4. QFileInfo
4.1 简介
QFileInfo类提供与系统无关的文件信息,QFileInfo提供了关于文件的名称和在文件系统中的位置(路径)、它的访问权限以及它是目录还是符号链接等信息。文件的大小和最后修改/读取时间也可用。
4.2 常用方法
bool isDir() const //.如果该对象指向目录或指向目录的符号链接,则返回true;否则返回false。
bool isFile() const //.如果该对象指向文件或指向文件的符号链接,则返回true。如果对象指向的不是文件,比如目录,则返回false。
bool isHidden() const //.如果这是一个“隐藏”文件,则返回true;否则返回false。
bool isSymLink() const //.如果该对象指向符号链接,则返回true;否则返回false。
QString symLinkTarget() const //.返回符号链接指向的文件或目录的绝对路径,如果对象不是符号链接,则返回空字符串。
QString suffix() const //.返回文件的后缀(扩展名)。
QString completeSuffix() const //.返回文件的完整后缀(扩展名)。
QString fileName() const //.返回文件的名称(不包括路径)。
QString baseName() const //.返回文件的基本名称,不包含路径。
QString filePath() const //.返回文件名,包括路径(可以是绝对的或相对的)。
QString absoluteFilePath() const //.返回包含文件名的绝对路径。
QString path() const //.返回文件的路径。这不包括文件名。
qint64 size() const //.以字节为单位返回文件大小。如果文件不存在或无法获取,则返回0。
QDateTime birthTime() const //.返回文件创建/生成的日期和时间。
QDateTime lastModified() const //.返回文件最后修改的日期和本地时间。
示例:
//第一种构造方式
QFile file("./123.txt");
QFileInfo info(file);
//第二种构造方式
QFileInfo info("../QFile-test/what.txt");qDebug() << info.size(); //文件大小
qDebug() << info.absoluteFilePath(); //文件绝对路径(包括文件名)
qDebug() << info.absolutePath(); //绝对路径(不包括文件名)
qDebug() << info.absoluteDir(); //绝对路径 QDir
qDebug() << info.path(); //文件路径
qDebug() << info.filePath(); //返回文件名,包括路径(可以是绝对路径也可以是相对路径)。
qDebug() << info.fileName(); //带后缀的文件名
qDebug() << info.baseName(); //不带后缀的文件名
qDebug() << info.suffix(); //获取文件后缀
5. QDir
5.1 简介
QDir类提供对目录结构及其内容的访问。
QDir用于操作路径名、访问有关路径和文件的信息以及操作底层文件系统。它也可以用来访问Qt的资源系统。
Qt使用“/”作为通用目录分隔符,就像在url中使用“/”作为路径分隔符一样。如果您总是使用“/”作为目录分隔符,Qt将转换您的路径以符合底层操作系统。
QDir可以使用相对路径或绝对路径指向文件。绝对路径以目录分隔符开始(在Windows下,可以在前面加上驱动器规范)。相对文件名以目录名或文件名开头,并指定相对于当前目录的路径。
5.2 QDir功能
(1)、目录分隔符统一使用’/’
(2)、能够对目录进行任意操作(创建、删除、重命名)
bool mkdir(const QString &dirName) const
bool mkpath(const QString &dirPath) const
bool rmdir(const QString &dirName) const //删除子目录(必须为空才能删除)
bool rmpath(const QString &dirPath) const //删除路径(必须为空才能删除)
bool remove(const QString &fileName) //删除指定文件
bool removeRecursively() //删除目录,包括它的所有内容
bool rename(const QString &oldName, const QString &newName) //重命名(3)、能够获取指定目录中的所有条目(文件和文件夹)
QFileInfoList entryInfoList(const QStringList &nameFilters, QDir::Filters filters = NoFilter, QDir::SortFlags sort = NoSort) const
QFileInfoList entryInfoList(QDir::Filters filters = NoFilter, QDir::SortFlags sort = NoSort) const
QStringList entryList(const QStringList &nameFilters, QDir::Filters filters = NoFilter, QDir::SortFlags sort = NoSort) const
QStringList entryList(QDir::Filters filters = NoFilter, QDir::SortFlags sort = NoSort) const(4)、获取常用路径
//返回应用程序当前目录的绝对路径
QDir current()
QString currentPath()
//返回用户主目录 C:/Users/Maye
QDir home()
QString homePath()//返回系统的临时目录。
QDir temp()
QString tempPath()
//返回根目录列表 C:/ D:/ ...
QFileInfoList drives()(5)、计算目录的大小
quint32 dirSize(const QString& dirName)
{ QDir dir(dirName); if (!dir.exists()) return ~0; quint32 size = 0; for (QFileInfo& info : dir.entryInfoList(QDir::Filter::NoDotAndDotDot | QDir::Files | QDir::Dirs)) { qDebug() << info.fileName(); if (info.isFile()) { size += info.size(); } else { size += dirSize(info.filePath()); } } return size;
}
6. QFileSystemWatcher
6.1 简介
QFileSystemWatcher类用于提供监视文件和目录修改的接口。
QFileSystemWatcher通过监控指定路径的列表,监视文件系统中文件和目录的变更。
调用addPath()函数可以监控一个特定的文件或目录。如果需要监控多个路径,可以使用addPaths()。通过使用removePath()和removePaths()函数来移除现有路径。
QFileSystemWatcher检查添加到它的每个路径,已添加到QFileSystemWatcher的文件可以使用的files()函数进行访问,目录则使用directories()函数进行访问。
当一个文件被修改、重命名或从磁盘上删除时,会发出fileChanged()信号。同样,当一个目录或它的内容被修改或删除时,会发射directoryChanged()信号。需要注意:文件一旦被重命名或从硬盘删除,目录一旦从磁盘上删除,QFileSystemWatcher将停止监控。
注:监控文件和目录进行修改的行为会消耗系统资源。这意味着,你的进程同时监控会有文件数量的限制。一些系统限制打开的文件描述符的数量默认为256。也就是说,如果你的进程试使用addPath()和addPaths()函数添加超过256个文件或目录到文件系统将会失败。
6.2 公有函数
-
构造函数
QFileSystemWatcher(const QStringList &paths, QObject *parent = nullptr)
QFileSystemWatcher(QObject *parent = nullptr)-
添加目录或文件
bool addPath(const QString &path)
QStringList addPaths(const QStringList &paths)-
获取在监控的目录或文件
QStringList directories() const
QStringList files() const-
从监控中移除目录或文件
bool removePath(const QString &path)
QStringList removePaths(const QStringList &paths)6.3 信号
-
目录或文件发生改变
void directoryChanged(const QString &path)
void fileChanged(const QString &path)
示例:
来实现一个文件/目录监控类型。
#include <QCoreApplication>
#include <QFileSystemWatcher>
#include <QDir>
#include <QFileInfo>
#include <QMap>
#include <QDebug>
class FileWatcher : public QObject
{ Q_OBJECT
public: FileWatcher():mFileWatcher(new QFileSystemWatcher(this)) { connect(mFileWatcher, &QFileSystemWatcher::directoryChanged, this, &FileWatcher::onDirChanged); connect(mFileWatcher, &QFileSystemWatcher::fileChanged, this, &FileWatcher::onFileChanged); }; void addWatcherPath(const QString&path) { //把每个目录和文件都添加监视 mFileWatcher->addPath(path); //如果监视的是目录,则把目录中的项保存起来 if(QFileInfo(path).isDir()) mCurContentsMap.insert(path,QDir(path).entryList(QDir::Filter::NoDotAndDotDot | QDir::Dirs | QDir::Files));
//遍历子项 QDir dir(path); for(QString ph : dir.entryList(QDir::Filter::NoDotAndDotDot | QDir::Dirs | QDir::Files)) { if(QFileInfo(ph).isFile()) { mFileWatcher->addPath(ph); } else //目录 { addWatcherPath(ph); } } }
public slots: void onDirChanged(const QString& path) { qDebug() << path << "dirChanged"<<mFileWatcher->directories(); //获取目录下所有项列表 auto curEntryList = QDir(path).entryList(QDir::Filter::NoDotAndDotDot | QDir::Dirs | QDir::Files);
//获取目录下原来项的列表 auto oldEntryList = mCurContentsMap[path];
//qDebug()<<"curEntryList"<<curEntryList; //qDebug()<<"oldEntryList"<<oldEntryList;
//把curEntryList和oldEntryList转成集合set QSet<QString> curDirSet(curEntryList.begin(),curEntryList.end()); QSet<QString> oldDirSet(oldEntryList.begin(),oldEntryList.end());
//更新设置 mCurContentsMap[path] = curEntryList;
//判断是否修改了文件:如果新老集合大小相等,说明只是文件名改变了 if(curDirSet.size() == oldDirSet.size()) { auto modifyDir = curDirSet - oldDirSet; if(!modifyDir.isEmpty()) { //对修改的文件进行操作 qDebug()<<"修改"<<modifyDir; } } //判断是否添加了文件 else if(curDirSet.size() > oldDirSet.size()) { auto addDir = curDirSet - oldDirSet; if(!addDir.isEmpty()) { //对添加的文件进行操作 qDebug()<<"添加"<<addDir; }
} //判断是否删除了文件 else if(curDirSet.size() < oldDirSet.size()) { auto delDir = curDirSet - oldDirSet; if(!delDir.isEmpty()) { //对删除的文件进行操作 qDebug()<<"删除"<<delDir; } } } void onFileChanged(const QString& file) { qDebug() << file << "fileChanged";
QFileInfo info(file); QString strPath = info.absolutePath(); QString strName = info.fileName();
qDebug() << QString("The file %1 at path %2 is updated").arg(strName).arg(strPath); }
private: QFileSystemWatcher *mFileWatcher; QMap<QString,QStringList> mCurContentsMap; //每个监控路径对应的列表
};
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{ QCoreApplication a(argc, argv);
FileWatcher watcher; watcher.addWatcherPath("./");
return a.exec();
}
#include"main.moc"
7. QStandardPaths
7.1 简介
QStandardPaths类提供了访问标准路径的方法。 所谓系统标准路径指的是本地文件系统中,用户的特定目录或系统的配置目录。比如在Windows系统中的“我的文档”,“视频”,“图片”等目录位置。
对于一个大型项目,系统的标准目录是保存数据,配置信息的一个非常有用的地方。例如,一个应用程序需要将下载好的文档保存在本地文件系统的某个地方,而它不能假设某个定好的路径是存在于磁盘上的。有的人可能会将这个文档保存在应用程序所在的工作目录中,当然这是个好方法,但有时应用程序并不希望将数据放在工作目录中,这是因为:
-
这会使得程序工作目录变得复杂,让用户来干预工作目录,这无疑是一件危险的事情,很可能会破坏程序。
-
有的程序会希望工作目录是只读的,所以禁止其它用户来对其进行修改。
-
如果某些配置文件是和其它程序是共享的,如若放置这些文件在某个程序的工作目录中,显然是不明智的做法,而最好的做法就是放在这些标准目录中啦。
对于系统标准目录,我们可以认定它是必然存在的(即使不存在,也可自动创建),但是不同的操作系统,可能有不一样的系统标准目录。例如“我的文档”目录位置
-
Windows:C:/Users/$username$/Documents
-
MacOs :~/Documents
-
Linux : ~/Documents
-
Android :/Documents,//Documents
-
IOS :/Documents
如果想要做跨平台的系统,像这些路径,你都得想办法获取,这只是一个我的文档,如果再加上“下载”,“图片”等标准路径,想想是不是都很麻烦。
然而,Qt却给我们提供了非常方便的类来获取这些标准目录路径,它就是马上要学习的QStandardPaths类。所有函数均为静态函数。
7.2 静态公有函数
(1) 返回给定位置类型的本地化显示名称,如果找不到相关位置,则返回空QString。
参数列表中StandardLocation type是一个枚举类型下面会解释所有类型
[static] QString displayName(QStandardPaths::StandardLocation type)
(2) 在指定路径中查找名为executableName的可执行文件,如果路径为空则查找系统路径。
[static] QString findExecutable(const QString &executableName, const QStringList &paths = QStringList())
(3) 在type的标准位置中查找名为fileName的文件或目录。
[static] QString locate(QStandardPaths::StandardLocation type, const QString &fileName, QStandardPaths::LocateOptions options = LocateFile)
(4) 根据文件名fileName在type的标准位置查找所有文件或目录。
[static] QStringList locateAll(QStandardPaths::StandardLocation type, const QString &fileName, QStandardPaths::LocateOptions options = LocateFile)
(5) 如果testMode为true,这将在QStandardPaths中启用一个特殊的“测试模式”,它将更改可写的位置以指向测试目录。 这将阻止自动测试读取或写入当前用户的配置。
[static] void setTestModeEnabled(bool testMode)
(6) 返回该类型文件所属的所有目录。
[static] QStringList standardLocations(QStandardPaths::StandardLocation type)
(7) 返回写入类型为文件的目录,如果无法确定位置,则返回空字符串。
[static] QString writableLocation(QStandardPaths::StandardLocation type)
7.3 enum QStandardPaths::StandardLocation
|
枚举常量 |
值 |
描述 |
|
QStandardPaths::DesktopLocation |
0 | 返回用户的桌面目录。这是一个泛型值。在没有桌面概念的系统上。 |
|
QStandardPaths::DocumentsLocation |
1 | 返回包含用户文档文件的目录。这是一个泛型值。返回的路径从来不是空的。 |
|
QStandardPaths::FontsLocation |
2 | 返回包含用户字体的目录。这是一个泛型值。注意,安装字体可能需要额外的、特定于平台的操作。 |
|
QStandardPaths::ApplicationsLocation |
3 | 返回包含用户应用程序(可执行程序、应用程序包或它们的快捷方式)的目录。这是一个泛型值。注意,安装应用程序可能需要额外的、特定于平台的操作。该目录中的文件、文件夹或快捷方式是特定于平台的。 |
|
QStandardPaths::MusicLocation |
4 | 返回包含用户音乐或其他音频文件的目录。这是一个泛型值。如果不存在专门用于音乐文件的目录,则返回一个用于存储用户文档的合理后备方案。 |
|
QStandardPaths::MoviesLocation |
5 | 返回包含用户电影和视频的目录。这是一个泛型值。如果不存在特定于电影文件的目录,则返回用于存储用户文档的合理的备用方案。 |
|
QStandardPaths::PicturesLocation |
6 | 返回包含用户图片或照片的目录。这是一个泛型值。如果没有特定的目录对于已经存在的图片文件,将返回存储用户文档的合理退步。 |
|
QStandardPaths::TempLocation |
7 | 返回可以存储临时文件的目录。返回值可能是特定于应用程序的,在此用户的其他应用程序之间共享,甚至在系统范围内共享。返回的路径从来不是空的。 |
|
QStandardPaths::HomeLocation |
8 | 返回用户的主目录(与QDir::homePath()相同)。在Unix系统上,这等于HOME环境变量。这个值可以是通用的,也可以是特定于应用程序的,但是返回的路径从来不是空的。 |
|
QStandardPaths::DataLocation |
9 | 返回与AppLocalDataLocation相同的值。此枚举值已弃用。使用AppDataLocation更可取,因为在Windows上,推荐使用漫游路径。 |
|
QStandardPaths::CacheLocation |
10 | 返回应该写入用户特定的非必要(缓存)数据的目录位置。这是一个特定于应用程序的目录。返回的路径从来不是空的。 |
|
QStandardPaths::GenericCacheLocation |
15 | 返回应写入跨应用程序共享的特定于用户的非必要(缓存)数据的目录位置。这是一个泛型值。注意,如果系统没有共享缓存的概念,则返回的路径可能为空。 |
|
QStandardPaths::GenericDataLocation |
11 | 返回可存储跨应用程序共享的持久数据的目录位置。这是一个泛型值。返回的路径从来不是空的。 |
|
QStandardPaths::RuntimeLocation |
12 | 返回应该写入运行时通信文件的目录位置,如Unix本地套接字。这是一个泛型值。在某些系统上,返回的路径可能为空。 |
|
QStandardPaths::ConfigLocation |
13 | 返回应该写入用户特定配置文件的目录位置。这可能是一个通用值或特定于应用程序的值,并且返回的路径永远不会为空。 |
|
QStandardPaths::DownloadLocation |
14 | 返回用户下载文件的目录。这是一个泛型值。如果不存在专门用于下载的目录,则返回用于存储用户文档的合理后备方案。 |
|
QStandardPaths::GenericConfigLocation |
16 | 返回应该写入多个应用程序之间共享的用户特定配置文件的目录位置。这是一个泛型值,返回的路径从不为空。 |
|
QStandardPaths::AppDataLocation |
17 | 返回可存储持久应用程序数据的目录位置。这是一个特定于应用程序的目录。要获取存储要与其他应用程序共享的数据的路径,请使用QStandardPaths::GenericDataLocation。返回的路径从来不是空的。在Windows操作系统上,这将返回漫游路径。这个enum值是在Qt 5.4中添加的。 |
|
QStandardPaths::AppLocalDataLocation |
DataLocation |
返回Windows操作系统的本地设置路径。在所有其他平台上,它返回与AppDataLocation相同的值。这个enum值是在Qt 5.4中添加的。 |
|
QStandardPaths::AppConfigLocation |
18 | 返回应该写入用户特定配置文件的目录位置。这是一个特定于应用程序的目录,返回的路径永远不会为空。这个enum值是在Qt 5.5中添加的。 |
7.4 使用方法
- displayName
qDebug() << "DesktopLocation: " << QStandardPaths::displayName(QStandardPaths::DesktopLocation);
qDebug() << "DocumentsLocation: " << QStandardPaths::displayName(QStandardPaths::DocumentsLocation);
qDebug() << "FontsLocation: " << QStandardPaths::displayName(QStandardPaths::FontsLocation);
qDebug() << "ApplicationsLocation: " << QStandardPaths::displayName(QStandardPaths::ApplicationsLocation);
qDebug() << "MusicLocation: " << QStandardPaths::displayName(QStandardPaths::MusicLocation);
qDebug() << "MoviesLocation: " << QStandardPaths::displayName(QStandardPaths::MoviesLocation);
qDebug() << "PicturesLocation: " << QStandardPaths::displayName(QStandardPaths::PicturesLocation);
qDebug() << "TempLocation: " << QStandardPaths::displayName(QStandardPaths::TempLocation);
qDebug() << "HomeLocation: " << QStandardPaths::displayName(QStandardPaths::HomeLocation);
qDebug() << "DataLocation: " << QStandardPaths::displayName(QStandardPaths::DataLocation);
qDebug() << "CacheLocation: " << QStandardPaths::displayName(QStandardPaths::CacheLocation);
qDebug() << "GenericCacheLocation: " << QStandardPaths::displayName(QStandardPaths::GenericCacheLocation);
qDebug() << "GenericDataLocation: " << QStandardPaths::displayName(QStandardPaths::GenericDataLocation);
qDebug() << "RuntimeLocation: " << QStandardPaths::displayName(QStandardPaths::RuntimeLocation);
qDebug() << "ConfigLocation: " << QStandardPaths::displayName(QStandardPaths::ConfigLocation);
qDebug() << "DownloadLocation: " << QStandardPaths::displayName(QStandardPaths::DownloadLocation);
qDebug() << "GenericConfigLocation: " << QStandardPaths::displayName(QStandardPaths::GenericConfigLocation);
qDebug() << "AppDataLocation: " << QStandardPaths::displayName(QStandardPaths::AppDataLocation);
qDebug() << "AppLocalDataLocation: " << QStandardPaths::displayName(QStandardPaths::AppLocalDataLocation);
qDebug() << "AppConfigLocation: " << QStandardPaths::displayName(QStandardPaths::AppConfigLocation);运行结果:

- writableLocation
qDebug() << "DesktopLocation: " << QStandardPaths::writableLocation(QStandardPaths::DesktopLocation);
qDebug() << "DocumentsLocation: " << QStandardPaths::writableLocation(QStandardPaths::DocumentsLocation);
qDebug() << "FontsLocation: " << QStandardPaths::writableLocation(QStandardPaths::FontsLocation);
qDebug() << "ApplicationsLocation: " << QStandardPaths::writableLocation(QStandardPaths::ApplicationsLocation);
qDebug() << "MusicLocation: " << QStandardPaths::writableLocation(QStandardPaths::MusicLocation);
qDebug() << "MoviesLocation: " << QStandardPaths::writableLocation(QStandardPaths::MoviesLocation);
qDebug() << "PicturesLocation: " << QStandardPaths::writableLocation(QStandardPaths::PicturesLocation);
qDebug() << "TempLocation: " << QStandardPaths::writableLocation(QStandardPaths::TempLocation);
qDebug() << "HomeLocation: " << QStandardPaths::writableLocation(QStandardPaths::HomeLocation);
qDebug() << "DataLocation: " << QStandardPaths::writableLocation(QStandardPaths::DataLocation);
qDebug() << "CacheLocation: " << QStandardPaths::writableLocation(QStandardPaths::CacheLocation);
qDebug() << "GenericCacheLocation: " << QStandardPaths::writableLocation(QStandardPaths::GenericCacheLocation);
qDebug() << "GenericDataLocation: " << QStandardPaths::writableLocation(QStandardPaths::GenericDataLocation);
qDebug() << "RuntimeLocation: " << QStandardPaths::writableLocation(QStandardPaths::RuntimeLocation);
qDebug() << "ConfigLocation: " << QStandardPaths::writableLocation(QStandardPaths::ConfigLocation);
qDebug() << "DownloadLocation: " << QStandardPaths::writableLocation(QStandardPaths::DownloadLocation);
qDebug() << "GenericConfigLocation: " << QStandardPaths::writableLocation(QStandardPaths::GenericConfigLocation);
qDebug() << "AppDataLocation: " << QStandardPaths::writableLocation(QStandardPaths::AppDataLocation);
qDebug() << "AppLocalDataLocation: " << QStandardPaths::writableLocation(QStandardPaths::AppLocalDataLocation);
qDebug() << "AppConfigLocation: " << QStandardPaths::writableLocation(QStandardPaths::AppConfigLocation);运行结果:
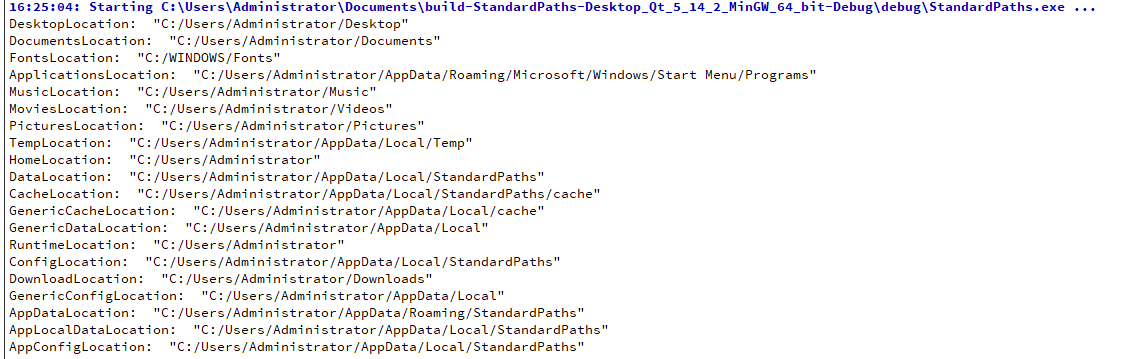
- standardLocations(推荐使用)
qDebug() << "DesktopLocation: " << QStandardPaths::standardLocations(QStandardPaths::DesktopLocation);
qDebug() << "DocumentsLocation: " << QStandardPaths::standardLocations(QStandardPaths::DocumentsLocation);
qDebug() << "FontsLocation: " << QStandardPaths::standardLocations(QStandardPaths::FontsLocation);
qDebug() << "ApplicationsLocation: " << QStandardPaths::standardLocations(QStandardPaths::ApplicationsLocation);
qDebug() << "MusicLocation: " << QStandardPaths::standardLocations(QStandardPaths::MusicLocation);
qDebug() << "MoviesLocation: " << QStandardPaths::standardLocations(QStandardPaths::MoviesLocation);
qDebug() << "PicturesLocation: " << QStandardPaths::standardLocations(QStandardPaths::PicturesLocation);
qDebug() << "TempLocation: " << QStandardPaths::standardLocations(QStandardPaths::TempLocation);
qDebug() << "HomeLocation: " << QStandardPaths::standardLocations(QStandardPaths::HomeLocation);
qDebug() << "DataLocation: " << QStandardPaths::standardLocations(QStandardPaths::DataLocation);
qDebug() << "CacheLocation: " << QStandardPaths::standardLocations(QStandardPaths::CacheLocation);
qDebug() << "GenericCacheLocation: " << QStandardPaths::standardLocations(QStandardPaths::GenericCacheLocation);
qDebug() << "GenericDataLocation: " << QStandardPaths::standardLocations(QStandardPaths::GenericDataLocation);
qDebug() << "RuntimeLocation: " << QStandardPaths::standardLocations(QStandardPaths::RuntimeLocation);
qDebug() << "ConfigLocation: " << QStandardPaths::standardLocations(QStandardPaths::ConfigLocation);
qDebug() << "DownloadLocation: " << QStandardPaths::standardLocations(QStandardPaths::DownloadLocation);
qDebug() << "GenericConfigLocation: " << QStandardPaths::standardLocations(QStandardPaths::GenericConfigLocation);
qDebug() << "AppDataLocation: " << QStandardPaths::standardLocations(QStandardPaths::AppDataLocation);
qDebug() << "AppLocalDataLocation: " << QStandardPaths::standardLocations(QStandardPaths::AppLocalDataLocation);
qDebug() << "AppConfigLocation: " << QStandardPaths::standardLocations(QStandardPaths::AppConfigLocation);运行结果:
7.5 在指定位置查找文件
- 在指定的路径中查找名为executableName的可执行文件,如果paths为空,则在系统路径中查找。 系统路径指PATH环境变量的值。 如果存在,返回可执行文件的绝对文件路径,如果没有找到,则返回空字符串。
- QString findExecutable(const QString &executableName, const QStringList &paths = QStringList())的使用
qDebug()<<QStandardPaths::findExecutable("calc.exe"); //只要设置了path环境变量,都可以找到
qDebug()<<QStandardPaths::findExecutable("7z.exe",QStringList()<<"D:\\MySoftWare\\7-Zip"); //如果没有设置path环境变量,可以自己指定多个路径
- 根据标准目录类型,在该目录中查找名为fileName的文件或目录。 返回找到的文件或目录的完整路径(取决于options)。 如果找不到这样的文件或目录,则返回一个空字符串
- QString locate(QStandardPaths::StandardLocation type, const QString &fileName, QStandardPaths::LocateOptions options = LocateFile)的使用
QStringList locateAll(QStandardPaths::StandardLocation type, const QString &fileName, QStandardPaths::LocateOptions options = LocateFile)
qDebug()<< QStandardPaths::locate(QStandardPaths::StandardLocation::DownloadLocation,"下拉.png");
8. QSettings
8.1 简介
用户通常希望应用程序在会话中记住它的设置(窗口大小和位置,选项等)。 这些信息通常存储在Windows上的系统注册表中(HKEY_CURRENT_USERSoftware/MySoft ),以及macOS和iOS上的属性列表文件中。 在Unix系统上,在缺乏标准的情况下,许多应用程序(包括KDE应用程序)使用INI文本文件。
QSettings是对这些技术的抽象,使您能够以可移植的方式保存和恢复应用程序设置。 它还支持自定义存储格式。
QSettings的API基于QVariant,因此我们可以保存很多的类型,如QString、QRect和QImage。
如果您所需要的只是一个非持久的基于内存的结构,那么可以考虑使用QMap<QString,QVariant>替代。
8.2 基本用法
创建QSettings对象时,必须传递公司或组织的名称以及应用程序的名称。 例如,如果你的程序名为QQ,而你的公司名为NiuBi,你将构造QSettings对象如下:
QSettings setting("NiuBi","QQ");QSettings对象既可以在堆栈上创建,也可以在堆上创建(即使用new)。 构造和销毁QSettings对象非常快。
如果你在应用程序的很多地方使用QSettings,你可能想要使用QCoreApplication::setOrganizationName()和QCoreApplication::setApplicationName()指定组织名称和应用程序名称,然后使用默认的QSettings构造函数:
QCoreApplication::setOrganizationName("NiuBi");
QCoreApplication::setOrganizationDomain("NiuBi.com");
QCoreApplication::setApplicationName("QQ");
...
QSettings settings;QSettings存储设置。 每个设置由一对(key,value)键值对(key为QStirng类型,value为QVariant)组成。 要写入设置,可以使用setValue()。 例如:
setting.setValue("size",QSize(640,480));
qDebug()<< setting.fileName(); //获取配置文件保存位置如果已经存在具有相同键的设置,则现有值将被新值覆盖。 为了提高效率,更改可能不会立即保存到永久存储中。 (可以调用sync()来立即提交更改。)
你可以使用value()获取设置的值:
QSize size = setting.value("size",QSize(250,250)).value<QSize>();如果没有指定名称的设置,QSettings返回一个空的QVariant(无效的)。你可以通过传递第二个参数给value()来指定另一个默认值(这里传了QSize(250,250),如果配置文件中没有size,就返回自己传的这个数据)。
配置文件格式
在windows下,默认为写入注册表,如果想要写入到.ini文件并保存到exe所在目录,该怎么设置呢?
QApplication::setOrganizationName("NiuBi");
QApplication::setApplicationName("QQ");
QSettings setting(QApplication::applicationDirPath()+"/qfile.ini" ,QSettings::Format::IniFormat);
8.3 公有函数
常用函数
-
设置将key设置为value的值。 如果键已经存在,则覆盖前面的值。
void setValue(const QString &key, const QVariant &value)-
返回设置键的值。 如果该设置不存在,则返回defaultValue。
如果没有指定默认值,则返回一个默认的QVariant。
QVariant QSettings::value(const QString &key, const QVariant &defaultValue = QVariant()) const-
将任何未保存的更改写入永久存储,并重新加载与此同时被另一个应用程序更改的任何设置。
这个函数会定期从QSettings的析构函数和事件循环中自动调用,所以您通常不需要自己调用它。
void QSettings::sync()-
返回一个状态码,指示QSettings遇到的第一个错误,如果没有错误发生,则返回QSettings::NoError。
QSettings::Status status() const-
删除设置键和键的任何子设置。
void remove(const QString &key)-
返回使用该QSettings对象写入的设置存储的路径。
在Windows上,如果格式为QSettings::NativeFormat,则返回值为系统注册表路径,而不是文件路径。
QString QSettings::fileName() const分组函数
-
向当前组添加前缀。
void beginGroup(const QString &prefix)void endGroup()-
返回当前组。
QString QSettings::group() const-
向当前组添加前缀并开始从数组读取。 返回数组的大小。[有案例]
int beginReadArray(const QString &prefix)-
向当前组添加前缀,并开始写入大小为size的数组。 如果size为-1(默认值),则根据写入的条目的索引自动确定size。 [有案例]
void beginWriteArray(const QString &prefix, int size = -1)-
关闭数组
void endArray()-
将当前数组的索引设置为i。调用setValue()、value()、remove()和contains()等函数将对该索引处的数组项进行操作。
void setArrayIndex(int i)8.4 操作ini文件
#include "widget.h"#include <QApplication>
#include <QSettings>
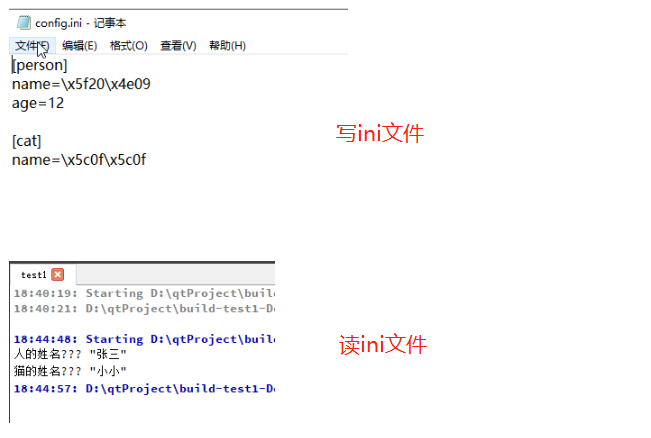
#include <QDebug>// 写ini配置文件
void setIni()
{QSettings * myini = new QSettings("config.ini", QSettings::IniFormat);myini->setValue("person/name", "张三");myini->setValue("person/age", "12");myini->setValue("cat/name", "小小");delete myini;
}// 读ini配置文件
void getIni()
{QSettings * myini = new QSettings("config.ini", QSettings::IniFormat);QString personName = myini->value("person/name").toString();QString catName = myini->value("cat/name").toString();delete myini;qDebug() << "人的姓名: " << personName ;qDebug() << "猫的姓名: " << catName ;
}int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{QApplication a(argc, argv);Widget w;w.show();// 写配置文件setIni();// 读配置文件getIni();return a.exec();
}
8.5 操作注册表
(1)写入注册表
#include <QSettings>void Widget::writeKey()
{//实例 QSettings//参数 1:注册表位置//参数 2:操作 windows 注册表 QSettings::NativeFormat//说明:QSettings::IniFormat 读写 ini 格式的配置文件,前面用过。QSettings *reg = new QSettings("HKEY_CURRENT_USER\\Software\\Qt01", QSettings::NativeFormat);//设定值有修改,没有创建。reg->setValue("键名 001","值 001");reg->setValue("键名 002",true);//用完删除 QSettingsdelete reg;
}
(2)读取注册表
#include <QSettings>
#include <QLabel>void Widget::readKey()
{//输出键值QLabel *label = new QLabel(this);label->setGeometry(QRect(50,50,200,25));QLabel *label2 = new QLabel(this);label2->setGeometry(QRect(50,80,200,25));//实例 QSettings//参数 1:如果没有按照章节 Qt01 进行,则注册表中没有 Qt01。QSettings *reg = new QSettings("HKEY_CURRENT_USER\\Software\\Qt01", QSettings::NativeFormat);QString ret = reg->value("键名 001").toString();//判断 value 是否为空,不为空则输出if(!ret.isEmpty()){label->setText("键名 001::"+reg->value("键名 001").toString());label2->setText("键名 002::"+reg->value("键名 002").toString());}else{qDebug()<<"键名 001 值为空!";}//删除 QSettingsdelete reg;
}运行结果:
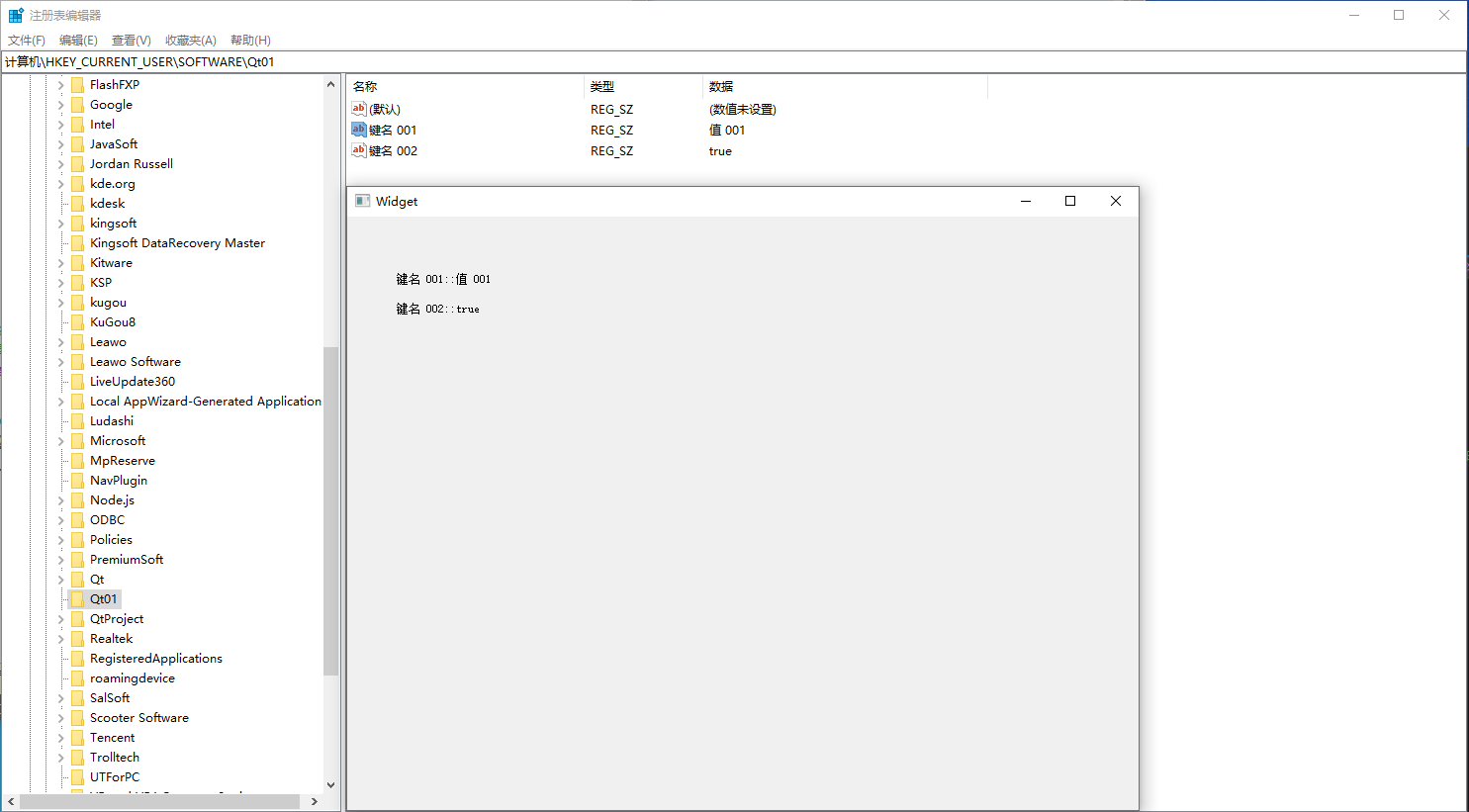
(3)修改IE浏览器默认主页
#include <QSettings>//实例 QSettings
QSettings *reg = new
QSettings("HKEY_CURRENT_USER\\Software\\Microsoft\\Internet Explorer\\Main", QSettings::NativeFormat);//判断 value 是否为空,不为空则输出
if(reg->value("Start Page") != "")
{//IE 默认主页修改为:百度首页reg->setValue("Start Page","http://www.baidu.com");
}//删除 QSettings
delete reg;

![[clickhouse] Clickhouse 关键特性的版本支持与演变](https://blog-static.cnblogs.com/files/johnnyzen/cnblogs-qq-group-qrcode.gif?t=1679679148)