目录
一、配置Nginx的Roles角色
1.1编写files/default.conf
1.2编写files/nginx.repo
1.3编写handlers/main.yml
1.4编写tasks/main.yml文件
1.5编写vars/main.yml文件
1.6测试运行结果,并不是真的执行任务
二、配置Mysql的Roles角色
2.1编写tasks/main.yml文件
2.2编写tasks/init.yml文件
2.3编写vars/main.yml定义变量
2.4测试运行结果,并不是真的执行任务
三、配置php的Roles角色
3.1编写files/index.php文件
3.2编写files/www.conf文件
3.3编写handlers/main.yml
3.4编写tasks/main.yml
3.5编写vars/main.yml文件
四、编写启动文件
五、启动并测试
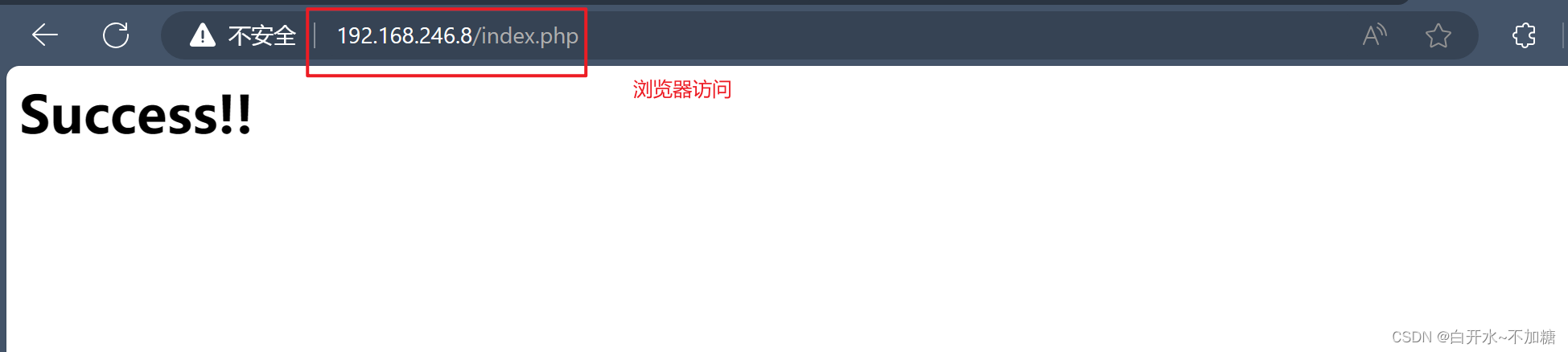
六、浏览器访问
环境准备
| 服务器类型 | IP地址 | 需要安装的组件 |
|---|---|---|
| Ansible管理服务器 | 192.168.246.7 | Ansible |
| 被管理客户端 | 192.168.246.8 | LNMP |
被管理节点(192.168.246.7)
yum install epel-release -y
yum install -y ansible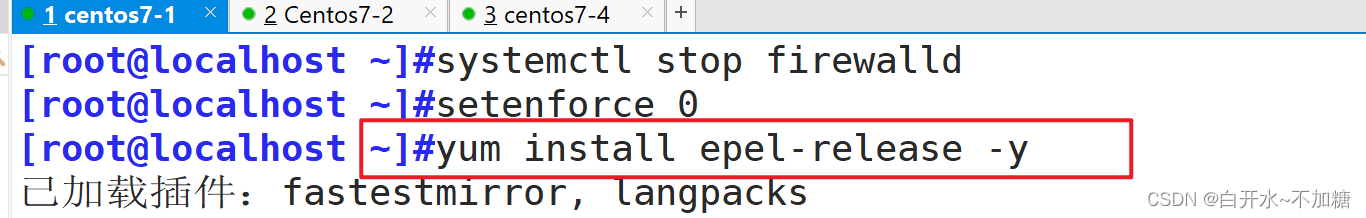


密钥认证
ssh-keygen -t rsa
sshpass -p '123' ssh-copy-id root@192.168.246.8所有节点
systemctl stop firewalld.service
setenforce 0准备角色、目录准备每个角色的子目录、准备main.yaml文件
mkdir /etc/ansible/roles/nginx/{files,templates,tasks,handlers,vars,defaults,meta} -p
mkdir /etc/ansible/roles/mysql/{files,templates,tasks,handlers,vars,defaults,meta} -p
mkdir /etc/ansible/roles/php/{files,templates,tasks,handlers,vars,defaults,meta} -p
touch /etc/ansible/roles/nginx/{defaults,vars,tasks,meta,handlers}/main.yml
touch /etc/ansible/roles/mysql/{defaults,vars,tasks,meta,handlers}/main.yml
touch /etc/ansible/roles/php/{defaults,vars,tasks,meta,handlers}/main.yml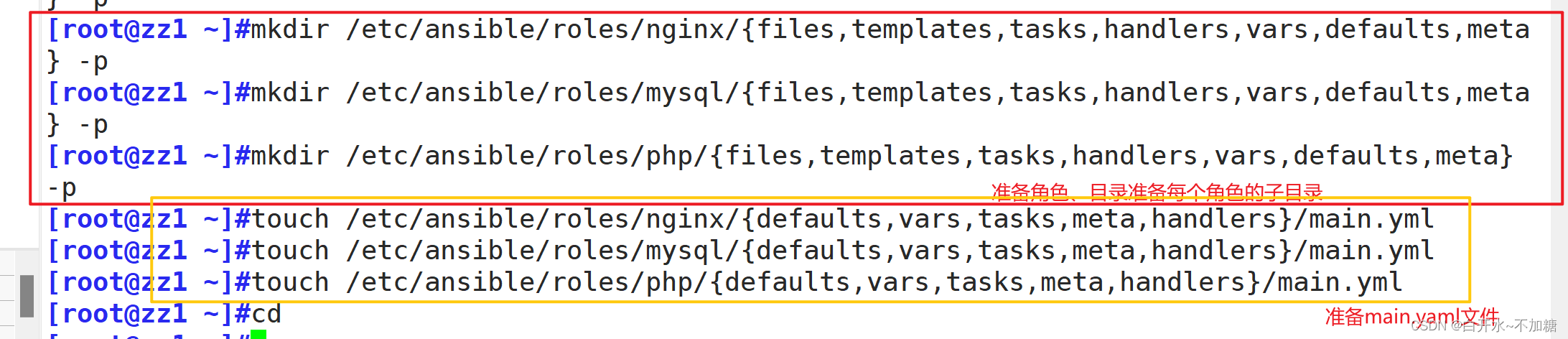

一、配置Nginx的Roles角色
files:用来存放由 copy 模块或 script 模块调用的文件。
1.1编写files/default.conf
编写Nginx配置文件
vim /etc/ansible/roles/nginx/files/default.conf
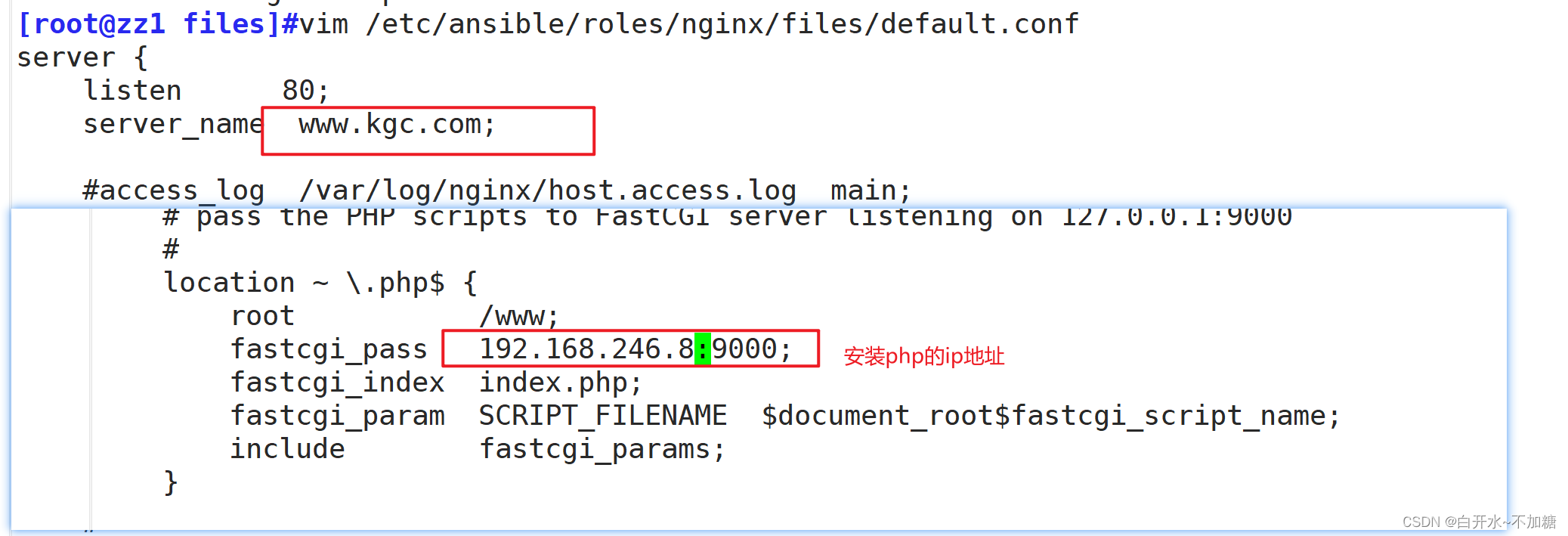
server {listen 80;server_name www.kgc.com;#access_log /var/log/nginx/host.access.log main;location / {root /usr/share/nginx/html;index index.html index.htm;}#error_page 404 /404.html;# redirect server error pages to the static page /50x.html#error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;location = /50x.html {root /usr/share/nginx/html;}# proxy the PHP scripts to Apache listening on 127.0.0.1:80##location ~ \.php$ {# proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1;#}# pass the PHP scripts to FastCGI server listening on 127.0.0.1:9000
# location ~ \.php$ {root /www;fastcgi_pass 192.168.246.8:9000;fastcgi_index index.php;fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name;include fastcgi_params; } # deny access to .htaccess files, if Apache's document root# concurs with nginx's one # #location ~ /\.ht {# deny all;#}
}1.2编写files/nginx.repo
编写Nginx安装文件
vim /etc/ansible/roles/nginx/files/nginx.repo
[nginx]
name=nginx repo
baseurl=http://nginx.org/packages/centos/7/$basearch/
gpgcheck=0
enabled=11.3编写handlers/main.yml
编写Nginx控制器文件
vim /etc/ansible/roles/nginx/handlers/main.yml
- name: restart nginxservice: name={{svc}} state=restarted
1.4编写tasks/main.yml文件
编写Nginx任务文件
vim /etc/ansible/roles/nginx/tasks/main.yml
- name: disable selinuxcommand: '/usr/sbin/setenforce 0'ignore_errors: true
- name: disable firewalldservice: name=firewalld state=stopped enabled=no
- name: upload nginx repocopy: src=nginx.repo dest=/etc/yum.repos.d/nginx.repo
- name: install nginxyum: name={{app}} state=latest
- name: prepare nginx configuration filecopy: src=default.conf dest=/etc/nginx/conf.d/default.conf
- name: start nginxservice: name={{svc}} state=started enabled=yes
ignore_errors: true这个设置通常用于在执行Ansible playbook时忽略特定任务的错误,即使任务失败也不会导致整个playbook的失败。这在某些情况下可能很有用,例如当某些任务失败但不希望影响整体执行时。设置ignore_errors: true后,Ansible会继续执行其他任务,而不会因为特定任务的失败而停止整个过程。
1.5编写vars/main.yml文件
编写Nginx变量文件
vim /etc/ansible/roles/nginx/vars/main.yml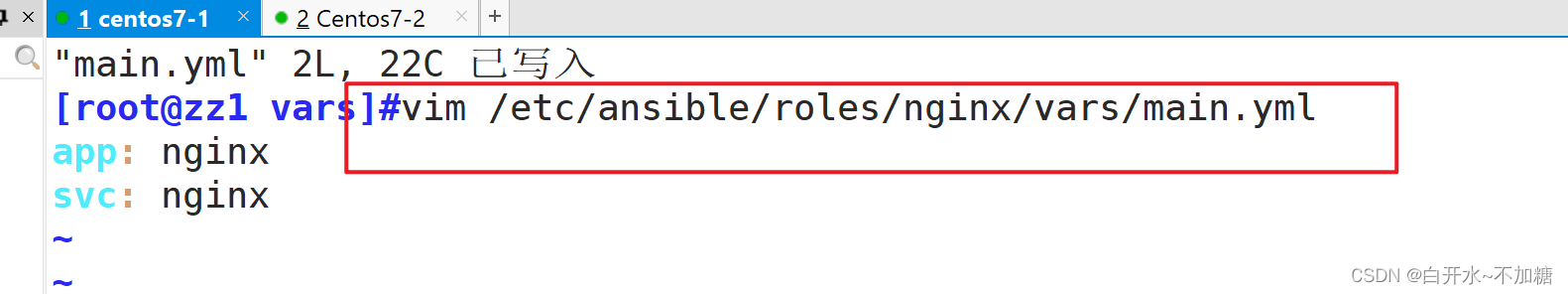
1.6测试运行结果,并不是真的执行任务

---
- name: lnmp nginxhosts: webserversremote_user: rootroles:- nginxansible-playbook role_lnmp.yml -C
二、配置Mysql的Roles角色
2.1编写tasks/main.yml文件
编写Mysql任务文件
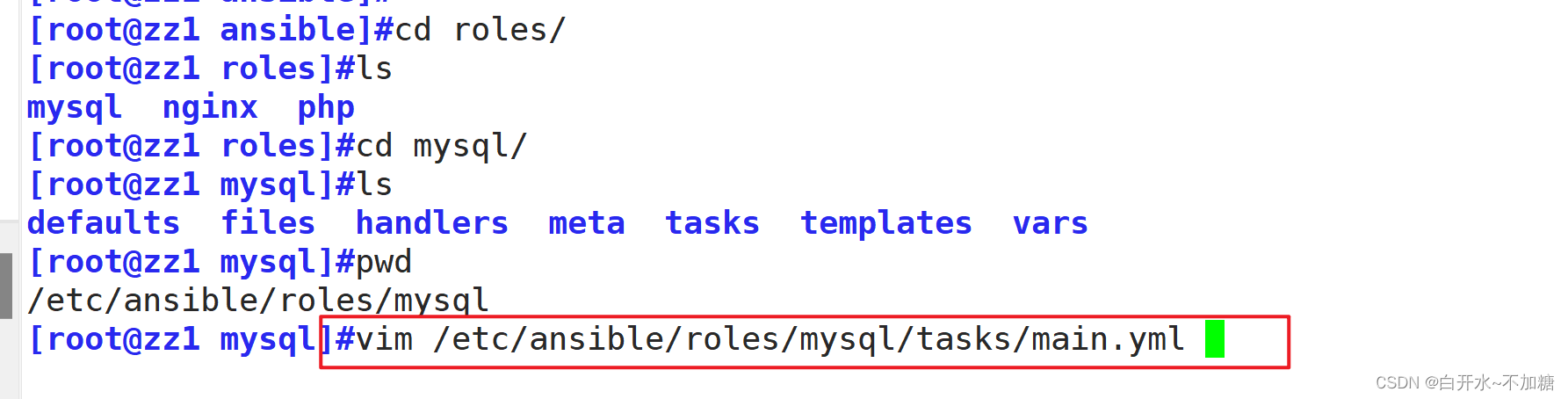
vim /etc/ansible/roles/mysql/tasks/main.yml---
- include: init.yml- name: install mysql repo firstyum: name={{repo}}- name: install mysql repo secondshell: "sed -i 's#gpgcheck=1#gpgcheck=0#' /etc/yum.repos.d/mysql-community.repo"
- name: install mysql appyum: name={{app}}- name: mysql startservice: name=mysqld state=started enabled=1- name: first passwordshell: mysql -uroot -p"{{passwd}}" --connect-expired-password -e "ALTER USER 'root'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED B
Y 'Admin@123';"- name: sudo loginshell: mysql -uroot -pAdmin@123 -e "grant all privileges on *.* to root@'%' identified by 'Admin@123' with g
rant option;"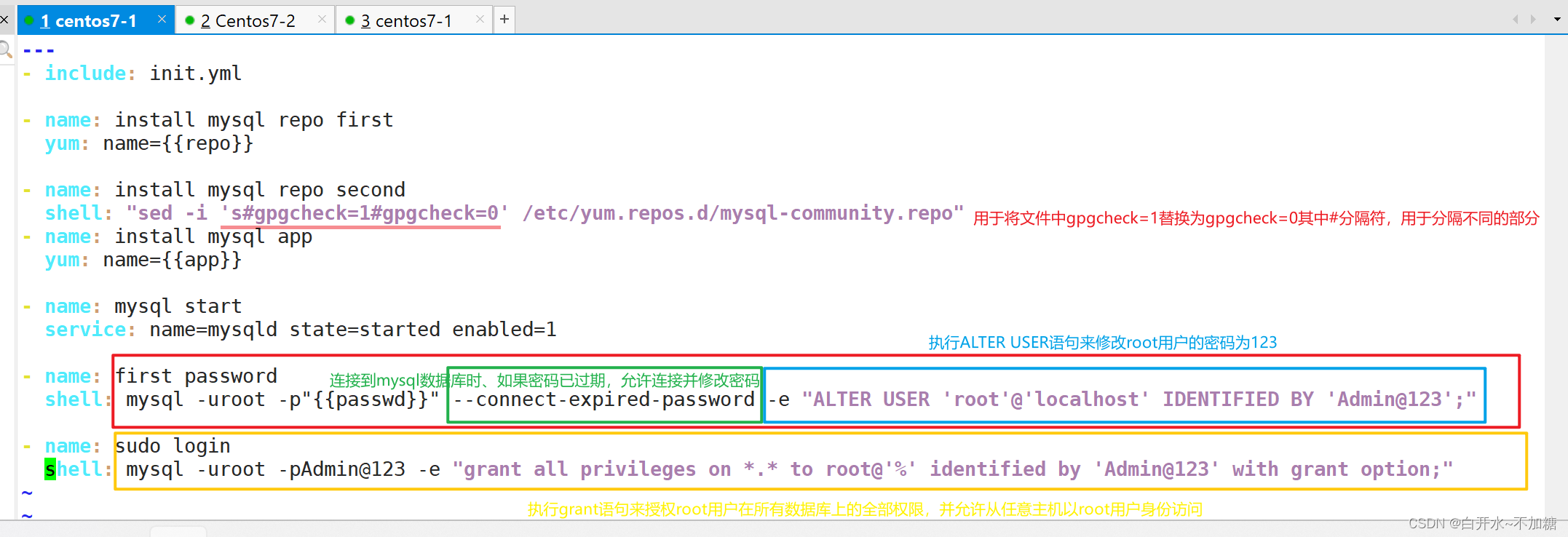
2.2编写tasks/init.yml文件
编写Mysql启动文件
[root@zz1 roles]#vim /etc/ansible/roles/mysql/tasks/init.yml- name: disable selinuxcommand: '/usr/sbin/setenforce 0'ignore_errors: true- name: disable firewalldservice: name=firewalld state=stopped enabled=no
2.3编写vars/main.yml定义变量
编写Mysql变量文件

vim /etc/ansible/roles/mysql/vars/main.ymlrepo: https://repo.mysql.com/mysql57-community-release-el7-11.noarch.rpmpasswd: $(grep "password" /var/log/mysqld.log | awk '{print $NF}')app: mysql-server从
/var/log/mysqld.log文件中提取包含"password"关键词的行,并使用awk命令打印该行的最后一个字段
2.4测试运行结果,并不是真的执行任务
[root@zz1 ansible]#vim role_lnmp.yml
---
- name: lnmp mysqlhosts: webserversremote_user: rootroles:- mysql
三、配置php的Roles角色
3.1编写files/index.php文件
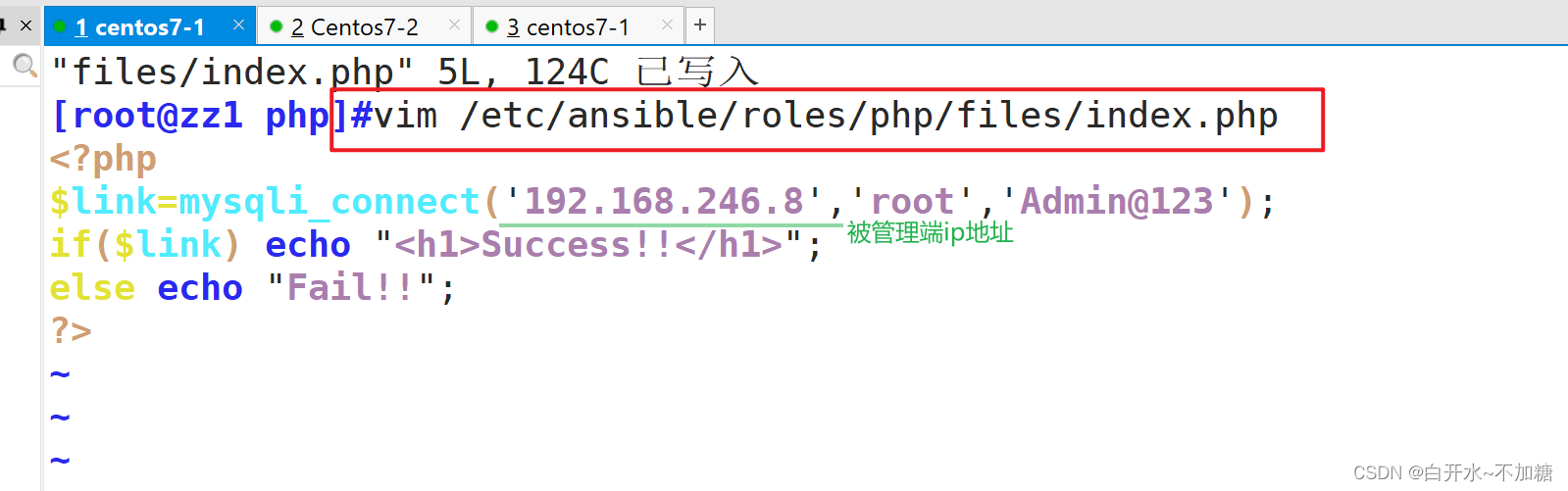
编写Php的页面文件
vim /etc/ansible/roles/php/files/index.php<?php
$link=mysqli_connect('192.168.246.8','root','Admin@123');
if($link) echo "<h1>Success!!</h1>";
else echo "Fail!!";
?>
3.2编写files/www.conf文件
; Start a new pool named 'www'.
[www]; Unix user/group of processes
; Note: The user is mandatory. If the group is not set, the default user's group
; will be used.
; RPM: apache Choosed to be able to access some dir as httpd
user = php
; RPM: Keep a group allowed to write in log dir.
group = php
; The address on which to accept FastCGI requests.
; Valid syntaxes are:
; 'ip.add.re.ss:port' - to listen on a TCP socket to a specific IPv4 address on
; a specific port;
; '[ip:6:addr:ess]:port' - to listen on a TCP socket to a specific IPv6 address on
; a specific port;
; 'port' - to listen on a TCP socket to all addresses
; (IPv6 and IPv4-mapped) on a specific port;
; '/path/to/unix/socket' - to listen on a unix socket.
; Note: This value is mandatory.
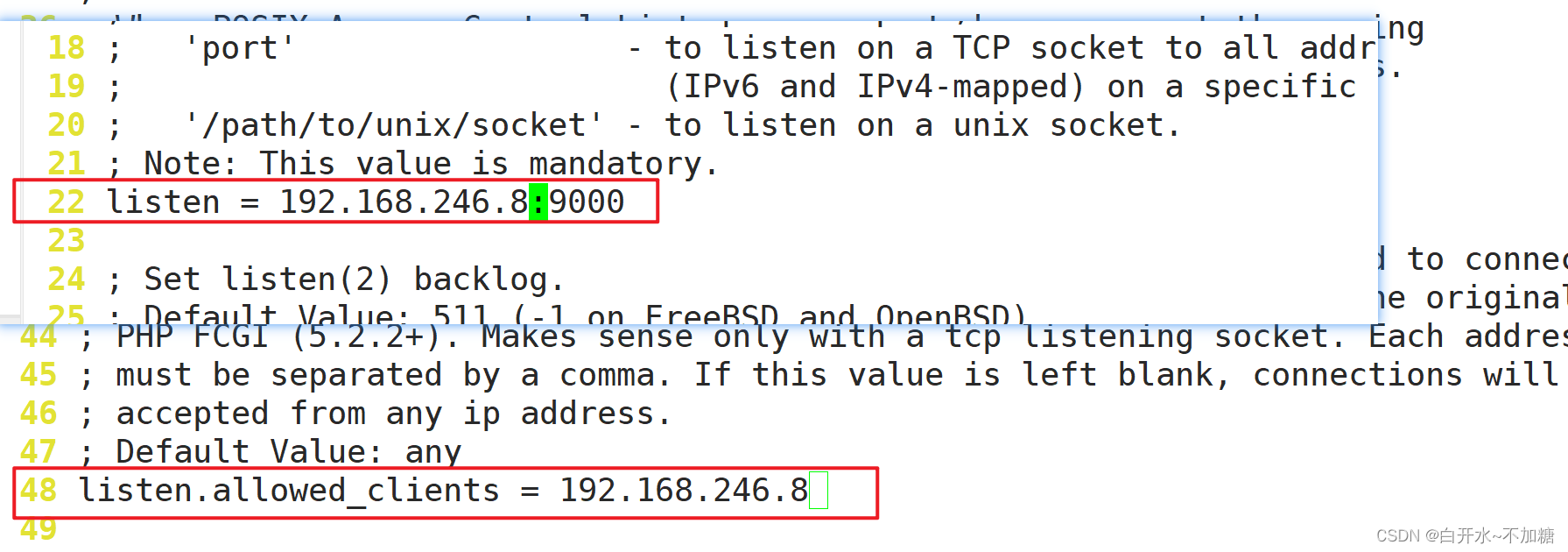
listen = 192.168.246.8:9000
; Set listen(2) backlog.
; Default Value: 511 (-1 on FreeBSD and OpenBSD)
;listen.backlog = 511
; Set permissions for unix socket, if one is used. In Linux, read/write
; permissions must be set in order to allow connections from a web server. Many
; BSD-derived systems allow connections regardless of permissions.
; Default Values: user and group are set as the running user
; mode is set to 0660
;listen.owner = nobody
;listen.group = nobody
;listen.mode = 0660
; When POSIX Access Control Lists are supported you can set them using
; these options, value is a comma separated list of user/group names.
; When set, listen.owner and listen.group are ignored
;listen.acl_users =
;listen.acl_groups =
; List of addresses (IPv4/IPv6) of FastCGI clients which are allowed to connect.
; Equivalent to the FCGI_WEB_SERVER_ADDRS environment variable in the original
; PHP FCGI (5.2.2+). Makes sense only with a tcp listening socket. Each address
; must be separated by a comma. If this value is left blank, connections will be
; accepted from any ip address.
; Default Value: any
listen.allowed_clients = 192.168.246.8
; Specify the nice(2) priority to apply to the pool processes (only if set)
; The value can vary from -19 (highest priority) to 20 (lower priority)
; Note: - It will only work if the FPM master process is launched as root
; - The pool processes will inherit the master process priority
; unless it specified otherwise
; Default Value: no set
; process.priority = -19
; Choose how the process manager will control the number of child processes.
; Possible Values:
; static - a fixed number (pm.max_children) of child processes;
; dynamic - the number of child processes are set dynamically based on the
; following directives. With this process management, there will be
; always at least 1 children.
; pm.max_children - the maximum number of children that can
; be alive at the same time.
; pm.start_servers - the number of children created on startup.
; pm.min_spare_servers - the minimum number of children in 'idle'
; state (waiting to process). If the number
; of 'idle' processes is less than this
; number then some children will be created.
; pm.max_spare_servers - the maximum number of children in 'idle'
; state (waiting to process). If the number
; of 'idle' processes is greater than this
; number then some children will be killed.
; ondemand - no children are created at startup. Children will be forked when
; new requests will connect. The following parameter are used:
; pm.max_children - the maximum number of children that
; can be alive at the same time.
; pm.process_idle_timeout - The number of seconds after which
; an idle process will be killed.
; Note: This value is mandatory.
pm = dynamic
; The number of child processes to be created when pm is set to 'static' and the
; maximum number of child processes when pm is set to 'dynamic' or 'ondemand'.
; This value sets the limit on the number of simultaneous requests that will be
; served. Equivalent to the ApacheMaxClients directive with mpm_prefork.
; Equivalent to the PHP_FCGI_CHILDREN environment variable in the original PHP
; CGI.
; Note: Used when pm is set to 'static', 'dynamic' or 'ondemand'
; Note: This value is mandatory.
pm.max_children = 50
; The number of child processes created on startup.
; Note: Used only when pm is set to 'dynamic'
; Default Value: min_spare_servers + (max_spare_servers - min_spare_servers) / 2
pm.start_servers = 5
; The desired minimum number of idle server processes.
; Note: Used only when pm is set to 'dynamic'
; Note: Mandatory when pm is set to 'dynamic'
pm.min_spare_servers = 5
; The desired maximum number of idle server processes.
; Note: Used only when pm is set to 'dynamic'
; Note: Mandatory when pm is set to 'dynamic'
pm.max_spare_servers = 35
; The number of seconds after which an idle process will be killed.
; Note: Used only when pm is set to 'ondemand'
; Default Value: 10s
;pm.process_idle_timeout = 10s;
; The number of requests each child process should execute before respawning.
; This can be useful to work around memory leaks in 3rd party libraries. For
; endless request processing specify '0'. Equivalent to PHP_FCGI_MAX_REQUESTS.
; Default Value: 0
;pm.max_requests = 500
; The URI to view the FPM status page. If this value is not set, no URI will be
; recognized as a status page. It shows the following informations:
; pool - the name of the pool;
; process manager - static, dynamic or ondemand;
; start time - the date and time FPM has started;
; start since - number of seconds since FPM has started;
; accepted conn - the number of request accepted by the pool;
; listen queue - the number of request in the queue of pending
; connections (see backlog in listen(2));
; max listen queue - the maximum number of requests in the queue
; of pending connections since FPM has started;
; listen queue len - the size of the socket queue of pending connections;
; idle processes - the number of idle processes;
; active processes - the number of active processes;
; total processes - the number of idle + active processes;
; max active processes - the maximum number of active processes since FPM
; has started;
; max children reached - number of times, the process limit has been reached,
; when pm tries to start more children (works only for
; pm 'dynamic' and 'ondemand');
; Value are updated in real time.
; Example output:
; pool: www
; process manager: static
; start time: 01/Jul/2011:17:53:49 +0200
; start since: 62636
; accepted conn: 190460
; listen queue: 0
; max listen queue: 1
; listen queue len: 42
; idle processes: 4
; active processes: 11
; total processes: 15
; max active processes: 12
; max children reached: 0
;
; By default the status page output is formatted as text/plain. Passing either
; 'html', 'xml' or 'json' in the query string will return the corresponding
; output syntax. Example:
; http://www.foo.bar/status
; http://www.foo.bar/status?json
; http://www.foo.bar/status?html
; http://www.foo.bar/status?xml
;
; By default the status page only outputs short status. Passing 'full' in the
; query string will also return status for each pool process.
; Example:
; http://www.foo.bar/status?full
; http://www.foo.bar/status?json&full
; http://www.foo.bar/status?html&full
; http://www.foo.bar/status?xml&full
; The Full status returns for each process:
; pid - the PID of the process;
; state - the state of the process (Idle, Running, ...);
; start time - the date and time the process has started;
; start since - the number of seconds since the process has started;
; requests - the number of requests the process has served;
; request duration - the duration in µs of the requests;
; request method - the request method (GET, POST, ...);
; request URI - the request URI with the query string;
; content length - the content length of the request (only with POST);
; user - the user (PHP_AUTH_USER) (or '-' if not set);
; script - the main script called (or '-' if not set);
; last request cpu - the %cpu the last request consumed
; it's always 0 if the process is not in Idle state
; because CPU calculation is done when the request
; processing has terminated;
; last request memory - the max amount of memory the last request consumed
; it's always 0 if the process is not in Idle state
; because memory calculation is done when the request
; processing has terminated;
; If the process is in Idle state, then informations are related to the
; last request the process has served. Otherwise informations are related to
; the current request being served.
; Example output:
; ************************
; pid: 31330
; state: Running
; start time: 01/Jul/2011:17:53:49 +0200
; start since: 63087
; requests: 12808
; request duration: 1250261
; request method: GET
; request URI: /test_mem.php?N=10000
; content length: 0
; user: -
; script: /home/fat/web/docs/php/test_mem.php
; last request cpu: 0.00
; last request memory: 0
;
; Note: There is a real-time FPM status monitoring sample web page available
; It's available in: @EXPANDED_DATADIR@/fpm/status.html
;
; Note: The value must start with a leading slash (/). The value can be
; anything, but it may not be a good idea to use the .php extension or it
; may conflict with a real PHP file.
; Default Value: not set
;pm.status_path = /status; The ping URI to call the monitoring page of FPM. If this value is not set, no
; URI will be recognized as a ping page. This could be used to test from outside
; that FPM is alive and responding, or to
; - create a graph of FPM availability (rrd or such);
; - remove a server from a group if it is not responding (load balancing);
; - trigger alerts for the operating team (24/7).
; Note: The value must start with a leading slash (/). The value can be
; anything, but it may not be a good idea to use the .php extension or it
; may conflict with a real PHP file.
; Default Value: not set
;ping.path = /ping; This directive may be used to customize the response of a ping request. The
; response is formatted as text/plain with a 200 response code.
; Default Value: pong
;ping.response = pong; The access log file
; Default: not set
;access.log = log/$pool.access.log; The access log format.
; The following syntax is allowed
; %%: the '%' character
; %C: %CPU used by the request
; it can accept the following format:
; - %{user}C for user CPU only
; - %{system}C for system CPU only
; - %{total}C for user + system CPU (default)
; %d: time taken to serve the request
; it can accept the following format:
; - %{seconds}d (default)
; - %{miliseconds}d
; - %{mili}d
; - %{microseconds}d
; - %{micro}d
; %e: an environment variable (same as $_ENV or $_SERVER)
; it must be associated with embraces to specify the name of the env
; variable. Some exemples:
; - server specifics like: %{REQUEST_METHOD}e or %{SERVER_PROTOCOL}e
; - HTTP headers like: %{HTTP_HOST}e or %{HTTP_USER_AGENT}e
; %f: script filename
; %l: content-length of the request (for POST request only)
; %m: request method
; %M: peak of memory allocated by PHP
; it can accept the following format:
; - %{bytes}M (default)
; - %{kilobytes}M
; - %{kilo}M
; - %{megabytes}M
; - %{mega}M
; %n: pool name
; %o: output header
; it must be associated with embraces to specify the name of the header:
; - %{Content-Type}o
; - %{X-Powered-By}o
; - %{Transfert-Encoding}o
; - ....
; %p: PID of the child that serviced the request
; %P: PID of the parent of the child that serviced the request
; %q: the query string
; %Q: the '?' character if query string exists
; %r: the request URI (without the query string, see %q and %Q)
; %R: remote IP address
; %s: status (response code)
; %t: server time the request was received
; it can accept a strftime(3) format:
; %d/%b/%Y:%H:%M:%S %z (default)
; The strftime(3) format must be encapsuled in a %{<strftime_format>}t tag
; e.g. for a ISO8601 formatted timestring, use: %{%Y-%m-%dT%H:%M:%S%z}t
; %T: time the log has been written (the request has finished)
; it can accept a strftime(3) format:
; %d/%b/%Y:%H:%M:%S %z (default)
; The strftime(3) format must be encapsuled in a %{<strftime_format>}t tag
; e.g. for a ISO8601 formatted timestring, use: %{%Y-%m-%dT%H:%M:%S%z}t
; %u: remote user
;
; Default: "%R - %u %t \"%m %r\" %s"
;access.format = "%R - %u %t \"%m %r%Q%q\" %s %f %{mili}d %{kilo}M %C%%"; The log file for slow requests
; Default Value: not set
; Note: slowlog is mandatory if request_slowlog_timeout is set
slowlog = /var/log/php-fpm/www-slow.log; The timeout for serving a single request after which a PHP backtrace will be
; dumped to the 'slowlog' file. A value of '0s' means 'off'.
; Available units: s(econds)(default), m(inutes), h(ours), or d(ays)
; Default Value: 0
;request_slowlog_timeout = 0; The timeout for serving a single request after which the worker process will
; be killed. This option should be used when the 'max_execution_time' ini option
; does not stop script execution for some reason. A value of '0' means 'off'.
; Available units: s(econds)(default), m(inutes), h(ours), or d(ays)
; Default Value: 0
;request_terminate_timeout = 0; Set open file descriptor rlimit.
; Default Value: system defined value
;rlimit_files = 1024; Set max core size rlimit.
; Possible Values: 'unlimited' or an integer greater or equal to 0
; Default Value: system defined value
;rlimit_core = 0; Chroot to this directory at the start. This value must be defined as an
; absolute path. When this value is not set, chroot is not used.
; Note: chrooting is a great security feature and should be used whenever
; possible. However, all PHP paths will be relative to the chroot
; (error_log, sessions.save_path, ...).
; Default Value: not set
;chroot =; Chdir to this directory at the start.
; Note: relative path can be used.
; Default Value: current directory or / when chroot
;chdir = /var/www; Redirect worker stdout and stderr into main error log. If not set, stdout and
; stderr will be redirected to /dev/null according to FastCGI specs.
; Note: on highloaded environement, this can cause some delay in the page
; process time (several ms).
; Default Value: no
;catch_workers_output = yes; Clear environment in FPM workers
; Prevents arbitrary environment variables from reaching FPM worker processes
; by clearing the environment in workers before env vars specified in this
; pool configuration are added.
; Setting to "no" will make all environment variables available to PHP code
; via getenv(), $_ENV and $_SERVER.
; Default Value: yes
;clear_env = no; Limits the extensions of the main script FPM will allow to parse. This can
; prevent configuration mistakes on the web server side. You should only limit
; FPM to .php extensions to prevent malicious users to use other extensions to
; exectute php code.
; Note: set an empty value to allow all extensions.
; Default Value: .php
;security.limit_extensions = .php .php3 .php4 .php5 .php7; Pass environment variables like LD_LIBRARY_PATH. All $VARIABLEs are taken from
; the current environment.
; Default Value: clean env
;env[HOSTNAME] = $HOSTNAME
;env[PATH] = /usr/local/bin:/usr/bin:/bin
;env[TMP] = /tmp
;env[TMPDIR] = /tmp
;env[TEMP] = /tmp; Additional php.ini defines, specific to this pool of workers. These settings
; overwrite the values previously defined in the php.ini. The directives are the
; same as the PHP SAPI:
; php_value/php_flag - you can set classic ini defines which can
; be overwritten from PHP call 'ini_set'.
; php_admin_value/php_admin_flag - these directives won't be overwritten by
; PHP call 'ini_set'
; For php_*flag, valid values are on, off, 1, 0, true, false, yes or no.
; Defining 'extension' will load the corresponding shared extension from
; extension_dir. Defining 'disable_functions' or 'disable_classes' will not
; overwrite previously defined php.ini values, but will append the new value
; instead.
; Default Value: nothing is defined by default except the values in php.ini and
; specified at startup with the -d argument
;php_admin_value[sendmail_path] = /usr/sbin/sendmail -t -i -f www@my.domain.com
;php_flag[display_errors] = off
php_admin_value[error_log] = /var/log/php-fpm/www-error.log
php_admin_flag[log_errors] = on
;php_admin_value[memory_limit] = 128M
; Set session path to a directory owned by process user
php_value[session.save_handler] = files
php_value[session.save_path] = /var/lib/php/session
php_value[soap.wsdl_cache_dir] = /var/lib/php/wsdlcache编写Php的配置文件

3.3编写handlers/main.yml
编写Php的控制器文件


---
- name: reload php-fpmservice: name={{svc}} state=restarted3.4编写tasks/main.yml
编写Php的任务文件
vim /etc/ansible/roles/php/tasks/main.yml
---
- name: disable selinuxcommand: '/usr/sbin/setenforce 0'ignore_errors: true- name: disable firewalldservice: name=firewalld state=stopped enabled=no- name: install php repoyum: name={{repo}}- name: install php appyum: name={{app}}ignore_errors: true- name: add php useruser: name=php shell=/sbin/nologin- name: create /www dirfile: path=/www state=directory- name: copy index.phpcopy: src=index.php dest=/www/index.php- name: copy configuration filecopy: src=www.conf dest=/etc/php-fpm.d/www.confnotify: reload php-fpm- name: modify php.inishell: "sed -i 's#;date.timezone =#date.timezone = Asia/shanghai#' /etc/php.ini"- name: start php-fpmservice: name={{svc}} state=started enabled=yes这个命令是用来通过sed命令在
/etc/php.ini文件中设置PHP的时区为"Asia/Shanghai"。具体来说:
sed是一个流编辑器,用来处理文本流。-i参数表示直接修改文件内容,而不是输出到标准输出。's#;date.timezone =#date.timezone = Asia/shanghai#'是sed的替换命令,用来将;date.timezone =替换为date.timezone = Asia/shanghai。/etc/php.ini是被修改的目标文件,即PHP的配置文件。
3.5编写vars/main.yml文件
编写Php的变量文件
[root@zz1 php]#vim /etc/ansible/roles/php/vars/main.ymlapp:
- php72w
- php72w-cli
- php72w-common
- php72w-devel
- php72w-embedded
- php72w-gd
- php72w-mbstring
- php72w-pdo
- php72w-xml
- php72w-fpm
- php72w-mysqlnd
- php72w-opcachesvc: php-fpmrepo:
- http://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/epel-release-latest-7.noarch.rpm
- http://mirror.webtatic.com/yum/el7/webtatic-release.rpm
四、编写启动文件
---
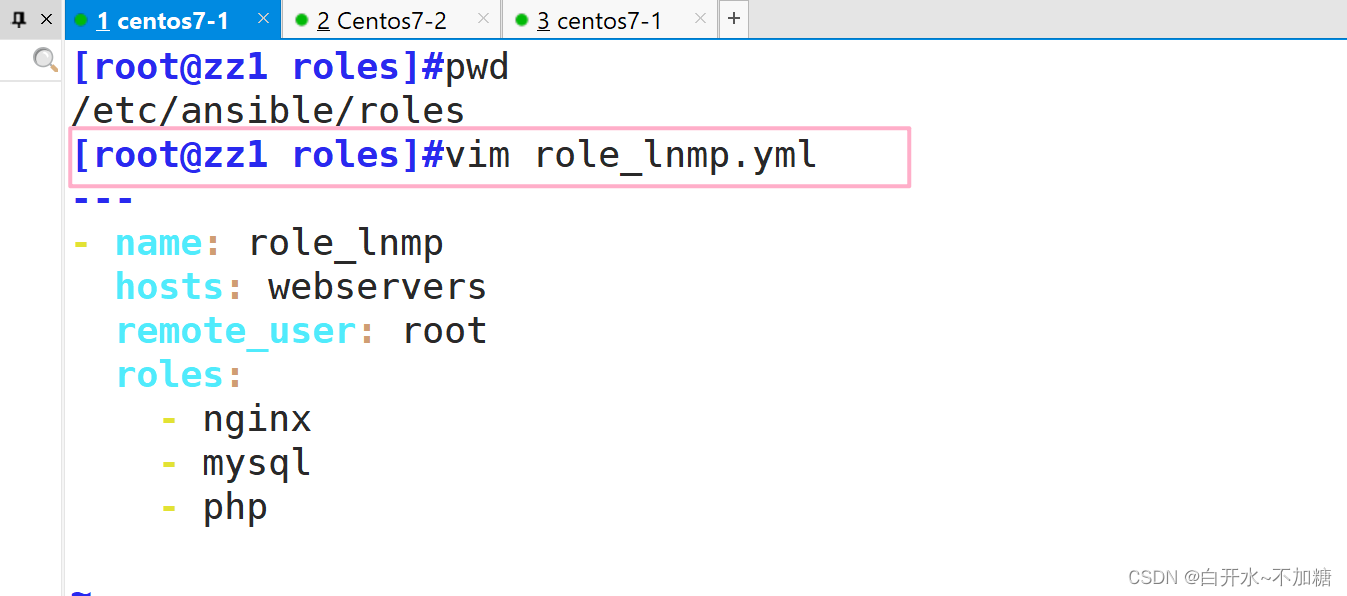
- hosts: webserversremote_user: rootroles:- nginx
- hosts: webserversremote_user: rootroles:- mysql
- hosts: webserversremote_user: rootroles:- php
五、启动并测试
ansible-playbook role_lnmp.yml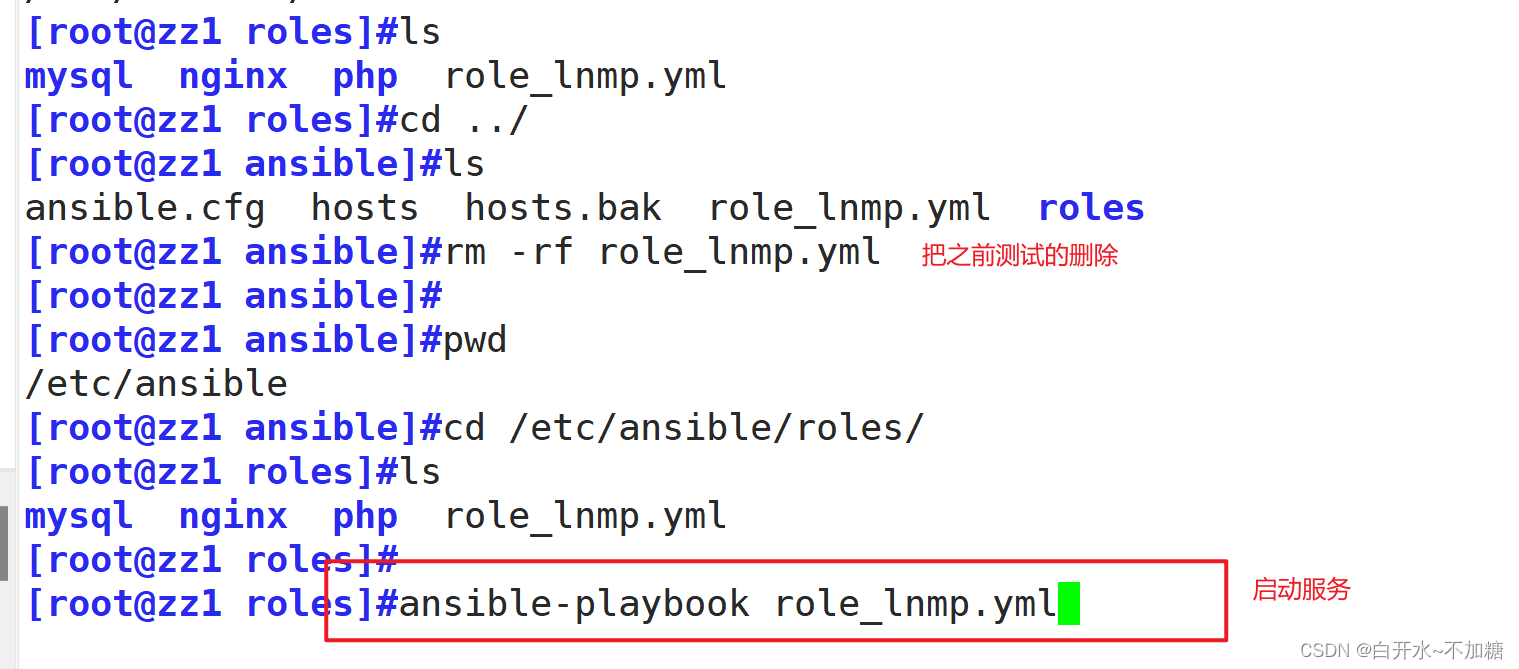
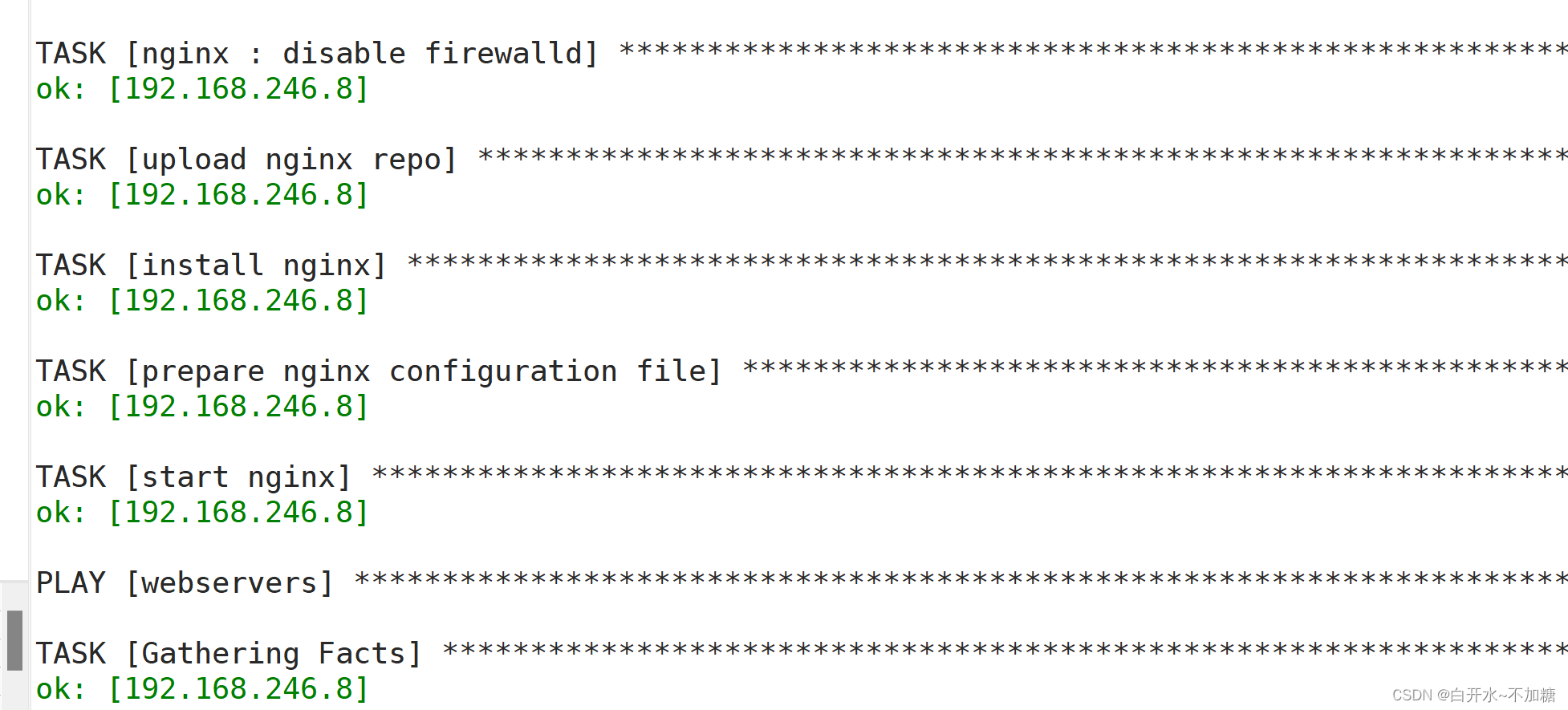
 六、浏览器访问
六、浏览器访问
192.168.246.8/index.php