数
- 2.3.5日期-日期 返回天数
- 2.4运算符重载类函数
- 2.4.1 >运算符重载
- 2.4.2 ==运算符重载
- 2.4.3 >=运算符重载
- 2.4.4 <运算符重载
- 2.4.5 <=运算符重载
- 2.4.6 !=运算符重载
- 2.4.7 前置++与后置++
- 2.4.8 前置--与后置--
- 3.完整代码+运行结果
- 4.结语
通过下面的学习我们将构建简单日期计算器的各种功能实现:

1.日期类Date的构造
这里的函数大多在日期类中声明,定义在类外部实现
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Date
{
public:// 获取某年某月的天数inline int GetMonthDay(int year, int month){int montharray[13] = { 0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31 };//如果是二月就需要判断是不是闰年if (month == 2 &&(((year % 4 == 0) && (year % 100 != 0)) || (year % 400 == 0))){return 29;}return montharray[month];//月份天数数组设置为13,方便直接按月份返回}// 全缺省的构造函数Date(int year = 1900, int month = 1, int day = 1);// 拷贝构造函数// d2(d1)Date(const Date& d);// 赋值运算符重载// d2 = d3 -> d2.operator=(&d2, d3)Date& operator=(const Date& d){if (*this != d){_year = d._year;_month = d._month;_day = d._day;return *this;}}// 析构函数~Date();//打印日期void Print(){cout << _year << "/" << _month << "/" << _day << endl;}// 日期+=天数Date& operator+=(int day);// 日期+天数Date operator+(int day);// 日期-天数Date operator-(int day);// 日期-=天数Date& operator-=(int day);// 前置++Date& operator++();// 后置++Date operator++(int);// 后置--Date operator--(int);// 前置--Date& operator--();// >运算符重载bool operator>(const Date& d);// ==运算符重载bool operator==(const Date& d);// >=运算符重载bool operator >= (const Date& d);// <运算符重载bool operator < (const Date& d);// <=运算符重载bool operator <= (const Date& d);// !=运算符重载bool operator != (const Date& d);// 日期-日期 返回天数int operator-(const Date& d);private:int _year;int _month;int _day;};
日期Date类主要分为成员函数与成员变量两个模块,
成员变量就是上面的int _year; int _month;int _day;是私有(private)的,这样做的目的是不想让别人得到自己的数据;
成员函数可以分为三类:
- 默认成员函数
- 日期计算类函数
- 运算符重载函数
成员函数是公有的(public),也就是说我们在类的外部也可访问和使用;下面我们将实现这些函数。
2.日期类Date的实现
2.1获取某年某月的天数
// 获取某年某月的天数
inline int GetMonthDay(int year, int month)
{int montharray[13] = { 0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31 };//如果是二月就需要判断是不是闰年if (month == 2 &&(((year % 4 == 0) && (year % 100 != 0)) || (year % 400 == 0))){return 29;}return montharray[month];//月份天数数组设置为13,方便直接按月份返回
}
这个函数对于我们后面完整实现日期类有着重要的作用,很多情况下都需要调用它,所以我们在最开始实现并将它设置成内联函数,以提高效率;
此外内联函数声明和定义最好不要分离,否则会出现链接错误,所以这里我们直接在类里面定义;
2.2默认成员函数的实现
2.2.1全缺省的构造函数
// 全缺省的构造函数
Date:: Date(int year, int month, int day)
{_year = year;_month = month;_day = day;//这里可以判断日期是否合理if (month >= 13 && day > GetMonthDay(year, month)){cout << "日期非法输入" << endl;}
}
注意这里在声明的时候给缺省值,定义的时候不写;全缺省的构造函数除了赋值外,如果用户输入13月或者2月31天等不正确的日期,我们还可以在函数内部判断日期是否非法;
2.2.2拷贝构造函数
// 拷贝构造函数
// d2(d1)
Date:: Date(const Date& d)
{_year = d._year;_month = d._month;_day = d._day;
}
2.2.3赋值运算符重载
// 赋值运算符重载// d2 = d3 -> d2.operator=(&d2, d3)Date& operator=(const Date& d){if (*this != d){_year = d._year;_month = d._month;_day = d._day;return *this;}}
赋值运算符重载如果在类中不显式实现,编译器会生成一个默认的。此时用户再在类外自己实现一个全局的赋值运算符重载,就和编译器在类中生成的默认赋值运算符重载冲突了,故赋值运算符重载只能是类的成员函数。所以我们在类里面声明和定义一起;
2.2.4析构函数
//析构函数
Date::~Date()
{_year = 0;_month = 0;_day = 0;
}
对于没有申请资源的类比如日期类,析构函数可以不写直接使用系统默认生成的就行;
2.3日期计算类函数
2.3.1日期+=天数
// 日期+=天数
Date& Date::operator+=(int day)
{_day += day;while (_day > GetMonthDay(_year, _month)){_day -= GetMonthDay(_year, _month);_month++;if (_month >= 13){_year++;_month = 1;}}return *this;
}
这里采用日满了月就+1,月满了年就+1的方式,此外还要注意每个月的天数都不同,2月不同年份天数也不同分为平年和润年,这就需要使用我们之前实现过的获取某年某月天数的函数了;和日期+天数不同的是,日期+=天数,自己原来的日期会变成+了天数之后的,而日期+天数原来的日期不变, 例如:
d1+=100之后,d1也变了;
这里介绍另一个成员函数Print();
void Print() { cout << _year << "/" << _month << "/" << _day << endl; }用来打印日期,包含在类里面;
2.3.2日期+天数
// 写法1:日期+天数
Date Date::operator+(int day)
{Date tmp = *this;tmp += day;//利用之前实现过的+=实现return tmp;
}
//写法2:日期+天数
Date Date::operator+(int day)
{
Date tmp = *this;
tmp._day += day;
while (tmp._day > GetMonthDay(tmp._year, tmp._month))
{tmp._day -= GetMonthDay(tmp._year, tmp._month);tmp._month++;if (tmp._month >= 13){tmp._year++;tmp._month = 1;}}
return tmp;
}
因为日期+天数,原来的日期是不变的,所以我们需要创建一个临时变量来存放+天数之后的日期并返回;这里有两种写法,一种对之前实现的+=直接使用,另一种就是再自己写一遍+的代码(和+=类似);
2.3.3日期-=天数
// 日期-=天数
Date& Date::operator-=(int day)
{_day -= day;while (_day < 0){_month--;if (_month == 0){_year--;_month = 12;}_day += GetMonthDay(_year, _month);}return *this;
}
2.3.4日期-天数
// 日期-天数
Date Date::operator-(int day)
{Date tmp = *this;/*tmp._day -= day;while (tmp._day < 0){tmp._month--;if (tmp._month == 0){tmp._year--;tmp._month = 12;}tmp._day += GetMonthDay(tmp._year, tmp._month);}*/tmp -= day;return tmp;
}
2.3.5日期-日期 返回天数
// 日期-日期 返回天数
int Date::operator-(const Date& d)
{//先找较大的日期Date max = *this;Date min = d;//如果*this的日期比d大的话就正常计数int flag = 1;//如果*this的日期比d小的话就先正常计数之后再*(-1)即可,-1用flag来标识if (*this < d){min = *this;max = d;flag = -1;}int CountDay = 0;while (min < max){++min;CountDay++;}return flag * CountDay;
}这里注意如果日期1-日期2<0;就要返回负数,反之返回正数;
所以我们使用flag来标识;
此外计算两个日期相差的天数可以直接++日期并利用CountDay来记录++了多少次,直到两个日期相等时,CountDay的值就是两个日期的差值,类似于追及问题;
当然也有别的方法来实现这里就写了这一种
2.4运算符重载类函数
2.4.1 >运算符重载
// >运算符重载
bool Date::operator>(const Date& d)
{//先比较年if (_year > d._year)return true;//比较月if (_year == d._year && _month > d._month)return true;//比较天if ((_year == d._year) && (_month == d._month) && (_day > d._day))return true;return false;}
2.4.2 ==运算符重载
// ==运算符重载
bool Date::operator==(const Date& d)
{if ((_year == d._year) && (_month == d._month) && (_day == d._day))return true;return false;
}
2.4.3 >=运算符重载
// >=运算符重载
bool Date::operator >= (const Date& d)
{if (*this > d || *this == d)return true;return false;
}
只需写了 > 和 == 或者 < 和 == 这两个运算符,后面的运算符重载就可以借助这两个运算符直接实现;
2.4.4 <运算符重载
// <运算符重载
bool Date::operator < (const Date& d)
{return !(*this >= d);
}
2.4.5 <=运算符重载
// <=运算符重载
bool Date::operator <= (const Date& d)
{return !(*this > d);
}2.4.6 !=运算符重载
// !=运算符重载
bool Date::operator != (const Date& d)
{return !(*this == d);
}2.4.7 前置++与后置++
- 前置++
返回++之后的值
// 前置++
Date& Date::operator++()
{/*_day++;if (_day > GetMonthDay(_year, _month)){_month++;if (_month >= 13){_year++;}}*/*this += 1;return *this;
}可以直接写,也可以利用前面实现的+=来实现
- 后置++
返回++之前的值
// 后置++
Date Date::operator++(int)
{Date tmp = *this;/*_day++;if (_day > GetMonthDay(_year, _month)){_month++;if (_month >= 13){_year++;}}*/*this += 1;return tmp;
}
这里因为是返回++之前的值,所以需要创建一个临时变量来存储++之前的日期并返回
2.4.8 前置–与后置–
- 前置–
// 前置--
Date& Date::operator--()
{return *this -= 1;
}- 后置–
// 后置--
Date Date:: operator--(int)
{Date tmp = *this;*this -= 1;return tmp;
}
3.完整代码+运行结果
- date.h
#pragma once
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Date
{friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const Date& d);friend istream& operator>>(istream& in, Date& d);public:// 获取某年某月的天数inline int GetMonthDay(int year, int month){int montharray[13] = { 0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31 };//如果是二月就需要判断是不是闰年if (month == 2 && (((year % 4 == 0) && (year % 100 != 0)) || (year % 400 == 0))){return 29;}return montharray[month];}// 全缺省的构造函数Date(int year = 1900, int month = 1, int day = 1);// 拷贝构造函数// d2(d1)Date(const Date& d);// 赋值运算符重载// d2 = d3 -> d2.operator=(&d2, d3)Date& operator=(const Date& d){if (*this != d){_year = d._year;_month = d._month;_day = d._day;return *this;}}// 析构函数~Date();// 日期+=天数Date& operator+=(int day);// 日期+天数Date operator+(int day);// 日期-天数Date operator-(int day);// 日期-=天数Date& operator-=(int day);// 前置++Date& operator++();// 后置++Date operator++(int);// 后置--Date operator--(int);// 前置--Date& operator--();// >运算符重载bool operator>(const Date& d);// ==运算符重载bool operator==(const Date& d);// >=运算符重载bool operator >= (const Date& d);// <运算符重载bool operator < (const Date& d);// <=运算符重载bool operator <= (const Date& d);// !=运算符重载bool operator != (const Date& d);// 日期-日期 返回天数int operator-(const Date& d);void Print(){cout << _year << "/" << _month << "/" << _day << endl;}private:int _year;int _month;int _day;};
- date.cpp
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include"date.h"// 全缺省的构造函数
Date::Date(int year, int month, int day)
{_year = year;_month = month;_day = day;//这里可以判断日期是否合理if (month >= 13 && day > GetMonthDay(year, month)){cout << "日期非法输入" << endl;}
}// 拷贝构造函数// d2(d1)
Date::Date(const Date& d)
{_year = d._year;_month = d._month;_day = d._day;
}// 日期+=天数
Date& Date::operator+=(int day)
{_day += day;while (_day > GetMonthDay(_year, _month)){_day -= GetMonthDay(_year, _month);_month++;if (_month >= 13){_year++;_month = 1;}}return *this;
}// 日期+天数
Date Date::operator+(int day)
{Date tmp = *this;//tmp._day += day;//while (tmp._day > GetMonthDay(tmp._year, tmp._month))//{// tmp._day -= GetMonthDay(tmp._year, tmp._month);// tmp._month++;// if (tmp._month >= 13)// {// tmp._year++;// tmp._month = 1;// }// //}tmp += day;return tmp;
}// 日期-=天数
Date& Date::operator-=(int day)
{_day -= day;while (_day < 0){_month--;if (_month == 0){_year--;_month = 12;}_day += GetMonthDay(_year, _month);}return *this;
}// 日期-天数
Date Date::operator-(int day)
{Date tmp = *this;/*tmp._day -= day;while (tmp._day < 0){tmp._month--;if (tmp._month == 0){tmp._year--;tmp._month = 12;}tmp._day += GetMonthDay(tmp._year, tmp._month);}*/tmp -= day;return tmp;
}// 前置++
Date& Date::operator++()
{/*_day++;if (_day > GetMonthDay(_year, _month)){_month++;if (_month >= 13){_year++;}}*/*this += 1;return *this;
}// 后置++
Date Date::operator++(int)
{Date tmp = *this;/*_day++;if (_day > GetMonthDay(_year, _month)){_month++;if (_month >= 13){_year++;}}*/*this += 1;return tmp;
}// 后置--
Date Date:: operator--(int)
{Date tmp = *this;*this -= 1;return tmp;
}// 前置--
Date& Date::operator--()
{return *this -= 1;
}// >运算符重载
bool Date::operator>(const Date& d)
{//先比较年if (_year > d._year)return true;//比较月if (_year == d._year && _month > d._month)return true;//比较天if ((_year == d._year) && (_month == d._month) && (_day > d._day))return true;return false;}// ==运算符重载
bool Date::operator==(const Date& d)
{if ((_year == d._year) && (_month == d._month) && (_day == d._day))return true;return false;
}// >=运算符重载
bool Date::operator >= (const Date& d)
{if (*this > d || *this == d)return true;return false;
}// <运算符重载
bool Date::operator < (const Date& d)
{return !(*this >= d);
}// <=运算符重载
bool Date::operator <= (const Date& d)
{return !(*this > d);
}// !=运算符重载
bool Date::operator != (const Date& d)
{return !(*this == d);
}// 日期-日期 返回天数
int Date::operator-(const Date& d)
{//先找较大的日期Date max = *this;Date min = d;//如果*this的日期比d大的话就正常计数int flag = 1;//如果*this的日期比d小的话就先正常计数之后再*(-1)即可,-1用flag来标识if (*this < d){min = *this;max = d;flag = -1;}int CountDay = 0;while (min < max){++min;CountDay++;}return flag * CountDay;
}//析构函数
Date::~Date()
{_year = 0;_month = 0;_day = 0;
}// //流输出
//ostream operator<<(ostream& out, const Date d)
//{
// out << d._year << "/" << d._month << "/" << d._day << endl;
// return out;
//}
//
//
流插入
//istream operator>>(istream& in, const Date d)
//{
// in >> d._year;
//}//流插入
ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const Date& d)
{out << d._year << "/" << d._month << "/" << d._day << endl;return out;
}//流提取
istream& operator>>(istream& in, Date& d)
{in >> d._year >> d._month >> d._day;return in;
}
- test.cpp
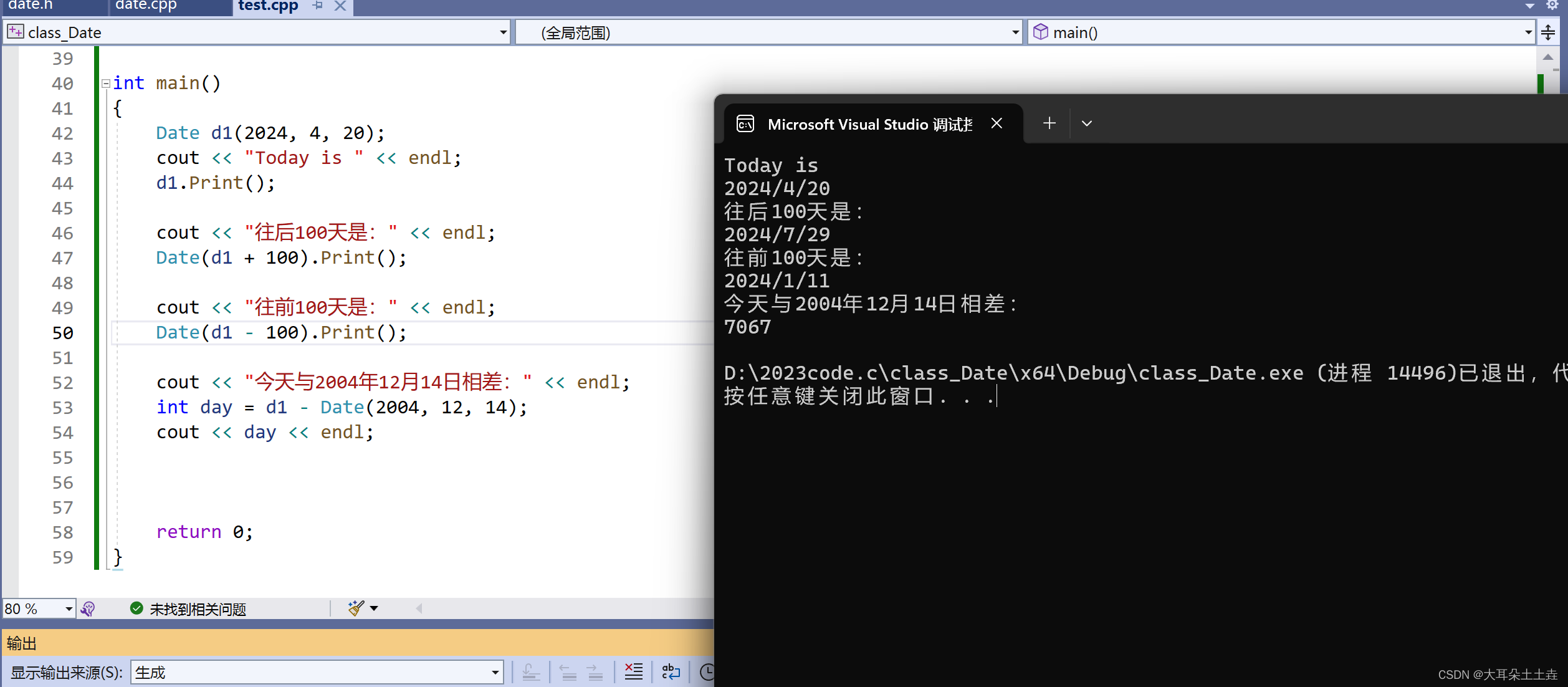
int main()
{Date d1(2024, 4, 20);cout << "Today is " << endl;d1.Print();cout << "往后100天是:" << endl;Date(d1 + 100).Print();cout << "往前100天是:" << endl;Date(d1 - 100).Print();cout << "今天与2004年12月14日相差:" << endl;int day = d1 - Date(2004, 12, 14);cout << day << endl;return 0;
}
结果如下:
4.结语
以上只是一个简单的日期类示例,实际的日期类可能还包括其他功能,例如日期的格式化等操作。这里只是提供了一个起点,大家可以根据自己的需求对日期类进行扩展。以上就是简单日期类的所有内容啦 ~ 完结撒花 ~🥳🎉🎉