概念
信号递达:实际执行信号的处理动作就是信号递达
信号未决:信号从产生到递达之间的状态就是信号未决(未决就是没有解决)
收到某信号后,把未决信号集中的此信号置为1(1表示未解决的信号),然后去阻塞信号集中查看此信号有没有被阻塞,如果没有被阻塞的话,那就去信号捕捉函数数组中查看该如何处理该信号
在阻塞信号集中,阻塞和未阻塞用一个bit表示就可以,在未决信号集中也是一样,因此阻塞和未决可以用相同的数据类型sigset_t来存储

发送信号
不管内核驱动调用kill_fasync发送信号,还是用户层调用kill系统调用,最终都会调通过__send_signal_locked,调用内核函数sigaddset来将信号加入信号集
kill_fasync__send_signal_locked
sys_kill__send_signal_locked
static int __send_signal_locked(int sig, struct kernel_siginfo *info,struct task_struct *t, enum pid_type type, bool force)
{struct sigpending *pending;struct sigqueue *q;int override_rlimit;int ret = 0, result;lockdep_assert_held(&t->sighand->siglock);result = TRACE_SIGNAL_IGNORED;if (!prepare_signal(sig, t, force))goto ret;pending = (type != PIDTYPE_PID) ? &t->signal->shared_pending : &t->pending;/** Short-circuit ignored signals and support queuing* exactly one non-rt signal, so that we can get more* detailed information about the cause of the signal.*/result = TRACE_SIGNAL_ALREADY_PENDING;if (legacy_queue(pending, sig))goto ret;result = TRACE_SIGNAL_DELIVERED;/** Skip useless siginfo allocation for SIGKILL and kernel threads.*/if ((sig == SIGKILL) || (t->flags & PF_KTHREAD))goto out_set;/** Real-time signals must be queued if sent by sigqueue, or* some other real-time mechanism. It is implementation* defined whether kill() does so. We attempt to do so, on* the principle of least surprise, but since kill is not* allowed to fail with EAGAIN when low on memory we just* make sure at least one signal gets delivered and don't* pass on the info struct.*/if (sig < SIGRTMIN)override_rlimit = (is_si_special(info) || info->si_code >= 0);elseoverride_rlimit = 0;//新分配一个sigqueue,将其加入pending队列q = __sigqueue_alloc(sig, t, GFP_ATOMIC, override_rlimit, 0);if (q) {list_add_tail(&q->list, &pending->list);switch ((unsigned long) info) {case (unsigned long) SEND_SIG_NOINFO:clear_siginfo(&q->info);q->info.si_signo = sig;q->info.si_errno = 0;q->info.si_code = SI_USER;q->info.si_pid = task_tgid_nr_ns(current,task_active_pid_ns(t));rcu_read_lock();q->info.si_uid =from_kuid_munged(task_cred_xxx(t, user_ns),current_uid());rcu_read_unlock();break;case (unsigned long) SEND_SIG_PRIV:clear_siginfo(&q->info);q->info.si_signo = sig;q->info.si_errno = 0;q->info.si_code = SI_KERNEL;q->info.si_pid = 0;q->info.si_uid = 0;break;default:copy_siginfo(&q->info, info);break;}} else if (!is_si_special(info) &&sig >= SIGRTMIN && info->si_code != SI_USER) {/** Queue overflow, abort. We may abort if the* signal was rt and sent by user using something* other than kill().*/result = TRACE_SIGNAL_OVERFLOW_FAIL;ret = -EAGAIN;goto ret;} else {/** This is a silent loss of information. We still* send the signal, but the *info bits are lost.*/result = TRACE_SIGNAL_LOSE_INFO;}out_set:signalfd_notify(t, sig);sigaddset(&pending->signal, sig);/* Let multiprocess signals appear after on-going forks */if (type > PIDTYPE_TGID) {struct multiprocess_signals *delayed;hlist_for_each_entry(delayed, &t->signal->multiprocess, node) {sigset_t *signal = &delayed->signal;/* Can't queue both a stop and a continue signal */if (sig == SIGCONT)sigdelsetmask(signal, SIG_KERNEL_STOP_MASK);else if (sig_kernel_stop(sig))sigdelset(signal, SIGCONT);sigaddset(signal, sig);}}//唤醒进程complete_signal(sig, t, type);
ret:trace_signal_generate(sig, info, t, type != PIDTYPE_PID, result);return ret;
}应用层接口
1.int sigemptyset(sigset_t* set);
功能:初始化信号集(把set所指向的信号集中的所有信号的对应bit清零,表示该信号集不包含任何有效信号)
2.int sigfillset(sigset_t* set);
功能:初始化信号集(把set所指向的信号集中的所有信号的对应bit置为1,表示该信号集包含所有的有效信号)
3.int sigaddset(sigset_t* set,int signo);
功能:添加有效信号signo(把编号为signo的信号在位图中的bit从0变为1)
4.int sigdelset(sigset_t* set,int signo);
功能:删除有效信号signor(把编号为signo的信号在位图中的bit从1变为0)
5.int sigismember(const sigset_t* set,int signo);
功能:用于判断信号集中的有效信号是否包含编号为signor的信号
6.int sigprocmask(int how,const sigset_t* set,sigset_t* oset);
功能:可以读取或更改进程的阻塞信号集(信号屏蔽字);SIGKILL和SIGSTOP不能被阻塞
7.int sigpending(sigset_t* set);
功能:读取当前进程的未决信号集,通过参数set传出
8.sighandler_t signal(int signum, sighandler_t handler);
功能:handler需要用户自定义处理信号的方式;也可以是SIG_IGN:忽略该信号;SIG_DFL:采用系统默认方式处理信号
SIGKILL和SIGSTOP不能阻塞原因
见sigprocmask内核代码
void set_current_blocked(sigset_t *newset)
{sigdelsetmask(newset, sigmask(SIGKILL) | sigmask(SIGSTOP));__set_current_blocked(newset);
}void __set_current_blocked(const sigset_t *newset)
{struct task_struct *tsk = current;/** In case the signal mask hasn't changed, there is nothing we need* to do. The current->blocked shouldn't be modified by other task.*/if (sigequalsets(&tsk->blocked, newset))return;spin_lock_irq(&tsk->sighand->siglock);__set_task_blocked(tsk, newset);spin_unlock_irq(&tsk->sighand->siglock);
}/** This is also useful for kernel threads that want to temporarily* (or permanently) block certain signals.** NOTE! Unlike the user-mode sys_sigprocmask(), the kernel* interface happily blocks "unblockable" signals like SIGKILL* and friends.*/
int sigprocmask(int how, sigset_t *set, sigset_t *oldset)
{struct task_struct *tsk = current;sigset_t newset;/* Lockless, only current can change ->blocked, never from irq */if (oldset)*oldset = tsk->blocked;switch (how) {case SIG_BLOCK:sigorsets(&newset, &tsk->blocked, set);break;case SIG_UNBLOCK:sigandnsets(&newset, &tsk->blocked, set);break;case SIG_SETMASK:newset = *set;break;default:return -EINVAL;}__set_current_blocked(&newset);return 0;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(sigprocmask);执行流程
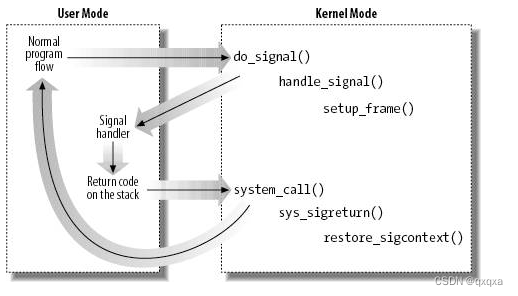
目标进程在从内核态返回用户态的过程中检测是否有挂起的信号,发现有挂起的信号则从链表中每次拿出一个信号事件进行处理直到链表为空
自定义处理函数
对于有通过 signal、sigaction 注册信号处理函数的信号,设定堆栈后跳转到用户态的信号处理函数开始执行,此函数返回后触发一个 sigreturn 系统调用后再次回到内核,然后恢复旧的堆栈继续运行
默认处理
对于 SIGKILL、SIGSTOP 这两种不可被用户程序捕获的信号,以及设定了 SIG_IGN、SIG_DFL 行为的信号而言,这些信号的处理过程均在内核态完成。
对于SIG_DFL,默认行为是dump 的信号处理可能会进程工作目录下创建一个core 文件. 这个文件列出了进程的地址空间和cpu 寄存器的值.
do_signal 创建这个文件后, 就会杀死整个线程组. 剩下18 个信号的默认处理是terminate, 这仅仅是简单地杀死整个线程组. 为此,do_signal 调用了do_group_exit
处理流程
el0_svc执行系统调用后,会通过ret_fast_syscall返回用户空间,会执行do_work_pending
ret_fast_syscall:
__ret_fast_syscall:UNWIND(.fnstart )UNWIND(.cantunwind )str r0, [sp, #S_R0 + S_OFF]! @ save returned r0
#if IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_DEBUG_RSEQ)/* do_rseq_syscall needs interrupts enabled. */mov r0, sp @ 'regs'bl do_rseq_syscall
#endifdisable_irq_notrace @ disable interruptsldr r2, [tsk, #TI_ADDR_LIMIT]cmp r2, #TASK_SIZEblne addr_limit_check_failedldr r1, [tsk, #TI_FLAGS] @ re-check for syscall tracingtst r1, #_TIF_SYSCALL_WORK | _TIF_WORK_MASKbeq no_work_pendingUNWIND(.fnend )
ENDPROC(ret_fast_syscall)/* Slower path - fall through to work_pending */
#endiftst r1, #_TIF_SYSCALL_WORKbne __sys_trace_return_nosave
slow_work_pending:mov r0, sp @ 'regs'mov r2, why @ 'syscall'bl do_work_pendingcmp r0, #0beq no_work_pendingmovlt scno, #(__NR_restart_syscall - __NR_SYSCALL_BASE)ldmia sp, {r0 - r6} @ have to reload r0 - r6b local_restart @ ... and off we go
ENDPROC(ret_fast_syscall)do_work_pending调用do_signal对信号做处理
asmlinkage int
do_work_pending(struct pt_regs *regs, unsigned int thread_flags, int syscall)
{/** The assembly code enters us with IRQs off, but it hasn't* informed the tracing code of that for efficiency reasons.* Update the trace code with the current status.*/trace_hardirqs_off();do {if (likely(thread_flags & _TIF_NEED_RESCHED)) {schedule();} else {if (unlikely(!user_mode(regs)))return 0;local_irq_enable();if (thread_flags & _TIF_SIGPENDING) {int restart = do_signal(regs, syscall);if (unlikely(restart)) {/** Restart without handlers.* Deal with it without leaving* the kernel space.*/return restart;}syscall = 0;} else if (thread_flags & _TIF_UPROBE) {uprobe_notify_resume(regs);} else {clear_thread_flag(TIF_NOTIFY_RESUME);tracehook_notify_resume(regs);rseq_handle_notify_resume(NULL, regs);}}local_irq_disable();thread_flags = current_thread_info()->flags;} while (thread_flags & _TIF_WORK_MASK);return 0;
}简化框图如下