1 前言
Shader Graph 16.0.3 中有 208 个 Node(节点),本文梳理了 Shader Graph 中大部分 Node 的释义,官方介绍详见→Node-Library。
选中节点后,右键弹出菜单栏,点击 Open Documentation(或 按 F1 键),浏览器中将跳转到该节点的官方释义网页。
Shader Graph 通过图像的形式表达了顶点变换和片元着色流程,其背后都是一些列的数学理论支撑着,为更好地理解 Shader Graph 中的 Node,推荐读者学习以下内容。
-
渲染管线
-
空间和变换
-
Shader常量、变量、结构体、函数
-
法线贴图和凹凸映射
-
屏幕深度和法线纹理简介
-
Shader Graph简介
2 Artistic(美术)
Artistic 官方介绍详见→Artistic Nodes。
2.1 Adjustment(颜色调整)
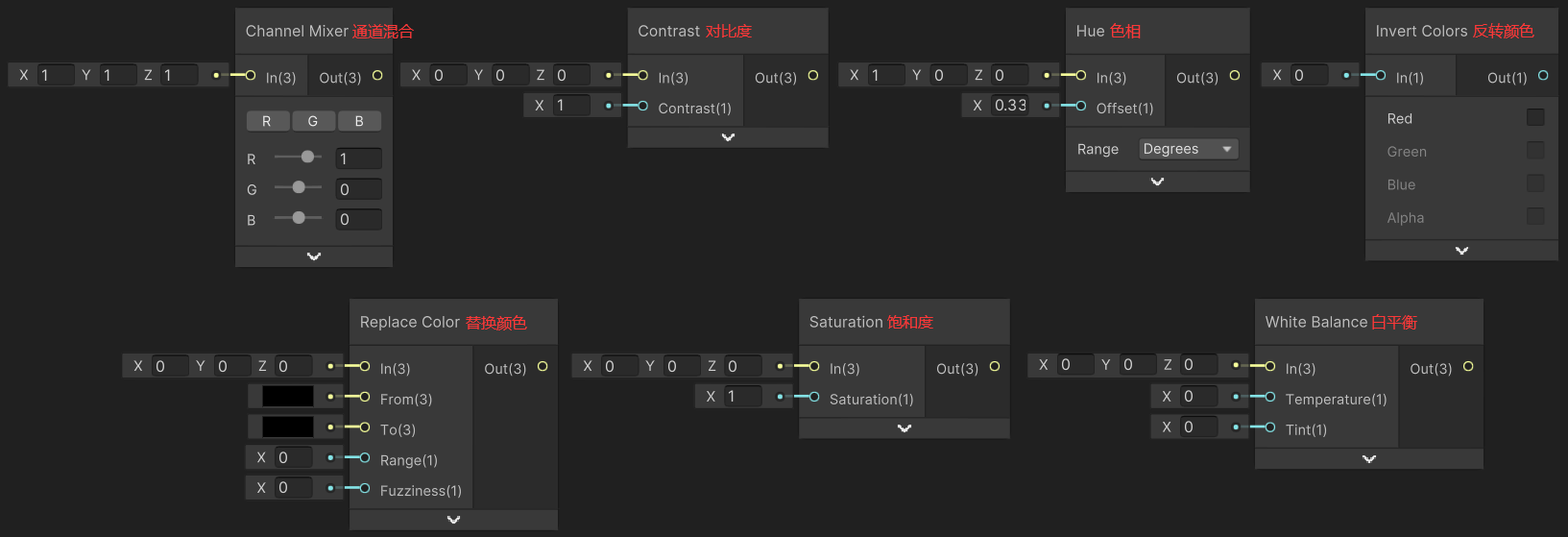
1)Channel Mixer(通道混合)
Channel Mixer 节点用于通道混合,根据混合权重对每个通道进行混合,_ChannelMixer_Red、_ChannelMixer_Green、_ChannelMixer_Blue 分别为红色、绿色、蓝色通道的权重向量。
void ChannelMixer(float3 In, float3 _ChannelMixer_Red, float3 _ChannelMixer_Green, float3 _ChannelMixer_Blue, out float3 Out) {Out = float3(dot(In, _ChannelMixer_Red), dot(In, _ChannelMixer_Green), dot(In, _ChannelMixer_Blue));
}2)Contrast(调整对比度)
Contrast 节点用于调整对比度。
void Contrast(float3 In, float Contrast, out float3 Out) {float midpoint = pow(0.5, 2.2); // 约等于0.217638Out = (In - midpoint) * Contrast + midpoint;
}说明:midpoint = pow(0.5, 2.2) 是对 0.5 进行了伽马编码(详见伽马校正),解决亮度异常问题。
3)Hue(调整色相)
Hue 节点用于调整色相,其实现见→Hue Node。
void Hue(float3 In, float Offset, out float3 Out)说明:色相调整有 2 种模式:Degrees、 Normalized。在可视化界面中,色相的调整一般通过色相环实现,offset 就对应色相环中的角度,在 Degrees 模式下,offset 取值范围是 0 ~ 360°,在 Normalized 模式下,offest 取值范围是 0 ~ 1。
4)Invert Colors(反转颜色)
Invert Colors 节点用于反转颜色。
void InvertColors(float4 In, float4 InvertColors, out float4 Out) {Out = abs(InvertColors - In);
}5)Replace Color(替换颜色)
Replace Color 节点用于替换颜色,如果输入颜色与 From 颜色比较接近,就将输入颜色替换为 To 颜色,Range 是输入颜色被替换的边界,Fuzziness 是模糊系数。
void ReplaceColor(float3 In, float3 From, float3 To, float Range, float Fuzziness, out float3 Out) {float Distance = distance(From, In);Out = lerp(To, In, saturate((Distance - Range) / max(Fuzziness, 1e-5))); // 1e-5=0.00001, 避免Fuzziness为0时除数为0
}6)Saturation(调整饱和度)
Saturation 节点用于调整饱和度。
void Saturation(float3 In, float Saturation, out float3 Out) {float luma = dot(In, float3(0.2126729, 0.7151522, 0.0721750));Out = luma.xxx + Saturation.xxx * (In - luma.xxx);
}7)White Balance(调整白平衡)
White Balance 节点用于调整白平衡,其实现见→White Balance Node,Temperature 用于调整色温,Tint 用于调整色调。
void WhiteBalance(float3 In, float Temperature, float Tint, out float3 Out)2.2 Blend(颜色混合)
Blend 节点用于混合两种颜色。

Mode 取值有:Burn、Darken、Difference、Dodge、Divide、Exclusion、Hard Light、Hard Mix、Lighten、Linear Burn、Linear Dodge、Linear Light、Linear Light Add Sub、Multiply、Negation、Overlay(默认值)、Pin Light、Screen、Soft Light、Subtract、Vivid Light、Overwrite。不同 Mode 对应的混合函数详见→Blend Node。
2.3 Filter(滤波器)
Filter 里只有一个 Node:Dither,它用于模拟颜色随机振动,它通过一个 4 x 4 的矩阵模拟伪随机振动,这个矩阵的每一行和每一列都呈波浪状(一大一小交错排列)。

void Dither(float4 In, float4 ScreenPosition, out float4 Out) {float2 uv = ScreenPosition.xy * _ScreenParams.xy;float DITHER_THRESHOLDS[16] = {1.0 / 17.0, 9.0 / 17.0, 3.0 / 17.0, 11.0 / 17.0,13.0 / 17.0, 5.0 / 17.0, 15.0 / 17.0, 7.0 / 17.0,4.0 / 17.0, 12.0 / 17.0, 2.0 / 17.0, 10.0 / 17.0,16.0 / 17.0, 8.0 / 17.0, 14.0 / 17.0, 6.0 / 17.0};uint index = (uint(uv.x) % 4) * 4 + uint(uv.y) % 4;Out = In - DITHER_THRESHOLDS[index];
}说明:对于 ScreenPosition 的取值,用户可以自己输入,也可以使用 Unity 自带的取值,主要有:Default、Raw、Center、Tiled。
2.4 Mask(遮罩)
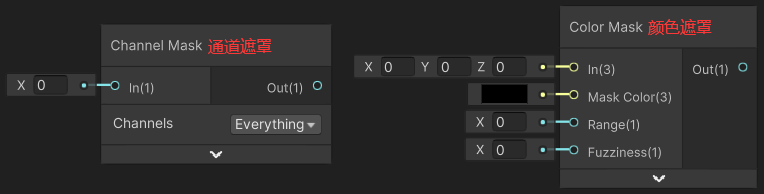
1)Channel Mask(通道遮罩)
Channel Mask 节点用于遮罩通道,将被遮罩的通道置为 0,如下是将 RG 通道遮罩的代码逻辑。
void ChannelMask_RedGreen(float4 In, out float4 Out) {Out = float4(0, 0, In.b, In.a);
}2)Color Mask(颜色遮罩)
Color Mask 节点用于颜色遮罩,计算输入颜色与目标颜色的近似程度,比较接近就输出 1,偏移比较大就输出 0。
void ColorMask(float3 In, float3 MaskColor, float Range, float Fuzziness, out float4 Out) {float Distance = distance(MaskColor, In);Out = saturate(1 - (Distance - Range) / max(Fuzziness, 1e-5)); // 1e-5=0.00001, 避免Fuzziness为0时除数为0
}2.5 Normal(法线)
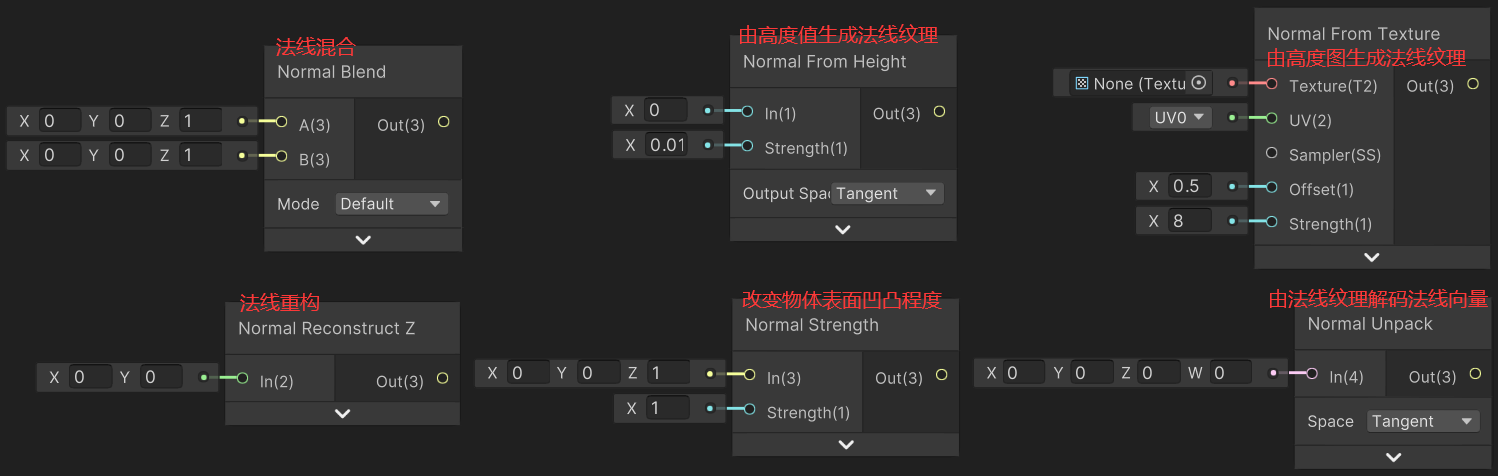
1)Normal Blend(法线混合)
Normal Blend 有 2 种模式:Default、Reoriented。
void NormalBlend(float3 A, float3 B, out float3 Out) { // Default模式Out = normalize(float3(A.rg + B.rg, A.b * B.b));
}void NormalBlend_Reoriented(float3 A, float3 B, out float3 Out) { // Reoriented模式float3 t = A.xyz + float3(0.0, 0.0, 1.0);float3 u = B.xyz * float3(-1.0, -1.0, 1.0);Out = (t / t.z) * dot(t, u) - u;
}2)Normal From Height(由高度值转换为法线纹理)
Normal From Height 节点用于将输入的高度值转换到法线纹理中。Output Space(输出空间)有:Tangent(切线空间)、World(世界空间)。源码详见→Normal From Height Node,它通过对 Position、In 求 ddx 和 ddy 等运算得到法线值。
void NormalFromHeight(float In, out float3 Out)3)Normal From Texture(由高度纹理转换为法线纹理)
Normal From Texture 节点用于将高度纹理转换为法线纹理。Offset 为高度采样 uv 偏移量,Strength 用于调整法线强度(物体表面凹凸程度)。
void NormalFromTexture(Texture texture, SamplerState Sampler, float2 UV, float Offset, float Strength, out float3 Out) {Offset = pow(Offset, 3) * 0.1;float2 offsetU = float2(UV.x + Offset, UV.y);float2 offsetV = float2(UV.x, UV.y + Offset);float normalSample = Texture.Sample(Sampler, UV);float uSample = Texture.Sample(Sampler, offsetU);float vSample = Texture.Sample(Sampler, offsetV);float3 va = float3(1, 0, (uSample - normalSample) * Strength); // 切线(高度图1m一个像素)float3 vb = float3(0, 1, (vSample - normalSample) * Strength); // 切线(高度图1m一个像素)Out = normalize(cross(va, vb)); // 通过2条切线向量叉乘得到法线向量
}4)Normal Reconstract Z(法线重构)
Normal Reconstract Z 节点用于重构法线向量,原来的 z 分量被抛弃,由 x、y 分量推导出,再对法线向量进行归一化。
void NormalReconstructZ(float2 In, out float3 Out) {float reconstructZ = sqrt(1.0 - saturate(dot(In.xy, In.xy)));float3 normalVector = float3(In.x, In.y, reconstructZ);Out = normalize(normalVector);
}5)Normal Strength(调整物体表面凹凸程度)
Normal Strength 节点用于调整法线强度(物体表面凹凸程度,案例见→法线贴图和凹凸映射)。注意,调整法线向量后需要归一化法线向量。
void NormalStrength(float3 In, float Strength, out float3 Out) {Out = {precision}3(In.rg * Strength, lerp(1, In.b, saturate(Strength)));
}说明:"{precision}3" 是一个类似于构造函数的语法,用于构建一个包含 3 个分量的向量。
6)Normal Unpack(由法线纹理解码法线向量)
Normal Unpack 节点用于从法线纹理中解码法线向量。Output Space(输出空间)有:Tangent(切线空间)、Object(模型空间)。
void NormalUnpack(float4 In, out float3 Out) { //TangentOut = UnpackNormalmapRGorAG(In);
}void NormalUnpackRGB(float4 In, out float3 Out) { // ObjectOut = UnpackNormalmapRGB(In);
}2.6 Utility(实用工具)
Utility 中只有 Colorspace Conversion 节点,用于进行 RGB、Linear、HSV 颜色空间之间的相互转换,源码详见→Colorspace Conversion Node。

3 Channel(通道)
Channel 官方介绍详见→Channel Nodes。

1)Combine(合并通道)
Combine 节点用于合并通道。
void Combine(float R, float G, float B, float A, out float4 RGBA, out float3 RGB, out float2 RG) {RGBA = float4(R, G, B, A);RGB = float3(R, G, B);RG = float2(R, G);
}
2)Flip(翻转通道)
Flip 节点用于翻转通道,即相应通道数值取反,Flip 取值为 0(未激活)或 1(激活)。
void Flip(float4 In, float4 Flip, out float4 Out) {Out = (Flip * -2 + 1) * In;
}3)Split(分离通道)
Split 节点用于分离通道,以下是输入为 2 维的情况,如果输入维数低于输出维数,高维通道补零输出。
void Split(float2 In, out float R, out float G, out float B, out float A) {R = In[0];G = In[1];B = 0;A = 0;
}4)Swizzle(交换通道)
Swizzle 节点用于交换通道,根据 Mask 中通道的顺序重组通道。如下是其中一种交换方式。
float4 _Swizzle_Out = In.xzyw;4 Input(输入)
Input 官方介绍详见→Input Nodes。
4.1 Basic(基础变量)
Basic 中是一些基础的变量节点,如:Boolean、Constant、Float、Integer、Slider、Time、Color、Vector2、Vector3、Vector4。
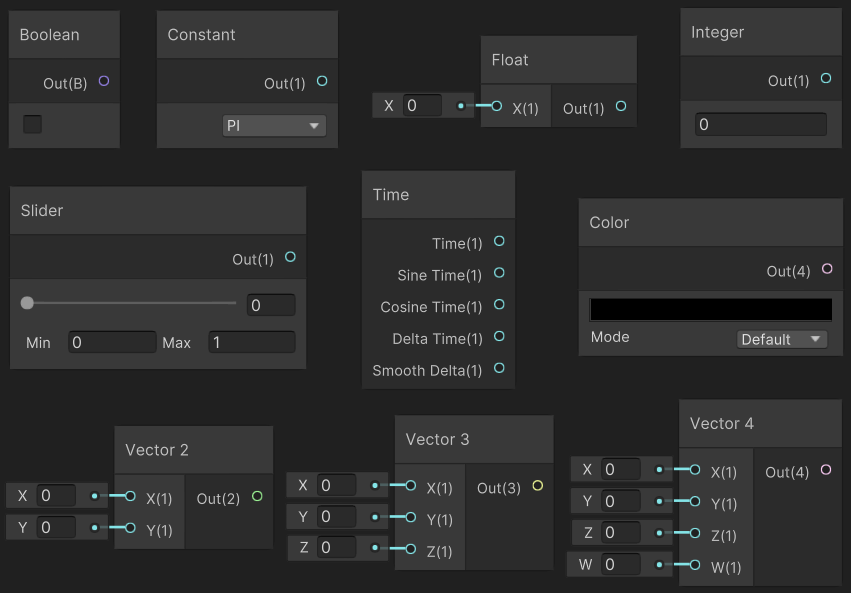
4.2 Geometry(顶点几何属性)
Geometry 中提供了访问顶点或片元几何属性的节点,如:Position、Screen Position、UV、Vertex Color、Tangent Vector、Bitangent Vector、Normal Vector、View Direction、View Vector。

- Position:顶点或片元的坐标,Space 取值有:Object(模型空间)、World(世界空间)、View(观察空间)、Tangent(切线空间)、Absolute World(绝对世界空间)。对于所有可编程渲染管线,Absolute World 选项始终返回对象在场景中的绝对世界位置,World 选项返回所选的可编程渲染管线的默认世界空间。HDRP(高清渲染管线)使用 Camera Relative 作为默认世界空间,URP(通用渲染管线)使用 Absolute World 作为默认世界空间。
- Screen Position:顶点或片元的屏幕坐标,Mode 取值有:Default、Raw、Center、Tiled。
- UV:顶点或片元的 UV 坐标。
- Vertex Color:顶点或片元的颜色。
- Tangent Vector:顶点或片元的切线向量,Space 取值有:Object(模型空间)、World(世界空间)、View(观察空间)、Tangent(切线空间)。
- Bitangent Vector:顶点或片元的副切线向量,Space 取值有:Object(模型空间)、World(世界空间)、View(观察空间)、Tangent(切线空间)。
- Normal Vector:顶点或片元的法线向量,Space 取值有:Object(模型空间)、World(世界空间)、View(观察空间)、Tangent(切线空间)。
- View Direction:顶点或片元的观察向量(顶点指向相机,已归一化),Space 取值有:Object(模型空间)、World(世界空间)、View(观察空间)、Tangent(切线空间)。
- View Vector:顶点或片元的观察向量(顶点指向相机,未归一化),Space 取值有:Object(模型空间)、World(世界空间)、View(观察空间)、Tangent(切线空间)。
Screen Position 不同模式下的实现如下。
// Default, 归一化的设备坐标(NDC), x、y值域: [0, 1]
float4 Out = float4(IN.NDCPosition.xy, 0, 0);
// Raw, 屏幕坐标, x值域: [0, w], y值域: [0, w]
float4 Out = IN.ScreenPosition;
// Center, 标准化的设备坐标, x、y值域: [-1, 1]
float4 Out = float4(IN.NDCPosition.xy * 2 - 1, 0, 0);
// Tiled, x值域: [-screenWidth/screenHeight, screenWidth/screenHeight], y值域: [-1, 1]
float4 Out = frac(float4((IN.NDCPosition.x * 2 - 1) * _ScreenParams.x / _ScreenParams.y, IN.{0}.y * 2 - 1, 0, 0));
// Pixel, 像素坐标, x值域: [0, screenWidth], y值域: [0, screenHeight]
float4 Out = float4(IN.PixelPosition.xy, 0, 0);
4.3 Gradient(渐变颜色)
Blackbody、Gradient、Sample Gradient 节点都是用于生成渐变颜色。

1) Blackbody(黑体辐射渐变采样)
Blackbody 节点通过模拟黑体辐射渐变采样得到渐变颜色,其实现见→Blackbody Node,它基于 Mitchell Charity 收集的数据,输出线性 RGB 空间的颜色,并使用一个 D65 白点和一个 CIE 1964 10 度的颜色空间执行转换,Temperature 为采样的温度或温度贴图(以开尔文为单位)。
void Blackbody(float Temperature, out float3 Out)2)Gradient(生成渐变对象)
Gradient 节点用于生成 Gradient 渐变对象,它通过 2 个 Color 和 2 个 Alpha 参数计算得到,实现见→Gradient Node。

3)Sample Gradient(渐变采样)
Sample Gradient 节点用于对 Gradient 进行渐变采样,其实现见→Sample Gradient Node,Time 为采样渐变的时间点 (0.0–1.0)。
void SampleGradient(float4 Gradient, float Time, out float4 Out)4.4 Lighting(光照)
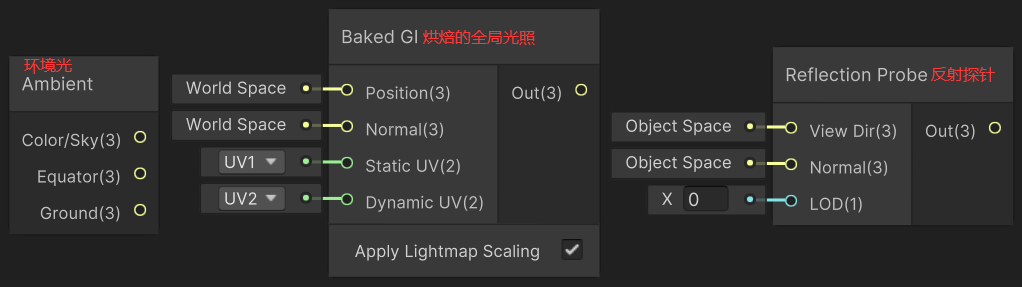
1)Ambient(环境光)
Ambient 节点用于获取环境光颜色。
float3 _Ambient_ColorSky = SHADERGRAPH_AMBIENT_SKY;
float3 _Ambient_Equator = SHADERGRAPH_AMBIENT_EQUATOR;
float3 _Ambient_Ground = SHADERGRAPH_AMBIENT_GROUND;2)Baked GI(烘焙的全局光照)
Baked GI 节点用于获取烘焙的全局光照颜色,Position 为顶点坐标(世界空间),Normal 为顶点法线(世界空间)、StaticUV 为静态 lightmap 的纹理坐标、DynamicUV 为动态 lightmap 的纹理坐标。
void BakedGI(float3 Position, float3 Normal, float2 StaticUV, float2 DynamicUV, out float Out) {Out = SHADERGRAPH_BAKED_GI(Position, Normal, StaticUV, DynamicUV, false);
}3)Reflection Probe(反射探针)
Reflection Probe 节点用于获取反射探针颜色。ViewDire 为顶点的坐标(模型空间),Normal 为顶点的法线向量(模型空间)。
void ReflectionProbe(float3 ViewDir, float3 Normal, float LOD, out float3 Out) {Out = SHADERGRAPH_REFLECTION_PROBE(ViewDir, Normal, LOD);
}4)Main Light Direction
Main Light Direction 节点用于获取顶点指向光源的单位方向向量(世界空间)。Shader Graph 13.1.9(2022.1+)版本才开始出现 Main Light Direction 节点。如果用户的 Shader Graph 版本较低,可以通过 8.2 节中 Custom Function 节点创建自定义函数,获取灯光方向。
4.5 Matrix(矩阵)
Matrix 中包含 Matrix 2x2、Matrix 3x3、Matrix 4x4、Transformation Matrix 节点。
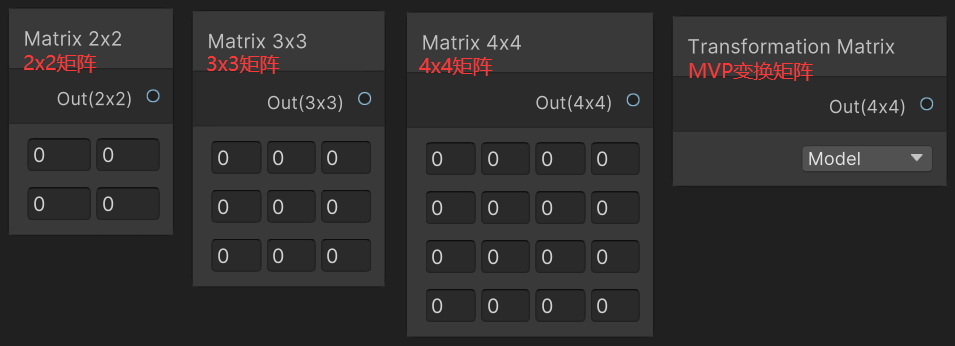
Transformation Matrix 节点可以获取到 Model、Inverse Model、View、Inverse View、Projection、Inverse Projection、View Projection、Inverse View Projection 矩阵,实现如下。
// Model, [模型空间->世界空间]的变换矩阵M
float4x4 _TransformationMatrix_Out = UNITY_MATRIX_M;
// InverseModel, [世界空间->模型空间]的变换矩阵I_M
float4x4 _TransformationMatrix_Out = UNITY_MATRIX_I_M;
// View, [世界空间->观察空间]的变换矩阵V
float4x4 _TransformationMatrix_Out = UNITY_MATRIX_V;
// InverseView, [观察空间->世界空间]的变换矩阵I_V
float4x4 _TransformationMatrix_Out = UNITY_MATRIX_I_V;
// Projection, [观察空间->裁剪空间]的变换矩阵P
float4x4 _TransformationMatrix_Out = UNITY_MATRIX_P;
// InverseProjection, [裁剪空间->观察空间]的变换矩阵I_P
float4x4 _TransformationMatrix_Out = UNITY_MATRIX_I_P;
// ViewProjection, [世界空间->裁剪空间]的变换矩阵VP
float4x4 _TransformationMatrix_Out = UNITY_MATRIX_VP;
// InverseViewProjection, [裁剪空间->世界空间]的变换矩阵I_VP
float4x4 _TransformationMatrix_Out = UNITY_MATRIX_I_VP;4.6 Scene(场景参数)

1)Camera(相机参数)
Camera 节点用于获取相机的以下属性。
- Position:相机的坐标(世界空间),代码:_WorldSpaceCameraPos。
- Direction:相机的 forward 向量。
- Orthographic:如果摄像机是正交摄像机,则返回 1,否则返回 0,代码:unity_OrthoParams.w。
- Near Plane:近裁剪平面到相机的距离,代码:_ProjectionParams.y。
- Far Plane:远裁剪平面到相机的距离,代码:_ProjectionParams.z。
- Z Buffer Sign:使用反转的 Z 缓冲区时返回 -1,否则返回 1,代码:_ProjectionParams.x。
- Width:摄像机的宽度(如果是正交摄像机),unity_OrthoParams.x。
- Height:摄像机的高度(如果是正交摄像机),unity_OrthoParams.y。
2)Fog(雾效参数)
Fog 节点用于获取 Color(雾效颜色)和 Density(裁剪空间深度处的雾效强度)。
void Fog(float3 Position, out float4 Color, out float Density) {SHADERGRAPH_FOG(Position, Color, Density);
}3)Object(对象参数)
Object 节点用于获取当前渲染对象在世界空间中的位置缩放。
float3 _Object_Position = SHADERGRAPH_OBJECT_POSITION;
float3 _Object_Scale = float3(length(float3(UNITY_MATRIX_M[0].x, UNITY_MATRIX_M[1].x, UNITY_MATRIX_M[2].x)),length(float3(UNITY_MATRIX_M[0].y, UNITY_MATRIX_M[1].y, UNITY_MATRIX_M[2].y)),length(float3(UNITY_MATRIX_M[0].z, UNITY_MATRIX_M[1].z, UNITY_MATRIX_M[2].z)));4)Scene Color(场景颜色)
Scene Color 节点用于获取 UV 处的颜色缓冲区的颜色值。
void SceneColor(float4 UV, out float3 Out) {Out = SHADERGRAPH_SAMPLE_SCENE_COLOR(UV);
}说明:在通用渲染管线中,此节点返回 Camera Opaque Texture 的值,此纹理的内容仅适用于透明对象。将主节点的 Material Options 面板上的 Surface Type 下拉选单设置为 Transparent 可以从此节点接收正确的值。
5)Scene Depth(场景深度)
Scene Depth 节点用于获取 UV 处的深度缓冲区的深度值。
void SceneDepth_Raw(float4 UV, out float Out) {Out = SHADERGRAPH_SAMPLE_SCENE_DEPTH(UV);
}6)Screen(屏幕参数)
Screen 节点用于获取屏幕的宽度和高度参数。
float _Screen_Width = _ScreenParams.x;
float _Screen_Height = _ScreenParams.y;4.7 Texture(纹理)
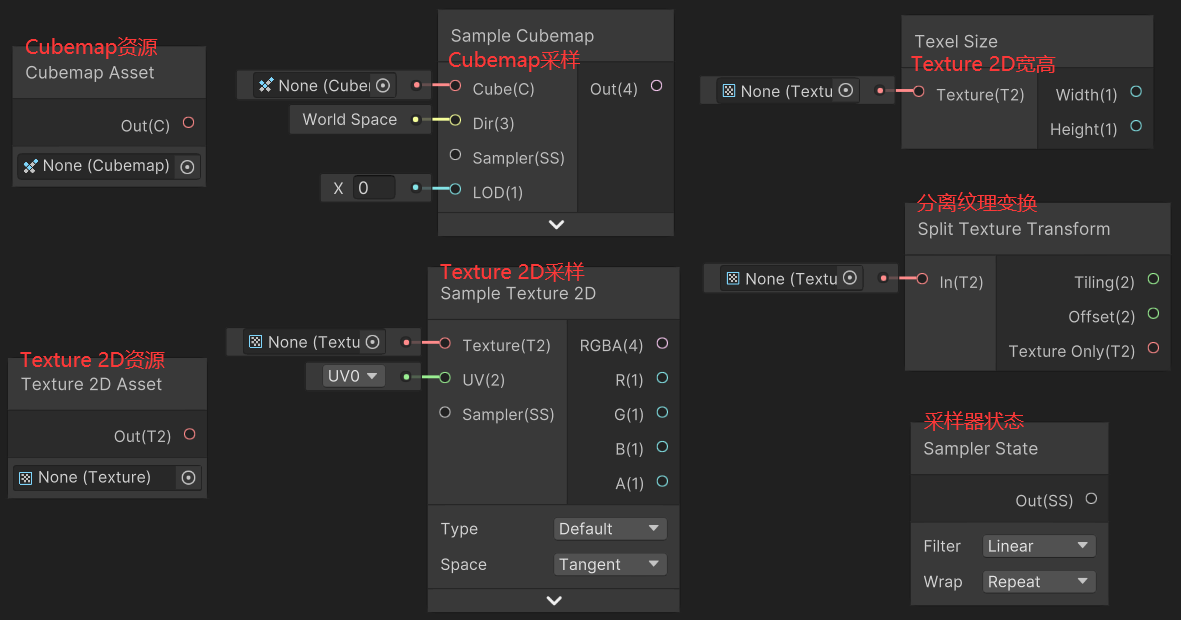
1)Texture 2D Asset 和 Cubemap Asset
Texture 2D Asset 节点用于导入 Texture 2D 资源,Cubemap Asset 节点用于导入 Cubemap 资源。
2)Sample Texture 2D 和 Sample Cubemap
Sample Texture 2D 节点用于对 Texture 2D 进行采样,Sample Cubemap 节点用于对 Cubemap 进行采样。
3)Texel Size(Texture 2D 的宽高)
Texel Size 节点用于获取 Texture 2D 的宽度和高度。
float _TexelSize_Width = Texture_TexelSize.z;
float _TexelSize_Height = Texture_TexelSize.w;4)Split Texture Transform(Texture 2D 的缩放和偏移)
Split Texture Transform 节点用于 Texture 2D 的 Tiling(缩放)和 Offset(偏移)属性。
5)Sampler State(采样器的状态配置)
Sampler State 节点用于配置采样器的状态。Filter 定义了采样的滤波模式,选项有:Linear、Point、Trilinear;Wrap 定义了采样的包裹模式,选项有:Repeat、Clamp、Mirror、MirrorOnce。
5 Math(数学)
Math 官方介绍详见→Math Nodes,其中引用 Shader 中的函数释义详见→Shader常量、变量、结构体、函数。
5.1 Basic(基础运算)
// 加法, Out=A+B
void Add(float4 A, float4 B, out float4 Out)
// 减法, Out=A-B
void Subtract(float4 A, float4 B, out float4 Out)
// 乘法
void Multiply(float4 A, float4 B, out float4 Out) // Out=A*B
void Multiply(float4 A, float4x4 B, out float4 Out) // Out=mul(A,B)
void Multiply(float4x4 A, float4x4 B, out float4x4 Out) // Out=mul(A,B)
// 除法, Out=A/B
void Divide(float4 A, float4 B, out float4 Out)
// 幂运算, Out=pow(A,B)
void Power(float4 A, float4 B, out float4 Out)
// 平方根, Out=sqrt(In)
void SquareRoot(float4 In, out float4 Out)5.2 Advanced(高级运算)
// 绝对值, Out=abs(In)
void Absolute(float4 In, out float4 Out)
// 取反, Out=-1*In
void Negate(float4 In, out float4 Out)
// 倒数
void Reciprocal(float4 In, out float4 Out) // Out=1.0/In
void Reciprocal_Fast(float4 In, out float4 Out) // Out=rcp(In)
// 取余, Out=fmod(A,B)
void Modulo(float4 A, float4 B, out float4 Out)
// 指数
void Exponential(float4 In, out float4 Out) // Out=exp(In)
void Exponential2(float4 In, out float4 Out) // Out=exp2(In)
// 对数
void Log(float4 In, out float4 Out) // Out=log(In)
void Log2(float4 In, out float4 Out) // Out=log2(In)
void Log10(float4 In, out float4 Out) // Out=log10(In)
// 反平方根
void ReciprocalSquareRoot(float4 In, out float4 Out) // Out=rsqrt(In)
// 模长, Out=length(In)
void Length(float4 In, out float Out)
// 归一化
void Normalize(float4 In, out float4 Out) // Out=normalize(In)
// 多色调分色显示, Out=floor(In/(1/Steps))*(1/Steps)
void Posterize(float4 In, float4 Steps, out float4 Out)5.3 Trigonometry(三角函数运算)
// 角度转弧度, Out=radians(In)
void DegreesToRadians(float4 In, out float4 Out)
// 弧度转角度, Out=degrees(In)
void RadiansToDegrees(float4 In, out float4 Out)
// 正弦, Out=sin(In)
void Sine(float4 In, out float4 Out)
// 余弦, Out=cos(In)
void Cosine(float4 In, out float4 Out)
// 正切, Out=tan(In)
void Tangent(float4 In, out float4 Out)
// 反正弦, Out=asin(In)
void Arcsine(float4 In, out float4 Out)
// 反余弦, Out=acos(In)
void Arccosine(float4 In, out float4 Out)
// 反正切
void Arctangent(float4 In, out float4 Out) // Out=atan(In)
void Arctangent2(float4 A, float4 B, out float4 Out) // Out=atan2(A,B)
// 双曲正弦, Out=sinh(In)
void HyperbolicSine(float4 In, out float4 Out)
// 双曲余弦, Out=cosh(In)
void HyperbolicCosine(float4 In, out float4 Out)
// 双曲正切, Out=tanh(In)
void HyperbolicTangent(float4 In, out float4 Out)5.4 Range(范围运算)
// 最大值, Out=max(A,B)
void Maximum(float4 A, float4 B, out float4 Out)
// 最小值, Out=min(A,B)
void Minimum(float4 A, float4 B, out float4 Out)
// 限界, Out=clamp(In,Min,Max)
void Clamp(float4 In, float4 Min, float4 Max, out float4 Out)
// 0-1限界, Out=saturate(In)
void Saturate(float4 In, out float4 Out)
// 取小数部分, Out=frac(In)
void Fraction(float4 In, out float4 Out)
// 1减, Out=1-In
void OneMinus(float4 In, out float4 Out)
// 重映射, Out=OutMinMax.x+(In-InMinMax.x)*(OutMinMax.y-OutMinMax.x)/(InMinMax.y-InMinMax.x)
void Remap(float4 In, float2 InMinMax, float2 OutMinMax, out float4 Out)
// 伪随机数生成器
void RandomRange(float2 Seed, float Min, float Max, out float Out) {float randomno = frac(sin(dot(Seed, float2(12.9898, 78.233)))*43758.5453);Out = lerp(Min, Max, randomno);
}
5.5 Round(取整运算)
// 正负符合, Out=sign(In)
void Sign(float4 In, out float4 Out)
// 取整数部分, Out=trunc(In)
void Truncate(float4 In, out float4 Out)
// 向上取整, Out=ceil(In)
void Ceiling(float4 In, out float4 Out)
// 向下取整, Out=floor(In)
void Floor(float4 In, out float4 Out)
// 四舍五入取整, Out=round(In)
void Round(float4 In, out float4 Out)
// 边界判断, Out=step(Edge,In), 即: In>=Edge时, 返回1, 否则返回0
void Step(float4 Edge, float4 In, out float4 Out)5.6 Interpolation(插值运算)
// 插值, Out=lerp(A,B,T), 即: Out=(1-T)*A+T*B
void Lerp(float4 A, float4 B, float4 T, out float4 Out)
// 反插值, Out=(T-A)/(B-A)
void InverseLerp(float4 A, float4 B, float4 T, out float4 Out)
// 平滑插值, Out=smoothstep(Edge1,Edge2,In), 即: k=saturate((In-Edge1)/(Edge2-Edge1)), Out=k*k*(3-2*k)
void Smoothstep(float4 Edge1, float4 Edge2, float4 In, out float4 Out)5.7 Vector(向量运算)
// 两点间距离, Out=distance(A,B)
void Distance(float4 A, float4 B, out float Out)
// 向量点乘, Out=dot(A,B)
void DotProduct(float4 A, float4 B, out float Out)
// 向量叉乘, Out=cross(A,B)
void CrossProduct(float3 A, float3 B, out float3 Out)
// 向量投影, Out=B*dot(A,B)/dot(B, B)
void Projection(float4 A, float4 B, out float4 Out)
// 向量反射, Out=reflect(In,Normal), In和Normal不需要归一化
void Reflection(float4 In, float4 Normal, out float4 Out)
// 菲涅尔效应, Out=pow((1.0-saturate(dot(normalize(Normal),normalize(ViewDir)))),Power)
void FresnelEffect(float3 Normal, float3 ViewDir, float Power, out float Out)
// 绕轴旋转
void RotateAboutAxis(float3 In, float3 Axis, float Rotation, out float3 Out)
// 球形遮罩, Out =1-saturate((distance(Coords,Center)-Radius)/(1-Hardness)), 即: 球内返回1, 求外返回零
void SphereMask(float4 Coords, float4 Center, float Radius, float Hardness, out float4 Out)
// 坐标或向量空间变换, 可以进行Object、World、View、Tangent、Absolute World空间之间变换
void Transform(float4 In, out float4 Out)
5.8 Matrix(矩阵运算)
// 构建矩阵
void MatrixConstruction(float4 M0, float4 M1, float4 M2, float3 M3, out float4x4 Out4x4, out float3x3 Out3x3, out float2x2 Out2x2)
// 计算矩阵的秩, Out=determinant(In)
void MatrixDeterminant(float4x4 In, out float Out)
// 分离矩阵的行向量或列向量
void MatrixSplit(float4x4 In, out float4 M0, out float4 M1, out float4 M2, out float4 M3)
// 矩阵转置, Out=transpose(In)
void MatrixTranspose(float4x4 In, out float4x4 Out)5.9 Derivative(导数运算)
// Out=ddx(In)
void DDX(float4 In, out float4 Out)
// Out=ddxy(In)
void DDXY(float4 In, out float4 Out)
// Out=ddy(In)
void DDY(float4 In, out float4 Out)5.10 Wave(波运算)
// 锯齿波, Out=2*(In-floor(0.5 + In))
void SawtoothWave(float4 In, out float4 Out)
// 方波, Out=1.0-2.0*round(frac(In))
void SquareWave(float4 In, out float4 Out)
// 三角波, Out=2.0*abs(2*(In-floor(0.5+In)))-1.0
void TriangleWave(float4 In, out float4 Out)
// 带噪声的正弦波
void NoiseSineWave(float4 In, float2 MinMax, out float4 Out) {float sinIn = sin(In);float sinInOffset = sin(In + 1.0);float randomno = frac(sin((sinIn - sinInOffset) * (12.9898 + 78.233))*43758.5453);float noise = lerp(MinMax.x, MinMax.y, randomno);Out = sinIn + noise;
}6 Procedural(程序纹理)
Procedural 官方介绍详见→Procedural Nodes。
6.1 Noise(噪声纹理)
Noise 下面有 Gradient Noise(梯度噪声)、Simple Noise(简单噪声)、Voronoi(泰森多边形)。噪声纹理应用:选中物体消融特效、消融特效、流动雾效。
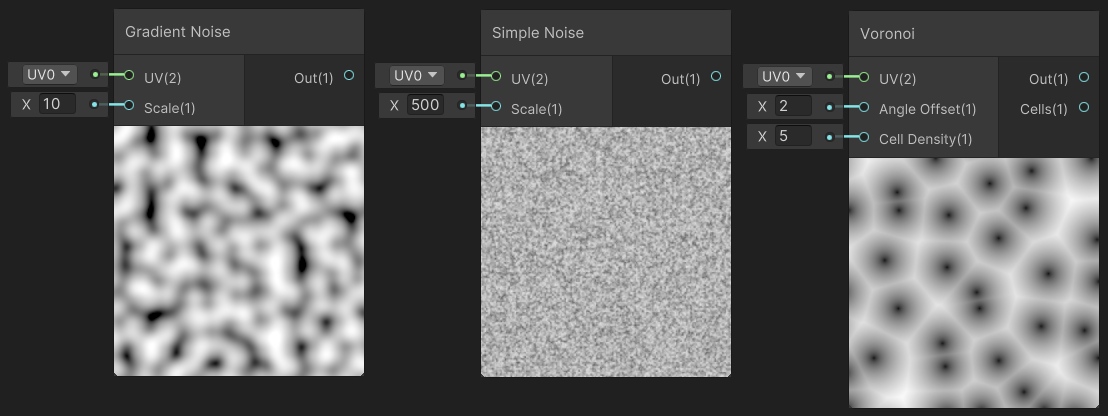
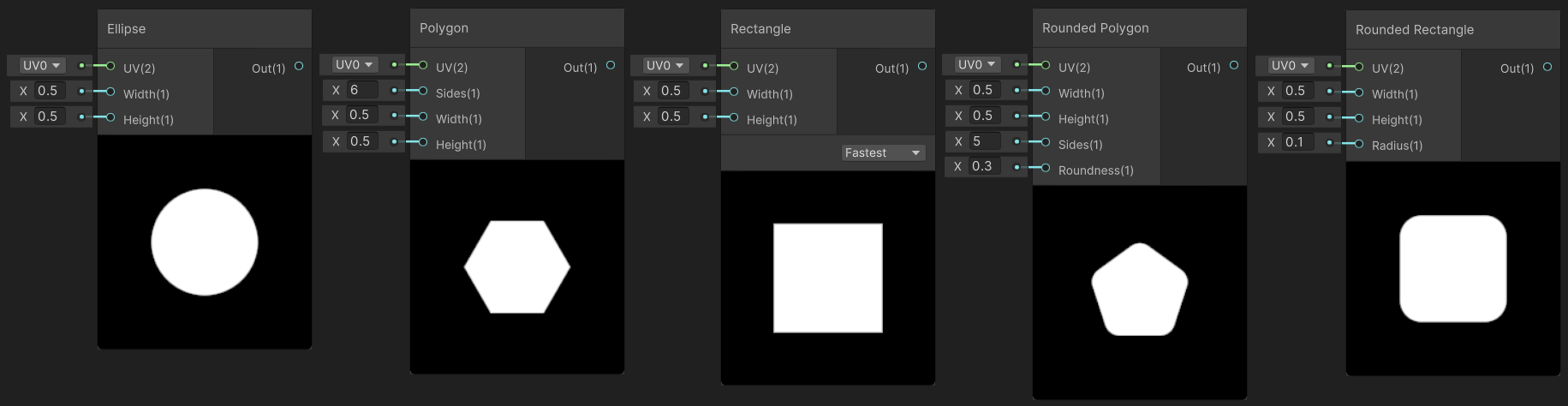
6.2 Shapes(形状纹理)
Shapes 下面有 Ellipse(椭圆)、Polygon(多边形)、Rectangle(矩形)、Rounded Polygon(圆角多边形)、Rounded Rectangle(圆角矩形)。
7 UV(UV 变换)
UV 官方介绍详见→UV Nodes。
1)Flipbook(翻书 uv 变换)
Flipbook 节点用于做翻书动画,实现见→Flipbook Node,Width 和 Height 分别为水平和垂直区块的数量,Tile 为当前区块索引。
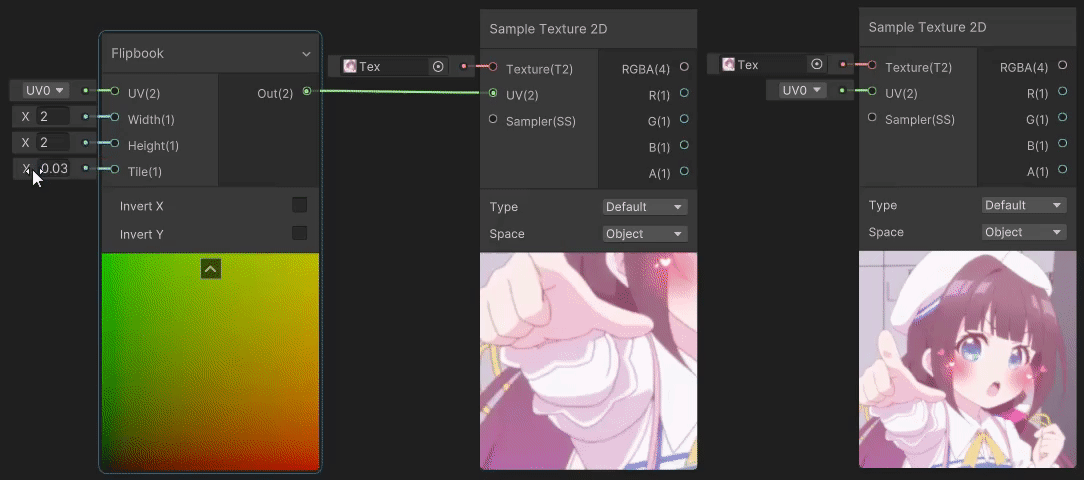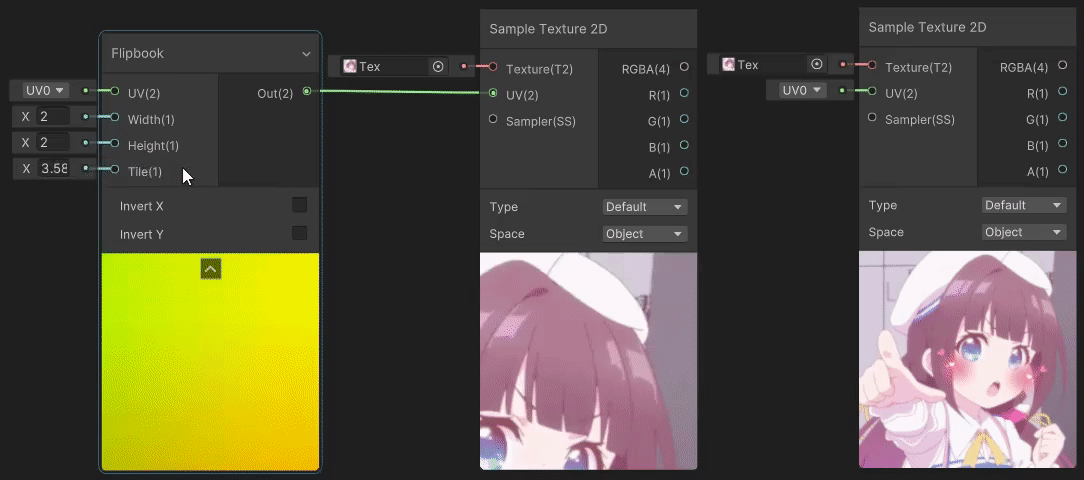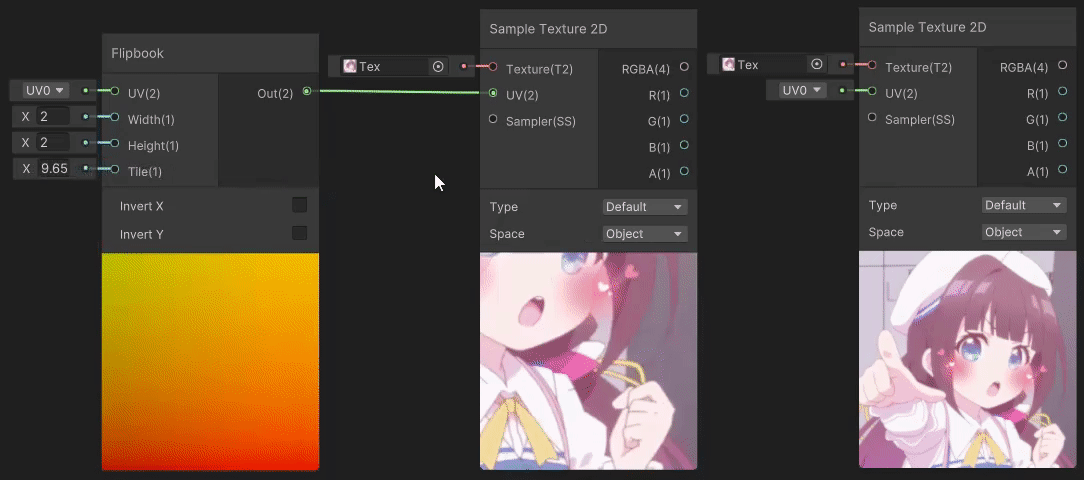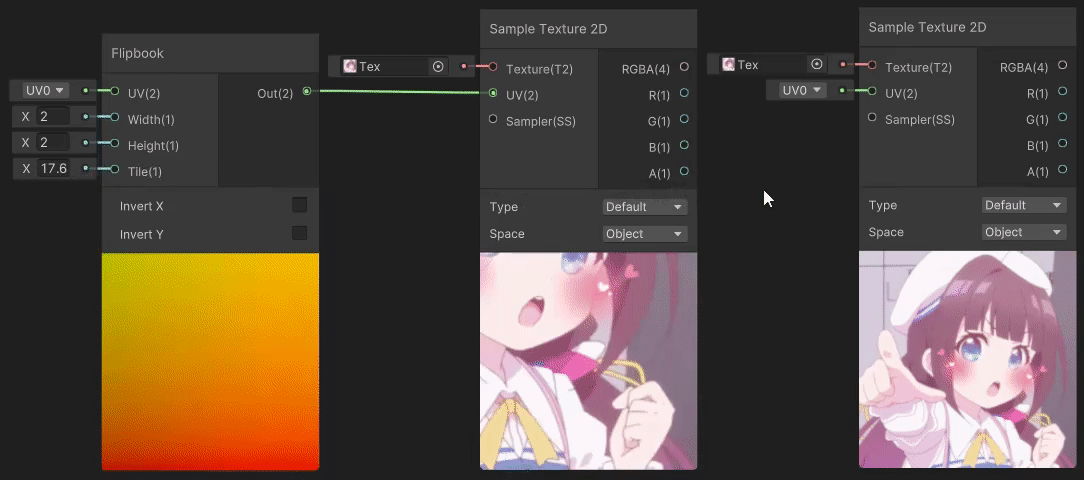
2)Polar Coordinates(极坐标 uv 变换)
Polar Coordinates 节点用于将直角坐标系下的 uv 坐标转换为极坐标系下的坐标,实现见→Polar Coordinates。
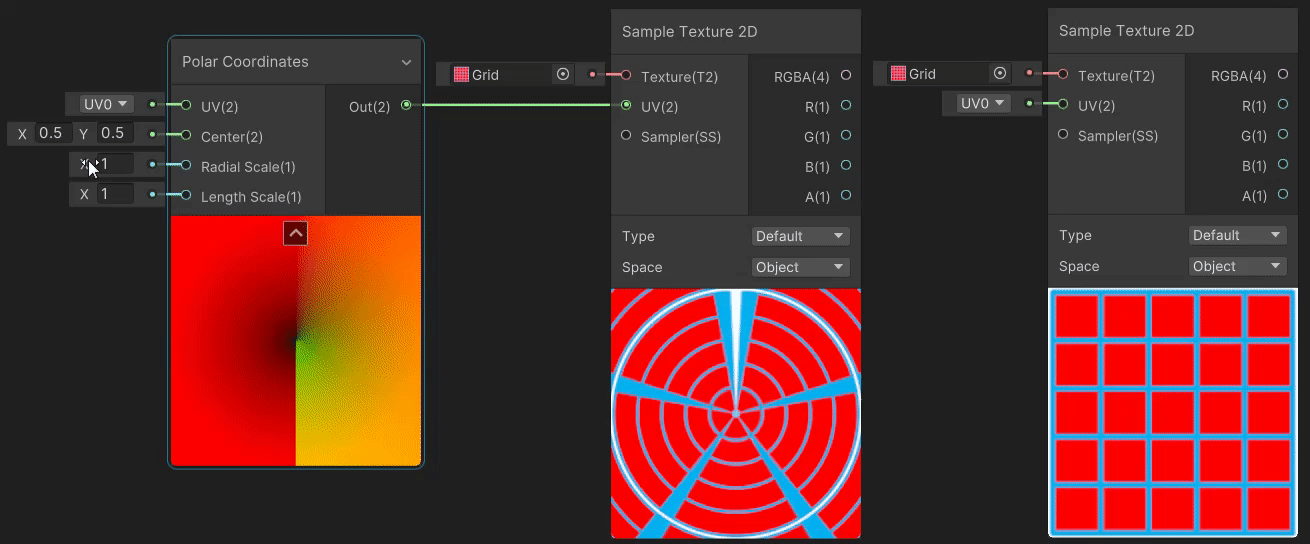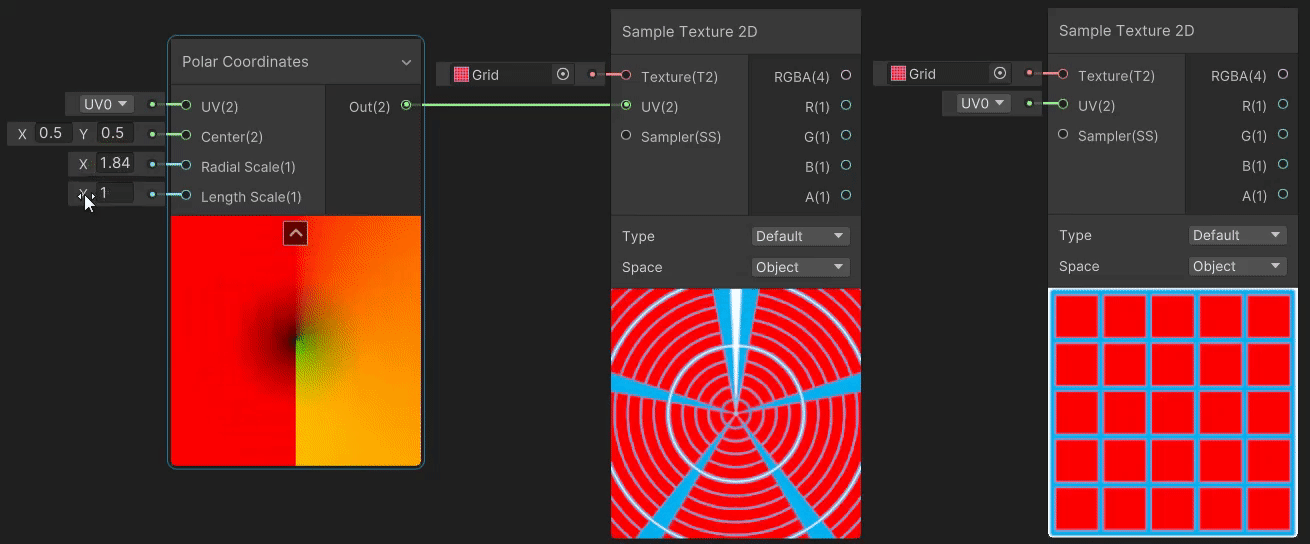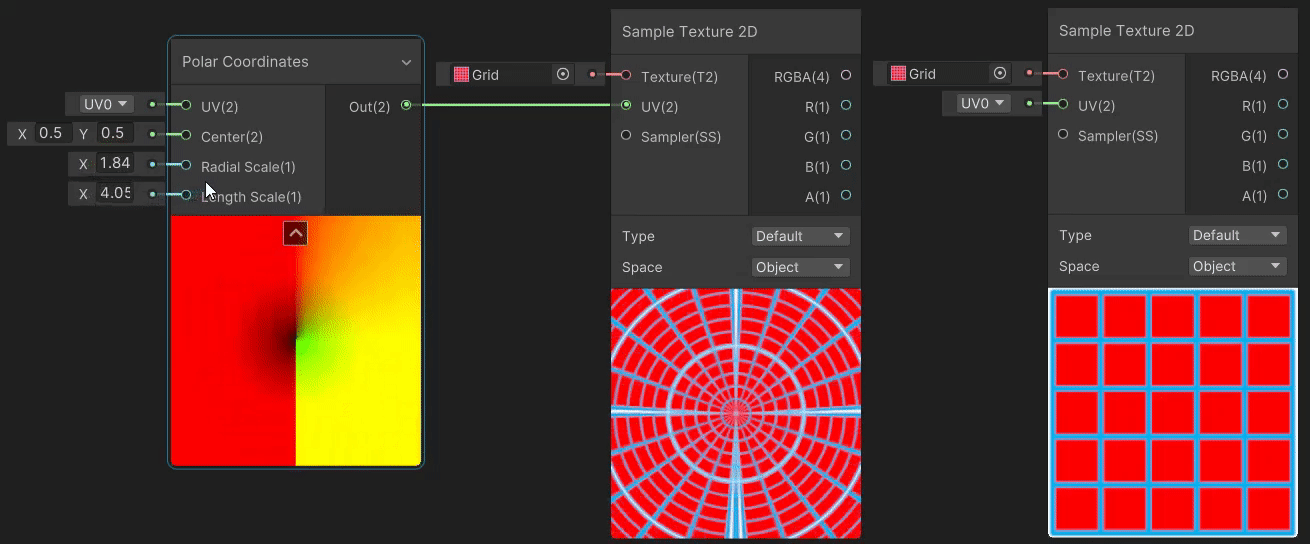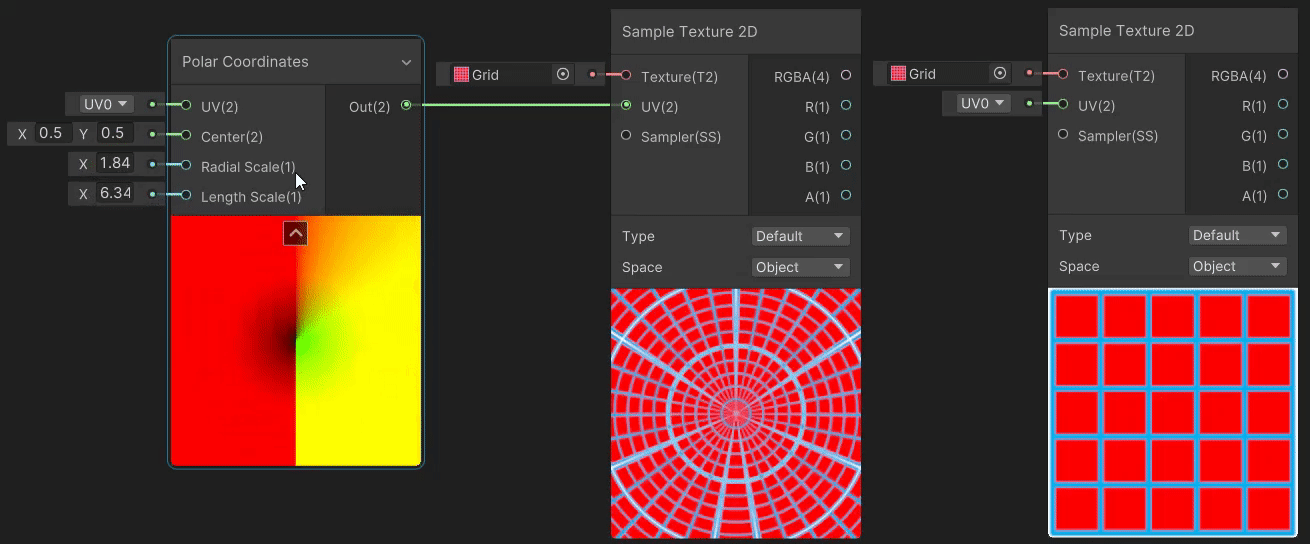
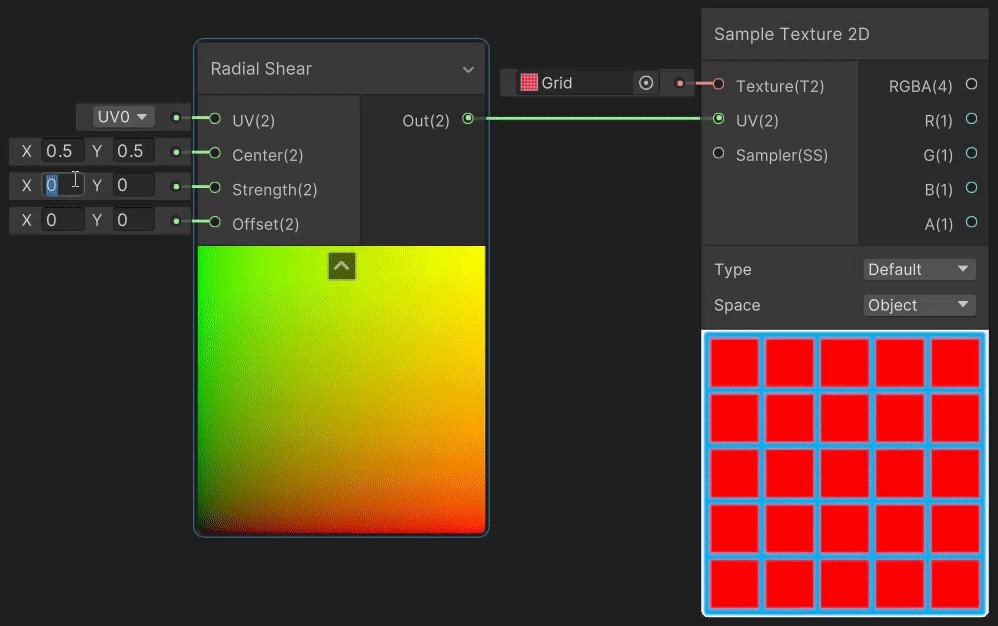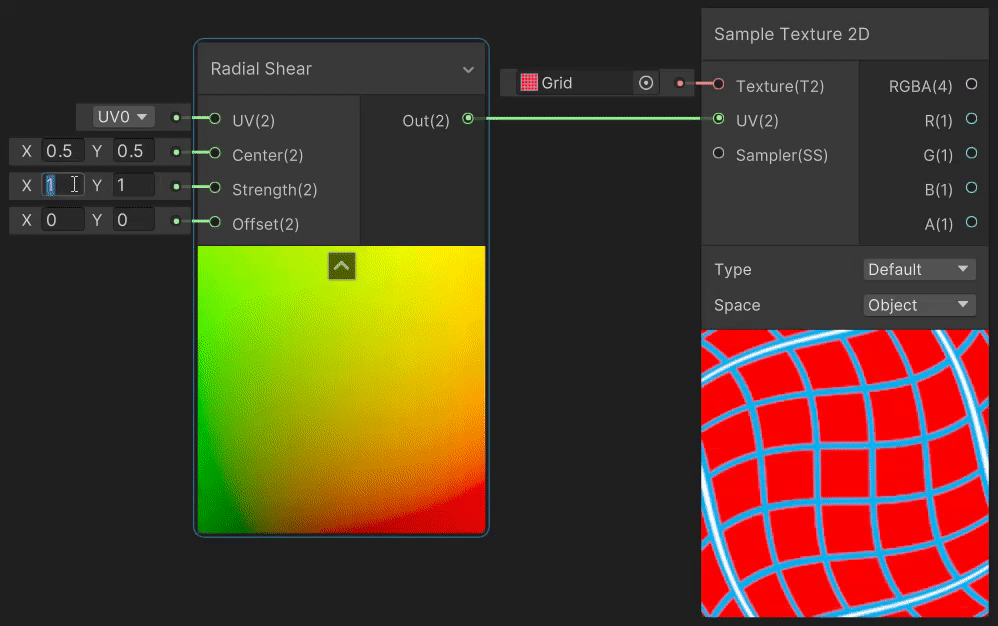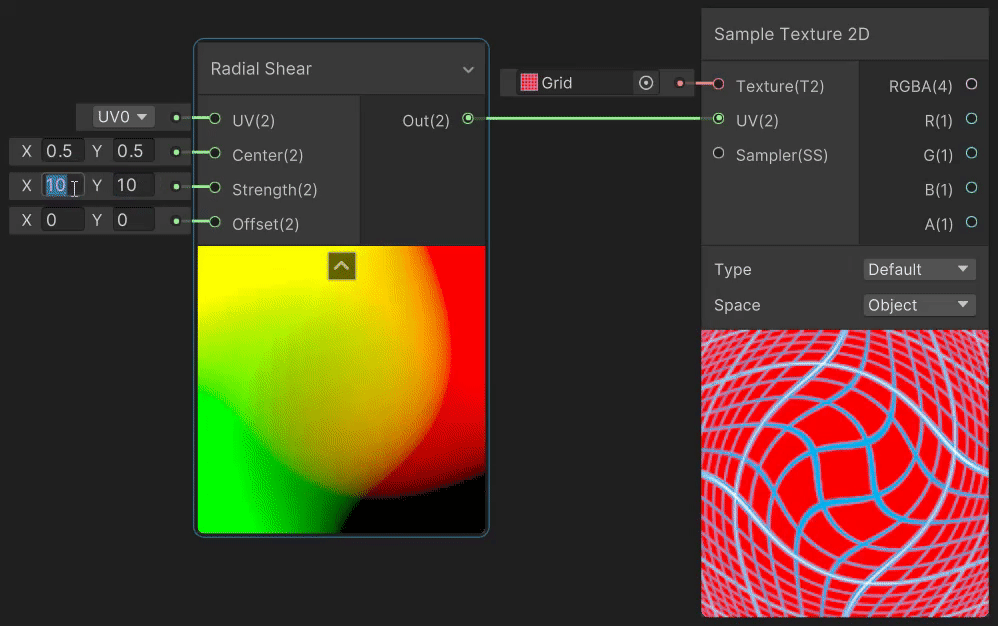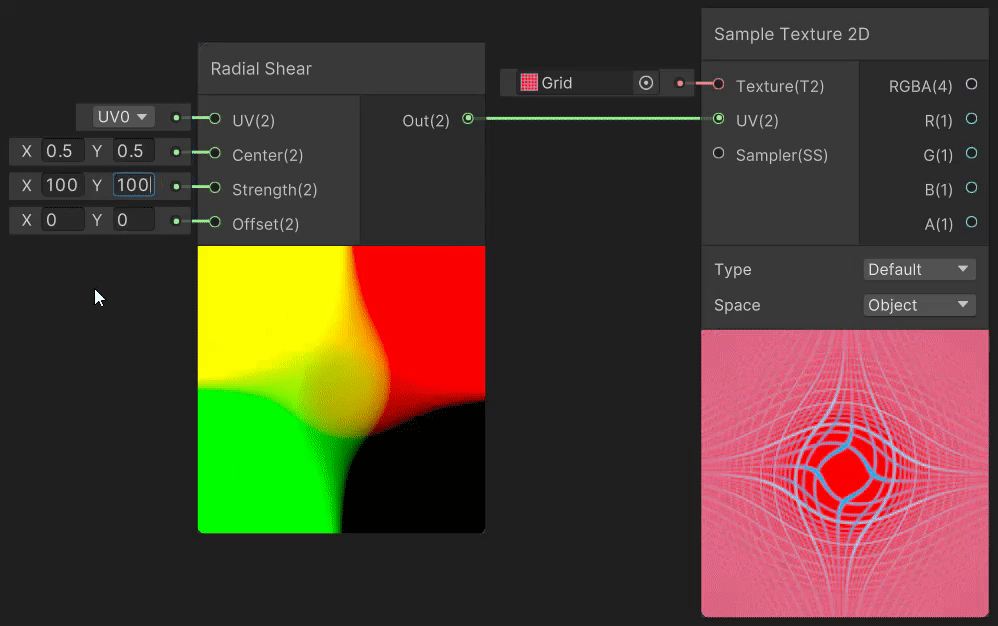
3)Radial Shear(径向剪切 uv 变换)
Radial Shear 节点用于模拟波的径向剪切变形效果,实现见→Radial Shear Node。
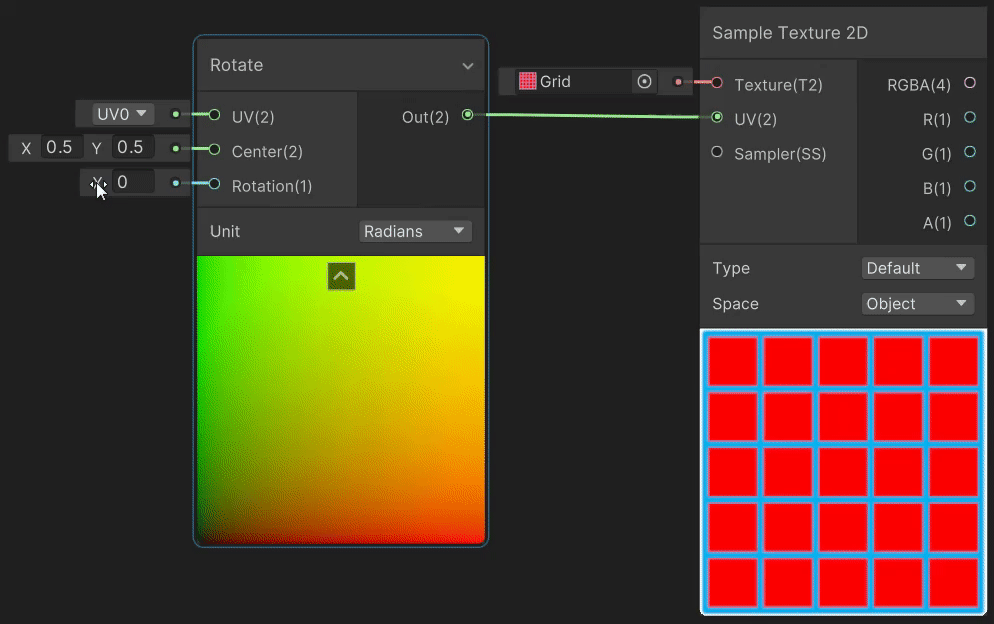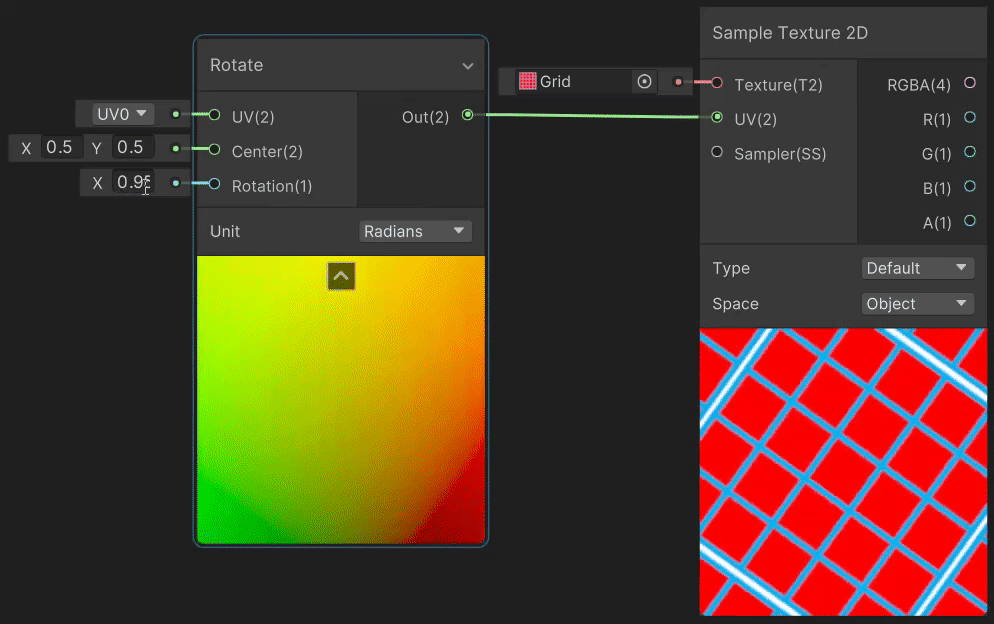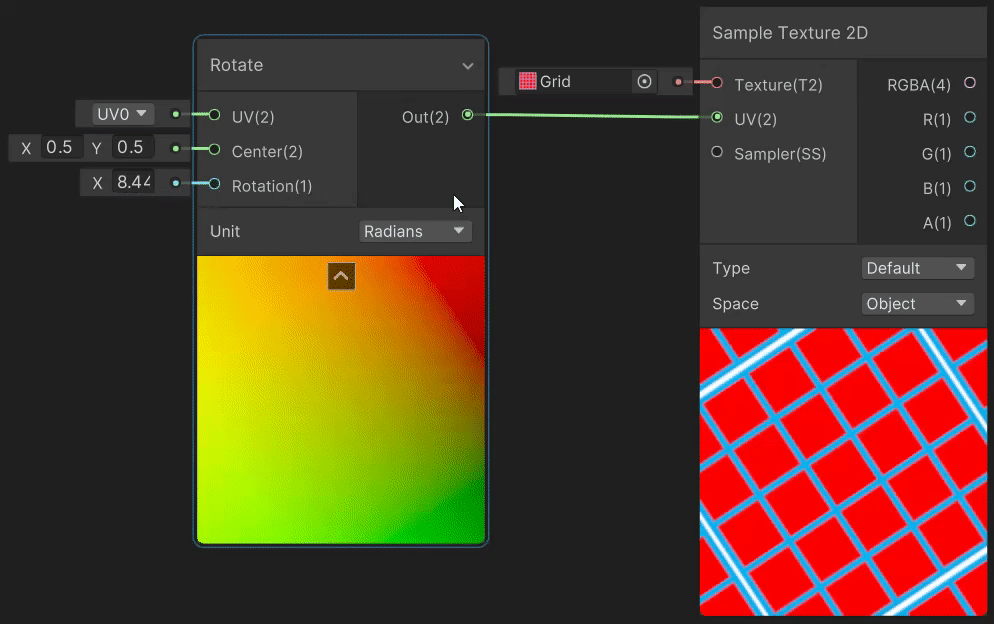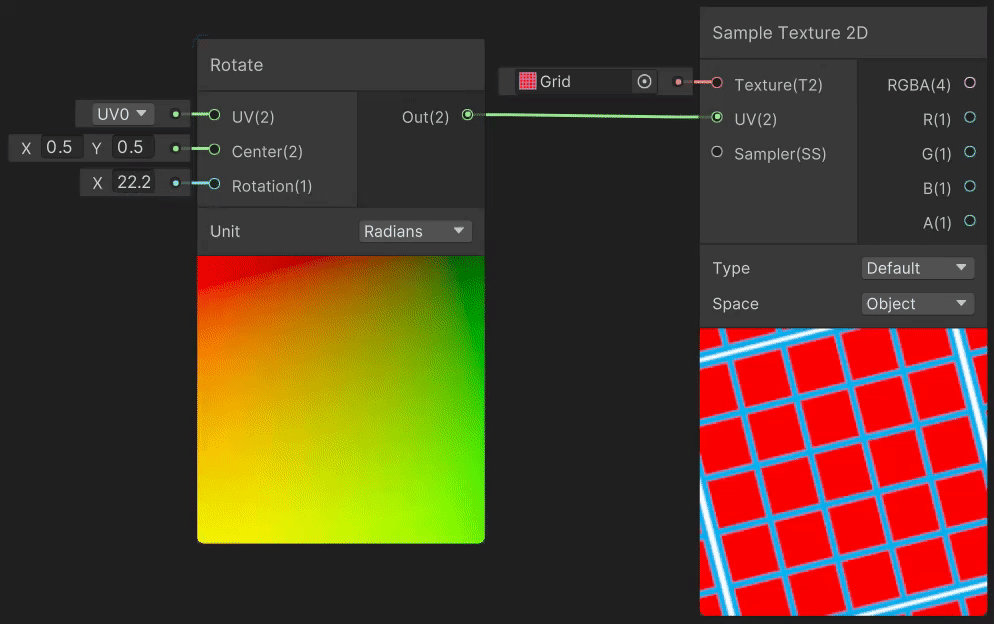
4)Rotate(旋转 uv 变换)
Rotate 节点用于实现纹理旋转效果,实现见→Rotate Node。
5)Spherize(球形变形 uv 变换)
Spherize 节点用于模拟鱼眼镜头的球形变形效果,实现见→Spherize。

6)Tiling And Offset(缩放和偏移 uv 变换)
Tiling And Offset 节点用于缩放和偏移 uv 坐标。
void TilingAndOffset(float2 UV, float2 Tiling, float2 Offset, out float2 Out) {Out = UV * Tiling + Offset;
}7)Twirl(旋转变形 uv 变换)
Twirl 节点用于模拟黑洞的旋转变形效果,实现见→Twirl Node。

8 Utility(实用工具)
Utility 官方介绍详见→Utility Nodes。
8.1 Logic(逻辑判断)
// 与运算, Out=A&&B
void And(float A, float B, out float Out)
// 或运算, Out=A||B
void Or(float In, out float Out)
// 非运算, Out=!In
void Not(float In, out float Out)
// 全true, Out=all(In), 即: 如果In中每个分量都不为零则返回1, 否则返回0
void All(float4 In, out float Out)
// 存在一true, Out=any(In), 即: 如果In中存在一个分量不为零则返回1, 否则返回0
void Any(float4 In, out float Out)
// 全非判断, Out=!A&&!B
void Nand(float A, float B, out float Out)
// 无穷数判断, Out = isinf(In)
void IsInfinite(float In, out float Out)
// 未知数判断, Out=(In<0.0||In>0.0||In==0.0)?0:1
void IsNan(float In, out float Out)
// 分支, Out=Predicate?True:False
void Branch(float Predicate, float4 True, float4 False, out float4 Out)
// 比较A和B的大小, 运算符可以选择: Equal、Not Equal、Less、Less Or Equal、Greater、Greater Or Equal
void Comparison(float A, float B, out float Out)
// 如果当前渲染正面则返回1,如果渲染背面则返回0
void IsFrontFaceNode(out float Out)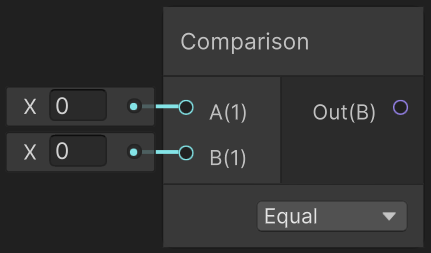
8.2 Custom Function(自定义函数)
自定义函数节点允许用户通过脚本自定义节点的运算逻辑,官方介绍见→Custom Function Node。
4.4 4)节提过,Shader Graph 13.1.9(2022.1+)版本才开始出现 Main Light Direction 节点,如果用户想在低版本的 Shader Graph 中获取灯光方向,可以通过 Custom Function 实现。下面将通过 Custom Function 实现 Main Light Direction 节点的功能。Shader Graph简介 中基于自定义的 Main Light 实现了漫反射光照效果。
创建 Custom Function 节点,选中后,在 Node Settings 中配置如下,SHADERGRAPH_PREVIEW 用来判断是否是预览窗口。

#if SHADERGRAPH_PREVIEWDirection = half3(0.5, 0.5, 0);Color = half4(1, 0, 0, 1);
#elseLight light = GetMainLight();Direction = light.direction;Color = light.color;
#endif