8.13 刷题记录
- 6. 反转链表
- 方法一: 迭代
- 方法二:递归
- 7. 合并两个排序的链表
- 8. 复杂链表的复刻
- 9. 二叉搜索树与双向链表
6. 反转链表
原题链接
方法一: 迭代
1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4
i j
1 <- 2 -> 3 -> 4
i j
就像这样迭代
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* ListNode *next;* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}* };*/
class Solution {
public:ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {ListNode *prev = nullptr;ListNode *cur = head;while (cur){ListNode *next = cur->next;cur->next = prev;prev = cur, cur = next;}return prev;}
};
方法二:递归
1->2->3->4
因为用递归,翻转顺序指定是
从后往前
但是注意的是,返回的值应该是头节点,也就是4的值
那么如何递归?
- 接收返回值
- 递归当前两个节点
- 返回返回值
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* ListNode *next;* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}* };*/
class Solution {
public:ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {if (!head || !head->next) return head;ListNode *tail = reverseList(head->next);head->next->next = head;head->next = nullptr;return tail;}
};
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* public class ListNode {* int val;* ListNode next;* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }* }*/
class Solution {public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {if(head == null)return null;ListNode l = head.next;head.next = null;while(l != null){ListNode ll = l.next;l.next = head;head = l;l = ll;}return head;}
}
7. 合并两个排序的链表
原题链接
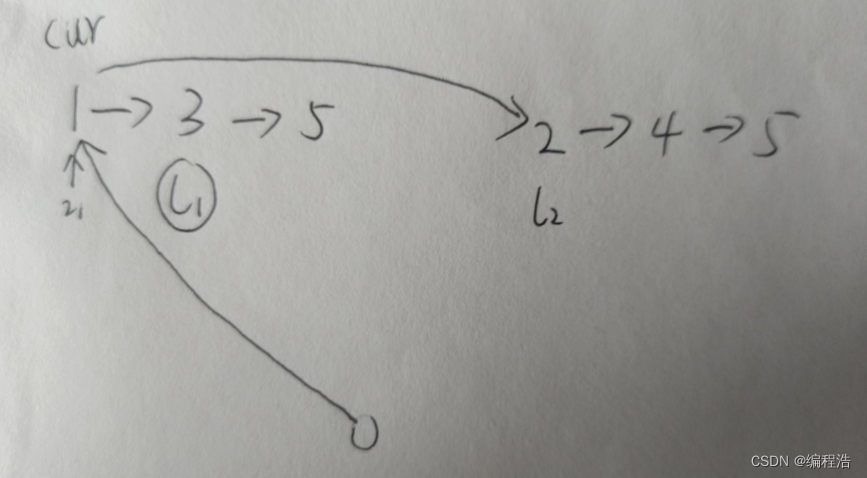
定义一个头节点,然后定义一个链表cur指向辅助
主要是完成
直接在两个表上的链路连接
比如 1->3 2->4合并
因为1小于2
那么直接让1->2(前提 l1的角标已经移到3)
如图
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* ListNode *next;* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}* };*/
class Solution {
public:ListNode* merge(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2) {ListNode *dummy = new ListNode(0);ListNode *cur = dummy;while (l1 != NULL && l2 != NULL) {if (l1 -> val < l2 -> val) {cur -> next = l1;l1 = l1 -> next;}else {cur -> next = l2;l2 = l2 -> next;}cur = cur -> next;}cur -> next = (l1 != NULL ? l1 : l2);return dummy -> next;}
};
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* public class ListNode {* int val;* ListNode next;* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }* }*/
class Solution {public ListNode merge(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {// 1. 先判空if(l1 == null) return l2;if(l2 == null) return l1;// 2. 创建头节点 便于返回答案ListNode Head = new ListNode(0);ListNode cur = Head;while(l1 != null && l2 != null){ListNode p1 = l1.next;ListNode p2 = l2.next;if(l1.val <= l2.val){cur.next = l1;l1 = p1;} else {cur.next = l2;l2 = p2;}cur = cur.next;}if(l1 == null && l2 != null)cur.next = l2;if(l1 != null && l2 == null)cur.next = l1;return Head.next;}
}
8. 复杂链表的复刻
原题链接

/*** Definition for singly-linked list with a random pointer.* struct ListNode {* int val;* ListNode *next, *random;* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL), random(NULL) {}* };*/
class Solution {
public:ListNode *copyRandomList(ListNode *head) {for(auto p = head; p ; ) //遍历原链表{ auto np = new ListNode(p->val); //复刻节点auto next = p->next; //留存原链表当前节点p的下一个节点p->next = np;//将原链表当前节点p指向复刻节点np->next = next;//复刻节点np指向原链表当前节点的下一个节点p = next; //p指针后移}for (auto p = head; p; p = p->next->next)//对原链表random指针的复刻。{if (p->random)p->next->random = p->random->next;}auto dummy = new ListNode(-1); //虚拟头结点auto cur = dummy; //尾节点for (auto p = head; p; p = p->next) //将原链表和复刻链表拆分出来,并将原链表复原。{cur->next = p->next;cur = cur->next;p->next = p->next->next;}return dummy->next;}
};
/*** Definition for singly-linked list with a random pointer.* class ListNode {* int val;* ListNode next, random;* ListNode(int x) { this.val = x; }* };*/
class Solution {public ListNode copyRandomList(ListNode head) {if(head == null)return null;ListNode cur = head;while(cur != null){ListNode temp = new ListNode(cur.val);temp.next = cur.next;cur.next = temp;cur = cur.next.next;}cur = head;while(cur != null){ListNode temp = cur.next;if(cur.random != null){temp.random = cur.random.next;} else {temp.random = new ListNode(-1);}cur = cur.next.next;}// 创建一个头节点 便于返回节点ListNode H = new ListNode(0);H.next = head.next;cur = head;while(cur != null){ListNode temp = cur.next;cur.next = cur.next.next;if(temp.next != null){temp.next = temp.next.next;}cur = cur.next;}return H.next;}
}
9. 二叉搜索树与双向链表
原题链接
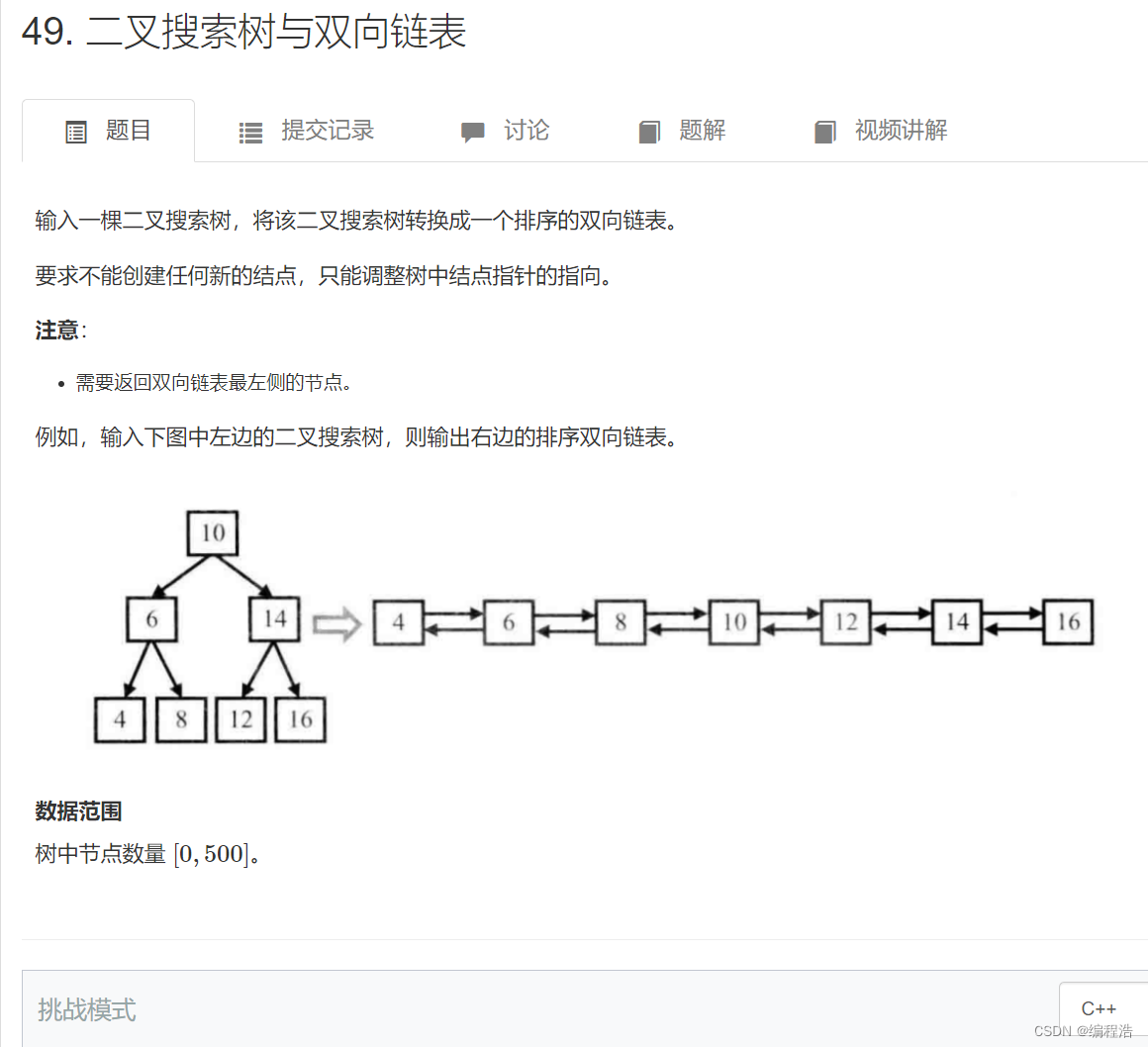
就在中序递归遍历的基础上改了一点点,用一个pre指针保存中序遍历的前一个结点。
因为是中序遍历,遍历顺序就是双线链表的建立顺序;
每一个结点访问时它的左子树肯定被访问过了,所以放心大胆的改它的left指针,不怕树断掉;
同理,pre指向的结点保存的数肯定小于当前结点,所以其左右子树肯定都访问过了,所以其right指针也可以直接改。
最后需要一直向左找到双向链表的头结点。
/*** Definition for a binary tree node.* struct TreeNode {* int val;* TreeNode *left;* TreeNode *right;* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}* };*/
class Solution {
public:TreeNode* pre = NULL;TreeNode* convert(TreeNode* root) {dfs(root);while(root && root->left) root = root->left;return root;}void dfs(TreeNode* root){if(!root) return;dfs(root->left);root->left = pre;if(pre) pre->right = root;pre = root;dfs(root->right);}
};
class Solution {TreeNode first = null;TreeNode last = null;public TreeNode convert(TreeNode root) {helper(root);return first;}private void helper(TreeNode node) {if (node == null) {return;}helper(node.left);if (last == null) {first = node;} else {last.right = node;node.left = last;}last = node;helper(node.right);}
}