注意到,对于一棵树 \(T\) 的任一直径 \(a-b\),对于任意一点 \(u\),离 \(u\) 最远的点一定是 \(a\) 或 \(b\)。
考虑反证:如图,如果存在点 \(c\) 使得 \(dis(u,c)>\max(dis(u,a),dis(u,b))\)。
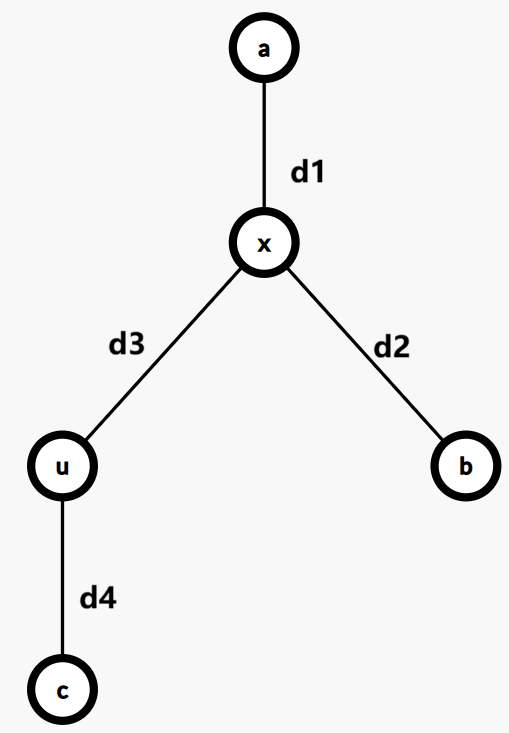
如图,\(a-b\) 为直径,\(d2>d1\)。因为有 \(d4>d3+d2\),所以有 \(d2+d3+d4>2d2+2d3>d1+d2\),所以 \(a-b\) 不是直径。
所以只要任找一条直径 \(x-y\),分别处理出以 \(x,y\) 为根时的倍增数组,询问时找到离自己更远的端点,倍增 \(k\) 步即可。
不存在输出 -1。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;const int N = 2e5 + 5, K = 20;
vector<int> e[N];
int n, st[N][K], st2[N][K], d[N];pair<int, int> dfs(int x, int fa)
{pair<int, int> ans = {0, x};for(int i : e[x]){if(i == fa) continue;auto t = dfs(i, x);t.first ++;ans = max(ans, t);}return ans;
}int dep[N], dep2[N];
void dfs2(int x, int fa, int d, int dep[N], int st[N][K])
{dep[x] = d;st[x][0] = fa;for(int i = 1; i < K; i ++)st[x][i] = st[st[x][i - 1]][i - 1];for(int i : e[x]){if(i == fa) continue;dfs2(i, x, d + 1, dep, st);}
}signed main()
{ios::sync_with_stdio(0);cin.tie(0);cin >> n;for(int i = 1; i < n; i ++){int x, y; cin >> x >> y;e[x].push_back(y);e[y].push_back(x);}int l = dfs(1, 0).second;int r = dfs(l, 0).second;dfs2(l, 0, 1, dep, st);dfs2(r, 0, 1, dep2, st2);int q; cin >> q;while(q --){int x, k; cin >> x >> k;if(dep[x] > dep2[x]){for(int i = K - 1; i >= 0; i --)if((k >> i) & 1) x = st[x][i];}else{for(int i = K - 1; i >= 0; i --)if((k >> i) & 1) x = st2[x][i];}if(!x) cout << -1 << "\n";else cout << x << "\n";}return 0;
}