1. 同步互斥概述
在多任务操作系统中,同时运行的多个任务可能都需要访问/使用同一种资源多个任务之间有依赖关系,某个任务的运行依赖于另一个任务同步和互斥就是用于解决这两个问题的。
互斥:一个公共资源同一时刻只能被一个进程或线程使用,多个进程或线程不能同时使用公共资源。POSIX标准中进程和线程同步和互斥的方法,主要有信号量和互斥锁两种方式。
同步:两个或两个以上的进程或线程在运行过程中协同步调,按预定的先后次序运行。
同步就是在互斥的基础上有顺序。
2. 互斥锁
mutex是一种简单的加锁的方法来控制对共享资源的访问,mutex只有两种状态,即上锁(lock)和解锁(unlock)。在访问该资源前,首先应申请mutex,如果mutex处于unlock状态,则会申请到 mutex并立即lock;如果mutex处于lock状态,则默认阻塞申请者。unlock操作应该由lock者进行。
2.1 创建互斥锁
mutex用pthread_mutex_t 数据类型表示,在使用互斥锁前,必须先对它进行初始化。
2.2 静态分配的互斥锁:
pthread_mutex_t mutex = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;
2.3 动态分配互斥锁:
pthread_mutex_t mutex;
pthread_mutex_init(&mutex, NULL);在所有使用过此互斥锁的线程都不再需要使用时候,应调用销毁互斥锁;
2.4 销毁互斥锁
pthread_mutex_destroy
3. 初始化互斥锁(pthread_mutex_init)
需要包含的头文件:
#include <pthread.h>函数结构:int pthread_mutex_init(pthread_mutex_t* mutex, const pthread_mutexattr_t* attr);
功能:初始化一个互斥锁
参数:
mutex:指定的互斥锁
mutexattr:互斥锁的属性,为NULL表示默认属性
返回值:
成功:0
失败:非0
4. 互斥锁上锁(pthread_mutex_lock)
需要包含的头文件:
#include <pthread.h>int pthread_mutex_lock(pthread_mutex_t* mutex);
功能:对互斥锁上锁,若已经上锁,则调用者一直阻塞到互斥锁解锁
参数:
- mutex:指定的互斥锁
返回值:
- 成功:0
- 失败:非0
4.1 非阻塞(pthread_mutex_trylock)
需要包含的头文件:
#include <pthread.h>int pthread_mutex_trylock(pthread_mutex_t* mutex);
功能:对互斥锁上锁,若已经上锁,则上锁失败,函数立即返回。
参数:
- mutex:互斥锁地址。
返回值:
- 成功:0
- 失败:非0
5. 互斥锁解锁(pthread_mutex_unlock)
需要包含的头文件:
#include <pthread.h>函数结构:int pthread_mutex_unlock(pthread_mutex_t * mutex);
功能:对指定的互斥锁解锁。
参数:
- mutex:互斥锁地址。
返回值:
- 成功:0
- 失败:非0
6. 互斥锁销毁(pthread_mutex_destroy)
需要包含的头文件:
#include <pthread.h>函数结构:int pthread_mutex_destroy(pthread_mutex_t * mutex);
功能:销毁指定一个互斥锁。
参数:
- mutex:互斥锁地址。
返回值:
- 成功:0
- 失败:非0
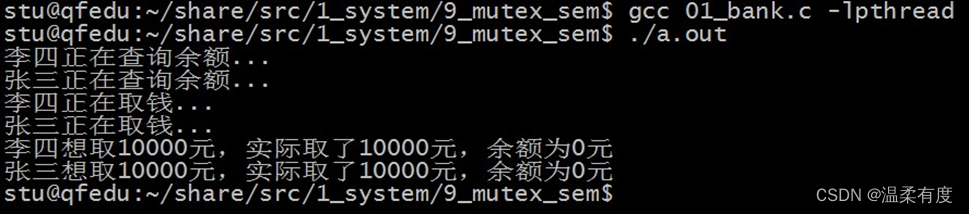
7. 不使用互斥锁
代码演示:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
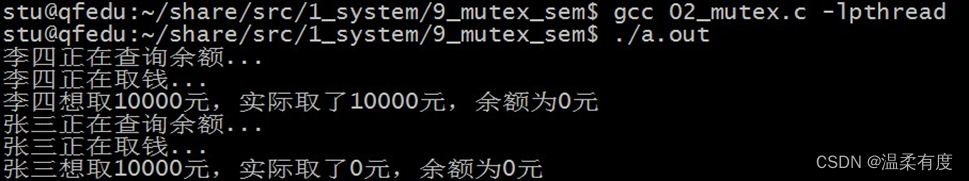
#include <pthread.h>int money = 10000;void *pthread_fun1(void *arg)
{int get, yu, shiji;get = 10000;printf("张三正在查询余额...\n");sleep(1);yu = money;printf("张三正在取钱...\n");sleep(1);if(get > yu){shiji = 0;}else {shiji = get;yu = yu - get;money = yu;}printf("张三想取%d元,实际取了%d元,余额为%d元\n", get, shiji, yu);pthread_exit(NULL);
}void *pthread_fun2(void *arg)
{int get, yu, shiji;get = 10000;printf("李四正在查询余额...\n");sleep(1);yu = money;printf("李四正在取钱...\n");sleep(1);if(get > yu){shiji = 0;}else {shiji = get;yu = yu - get;money = yu;}printf("李四想取%d元,实际取了%d元,余额为%d元\n", get, shiji, yu);pthread_exit(NULL);
}int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{pthread_t thread1, thread2;if(pthread_create(&thread1, NULL, pthread_fun1, NULL) != 0){perror("fail to pthread_create");exit(1);}if(pthread_create(&thread2, NULL, pthread_fun2, NULL) != 0){perror("fail to pthread_create");exit(1);}pthread_join(thread1, NULL);pthread_join(thread2, NULL);return 0;
}执行结果:
8. 使用互斥锁
代码演示:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <pthread.h>//通过互斥锁解决线程间互斥问题int money = 10000;//第一步:创建互斥锁(由于两个线程操作同一个互斥锁,所以定义在全局更加方便一点)
pthread_mutex_t mymutex;void *pthread_fun1(void *arg)
{int get, yu, shiji;get = 10000;//第三步:对共享资源的操作进行上锁pthread_mutex_lock(&mymutex);printf("张三正在查询余额...\n");sleep(1);yu = money;printf("张三正在取钱...\n");sleep(1);if(get > yu){shiji = 0;}else {shiji = get;yu = yu - get;money = yu;}printf("张三想取%d元,实际取了%d元,余额为%d元\n", get, shiji, yu);//第四步:当共享资源的操作执行完毕后,对互斥锁执行解锁操作pthread_mutex_unlock(&mymutex);pthread_exit(NULL);
}void *pthread_fun2(void *arg)
{int get, yu, shiji;get = 10000;//第三步:对共享资源的操作进行上锁pthread_mutex_lock(&mymutex);printf("李四正在查询余额...\n");sleep(1);yu = money;printf("李四正在取钱...\n");sleep(1);if(get > yu){shiji = 0;}else {shiji = get;yu = yu - get;money = yu;}printf("李四想取%d元,实际取了%d元,余额为%d元\n", get, shiji, yu);//第四步:当共享资源的操作执行完毕后,对互斥锁执行解锁操作pthread_mutex_unlock(&mymutex);pthread_exit(NULL);
}int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{//第二步:初始化互斥锁pthread_mutex_init(&mymutex, NULL);pthread_t thread1, thread2;if(pthread_create(&thread1, NULL, pthread_fun1, NULL) != 0){perror("fail to pthread_create");exit(1);}if(pthread_create(&thread2, NULL, pthread_fun2, NULL) != 0){perror("fail to pthread_create");exit(1);}pthread_join(thread1, NULL);pthread_join(thread2, NULL);//第五步:当互斥锁使用完毕后,要销毁pthread_mutex_destroy(&mymutex);return 0;
}执行结果: