一 为什么引入智能指针?解决了什么问题?
C++ 程序设计中使用堆内存是非常频繁的操作,堆内存的申请和释放都由程序员自己管理。但使用普通指针,容易造成内存泄露(忘记释放)、二次释放、程序发生异常时内存泄露等问题等。
另外,使用普通指针容易产生 野指针、悬空指针 等问题。
所以 C++11 就引入了智能指针来管理内存。
二 常用的智能指针与区别
常用智能指针有 shared_ptr、unique_ptr 与 weak_ptr
- unique_ptr: 独占式指针,同一时刻只允许有一个 unique_ptr 指针指向一个对象
- shared_ptr: 共享式指针,同一时刻允许多个 shared_ptr 指针指向同一个对象。
- 缺点:出现相互引用时,容易导致死锁或者内存无法释放内存的问题
- weak_ptr: 为了解决 shared_ptr 相互引用可能导致的死锁或无法释放内存的问题而引入,通常与shared_ptr 配合使用。但是由于缺少引用计数,一旦最后一个指向对象的shared_ptr被销毁,对象就会被释放。即使有weak_ptr指向对象,对象也还是会被释放。 C++11智能指针(weak_ptr) - 简书 (jianshu.com)
三 常用智能指针使用例子
1 unique_ptr 例子
unique_ptr 是一个独享所有权的智能指针
#include<memory>
#include<string>
#include<iostream>class Person
{
public:Person(std::string name):m_name(name){std::cout << "Person constructor name: " << m_name << std::endl;}~Person(){std::cout << "Person destructor name: " << m_name << std::endl;}private:std::string m_name;
};#include<memory>void testUniquePtr()
{std::unique_ptr<Person> p1_ptr(new Person("P1 ---"));std::unique_ptr<Person> p2_ptr = std::move(p1_ptr);// std::unique_ptr<Person> p3_ptr = p2_ptr; // 编译不过// std::unique_ptr<Person> p4_ptr(p2_ptr); // 编译不过}int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{testUniquePtr();return 0;
}
输出
2 shared_ptr 例子
#include<memory>
#include<iostream>
#include<string>using namespace std;void testSharedPtr()
{shared_ptr<string> pa(new string("PAAAA"));shared_ptr<string> pb(new string("PBBBB"));cout << "*pa " << *pa << endl;//CHNcout << "pa.use_count " << pa.use_count() << endl;//1cout << "*pb " << *pb << endl;//USAcout << "pb.use_count " << pb.use_count() << endl;//1pa = pb;cout << *pa << endl;//USAcout << "pa.use_count " << pa.use_count() << endl;//2:pa和pb指向同一个资源USA了,该资源的计数为2,所以pb、pb都输出2cout << "pb.use_count " << pb.use_count() << endl;//2pa.reset();pb.reset();cout << "pa.use_count " << pa.use_count() << endl;//0cout << "pb.use_count " << pb.use_count() << endl;//0
}int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{testSharedPtr();return 0;
}
3 weak_ptr 例子
3.1 shared_ptr 相互引用的问题
// a.h
#include<memory>class B;class A
{
public:A(){std::cout << "A constructor ---" << std::endl;}~A(){std::cout << "A destructor ---" << std::endl;}public:std::shared_ptr<B> m_b_ptr;
};// b.h
#include<memory>class A;class B
{
public:B(){std::cout << "A constructor ---" << std::endl;}~B(){std::cout << "A destructor ---" << std::endl;}public:std::shared_ptr<A> m_a_ptr;
};// main.cpp
void testSharedPtr()
{std::shared_ptr<A> pa(new A);cout << "pa.use_count " << pa.use_count() << endl;//1std::shared_ptr<B> pb(new B);cout << "pb.use_count " << pb.use_count() << endl;//1pa->m_b_ptr = pb;cout << "pb.use_count " << pb.use_count() << endl;//2cout << "pa.use_count " << pa.use_count() << endl;//1pb->m_a_ptr = pa;//由于share_ptr是共享资源,所以pb所指向的资源的引用计数也会加1cout << "pb.use_count " << pb.use_count() << endl;//2cout << "pa.use_count " << pa.use_count() << endl;//2}int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{testSharedPtr();return 0;
}输出 :
通过输出可以看到未执行析构函数,存在内存泄漏。
引用计数分别增加到了 2 ,不为 0 就意味着无法释放内存。
3.2 weak_ptr 与 share_ptr 使用
// a.h
#include<memory>class B;class A
{
public:A(){std::cout << "A constructor ---" << std::endl;}~A(){std::cout << "A destructor ---" << std::endl;}public:std::weak_ptr<B> m_b_ptr;
};// b.h
#include<memory>class A;class B
{
public:B(){std::cout << "A constructor ---" << std::endl;}~B(){std::cout << "A destructor ---" << std::endl;}public:std::shared_ptr<A> m_a_ptr;
};// main.cpp
void testWeakPtr()
{std::shared_ptr<A> pa(new A);cout << "pa.use_count " << pa.use_count() << endl;//1std::shared_ptr<B> pb(new B);cout << "pb.use_count " << pb.use_count() << endl;//1pa->m_b_ptr = pb;cout << "pb.use_count " << pb.use_count() << endl;//1cout << "pa.use_count " << pa.use_count() << endl;//2pb->m_a_ptr = pa;cout << "pb.use_count " << pb.use_count() << endl;//1 由于 weak_ptr 是弱引用,不会增加引用计数cout << "pa.use_count " << pa.use_count() << endl;//2 由于share_ptr是共享资源,所以pb所指向的资源的引用计数也会加1}int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{testWeakPtr();return 0;
}输出:

通过输出可以看到执行析构函数,不存在内存泄漏。
// 资源B的引用计数一直就只有1,当pb析构时,B的计数减一,变为0,B得到释放,
// B释放的同时也会使A的计数减一,同时pa自己析构时也会使资源A的计数减一,那么A的计数为0,A得到释放。
四 智能指针的原理与简单实现
智能指针实际运用的就是c++ 中的 RAII 技术,详情见 C++ 学习系列 二 -- RAII 机制_在河之洲木水的博客-CSDN博客
1. unique_ptr
因为是独占型指针,不可以拷贝与赋值,所以需要禁止拷贝构造函数与赋值函数
// my_nuique_ptr.h
template<typename T>
class my_unique_ptr
{
public:my_unique_ptr(T* ptr = nullptr);~my_unique_ptr();my_unique_ptr(my_unique_ptr&& other_ptr); // c++ 中声明移动构造函数后,则自动禁用拷贝构造函数my_unique_ptr& operator=(my_unique_ptr&& other_ptr); // c++ 中声明移动赋值函数后,则自动禁用拷贝赋值函数T& operator*() const; // 指针的基本操作,取值T* operator->() const;operator bool() const; // 提供一个本类型到bool的隐式转换,不允许使用参数private:T* m_ptr;
};template<typename T>
my_unique_ptr<T>::my_unique_ptr(T* ptr):m_ptr(ptr)
{}template<typename T>
my_unique_ptr<T>::~my_unique_ptr()
{delete m_ptr;
}template<typename T>
my_unique_ptr<T>::my_unique_ptr(my_unique_ptr&& other_ptr)
{this->m_ptr = other_ptr.m_ptr;other_ptr.m_ptr = nullptr;
}template<typename T>
my_unique_ptr<T>&
my_unique_ptr<T>::operator=(my_unique_ptr&& other_ptr)
{this->m_ptr = other_ptr.m_ptr;other_ptr.m_ptr = nullptr;return this;
}template<typename T>
T& my_unique_ptr<T>::operator*() const
{return *m_ptr;
}template<typename T>
T* my_unique_ptr<T>::operator->() const
{return m_ptr;
}template<typename T>
my_unique_ptr<T>::operator bool() const
{return m_ptr;
}// main.cpp#include<iostream>
#include"my_unique_ptr.h"void testFunc2()
{my_unique_ptr<Person> my_ptr(new Person("p1 ------"));std::cout << "person name1: "<<my_ptr->getName() << std::endl;my_unique_ptr<Person> my_ptr2(std::move(my_ptr));std::cout << "person name2: "<<my_ptr2->getName() << std::endl;//my_unique_ptr<Person> my_ptr3 = my_ptr; // 编译失败// my_unique_ptr<Person> my_ptr4(my_ptr); // 编译失败}int main()
{testFunc2();return 0;
}输出:
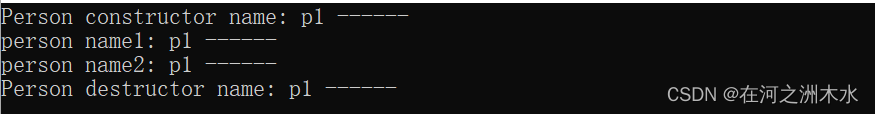
2. shared_ptr
shared_ptr 是共享型指针,同一时刻可以右多个指针指向同一个对象,只有最后一个指针离开作用域时,才会调用对象的析构函数,释放对象中的资源。
那么是如何实现的呢?
答案是:利用引用计数法。在 类 shared_ptr 中定义一个成员变量引用计数 share_count ,当有一个指针指向相同的对象时,就将 share_count 就自增 1,为了各 shared_ptr 的引用计数 share_count 同时增加,可以将 share_count 手动开辟一个空间,用普通指针指向它。
若是考虑到多线程的场景,还应该将 引用计数 share_count 加上锁才可以。
// my_shared_ptr.h
#include <mutex>
static std::mutex gMutex;template<typename T>
class my_shared_ptr
{
public:my_shared_ptr(T* ptr = nullptr);~my_shared_ptr();my_shared_ptr(my_shared_ptr& other_ptr);my_shared_ptr& operator=(my_shared_ptr& other_ptr);T& operator*();T* operator->();int user_count();private:void addCount();void minusCount();T* m_ptr;int* share_count = nullptr;
};template<typename T>
my_shared_ptr<T>::my_shared_ptr(T* ptr):m_ptr(ptr)
{if(!share_count){share_count = new int(1);}
}template<typename T>
my_shared_ptr<T>::~my_shared_ptr()
{minusCount();if((*this->share_count) == 0 && m_ptr)delete m_ptr;
}template<typename T>
my_shared_ptr<T>::my_shared_ptr(my_shared_ptr& other_ptr)
{this->m_ptr = other_ptr.m_ptr;this->share_count = other_ptr.share_count;addCount();
}template<typename T>
my_shared_ptr<T>& my_shared_ptr<T>::operator=(my_shared_ptr& other_ptr)
{this->m_ptr = other_ptr.m_ptr;this->share_count = other_ptr.share_count;addCount();return *this;
}template<typename T>
T& my_shared_ptr<T>::operator*()
{return *this->m_ptr;
}template<typename T>
T* my_shared_ptr<T>::operator->()
{return this->m_ptr;
}template<typename T>
void my_shared_ptr<T>::addCount()
{std::lock_guard<std::mutex> guard(gMutex);(*this->share_count)++;
}template<typename T>
void my_shared_ptr<T>::minusCount()
{std::lock_guard<std::mutex> guard(gMutex);(*this->share_count)--;
}template<typename T>
int my_shared_ptr<T>::user_count()
{return *this->share_count;
}// person.h
#include<string>class Person
{
public:Person(std::string name);Person(const Person& p);~Person();std::string& getName();private:std::string m_name;
};// person.cpp
#include "person.h"
#include<iostream>
Person::Person(std::string name):m_name(name)
{std::cout << "Person constructor name: " << m_name << std::endl;
}Person::Person(const Person& p)
{this->m_name = p.m_name;std::cout << "Person copy constructor name: " << this->m_name << std::endl;
}Person::~Person()
{std::cout << "Person destructor name: " << m_name << std::endl;
}std::string& Person::getName()
{return m_name;
}// main.cppvoid testMySharedPtr()
{my_shared_ptr<Person> ptr1(new Person("ptr1 ---"));std::cout << "ptr1 user_count: " << ptr1.user_count() << std::endl;my_shared_ptr<Person> ptr2(ptr1);std::cout << "ptr1 user_count: " << ptr1.user_count() << std::endl;std::cout << "ptr2 user_count: " << ptr2.user_count() << std::endl;my_shared_ptr<Person> ptr3 = ptr2;std::cout << "ptr1 user_count: " << ptr1.user_count() << std::endl;std::cout << "ptr2 user_count: " << ptr2.user_count() << std::endl;std::cout << "ptr3 user_count: " << ptr3.user_count() << std::endl;}int main()
{testMySharedPtr();return 0;
}
输出
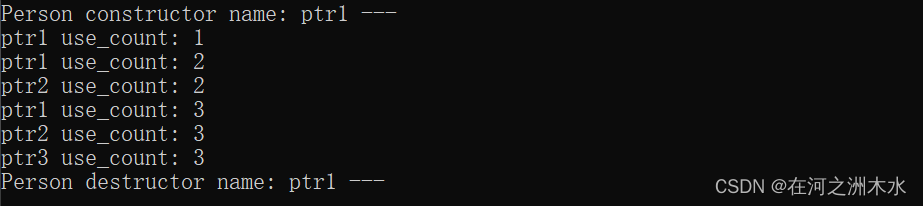
3. weak_ptr
前面提到过,weak_ptr 是与 shared_ptr 配合使用的,weak_ptr 无引用计数。
// my_weak_ptr.h
template<typename T>
class my_weak_ptr
{
public:my_weak_ptr(T* ptr = nullptr);~my_weak_ptr();my_weak_ptr(my_weak_ptr& other_ptr);my_weak_ptr& operator=(my_weak_ptr& other_ptr);T& operator*();T* operator->();private:T* m_ptr;
};template<typename T>
my_weak_ptr<T>::my_weak_ptr(T* ptr):m_ptr(ptr)
{}template<typename T>
my_weak_ptr<T>::~my_weak_ptr()
{if(m_ptr)delete m_ptr;
}template<typename T>
my_weak_ptr<T>::my_weak_ptr(my_weak_ptr& other_ptr)
{this->m_ptr = other_ptr.m_ptr;
}template<typename T>
my_weak_ptr<T>& my_weak_ptr<T>::operator=(my_weak_ptr& other_ptr)
{this->m_ptr = other_ptr.m_ptr;return *this;
}template<typename T>
T& my_weak_ptr<T>::operator*()
{return *this->m_ptr;
}template<typename T>
T* my_weak_ptr<T>::operator->()
{return this->m_ptr;
}// A.h
#include"my_weak_ptr.h"class B;class A
{
public:A();~A();public:my_weak_ptr<B> m_b_ptr;
};// A.cpp
A::A()
{std::cout << "A constructor ---" << std::endl;}A::~A()
{std::cout << "A destructor ---" << std::endl;
}// B.h
#include"my_shared_ptr.h"class A;class B
{
public:B();~B();public:my_shared_ptr<A> m_a_ptr;
};// B.cpp
#include "b.h"
#include<iostream>
B::B()
{std::cout << "B constructor ---" << std::endl;}B::~B()
{std::cout << "B destructor -- " << std::endl;
}// main.cppvoid testMyWeakPtr()
{my_shared_ptr<A> pa(new A);my_weak_ptr<B> pb(new B);pa->m_b_ptr = pb;pb->m_a_ptr = pa;}int main()
{testMyWeakPtr();return 0;
}
输出:

忽视其中 B 析构了两次,通过结果可以看到,A 与 B 均能够析构。