题目1 226. 翻转二叉树
给你一棵二叉树的根节点 root ,翻转这棵二叉树,并返回其根节点。
示例 1:

输入:root = [4,2,7,1,3,6,9]
输出:[4,7,2,9,6,3,1]
示例 2:
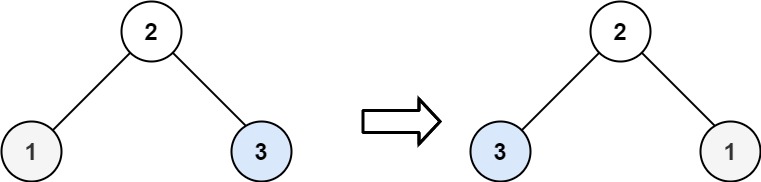
输入:root = [2,1,3]
输出:[2,3,1]
示例 3:
输入:root = []
输出:[]
提示:
- 树中节点数目范围在
[0, 100]内 -100 <= Node.val <= 100
思路
这道题可以用先序,中序,后序或者层序遍历去做,思路都是类似的。
递归调用
注意递归结束条件是root为nullptr,在每个非空结点上进行左右孩子指针的交换就行了。
代码
/*** Definition for a binary tree node.* struct TreeNode {* int val;* TreeNode *left;* TreeNode *right;* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}* };*/
class Solution {
public:TreeNode* invertTree(TreeNode* root) {if(root == nullptr) return root;TreeNode* tmp = root->left;root->left = root->right;root->right = tmp;invertTree(root->left);invertTree(root->right);return root;}
};
迭代遍历翻转
使用一个辅助的栈或者队列来存储子结点就可以做了。
代码
class Solution {
public:TreeNode* invertTree(TreeNode* root) {stack<TreeNode*> nodeStack;nodeStack.push(root);while(!nodeStack.empty()){TreeNode* curNode = nodeStack.top();nodeStack.pop();if(curNode == nullptr)continue;nodeStack.push(curNode->left);nodeStack.push(curNode->right);swap(curNode->left, curNode->right);}return root;}
};
题目2 101. 对称二叉树
给你一个二叉树的根节点 root , 检查它是否轴对称。
示例 1:
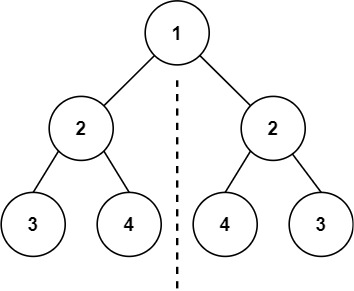
输入:root = [1,2,2,3,4,4,3]
输出:true
示例 2:
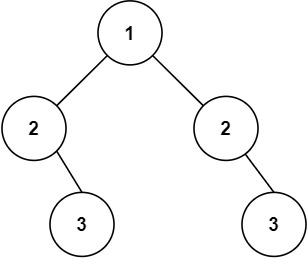
输入:root = [1,2,2,null,3,null,3]
输出:false
提示:
- 树中节点数目在范围
[1, 1000]内 -100 <= Node.val <= 100
思路
这道题就是将树拆分为左右两个子树,对子树进行相反方向的遍历比较就行了,可以使用递归法和迭代法,思路是类似的我用的是迭代法。
迭代法
class Solution {
public:bool isSymmetric(TreeNode* root) {if(!root->left && !root->right)return true;stack<TreeNode*> nodeStack1, nodeStack2;nodeStack1.push(root->left);nodeStack2.push(root->right);while(!nodeStack1.empty() && !nodeStack2.empty()){TreeNode* lft = nodeStack1.top(),* rht = nodeStack2.top();nodeStack1.pop();nodeStack2.pop();if(!lft && !rht){continue;}if(!lft || !rht || lft->val != rht->val)return false;
#define PUSH(STACK, NODE, POSITION) \STACK.push(NODE->POSITION);PUSH(nodeStack1, lft, left);PUSH(nodeStack1, lft, right);PUSH(nodeStack2, rht, right);PUSH(nodeStack2, rht, left);
#undef PUSH}return nodeStack1.empty() && nodeStack2.empty();}
题目3 104. 二叉树的最大深度
给定一个二叉树 root ,返回其最大深度。
二叉树的 最大深度 是指从根节点到最远叶子节点的最长路径上的节点数。
示例 1:

输入:root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
输出:3
示例 2:
输入:root = [1,null,2]
输出:2
提示:
- 树中节点的数量在
[0, 104]区间内。 -100 <= Node.val <= 100
思路
这道题可以用递归法(前,后序遍历)或者迭代法(层序遍历)来计算出深度,基础题。
递归法
/*** Definition for a binary tree node.* struct TreeNode {* int val;* TreeNode *left;* TreeNode *right;* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}* };*/
class Solution {
public:int Nextdepth(TreeNode* root){if(!root){return 0;}return 1 + max(Nextdepth(root->left), Nextdepth(root->right));}int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {return Nextdepth(root);}
};
迭代法
class Solution {
public:int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {if(!root)return 0;queue<TreeNode*> nodeQueue;nodeQueue.push(root);int depth = 0;while(!nodeQueue.empty()){int num = nodeQueue.size();for(int i = 0; i < num; i++){TreeNode* node = nodeQueue.front();nodeQueue.pop();if(node->left)nodeQueue.push(node->left);if(node->right)nodeQueue.push(node->right);}depth++;}return depth;}
};
题目4 111. 二叉树的最小深度
给定一个二叉树,找出其最小深度。
最小深度是从根节点到最近叶子节点的最短路径上的节点数量。
说明:叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
示例 1:

输入:root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
输出:2
示例 2:
输入:root = [2,null,3,null,4,null,5,null,6]
输出:5
提示:
- 树中节点数的范围在
[0, 105]内 -1000 <= Node.val <= 1000
思路
和最大深度类似考察基本功,用递归法遍历每一个结点获取最小深度之后累加得到结果;或者用层序遍历迭代到最浅的无双child节点终止。
递归法
class Solution {
public:int NextDepth(TreeNode* root){if(!root)return 0;if(!root->left && root->right)return 1 + NextDepth(root->right);if(root->left && !root->right)return 1 + NextDepth(root->left);return 1 + min(NextDepth(root->left), NextDepth(root->right));}int minDepth(TreeNode* root) {if(!root)return 0;return NextDepth(root);}
};
迭代法
class Solution {
public:int minDepth(TreeNode* root) {if(!root)return 0;queue<TreeNode*> nodeQueue;nodeQueue.push(root);int result = 0;while(!nodeQueue.empty()){int num = nodeQueue.size();for(int i = 0; i < num; i++){TreeNode* curNode = nodeQueue.front();nodeQueue.pop();//若节点无左右child,则为最浅的节点,返回最小深度if(!curNode->left && !curNode->right){return result + 1;}if(curNode->left)nodeQueue.push(curNode->left);if(curNode->right)nodeQueue.push(curNode->right);}result++;}return result;}
};