目录
1.表的增删查改
2.Create
2.1单行数据 + 全列插入
2.2 多行数据指定列插入
2.3插入否则更新
2.4替换
3.Retrieve
3.1select列
3.2where条件
3.3结果排序
3.4筛选分页结果
4.Update
5.Delete
总结
前言
hello,各位小伙伴大家好,又和大家见面了。前面我们对于表的定义语言进行了详细的学习,接下来,在表创建好的基础上,对表的操作语言进行进一步学习,本篇文章介绍的思路是首先介绍语法,然后结合对应的案例对语法进行学习。相信看完本篇文章对表中数据的增删查改就不会有任何问题了。

1.表的增删查改
包含四个操作分别是:Create(创建), Retrieve(读取),Update(更新),Delete(删除)
下面我们就对每个操作具体来看看
2.Create
语法:
INSERT [INTO] table_name
[(column [, column] ...)]
VALUES (value_list) [, (value_list)] ...
value_list: value, [, value] ...案例:创建一张学生表
mysql> create table if not exists student(-> id int primary key auto_increment,-> name varchar(20) not null,-> sn int not null unique comment '学号',-> qq varchar(20)-> );
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.04 sec)2.1单行数据 + 全列插入
--插入数据
mysql> insert into student values(1,'张三',1,'123456');
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec)mysql> insert into student values(2,'李四',2,'1234578');
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec)--查看插入结果
mysql> select* from student;
+----+--------+----+---------+
| id | name | sn | qq |
+----+--------+----+---------+
| 1 | 张三 | 1 | 123456 |
| 2 | 李四 | 2 | 1234578 |
+----+--------+----+---------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
2.2 多行数据指定列插入
--插入两条数据
mysql> insert into student(name,sn,qq) values ('赵六',4,'274567'),('田七',5,'2467764');
Query OK, 2 rows affected (0.01 sec)
Records: 2 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
--查看结果
mysql> select* from student;
+----+--------+----+---------+
| id | name | sn | qq |
+----+--------+----+---------+
| 1 | 张三 | 1 | 123456 |
| 2 | 李四 | 2 | 1234578 |
| 3 | 王五 | 3 | 234567 |
| 4 | 赵六 | 4 | 274567 |
| 5 | 田七 | 5 | 2467764 |
+----+--------+----+---------+
5 rows in set (0.00 sec)
2.3插入否则更新
由于主键或者唯一键对应的值已经存在导致插入失败
--主键冲突
mysql> insert into student values (5,'张飞',6,'2345321');
ERROR 1062 (23000): Duplicate entry '5' for key 'PRIMARY'
--唯一键冲突
mysql> insert into student values (6,'张飞',5,'2345321');
ERROR 1062 (23000): Duplicate entry '5' for key 'sn'解决方式:可以选择性的进行同步更新操作
语法:
insert... on duplicate key update
column = value [, column = value] ...--修改前:
mysql> select* from student;
+----+--------+----+---------+
| id | name | sn | qq |
+----+--------+----+---------+
| 1 | 张三 | 1 | 123456 |
| 2 | 李四 | 2 | 1234578 |
| 3 | 王五 | 3 | 234567 |
| 4 | 赵六 | 4 | 274567 |
| 5 | 田七 | 5 | 2467764 |
+----+--------+----+---------+
--修改后:
mysql> insert into student (id,name,sn) values(5,'张飞',6) on duplicate key update name='张飞',sn = 6;
Query OK, 2 rows affected (0.01 sec)mysql> select* from student;
+----+--------+----+---------+
| id | name | sn | qq |
+----+--------+----+---------+
| 1 | 张三 | 1 | 123456 |
| 2 | 李四 | 2 | 1234578 |
| 3 | 王五 | 3 | 234567 |
| 4 | 赵六 | 4 | 274567 |
| 5 | 张飞 | 6 | 2467764 |
+----+--------+----+---------+
5 rows in set (0.00 sec)
0 row affected: 表中有冲突数据,但冲突数据的值和 update 的值相等
1 row affected: 表中没有冲突数据,数据被插入
2 row affected: 表中有冲突数据,并且数据已经被更新
通过 MySQL 函数获取受到影响的数据行数
SELECT ROW_COUNT();
+-------------+
| ROW_COUNT() |
+-------------+
| 2 |
+-------------+2.4替换
关键字:replace
特点:
a.主键或唯一键没有冲突则直接插入;
b.主键或唯一键如果冲突则删除后再插入;
--替换前:
mysql> select* from student;
+----+--------+----+---------+
| id | name | sn | qq |
+----+--------+----+---------+
| 1 | 张三 | 1 | 123456 |
| 2 | 李四 | 2 | 1234578 |
| 3 | 王五 | 3 | 234567 |
| 4 | 赵六 | 4 | 274567 |
| 5 | 张飞 | 6 | 2467764 |
+----+--------+----+---------+
--替换后:mysql> replace into student (sn,name) values (4,'刘备');
Query OK, 2 rows affected (0.00 sec)mysql> select* from student;
+----+--------+----+---------+
| id | name | sn | qq |
+----+--------+----+---------+
| 1 | 张三 | 1 | 123456 |
| 2 | 李四 | 2 | 1234578 |
| 3 | 王五 | 3 | 234567 |
| 5 | 张飞 | 6 | 2467764 |
| 6 | 刘备 | 4 | NULL |
+----+--------+----+---------+
3.Retrieve
语法:
SELECT
[DISTINCT] {* | {column [, column] ...}
[FROM table_name]
[WHERE ...]
[ORDER BY column [ASC | DESC], ...]
LIMIT ...案例:
-- 创建表结构
CREATE TABLE exam_result (
id INT UNSIGNED PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,
name VARCHAR(20) NOT NULL COMMENT '同学姓名',
chinese float DEFAULT 0.0 COMMENT '语文成绩',
math float DEFAULT 0.0 COMMENT '数学成绩',
english float DEFAULT 0.0 COMMENT '英语成绩'
);
-- 插入测试数据
INSERT INTO exam_result (name, chinese, math, english) VALUES
('唐三藏', 67, 98, 56),
('孙悟空', 87, 78, 77),
('猪悟能', 88, 98, 90),
('曹孟德', 82, 84, 67),
('刘玄德', 55, 85, 45),
('孙权', 70, 73, 78),
('宋公明', 75, 65, 30);
Query OK, 7 rows affected (0.00 sec)
Records: 7 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 03.1select列
1.全列查询
通常情况下不建议使用 * 进行全列查询,*表示查询所有的列
1. 查询的列越多,意味着需要传输的数据量越大;
2. 可能会影响到索引的使用。
mysql> select* from exam_result;
+----+-----------+---------+------+---------+
| id | name | chinese | math | english |
+----+-----------+---------+------+---------+
| 1 | 唐三藏 | 67 | 98 | 56 |
| 2 | 孙悟空 | 87 | 78 | 77 |
| 3 | 猪悟能 | 88 | 98 | 90 |
| 4 | 曹孟德 | 82 | 84 | 67 |
| 5 | 刘玄德 | 55 | 85 | 45 |
| 6 | 孙权 | 70 | 73 | 78 |
| 7 | 宋公明 | 75 | 65 | 30 |
+----+-----------+---------+------+---------+
7 rows in set (0.00 sec)
2.指定列查询
指定列的顺序不需要按定义表的顺序来:
mysql> select id,name from exam_result;
+----+-----------+
| id | name |
+----+-----------+
| 1 | 唐三藏 |
| 2 | 孙悟空 |
| 3 | 猪悟能 |
| 4 | 曹孟德 |
| 5 | 刘玄德 |
| 6 | 孙权 |
| 7 | 宋公明 |
+----+-----------+
7 rows in set (0.00 sec)
3.查询字段为表达式
a.表达式不包含字段:
mysql> select id,name,10 from exam_result;
+----+-----------+----+
| id | name | 10 |
+----+-----------+----+
| 1 | 唐三藏 | 10 |
| 2 | 孙悟空 | 10 |
| 3 | 猪悟能 | 10 |
| 4 | 曹孟德 | 10 |
| 5 | 刘玄德 | 10 |
| 6 | 孙权 | 10 |
| 7 | 宋公明 | 10 |
+----+-----------+----+
7 rows in set (0.00 sec)
b.表达式包含一个字段:
mysql> select id,name,math+10 from exam_result;
+----+-----------+---------+
| id | name | math+10 |
+----+-----------+---------+
| 1 | 唐三藏 | 108 |
| 2 | 孙悟空 | 88 |
| 3 | 猪悟能 | 108 |
| 4 | 曹孟德 | 94 |
| 5 | 刘玄德 | 95 |
| 6 | 孙权 | 83 |
| 7 | 宋公明 | 75 |
+----+-----------+---------+
c.表达式包含多个字段:
mysql> select id,name,math+chinese+english from exam_result;
+----+-----------+----------------------+
| id | name | math+chinese+english |
+----+-----------+----------------------+
| 1 | 唐三藏 | 221 |
| 2 | 孙悟空 | 242 |
| 3 | 猪悟能 | 276 |
| 4 | 曹孟德 | 233 |
| 5 | 刘玄德 | 185 |
| 6 | 孙权 | 221 |
| 7 | 宋公明 | 170 |
+----+-----------+----------------------+
4.为查询结果指定别名
语法:
SELECT column [AS] alias_name [...] FROM table_name;mysql> select id,name,math+chinese+english 总分 from exam_result;
+----+-----------+--------+
| id | name | 总分 |
+----+-----------+--------+
| 1 | 唐三藏 | 221 |
| 2 | 孙悟空 | 242 |
| 3 | 猪悟能 | 276 |
| 4 | 曹孟德 | 233 |
| 5 | 刘玄德 | 185 |
| 6 | 孙权 | 221 |
| 7 | 宋公明 | 170 |
+----+-----------+--------+
7 rows in set (0.00 sec)
注:as是可以省略的
5.结果去重
--去重前:
mysql> select math from exam_result;
+------+
| math |
+------+
| 98 |
| 78 |
| 98 |
| 84 |
| 85 |
| 73 |
| 65 |
+------+
7 rows in set (0.00 sec)--去重结果:
mysql> select distinct math from exam_result;
+------+
| math |
+------+
| 98 |
| 78 |
| 84 |
| 85 |
| 73 |
| 65 |
+------+
6 rows in set (0.00 sec)
3.2where条件
在学习where条件之前,先来了解一下MySQL中的比较运算符,了解了这些运算符之后才能按照实际需求灵活的使用where条件。
比较运算符:
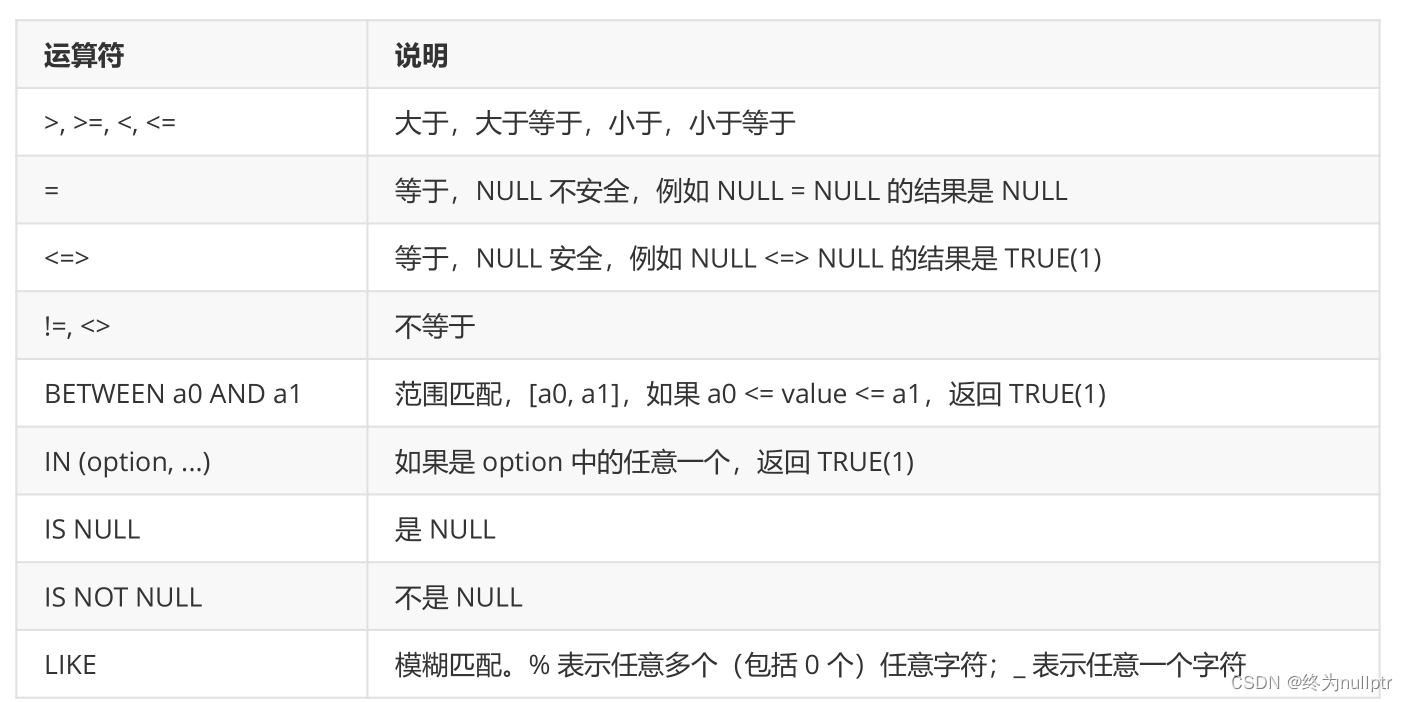
逻辑运算符:
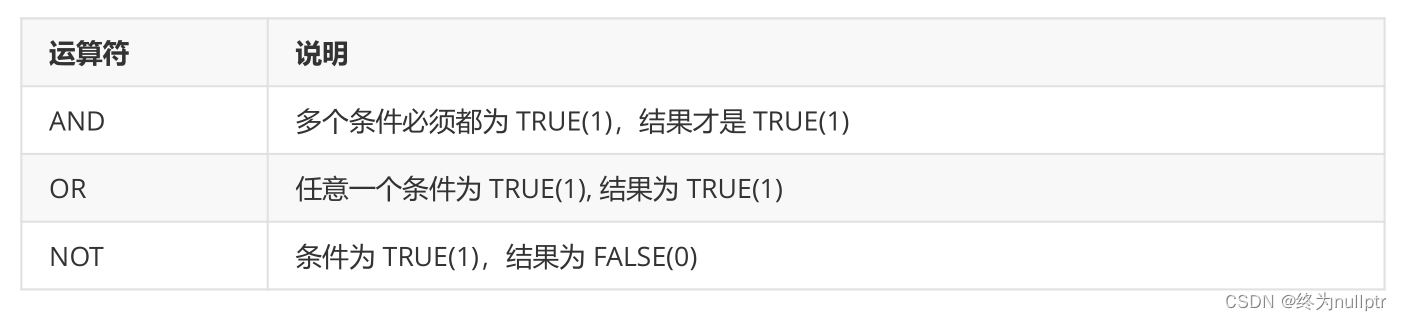 首先,对这些运算符有一个宏观的认识之后,接下来我们一起根据实际的案例,对每一种运算进行学习。
首先,对这些运算符有一个宏观的认识之后,接下来我们一起根据实际的案例,对每一种运算进行学习。
案例:
1.英语不及格的同学及英语成绩 ( < 60 )
mysql> select name,english from exam_result where english < 60;
+-----------+---------+
| name | english |
+-----------+---------+
| 唐三藏 | 56 |
| 刘玄德 | 45 |
| 宋公明 | 30 |
+-----------+---------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
2.语文成绩在 [80, 90] 分的同学及语文成绩
方法1:使用and条件连接,and表示前面的条件和后面的条件都满足才执行:
mysql> select name,chinese from exam_result where chinese >= 80 and chinese <= 90;
+-----------+---------+
| name | chinese |
+-----------+---------+
| 孙悟空 | 87 |
| 猪悟能 | 88 |
| 曹孟德 | 82 |
+-----------+---------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
方法2:使用between and 连接:
mysql> select name,chinese from exam_result where chinese between 80 and 90;
+-----------+---------+
| name | chinese |
+-----------+---------+
| 孙悟空 | 87 |
| 猪悟能 | 88 |
| 曹孟德 | 82 |
+-----------+---------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
3.数学成绩是 58 或者 59 或者 98 或者 99 分的同学及数学成绩
方法1:使用or条件连接,or表示只要有一个条件为真则执行
mysql> select name,math from exam_result where math=58 or math=59 or math=98 or math=99;
+-----------+------+
| name | math |
+-----------+------+
| 唐三藏 | 98 |
| 猪悟能 | 98 |
+-----------+------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)方法2:使用in条件
mysql> select name,math from exam_result where math in (58,59,98,99);
+-----------+------+
| name | math |
+-----------+------+
| 唐三藏 | 98 |
| 猪悟能 | 98 |
+-----------+------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)4.姓孙的同学 及 孙某同学
使用like运算符
注:% 匹配任意多个(包括 0 个)任意字符
mysql> select name from exam_result where name like '孙%';
+-----------+
| name |
+-----------+
| 孙悟空 |
| 孙权 |
+-----------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
注:_严格匹配一个任意字符
mysql> select name from exam_result where name like '孙_';
+--------+
| name |
+--------+
| 孙权 |
+--------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)5.语文成绩好于英语成绩的同学
mysql> select name,chinese,english from exam_result where chinese > english;
+-----------+---------+---------+
| name | chinese | english |
+-----------+---------+---------+
| 唐三藏 | 67 | 56 |
| 孙悟空 | 87 | 77 |
| 曹孟德 | 82 | 67 |
| 刘玄德 | 55 | 45 |
| 宋公明 | 75 | 30 |
+-----------+---------+---------+
6.总分在 200 分以下的同学
mysql> select name,chinese+math+english 总分 from exam_result where chinese+math+english < 200;
+-----------+--------+
| name | 总分 |
+-----------+--------+
| 刘玄德 | 185 |
| 宋公明 | 170 |
+-----------+--------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
注:在where条件中,别名不能被使用
mysql> select name,chinese+math+english 总分 from exam_result where 总分 < 200;
ERROR 1054 (42S22): Unknown column '总分' in 'where clause'
原因:where条件的执行在取别名之前
7.语文成绩 > 80 并且不姓孙的同学
mysql> select name,chinese from exam_result where chinese > 80 and name not like '孙%';
+-----------+---------+
| name | chinese |
+-----------+---------+
| 猪悟能 | 88 |
| 曹孟德 | 82 |
+-----------+---------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)8.孙某同学,否则要求总成绩 > 200 并且 语文成绩 < 数学成绩 并且 英语成绩 > 80
mysql> select name,chinese,math,english,chinese+math+english 总分 from exam_result where name like '孙%' or (chinese+math+english > 200 and chinesse < math and english > 80);
+-----------+---------+------+---------+--------+
| name | chinese | math | english | 总分 |
+-----------+---------+------+---------+--------+
| 孙悟空 | 87 | 78 | 77 | 242 |
| 猪悟能 | 88 | 98 | 90 | 276 |
| 孙权 | 70 | 73 | 78 | 221 |
+-----------+---------+------+---------+--------+
3 rows in set (0.01 sec)
9.NULL 的查询
--查询student表
mysql> select name,qq from student where qq is null;
+--------+------+
| name | qq |
+--------+------+
| 刘备 | NULL |
+--------+------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
10.NULL 和 NULL 的比较,= 和 <=> 的区别
NULL不参与比较 NULL=NULL的结果是NULL NULL<=>NULL的结果是1
mysql> select NULL = NULL;
+-------------+
| NULL = NULL |
+-------------+
| NULL |
+-------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)mysql> select NULL = 1;
+----------+
| NULL = 1 |
+----------+
| NULL |
+----------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)mysql> select NULL <=> 1;
+------------+
| NULL <=> 1 |
+------------+
| 0 |
+------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)3.3结果排序
语法:
-- ASC 为升序(从小到大)
-- DESC 为降序(从大到小)
-- 默认为 ASC
SELECT ... FROM table_name [WHERE ...]
ORDER BY column [ASC|DESC], [...];1.同学及数学成绩,按数学成绩升序显示
mysql> select name,math from exam_result order by math;
+-----------+------+
| name | math |
+-----------+------+
| 宋公明 | 65 |
| 孙权 | 73 |
| 孙悟空 | 78 |
| 曹孟德 | 84 |
| 刘玄德 | 85 |
| 唐三藏 | 98 |
| 猪悟能 | 98 |
+-----------+------+
7 rows in set (0.00 sec)
2.同学及 qq 号,按 qq 号排序显示
mysql> select name,qq from student order by qq;
+--------+---------+
| name | qq |
+--------+---------+
| 刘备 | NULL |
| 张三 | 123456 |
| 李四 | 1234578 |
| 王五 | 234567 |
| 张飞 | 2467764 |
+--------+---------+
5 rows in set (0.00 sec)
注:NULL视为比任何值小,升序出现在最上面
3.查询同学各门成绩,依次按数学降序,英语升序,语文升序的方式显示
mysql> select name,math,english,chinese from exam_result order by math desc,english,chinese;
+-----------+------+---------+---------+
| name | math | english | chinese |
+-----------+------+---------+---------+
| 唐三藏 | 98 | 56 | 67 |
| 猪悟能 | 98 | 90 | 88 |
| 刘玄德 | 85 | 45 | 55 |
| 曹孟德 | 84 | 67 | 82 |
| 孙悟空 | 78 | 77 | 87 |
| 孙权 | 73 | 78 | 70 |
| 宋公明 | 65 | 30 | 75 |
+-----------+------+---------+---------+
7 rows in set (0.00 sec)
4.查询同学及总分,由高到低
mysql> select name,chinese+math+english 总分 from exam_result order by 总分 desc;
+-----------+--------+
| name | 总分 |
+-----------+--------+
| 猪悟能 | 276 |
| 孙悟空 | 242 |
| 曹孟德 | 233 |
| 唐三藏 | 221 |
| 孙权 | 221 |
| 刘玄德 | 185 |
| 宋公明 | 170 |
+-----------+--------+
7 rows in set (0.00 sec)
注:order by子句中可以使用别名,原因排序是处在最后的位置中
5.查询姓孙的同学或者姓曹的同学数学成绩,结果按数学成绩由高到低显示
mysql> select name,math from exam_result where name like '孙%' or name like '曹%' order by math desc;
+-----------+------+
| name | math |
+-----------+------+
| 曹孟德 | 84 |
| 孙悟空 | 78 |
| 孙权 | 73 |
+-----------+------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
3.4筛选分页结果
语法:
-- 起始下标为 0
-- 从 s 开始,筛选 n 条结果
SELECT ... FROM table_name [WHERE ...] [ORDER BY ...] LIMIT s, n
-- 从 0 开始,筛选 n 条结果
SELECT ... FROM table_name [WHERE ...] [ORDER BY ...] LIMIT n;
;
-- 从 s 开始,筛选 n 条结果,比第二种用法更明确,建议使用
SELECT ... FROM table_name [WHERE ...] [ORDER BY ...] LIMIT n OFFSET s;对未知表进行查询时,最好加一条 LIMIT 1,避免因为表中数据过大,查询全表数据导致数据库卡死按 id 进行分页,每页 3 条记录,分别显示 第 1、2、3 页
--,之前表示开始位置,之后表示个数
mysql> select id,name,math,english,chinese from exam_result order by id limit 0,3;
+----+-----------+------+---------+---------+
| id | name | math | english | chinese |
+----+-----------+------+---------+---------+
| 1 | 唐三藏 | 98 | 56 | 67 |
| 2 | 孙悟空 | 78 | 77 | 87 |
| 3 | 猪悟能 | 98 | 90 | 88 |
+----+-----------+------+---------+---------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
--offset之前表示开始位置 offset之后表示偏移量
mysql> select id,name,math,english,chinese from exam_result order by id limit 3 offset 3;
+----+-----------+------+---------+---------+
| id | name | math | english | chinese |
+----+-----------+------+---------+---------+
| 4 | 曹孟德 | 84 | 67 | 82 |
| 5 | 刘玄德 | 85 | 45 | 55 |
| 6 | 孙权 | 73 | 78 | 70 |
+----+-----------+------+---------+---------+
4.Update
语法:
UPDATE table_name SET column = expr [, column = expr ...]
[WHERE ...] [ORDER BY ...] [LIMIT ...]案例:
1.将孙悟空同学的数学成绩变更为 80 分
mysql> update exam_result set math=80 where name='孙悟空';
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
Rows matched: 1 Changed: 1 Warnings: 0
--修改成功:
mysql> select name,math from exam_result where name='孙悟空';
+-----------+------+
| name | math |
+-----------+------+
| 孙悟空 | 80 |
+-----------+------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
2.将曹孟德同学的数学成绩变更为 60 分,语文成绩变更为 70 分
mysql> update exam_result set math=60,chinese=70 where name='曹孟德';
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
Rows matched: 1 Changed: 1 Warnings: 0mysql> select name,math,chinese from exam_result where name='曹孟德';
+-----------+------+---------+
| name | math | chinese |
+-----------+------+---------+
| 曹孟德 | 60 | 70 |
+-----------+------+---------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
3.将总成绩倒数前三的 3 位同学的数学成绩加上 30 分
mysql> update exam_result set math = math + 30 order by math+english+chinese limit 3;
Query OK, 3 rows affected (0.00 sec)
Rows matched: 3 Changed: 3 Warnings: 0
mysql> select name,math,math+english+chinese 总分 from exam_result order by 总分 limit 0,3;
+-----------+------+--------+
| name | math | 总分 |
+-----------+------+--------+
| 宋公明 | 95 | 200 |
| 刘玄德 | 115 | 215 |
| 唐三藏 | 98 | 221 |
+-----------+------+--------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
4.将所有同学的语文成绩更新为原来的 2 倍
mysql> update exam_result set chinese = chinese*2;
Query OK, 7 rows affected (0.01 sec)
Rows matched: 7 Changed: 7 Warnings: 0mysql> select* from exam_result;
+----+-----------+---------+------+---------+
| id | name | chinese | math | english |
+----+-----------+---------+------+---------+
| 1 | 唐三藏 | 134 | 98 | 56 |
| 2 | 孙悟空 | 174 | 80 | 77 |
| 3 | 猪悟能 | 176 | 98 | 90 |
| 4 | 曹孟德 | 140 | 90 | 67 |
| 5 | 刘玄德 | 110 | 115 | 45 |
| 6 | 孙权 | 140 | 73 | 78 |
| 7 | 宋公明 | 150 | 95 | 30 |
+----+-----------+---------+------+---------+
5.Delete
删除数据
语法:
DELETE FROM table_name [WHERE ...] [ORDER BY ...] [LIMIT ...]1.删除孙悟空同学的考试成绩
mysql> delete from exam_result where name = '孙悟空';
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)mysql> select* from exam_result;
+----+-----------+---------+------+---------+
| id | name | chinese | math | english |
+----+-----------+---------+------+---------+
| 1 | 唐三藏 | 134 | 98 | 56 |
| 3 | 猪悟能 | 176 | 98 | 90 |
| 4 | 曹孟德 | 140 | 90 | 67 |
| 5 | 刘玄德 | 110 | 115 | 45 |
| 6 | 孙权 | 140 | 73 | 78 |
| 7 | 宋公明 | 150 | 95 | 30 |
+----+-----------+---------+------+---------+
6 rows in set (0.00 sec)2.删除整张表数据
-- 准备测试表
CREATE TABLE for_delete (
id INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,
name VARCHAR(20)
);
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.16 sec)
-- 插入测试数据
INSERT INTO for_delete (name) VALUES ('A'), ('B'), ('C');
Query OK, 3 rows affected (1.05 sec)
Records: 3 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
-- 查看测试数据
SELECT * FROM for_delete;
+----+------+
| id | name |
+----+------+
| 1 | A |
| 2 | B |
| 3 | C |
+----+------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
--删除整张表
mysql> delete from for_delete;
Query OK, 3 rows affected (0.01 sec)mysql> SELECT * FROM for_delete;
Empty set (0.00 sec)
-- 再插入一条数据,自增 id 在原值上增长
INSERT INTO for_delete (name) VALUES ('D');
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
-- 查看数据
SELECT * FROM for_delete;
+----+------+
| id | name |
+----+------+
| 4 | D |
+----+------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
-- 查看表结构,会有 AUTO_INCREMENT=n 项
mysql> show create table for_delete\G;
*************************** 1. row ***************************Table: for_delete
Create Table: CREATE TABLE `for_delete` (`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,`name` varchar(20) DEFAULT NULL,PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=5 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8
1 row in set (0.00 sec)ERROR:
No query specified3.截短表
语法:
TRUNCATE [TABLE] table_name使用规则:
1.只能对整表进行操作,不能像delete那样对部分数据进行操作;
2.实际上 MySQL 不对数据操作,所以比 DELETE 更快,但是TRUNCATE在删除数据的时候,并不经过真正的事物,所以无法回滚;
3.会重置auto_increment项;
案例:
-- 准备测试表
CREATE TABLE for_truncate (
id INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,
name VARCHAR(20)
);
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.16 sec)
-- 插入测试数据
INSERT INTO for_truncate (name) VALUES ('A'), ('B'), ('C');
Query OK, 3 rows affected (1.05 sec)
Records: 3 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
-- 查看测试数据
SELECT * FROM for_truncate;
+----+------+
| id | name |
+----+------+
| 1 | A |
| 2 | B |
| 3 | C |
+----+------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
-- 截断整表数据,注意影响行数是 0,所以实际上没有对数据真正操作
TRUNCATE for_truncate;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.10 sec)
-- 查看删除结果
SELECT * FROM for_truncate;
Empty set (0.00 sec)
-- 再插入一条数据,自增 id 在重新增长
INSERT INTO for_truncate (name) VALUES ('D');
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
-- 查看数据
SELECT * FROM for_truncate;
+----+------+
| id | name |
+----+------+
| 1 | D |
+----+------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
-- 查看表结构,会有 AUTO_INCREMENT=2 项
SHOW CREATE TABLE for_truncate\G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
Table: for_truncate
Create Table: CREATE TABLE `for_truncate` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`name` varchar(20) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=2 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8
1 row in set (0.00 sec)4.插入查询结果
语法
INSERT INTO table_name [(column [, column ...])] SELECT ...案例:删除表中的的重复复记录,重复的数据只能有一份
实现思路:创建一张空表,然后将去重的数据插入到空表中,然后进行重命名
具体细节如下:
-- 创建原数据表
CREATE TABLE duplicate_table (id int, name varchar(20));
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec)
-- 插入测试数据
INSERT INTO duplicate_table VALUES
(100, 'aaa'),
(100, 'aaa'),
(200, 'bbb'),
(200, 'bbb'),
(200, 'bbb'),
(300, 'ccc');
Query OK, 6 rows affected (0.00 sec)
Records: 6 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
-- 创建一张空表 no_duplicate_table,结构和 duplicate_table 一样
CREATE TABLE no_duplicate_table LIKE duplicate_table;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
-- 将 duplicate_table 的去重数据插入到 no_duplicate_table
INSERT INTO no_duplicate_table SELECT DISTINCT * FROM duplicate_table;
Query OK, 3 rows affected (0.00 sec)
Records: 3 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
-- 通过重命名表,实现原子的去重操作
RENAME TABLE duplicate_table TO old_duplicate_table,
no_duplicate_table TO duplicate_table;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
-- 查看最终结果
SELECT * FROM duplicate_table;
+------+------+
| id | name |
+------+------+
| 100 | aaa |
| 200 | bbb |
| 300 | ccc |
+------+------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)总结
以上就是MySQL表中对数据的增删查改操作,本篇文章为大家介绍的思路是首先介绍语法,然后再结合实际的案例对每个语法进行学习,希望大家也在学习的时候能够自己进行实际操作,相信一定会有很大的收获。期待我们下一次再见!