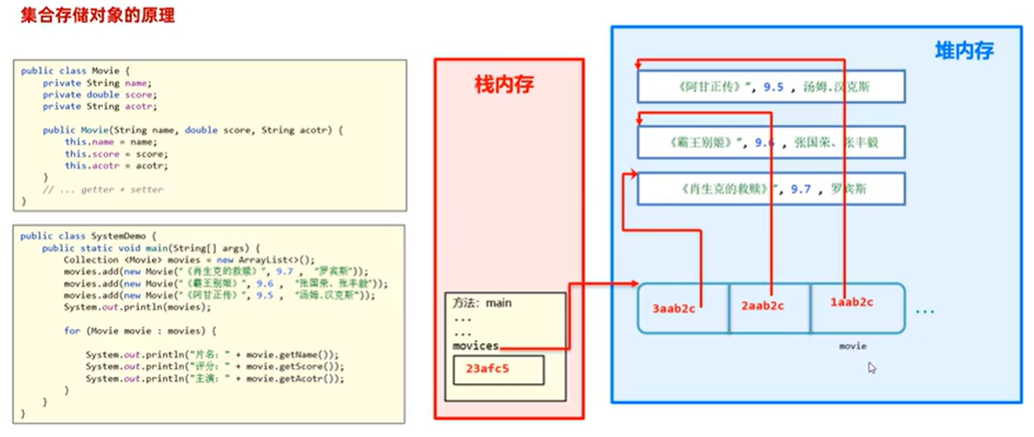
C#实战
ArrayList
using System;
using System.Collections;
using System.Security.Principal;
namespace ArrayList数组;
class Program
{static void Main(string[] args){#region 本质/* ArrayList是一个C#封装好的类本质是一个object类型的数组ArrayList,*/#endregion#region 声明//需要引用 命名空间using System.Collections;ArrayList array = new ArrayList();#endregion#region 增删查改array.Add(1);array.Add("");array.Add(true);int v = array.Add(new object());array.Add(new Test());// 把另一个容器增加到另一个容器array.AddRange(array);//删//指定元素array.Remove(1);//指定位置array.RemoveAt(0);array.RemoveAt(1);//清空//array.Clear();// 查Console.WriteLine(array[0]);//查看元素是否存在if (array.Contains("1")){}// 正向查找元素位置//找到返回值int index = array.IndexOf("1");Console.WriteLine(index);// 反向查找元素//int index2 = array.IndexOf(true);index = array.LastIndexOf(true);Console.WriteLine(index);// 改Console.WriteLine(array[0]);array[0] = "1"; Console.WriteLine(array[0]);#endregion#region 遍历//长度Console.WriteLine(array.Count);// 避免产生过多垃圾Console.WriteLine(array.Capacity);for (int i = 0; i < array.Count; i++){Console.WriteLine(array[i]);}foreach (var item in array){Console.WriteLine(item);}#endregion#region 装箱拆箱// ArrayList本质上可以自动扩容object数组int i2 = 1;array[0] = i2;// 装箱i2 = (int)array[0];Console.WriteLine(i2);#endregion}
}
Stack
using System;
using System.Collections;
namespace bascicprograme;class Test { }
class Program
{static void Main(string[] args){#region stack本质//stack是一个C#封装好的类/* 它的本质是object数组,只是封装了特殊的存储规则Stack是栈存储容器,栈是一种先进后出的数据结构先存入的数据后取出,后存入的数据先取出*/#endregion#region 声明Stack values = new Stack();#endregion#region 增取改查//压栈values.Push(1);values.Push(true);values.Push("1111");values.Push(new Test());#endregion#region 取//栈中不存在删除的概念//弹栈object v = values.Pop();Console.WriteLine(v);#endregion#region 查//1、栈无法查看指定位置元素//只能查看栈顶内容//2、查看元素是否存在于栈中v = values.Peek();Console.WriteLine(v);#endregion#region 改//栈无法改变其中的元素,只能压和弹//只能清空//values.Clear();#endregion#region 遍历Console.WriteLine(values.Count);//foreach遍历foreach (object item in values){ Console.WriteLine(item);}//另一种遍历方式//将栈转换为object数组//遍历出来顺序也是从栈顶到栈底object[] arr = values.ToArray();for (int i = 0; i < arr.Length; i++){Console.WriteLine(arr[i]);}// 循环弹栈while (values.Count>0){ object o = values.Pop();Console.WriteLine(o);}Console.WriteLine(values.Count);#endregion}}
Queue
using System;
using System.Collections;
namespace 队列;
class Test {}
class Program
{static void Main(string[] args){#region 队列本质/*queen是一个封装好的本质也是object数组只是封装了特殊的规则queue是对类存储容器队列是一种新进先出的数据结构先存入的数据先获取后存入的后获取*/#endregion#region 声明Queue queue = new Queue();#endregion#region 增取查改// 增queue.Enqueue(1);queue.Enqueue("2");queue.Enqueue(true);// 取object o = queue.Dequeue();Console.WriteLine(o);Console.WriteLine(queue.Dequeue());// 查// 查看头部元素但不会移除o = queue.Peek();Console.WriteLine(o);// 查看元素是否存在队列中if (queue.Contains("3")){Console.WriteLine("不存在");}// 改//只能清空,改不了//queue.Clear();queue.Enqueue(1);// 遍历//foreach (var item in queue){Console.WriteLine(item);}object[] arr = queue.ToArray();for (int i = 0; i < arr.Length; i++){Console.WriteLine(arr[i]);}// 循环出列while (queue.Count>0){o = queue.Dequeue();Console.WriteLine(o);}#endregion}
}
HashTable
using System;
using System.Collections;
namespace 哈希表练习题;//制作一个怪物管理器,提供创建怪物
//移除怪物的方法。每个怪物都有自己的唯一ID/// <summary>
/// 怪物管理器 因为一般 管理器 都是唯一的 所以把它做成 一个单例模式的对象
/// </summary>// 泛型单例
/*public class Singleton<T> where T : class, new()
{// 私有静态实例private static T instance;// 用于线程同步的锁对象private static readonly object lockObject = new object();// 公共的静态属性,用于获取唯一实例public static T Instance{get{// 双重检查锁定,提高性能if (instance == null){lock (lockObject){if (instance == null){instance = new T();}}}return instance;}}
}// 具体的单例类,继承自泛型单例基类
public class MySingleton : Singleton<T>
{// 可以在这里添加MySingleton特有的方法和属性private MySingleton() { }
}*/
class MonsterMgr
{ private static MonsterMgr instance = new MonsterMgr();private Hashtable monstersTable = new Hashtable();private MonsterMgr() { }public static MonsterMgr Instance{ get { return instance; }}private int monsterId = 0;public void AddMonster (){ Monster monster = new Monster(monsterId);Console.WriteLine("创建了{0}的怪物",monsterId);++monsterId;monstersTable.Add(monster.id,monster);}public void RemoveMonster(int monserID){if (monstersTable.ContainsKey(monserID)) {(monstersTable[monserID] as Monster).Dead();monstersTable.Remove(monserID);}}}class Monster
{ public int id;public Monster(int id) { this.id = id;}public void Dead(){Console.WriteLine("怪物{0}死亡",id);}}
class Program
{static void Main(string[] args){MonsterMgr.Instance.AddMonster();MonsterMgr.Instance.AddMonster();MonsterMgr.Instance.AddMonster();MonsterMgr.Instance.AddMonster();MonsterMgr.Instance.AddMonster();MonsterMgr.Instance.RemoveMonster(0);MonsterMgr.Instance.RemoveMonster(1);MonsterMgr.Instance.RemoveMonster(2);}
}
泛型
using System;
using System.Security.Cryptography;
namespace 泛型;
#region 泛型是什么
// 泛型实现了类型参数化,达到代码重用的目的
//通过类型参数化实现同一份代码操作多种类型
// 泛型相当于类型占位符
// 定义类或方法时使用替代付代表变量类型
// 当真正使用类或者方法时再具体指定类型
#endregion
#region 泛型分类
//基本语法
//class 类名<泛型占位字母>// 泛型函数
//基本语法
//函数名 <泛型占位字母>(参数)
#endregionclass TestClass<T> {public T Value;
}class TestClass2<T, A, B, C> { public T Value;public A Value1;public B Value5;public C Value6;};interface IClass<T> {T Value { get; set;}
}
// 继承
class Test : IClass<string>
{public string Value { get; set; }
}// 泛型方法class TestFun { public void Test<T> (T value) { Console.WriteLine (value);}public void Test2<T>(){ T t =default (T);Console.WriteLine (t);}public T Test3<T>(string V) {return default(T);}public void Test<T,K,M>(T t, K k ,M m) { }
}class TestFun<T> {public T Value;// 我们这个不叫泛型方法,T是泛型声明时候就制定在使用这个函数时候就不能再动态的变化了// 没加<>不是泛型public void Test(T t) { }
}// 泛型作用
/*不同类型对象相同逻辑处理就可以选择泛型使用泛型就可以一定程度上避免装箱拆箱*/class ArrayList<T>
{ private T[] array;private void Add(T value) { }private void Clear(){}private void Remove() { }}
class Program
{static void Main(string[] args){TestClass<int> t = new TestClass<int>(); t.Value = 1;Console.WriteLine(t.Value);TestClass<String> testClass = new TestClass<String>();testClass.Value = "555555555";Console.WriteLine(testClass.Value);TestClass2<int, string, float, double> testClass2 = new TestClass2<int, string, float, double>() { }; TestFun fun = new TestFun();fun.Test<string>("123");TestFun<int> fun2 = new TestFun<int>(); fun2.Test(11);}
}
泛型约束
using System;
using static System.Net.Mime.MediaTypeNames;
namespace 泛型的约束;#region 什么是泛型约束
/*让泛型的类型有一定限制关键字where泛型约束一共有六种值类型 where 泛型字母:struct引用类型 where 泛型字母:class存在无参公共构造函数 where 泛型字母:new()某个类本身或者其派生类 where 泛型字母:类名某个接口派生类型 where 泛型字母:接口名另一个泛型类型本身或者派生类型 where 泛型字母:另一个泛型字母
*/
#endregion#region 值类型约束
class Test1<T> where T : struct
{public T Value;public void TestFun<T>(T t) where T : struct { }
}
class Test2<T> where T : class
{public T Value;public void TestFun<T>(T t) where T : class{}
}
#endregion#region 公共无参构造函数
class Test3<T> where T : new()
{public T Value;public void TestFun<T>(T t) where T : new(){}
}#endregion
#region 类约束
class Test4<T> where T : Test1
{public T Value;public void TestFun<T>(T t) where T : Test1{}
}class Test3 : Test1
{ }
#endregion#region 接口约束
interface Ifly { }class Test5 : Ifly { }class Test6<T> where T : Ifly
{public T Value;public void TestFun<T>(T t) where T : Ifly{}
}#endregion
#region 另一个泛型约束
//U是T的派生类
class Test7<T, U> where T : U {public T Value;public void TestFun<T>(T t) where T : U{}}#endregion#region 约束的组合使用
class Test8<T> where T :class,new()
{public T Value;public void TestFun<T>(T t) where T : class, new(){}
}
#endregion#region 多个泛型有约束
class Test9<T,K> where T : class, new() where K : class
{public T Value;public void TestFun<T,K>(T t , K k) where T : class, new() where K : class{}
}
#endregion
class Program
{static void Main(string[] args){Test1<int> t = new Test1<int>();t.TestFun<float>(1.3f);Test2<object> t1 = new Test2<object>();Test2<Random> t2 = new Test2<Random>();t2.Value = new Random();t2.TestFun<object>(new object());Test4<Test3> test4 = new Test4<Test3>();Test4<Test1> test5 = new Test4<Test1>();Test6<Ifly> t5 = new Test6<Ifly>();t5.Value = new Test5();Test7<Test5, Ifly> t7 = new Test7<Test5, Ifly>();}
}List
namespace List链表;
class Program
{static void Main(string[] args){#region List本质//List#封装好的,本质是一个可变类型的泛型数组//List类帮助我们实现很多方法,比如泛型数组的增删改查#endregion#region 声明//需要引用命名空间List<string> list = new List<string>();list.Add("1");list.Add("1");List<int> list2 = new List<int>(); List<int> list3= new List<int>();list2.Add(2);list2.Add(2);list2.Add(2);list.AddRange(list);list2.AddRange(list3);// 删list.Remove("1");list.RemoveAt(0);// 查Console.WriteLine( list[0]);if (list.Contains("1")){Console.WriteLine("存在"); }int index = list.IndexOf("1");Console.WriteLine( index); // 找不到-1// 改Console.WriteLine(list[0]="333");list.Insert(0,"9999");Console.WriteLine(list[0]);// 遍历for (int i = 1; i < list.Count; i++){Console.WriteLine(list[i]);}Console.WriteLine(list.Capacity);#endregion}
}
Dictionary
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.IO;
namespace Dictionary字典;
class Program
{static void Main(string[] args){#region Dictionary/*可以将Dictionary理解为泛型的哈希table他也是基于键的哈希代码组织起来的键值对类型从哈希的object变为了自己可以制定的泛型*/#endregion#region 声明Dictionary<int, string> directory = new Dictionary<int, string>();#endregion#region 增删改查// 注意不能出现相同键directory.Add(1,"1");directory.Add(2,"22");directory.Add(3,"333");directory.Add(4,"4444");directory.Add(5,"55555");directory.Add(6,"666666");// 删除directory.Remove(1);//清空//directory.Clear();//查Console.WriteLine(directory[2]);// 找不到不会返回空,直接报错// 查看是否存在if (directory.ContainsKey(1)){ Console.WriteLine("存在");}if (directory.ContainsValue("22")){ Console.WriteLine("存在");}// 改Console.WriteLine(directory[2]="5555");//遍历foreach (var item in directory.Keys){Console.WriteLine(item);Console.WriteLine(directory[item]);}foreach (var item in directory.Values){ Console.WriteLine(item);}foreach (KeyValuePair<int,string> item in directory){ Console.WriteLine("键"+item.Key+"值"+item.Value);}#endregion}
}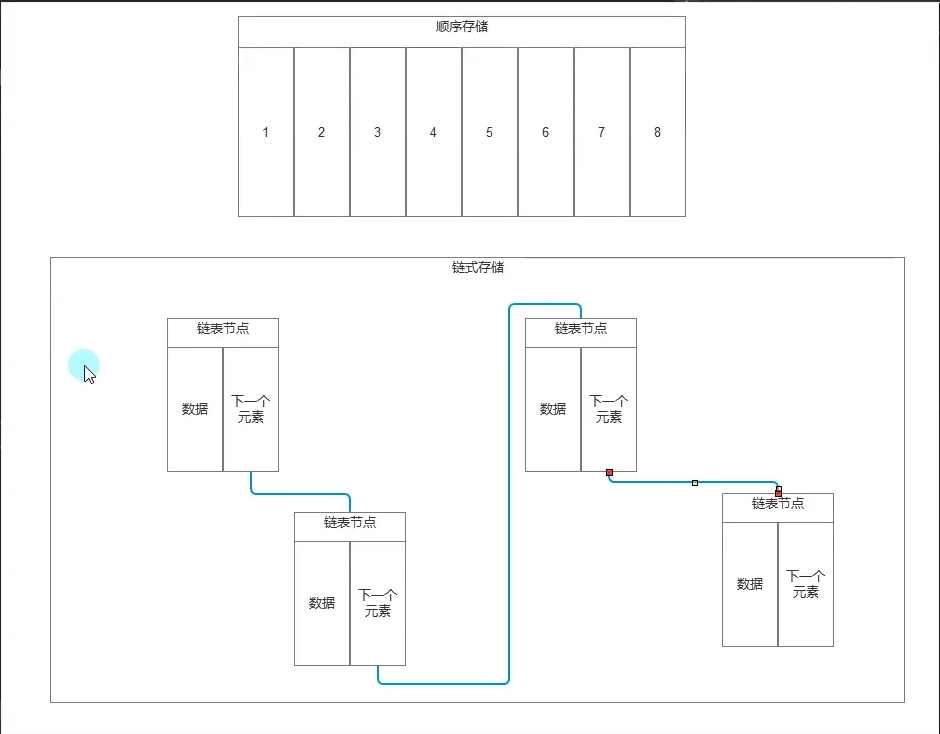
顺序存储和链式存储
using System;namespace Lesson9_顺序存储和链式存储
{class Program{static void Main(string[] args){Console.WriteLine("顺序存储和链式存储");#region 知识点一 数据结构 //数据结构//数据结构是计算机存储、组织数据的方式(规则)//数据结构是指相互之间存在一种或多种特定关系的数据元素的集合//比如自定义的一个 类 也可以称为一种数据结构 自己定义的数据组合规则//不要把数据结构想的太复杂//简单点理解,就是人定义的 存储数据 和 表示数据之间关系 的规则而已//常用的数据结构(前辈总结和制定的一些经典规则)//数组、栈、队列、链表、树、图、堆、散列表#endregion#region 知识点二 线性表//线性表是一种数据结构,是由n个具有相同特性的数据元素的有限序列//比如数组、ArrayList、Stack、Queue、链表等等#endregion//顺序存储和链式存储 是数据结构中两种 存储结构#region 知识点三 顺序存储//数组、Stack、Queue、List、ArrayList —— 顺序存储//只是 数组、Stack、Queue的 组织规则不同而已//顺序存储://用一组地址连续的存储单元依次存储线性表的各个数据元素#endregion#region 知识点四 链式存储//单向链表、双向链表、循环链表 —— 链式存储//链式存储(链接存储)://用一组任意的存储单元存储线性表中的各个数据元素#endregionLindedList<int> link = new LindedList<int>();link.Add(1);link.Add(2);link.Add(3);link.Add(4);LinkedNode<int> node = link.head;while(node != null){Console.WriteLine(node.value);node = node.nextNode;}link.Remove(2);node = link.head;while (node != null){Console.WriteLine(node.value);node = node.nextNode;}link.Remove(1);node = link.head;while (node != null){Console.WriteLine(node.value);node = node.nextNode;}link.Add(99);node = link.head;while (node != null){Console.WriteLine(node.value);node = node.nextNode;}}}#region 知识点五 自己实现一个最简单的单向链表/// <summary>/// 单向链表节点/// </summary>/// <typeparam name="T"></typeparam>class LinkedNode<T>{public T value;//这个存储下一个元素是谁 相当于钩子public LinkedNode<T> nextNode;public LinkedNode(T value){this.value = value;}}/// <summary>/// 单向链表类 管理 节点 管理 添加等等/// </summary>/// <typeparam name="T"></typeparam>class LindedList<T>{public LinkedNode<T> head;public LinkedNode<T> last;public void Add(T value){//添加节点 必然是new一个新的节点LinkedNode<T> node = new LinkedNode<T>(value);if( head == null ){head = node;last = node;}else{last.nextNode = node;last = node;}}public void Remove(T value){if( head == null ){return;}if( head.value.Equals(value) ){head = head.nextNode;//如果头节点 被移除 发现头节点变空//证明只有一个节点 那尾也要清空if( head == null ){last = null;}return;}LinkedNode<T> node = head;while(node.nextNode != null){if( node.nextNode.value.Equals(value) ){//让当前找到的这个元素的 上一个节点//指向 自己的下一个节点node.nextNode = node.nextNode.nextNode;break;}}}}#endregion#region 知识点六 顺序存储和链式存储的优缺点//从增删查改的角度去思考//增:链式存储 计算上 优于顺序存储 (中间插入时链式不用像顺序一样去移动位置)//删:链式存储 计算上 优于顺序存储 (中间删除时链式不用像顺序一样去移动位置)//查:顺序存储 使用上 优于链式存储 (数组可以直接通过下标得到元素,链式需要遍历)//改:顺序存储 使用上 优于链式存储 (数组可以直接通过下标得到元素,链式需要遍历)#endregion
}LinkedList
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;namespace Lesson10_LinkedList
{class Program{static void Main(string[] args){Console.WriteLine("LinkedList");#region 知识点一 LinkedList//LinkedList是一个C#为我们封装好的类//它的本质是一个可变类型的泛型双向链表#endregion#region 知识点二 申明//需要引用命名空间//using System.Collections.GenericLinkedList<int> linkedList = new LinkedList<int>();LinkedList<string> linkedList2 = new LinkedList<string>();//链表对象 需要掌握两个类//一个是链表本身 一个是链表节点类LinkedListNode#endregion#region 知识点三 增删查改#region 增//1.在链表尾部添加元素linkedList.AddLast(10);//2.在链表头部添加元素linkedList.AddFirst(20);//3.在某一个节点之后添加一个节点// 要指定节点 先得得到一个节点LinkedListNode<int> n = linkedList.Find(20);linkedList.AddAfter(n, 15);//4.在某一个节点之前添加一个节点// 要指定节点 先得得到一个节点linkedList.AddBefore(n, 11);#endregion#region 删//1.移除头节点linkedList.RemoveFirst();//2.移除尾节点linkedList.RemoveLast();//3.移除指定节点// 无法通过位置直接移除linkedList.Remove(20);//4.清空linkedList.Clear();linkedList.AddLast(1);linkedList.AddLast(2);linkedList.AddLast(3);linkedList.AddLast(4);#endregion#region 查//1.头节点LinkedListNode<int> first = linkedList.First;//2.尾节点LinkedListNode<int> last = linkedList.Last;//3.找到指定值的节点// 无法直接通过下标获取中间元素// 只有遍历查找指定位置元素LinkedListNode<int> node = linkedList.Find(3);Console.WriteLine(node.Value);node = linkedList.Find(5);//4.判断是否存在if( linkedList.Contains(1) ){Console.WriteLine("链表中存在1");}#endregion#region 改//要先得再改 得到节点 再改变其中的值Console.WriteLine(linkedList.First.Value);linkedList.First.Value = 10;Console.WriteLine(linkedList.First.Value);#endregion#endregion#region 知识点四 遍历//1.foreach遍历foreach (int item in linkedList){Console.WriteLine(item);}//2.通过节点遍历// 从头到尾Console.WriteLine("&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&");LinkedListNode<int> nowNode = linkedList.First;while (nowNode != null){Console.WriteLine(nowNode.Value);nowNode = nowNode.Next;}// 从尾到头Console.WriteLine("&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&");nowNode = linkedList.Last;while (nowNode != null){Console.WriteLine(nowNode.Value);nowNode = nowNode.Previous;}#endregion}}
}泛型栈和队列
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;namespace Lesson11_泛型栈和队列
{class Program{static void Main(string[] args){Console.WriteLine("泛型栈和队列");#region 知识点一 回顾数据容器#region 变量//无符号//byte ushort uint ulong//有符号//sbyte short int long//浮点数//float double decimal//特殊//char bool string#endregion#region 复杂数据容器//枚举 enum//结构体 struct//数组(一维、二维、交错) [] [,] [][]//类#endregion#region 数据集合//using System.Collections;//ArrayList object数据列表//Stack 栈 先进后出//Queue 队列 先进先出//Hashtable 哈希表 键值对#endregion#region 泛型数据集合//using System.Collections.Generic;//List 列表 泛型列表//Dictionary 字典 泛型哈希表//LinkedList 双向链表 //Statck 泛型栈//Queue 泛型队列#endregion#endregion#region 知识点二 泛型栈和队列//命名空间:using System.Collections.Generic;//使用上 和之前的Stack和Queue一模一样Stack<int> stack = new Stack<int>();Queue<object> queue = new Queue<object>();#endregion}}
}委托
using System;namespace Lesson12_委托
{#region 知识点一 委托是什么//委托是 函数(方法)的容器 //可以理解为表示函数(方法)的变量类型//用来 存储、传递函数(方法)//委托的本质是一个类,用来定义函数(方法)的类型(返回值和参数的类型)//不同的 函数(方法)必须对应和各自"格式"一致的委托#endregion#region 知识点二 基本语法//关键字 : delegate//语法:访问修饰符 delegate 返回值 委托名(参数列表);//写在哪里?//可以申明在namespace和class语句块中//更多的写在namespace中//简单记忆委托语法 就是 函数申明语法前面加一个delegate关键字#endregion#region 知识点三 定义自定义委托//访问修饰默认不写 为public 在别的命名空间中也能使用//private 其它命名空间就不能用了//一般使用public//申明了一个可以用来存储无参无返回值函数的容器//这里只是定义了规则 并没有使用delegate void MyFun();//委托规则的申明 是不能重名(同一语句块中)//表示用来装载或传递 返回值为int 有一个int参数的函数的 委托 容器规则public delegate int MyFun2(int a);//委托是支持 泛型的 可以让返回值和参数 可变 更方便我们的使用delegate T MyFun3<T, K>(T v, K k);#endregion#region 知识点四 使用定义好的委托//委托变量是函数的容器//委托常用在://1.作为类的成员//2.作为函数的参数class Test{public MyFun fun;public MyFun2 fun2;public Action action;public void TestFun( MyFun fun, MyFun2 fun2 ){//先处理一些别的逻辑 当这些逻辑处理完了 再执行传入的函数int i = 1;i *= 2;i += 2;//fun();//fun2(i);//this.fun = fun;//this.fun2 = fun2;}#region 增public void AddFun(MyFun fun, MyFun2 fun2){this.fun += fun;this.fun2 += fun2;}#endregion#region 删public void RemoveFun(MyFun fun, MyFun2 fun2){//this.fun = this.fun - fun;this.fun -= fun;this.fun2 -= fun2;}#endregion}#endregion#region 知识点五 委托变量可以存储多个函数(多播委托)#endregionclass Program{static void Main(string[] args){Console.WriteLine("委托");//专门用来装载 函数的 容器MyFun f = new MyFun(Fun);Console.WriteLine("1");Console.WriteLine("2");Console.WriteLine("3");Console.WriteLine("4");Console.WriteLine("5");f.Invoke();MyFun f2 = Fun;Console.WriteLine("1");Console.WriteLine("2");Console.WriteLine("3");Console.WriteLine("4");Console.WriteLine("5");f2();MyFun2 f3 = Fun2;Console.WriteLine(f3(1));MyFun2 f4 = new MyFun2(Fun2);Console.WriteLine(f4.Invoke(3));Test t = new Test();t.TestFun(Fun, Fun2);Console.WriteLine("***************");//如何用委托存储多个函数MyFun ff = null;//ff = ff + Fun;ff += Fun;ff += Fun3;ff();//从容器中移除指定的函数ff -= Fun;//多减 不会报错 无非就是不处理而已ff -= Fun;ff();//清空容器ff = null;if( ff != null ){ff();}#region 知识点六 系统定义好的委托//使用系统自带委托 需要引用using System;//无参无返回值Action action = Fun;action += Fun3;action();//可以指定返回值类型的 泛型委托Func<string> funcString = Fun4;Func<int> funcInt = Fun5;//可以传n个参数的 系统提供了 1到16个参数的委托 直接用就行了Action<int, string> action2 = Fun6;//可以穿n个参数的 并且有返回值的 系统也提供了 16个委托Func<int, int> func2 = Fun2;#endregion}static void Fun(){Console.WriteLine("张三做什么");}static void Fun3(){Console.WriteLine("李四做什么");}static string Fun4(){return "";}static int Fun5(){return 1;}static void Fun6(int i, string s){}static int Fun2(int value){return value;}}//总结//简单理解 委托 就是装载、传递函数的容器而已//可以用委托变量 来存储函数或者传递函数的//系统其实已经提供了很多委托给我们用 //Action:没有返回值,参数提供了 0~16个委托给我们用//Func:有返回值,参数提供了 0~16个委托给我们用
}练习题
using System;namespace Lesson12_练习题
{#region 练习题一//一家三口,妈妈做饭,爸爸妈妈和孩子都要吃饭//用委托模拟做饭——>开饭——>吃饭的过程abstract class Person{public abstract void Eat();}class Mother : Person{public Action beginEat;public override void Eat(){Console.WriteLine("妈妈吃饭");}public void DoFood(){Console.WriteLine("妈妈做饭");Console.WriteLine("妈妈做饭做好了");//执行委托函数if(beginEat != null){beginEat();}}}class Father:Person{public override void Eat(){Console.WriteLine("爸爸吃饭");}}class Son:Person{public override void Eat(){Console.WriteLine("孩子吃饭");}}#endregion#region 练习题二//怪物死亡后,玩家要加10块钱,界面要更新数据//成就要累加怪物击杀数,请用委托来模拟实现这些功能//只用写核心逻辑表现这个过程,不用写的太复杂class Monster{//当怪物死亡时 把自己作为参数传出去 public Action<Monster> deadDoSomthing;//怪物成员变量 特征 价值多少钱public int money = 10;public void Dead(){Console.WriteLine("怪物死亡");if(deadDoSomthing != null){deadDoSomthing(this);}//一般情况下 委托关联的函数 有加 就有减(或者直接清空)deadDoSomthing = null;}}class Player{private int myMoney = 0;public void MonsterDeadDoSomthing(Monster m){myMoney += m.money;Console.WriteLine("现在有{0}元钱", myMoney);}}class Panel{private int nowShowMoney = 0;public void MonsterDeadDo(Monster m){nowShowMoney += m.money;Console.WriteLine("当前面板显示{0}元钱", nowShowMoney);}}class CJ{private int nowKillMonsterNum = 0;public void MonsterDeadDo(Monster m){nowKillMonsterNum += 1;Console.WriteLine("当前击杀了{0}怪物", nowKillMonsterNum);}}#endregionclass Program{static void Main(string[] args){Console.WriteLine("委托练习题");Mother m = new Mother();Father f = new Father();Son s = new Son();//告诉妈妈 一会做好了 我要吃m.beginEat += f.Eat;m.beginEat += s.Eat;m.beginEat += m.Eat;//做饭m.DoFood();Monster monster = new Monster();Player p = new Player();Panel panel = new Panel();CJ cj = new CJ();monster.deadDoSomthing += p.MonsterDeadDoSomthing;monster.deadDoSomthing += panel.MonsterDeadDo;monster.deadDoSomthing += cj.MonsterDeadDo;monster.Dead();monster.Dead();Monster monster2 = new Monster();monster2.deadDoSomthing += p.MonsterDeadDoSomthing;monster2.deadDoSomthing += panel.MonsterDeadDo;monster2.deadDoSomthing += cj.MonsterDeadDo;monster2.Dead();}}
}事件
using System;namespace Lesson13_事件
{#region 知识点一 事件是什么//事件是基于委托的存在//事件是委托的安全包裹//让委托的使用更具有安全性//事件 是一种特殊的变量类型#endregion#region 知识点二 事件的使用//申明语法://访问修饰符 event 委托类型 事件名;//事件的使用://1.事件是作为 成员变量存在于类中//2.委托怎么用 事件就怎么用//事件相对于委托的区别://1.不能在类外部 赋值//2.不能再类外部 调用//注意://它只能作为成员存在于类和接口以及结构体中class Test{//委托成员变量 用于存储 函数的public Action myFun;//事件成员变量 用于存储 函数的public event Action myEvent;public Test(){//事件的使用和委托 一模一样 只是有些 细微的区别myFun = TestFun;myFun += TestFun;myFun -= TestFun;myFun();myFun.Invoke();myFun = null;myEvent = TestFun;myEvent += TestFun;myEvent -= TestFun;myEvent();myEvent.Invoke();myEvent = null;}public void DoEvent(){if(myEvent != null){myEvent();}}public void TestFun(){Console.WriteLine("123");}}#endregion#region 知识点三 为什么有事件//1.防止外部随意置空委托//2.防止外部随意调用委托//3.事件相当于对委托进行了一次封装 让其更加安全#endregionclass Program{static void Main(string[] args){Console.WriteLine("事件");Test t = new Test();//委托可以在外部赋值t.myFun = null;t.myFun = TestFun;t.myFun = t.myFun + TestFun;t.myFun += TestFun;//事件是不能再外部赋值的//t.myEvent = null;//t.myEvent = TestFun;//虽然不能直接赋值 但是可以 加减 去添加移除记录的函数t.myEvent += TestFun;t.myEvent -= TestFun;//委托是可以在外部调用的t.myFun();t.myFun.Invoke();//事件不能再外部调用//t.myEvent();//只能在类的内部去封装 调用t.DoEvent();Action a = TestFun;//事件 是不能作为临时变量在函数中使用的//event Action ae = TestFun;}static void TestFun(){}}//总结//事件和委托的区别//事件和委托的使用基本是一模一样的//事件就是特殊的委托//主要区别://1.事件不能再外部使用赋值=符号,只能使用+ - 委托 哪里都能用//2.事件 不能再外部执行 委托哪里都能执行//3.事件 不能作为 函数中的临时变量的 委托可以
}匿名函数
using System;namespace Lesson14_匿名函数
{class Program{static void Main(string[] args){Console.WriteLine("匿名函数");#region 知识点一 什么是匿名函数//顾名思义,就是没有名字的函数//匿名函数的使用主要是配合委托和事件进行使用//脱离委托和事件 是不会使用匿名函数的#endregion#region 知识点二 基本语法//delegate (参数列表)//{// //函数逻辑//};//何时使用?//1.函数中传递委托参数时//2.委托或事件赋值时#endregion#region 知识点三 使用//1.无参无返回//这样申明匿名函数 只是在申明函数而已 还没有调用//真正调用它的时候 是这个委托容器啥时候调用 就什么时候调用这个匿名函数Action a = delegate (){Console.WriteLine("匿名函数逻辑");};a();//2.有参Action<int, string> b = delegate (int a, string b){Console.WriteLine(a);Console.WriteLine(b);};b(100, "123");//3.有返回值Func<string> c = delegate (){return "123123";};Console.WriteLine(c());//4.一般情况会作为函数参数传递 或者 作为函数返回值Test t = new Test();Action ac = delegate (){Console.WriteLine("随参数传入的匿名函数逻辑");};t.Dosomthing(50, ac);// 参数传递t.Dosomthing(100, delegate (){Console.WriteLine("随参数传入的匿名函数逻辑");});// 返回值Action ac2 = t.GetFun();ac2();//一步到位 直接调用返回的 委托函数t.GetFun()();#endregion#region 知识点四 匿名函数的缺点//添加到委托或事件容器中后 不记录 无法单独移除Action ac3 = delegate (){Console.WriteLine("匿名函数一");};ac3 += delegate (){Console.WriteLine("匿名函数二");};ac3();//因为匿名函数没有名字 所以没有办法指定移除某一个匿名函数//此匿名函数 非彼匿名函数 不能通过看逻辑是否一样 就证明是一个 //ac3 -= delegate ()//{// Console.WriteLine("匿名函数一");//};ac3 = null;//ac3();#endregion}static void TestFun(){}}class Test{public Action action;//作为参数传递时public void Dosomthing(int a, Action fun){Console.WriteLine(a);fun();}//作为返回值public Action GetFun(){return delegate() {Console.WriteLine("函数内部返回的一个匿名函数逻辑");};}public void TestTTTT(){}}//总结//匿名函数 就是没有名字的函数//固定写法 //delegate(参数列表){}//主要是在 委托传递和存储时 为了方便可以直接使用倪敏该函数//缺点是 没有办法指定移除
}Lambad表达式
using System;namespace Lesson15_lambad表达式
{class Program{static void Main(string[] args){Console.WriteLine("lambad表达式");#region 知识点一 什么是lambad表达式//可以将lambad表达式 理解为匿名函数的简写//它除了写法不同外//使用上和匿名函数一模一样//都是和委托或者事件 配合使用的#endregion#region 知识点二 lambad表达式语法//匿名函数//delegate (参数列表)//{//};//lambad表达式//(参数列表) =>//{// //函数体//};#endregion#region 知识点三 使用//1.无参无返回Action a = () =>{Console.WriteLine("无参无返回值的lambad表达式");};a();//2.有参Action<int> a2 = (int value) =>{Console.WriteLine("有参数Lambad表达式{0}", value);};a2(100);//3.甚至参数类型都可以省略 参数类型和委托或事件容器一致Action<int> a3 = (value) =>{Console.WriteLine("省略参数类型的写法{0}", value);};a3(200);//4.有返回值Func<string, int> a4 = (value) =>{Console.WriteLine("有返回值有参数的那么大表达式{0}", value);return 1;};Console.WriteLine(a4("123123"));//其它传参使用等和匿名函数一样//缺点也是和匿名函数一样的#endregionTest t = new Test();t.DoSomthing();}}#region 知识点四 闭包//内层的函数可以引用包含在它外层的函数的变量//即使外层函数的执行已经终止//注意://该变量提供的值并非变量创建时的值,而是在父函数范围内的最终值。class Test{public event Action action;public Test(){int value = 10;//这里就形成了闭包//因为 当构造函数执行完毕时 其中申明的临时变量value的声明周期被改变了action = () =>{Console.WriteLine(value);};for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++){//此index 非彼indexint index = i;action += () =>{Console.WriteLine(index);};}}public void DoSomthing(){action();}}#endregion//总结//匿名函数的特殊写法 就是 lambad表达式//固定写法 就是 (参数列表)=>{}//参数列表 可以直接省略参数类型//主要在 委托传递和存储时 为了方便可以直接使用匿名函数或者lambad表达式//缺点:无法指定移除
}List排序
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Diagnostics.CodeAnalysis;namespace Lesson16_List排序
{class Item : IComparable<Item>{public int money;public Item(int money){this.money = money;}public int CompareTo(Item other){//返回值的含义//小于0://放在传入对象的前面//等于0://保持当前的位置不变//大于0://放在传入对象的后面//可以简单理解 传入对象的位置 就是0//如果你的返回为负数 就放在它的左边 也就前面//如果你返回正数 就放在它的右边 也就是后面if( this.money > other.money ){return -1;}else{return 1;}}}class ShopItem{public int id;public ShopItem(int id){this.id = id;}}class Program{static void Main(string[] args){Console.WriteLine("List排序");#region 知识点一 List自带排序方法List<int> list = new List<int>();list.Add(3);list.Add(2);list.Add(6);list.Add(1);list.Add(4);list.Add(5);for (int i = 0; i < list.Count; i++){Console.WriteLine(list[i]);}//list提供了排序方法list.Sort();Console.WriteLine("**************");for (int i = 0; i < list.Count; i++){Console.WriteLine(list[i]);}//ArrayList中也有Sort排序方法#endregion#region 知识点二 自定义类的排序List<Item> itemList = new List<Item>();itemList.Add(new Item(45));itemList.Add(new Item(10));itemList.Add(new Item(99));itemList.Add(new Item(24));itemList.Add(new Item(100));itemList.Add(new Item(12));//排序方法itemList.Sort();for (int i = 0; i < itemList.Count; i++){Console.WriteLine(itemList[i].money);}#endregion#region 知识点三 通过委托函数进行排序List<ShopItem> shopItems = new List<ShopItem>();shopItems.Add(new ShopItem(2));shopItems.Add(new ShopItem(1));shopItems.Add(new ShopItem(4));shopItems.Add(new ShopItem(3));shopItems.Add(new ShopItem(6));shopItems.Add(new ShopItem(5));//shopItems.Sort(SortShopItem);//匿名函数//shopItems.Sort(delegate (ShopItem a, ShopItem b)//{// if (a.id > b.id)// {// return -1;// }// else// {// return 1;// }//});//lambad表达式 配合 三目运算符的 完美呈现shopItems.Sort((a, b) =>{ return a.id > b.id ? 1 : -1;});Console.WriteLine("*********************");for (int i = 0; i < shopItems.Count; i++){Console.WriteLine(shopItems[i].id);}#endregion}static int SortShopItem( ShopItem a, ShopItem b ){//传入的两个对象 为列表中的两个对象//进行两两的比较 用左边的和右边的条件 比较//返回值规则 和之前一样 0做标准 负数在左(前) 正数在右(后)if (a.id > b.id){return -1;}else{return 1;}}}//总结//系统自带的变量(int,float,double.....) 一般都可以直接Sort//自定义类SOrt有两种方式//1.继承接口 IComparable//2.在Sort中传入委托函数}协变逆变
using System;namespace Lesson17_协变逆变
{#region 知识点一 什么是协变逆变//协变://和谐的变化,自然的变化//因为 里氏替换原则 父类可以装子类//所以 子类变父类 //比如 string 变成 object //感受是和谐的//逆变://逆常规的变化,不正常的变化//因为 里氏替换原则 父类可以装子类 但是子类不能装父类//所以 父类变子类 //比如 object 变成 string//感受是不和谐的//协变和逆变是用来修饰泛型的//协变:out //逆变:in//用于在泛型中 修饰 泛型字母的 //只有泛型接口和泛型委托能使用#endregion#region 知识点二 作用//1.返回值 和 参数//用out修饰的泛型 只能作为返回值delegate T TestOut<out T>();//用in修饰的泛型 只能作为参数delegate void TestIn<in T>(T t);//2.结合里氏替换原则理解class Father{}class Son:Father{}#endregionclass Program{static void Main(string[] args){Console.WriteLine("协变逆变");#region 知识点二 作用(结合里氏替换原则理解)//协变 父类总是能被子类替换// 看起来 就是 son ——> fatherTestOut<Son> os = () =>{return new Son();};TestOut<Father> of = os;Father f = of();//实际上 返回的 是os里面装的函数 返回的是Son//逆变 父类总是能被子类替换//看起来像是 father——>son 明明是传父类 但是你传子类 不和谐的TestIn<Father> iF = (value) =>{};TestIn<Son> iS = iF;iS(new Son());//实际上 调用的是 iF#endregion}}//总结//协变 out//逆变 in//用来修饰 泛型替代符的 只能修饰接口和委托中的泛型//作用两点//1.out修饰的泛型类型 只能作为返回值类型 in修饰的泛型类型 只能作为 参数类型//2.遵循里氏替换原则的 用out和in修饰的 泛型委托 可以相互装载(有父子关系的泛型)// 协变 父类泛型委托装子类泛型委托 逆变 子类泛型委托装父类泛型委托
}多线程
using System;
using System.Threading;namespace Lesson18_多线程
{class Program{static bool isRuning = true;static object obj = new object();static void Main(string[] args){Console.WriteLine("多线程");#region 知识点一 了解线程前先了解进程//进程(Process)是计算机中的程序关于某数据集合上的一次运行活动//是系统进行资源分配和调度的基本单位,是操作系统结构的基础//说人话:打开一个应用程序就是在操作系统上开启了一个进程//进程之间可以相互独立运行,互不干扰//进程之间也可以相互访问、操作#endregion#region 知识点二 什么是线程//操作系统能够进行运算调度的最小单位。//它被包含在进程之中,是进程中的实际运作单位//一条线程指的是进程中一个单一顺序的控制流,一个进程中可以并发多个线程//我们目前写的程序 都在主线程中//简单理解线程://就是代码从上到下运行的一条“管道”#endregion#region 知识点三 什么是多线程//我们可以通过代码 开启新的线程//可以同时运行代码的多条“管道” 就叫多线程#endregion#region 知识点四 语法相关//线程类 Thread//需要引用命名空间 using System.Threading;//1.申明一个新的线程 // 注意 线程执行的代码 需要封装到一个函数中// 新线程 将要执行的代码逻辑 被封装到了一个函数语句块中Thread t = new Thread(NewThreadLogic);//2.启动线程t.Start();//3.设置为后台线程//当前台线程都结束了的时候,整个程序也就结束了,即使还有后台线程正在运行//后台线程不会防止应用程序的进程被终止掉//如果不设置为后台线程 可能导致进程无法正常关闭t.IsBackground = true;//4.关闭释放一个线程//如果开启的线程中不是死循环 是能够结束的逻辑 那么 不用刻意的去关闭它//如果是死循环 想要中止这个线程 有两种方式//4.1-死循环中bool标识//Console.ReadKey();//isRuning = false;//Console.ReadKey();//4.2-通过线程提供的方法(注意在.Net core版本中无法中止 会报错)//中止线程//try//{// t.Abort();// t = null;//}//catch//{//}//5.线程休眠//让线程休眠多少毫秒 1s = 1000毫秒//在哪个线程里执行 就休眠哪个线程//Thread.Sleep(1000);#endregion#region 知识点五 线程之间共享数据//多个线程使用的内存是共享的,都属于该应用程序(进程)//所以要注意 当多线程 同时操作同一片内存区域时可能会出问题//可以通过加锁的形式避免问题//lock//当我们在多个线程当中想要访问同样的东西 进行逻辑处理时//为了避免不必要的逻辑顺序执行的差错//lock(引用类型对象)while(true){lock(obj){Console.SetCursorPosition(0, 0);Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Red;Console.Write("●");}}#endregion#region 知识点六 多线程对于我们的意义//可以用多线程专门处理一些复杂耗时的逻辑//比如 寻路、网络通信等等#endregion}static void NewThreadLogic(){//新开线程 执行的代码逻辑 在该函数语句块中while(isRuning){//Thread.Sleep(1000);//Console.WriteLine("新开线程代码逻辑");lock(obj){Console.SetCursorPosition(10, 5);Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Yellow;Console.Write("■");}}}}//总结//多线程是多个可以同时执行代码逻辑的“管道”//可以通过代码开启多线程,用多线程处理一些复杂的可能影响主线程流畅度的逻辑//关键字 Thread
}预处理
//定义一个符号
#define Unity4
#define Unity5
#define Unity2017
#define Unity2019
//取消定义一个符号
#undef Unity4#define IOS
#define Android
#define PCusing System;namespace Lesson19_预处理器指令
{class Program{static void Main(string[] args){Console.WriteLine("预处理器指令");#region 知识点一 什么是编译器//编译器是一种翻译程序//它用于将源语言程序翻译为目标语言程序//源语言程序:某种程序设计语言写成的,比如C#、C、C++、Java等语言写的程序//目标语言程序:二进制数表示的伪机器代码写的程序#endregion#region 知识点二 什么是预处理器指令//预处理器指令 指导编译器 在实际编译开始之前对信息进行预处理//预处理器指令 都是以#开始//预处理器指令不是语句,所以它们不以分号;结束//目前我们经常用到的 折叠代码块 就是预处理器指令#endregion#region 知识点三 常见的预处理器指令//1//#define//定义一个符号,类似一个没有值的变量//#undef//取消define定义的符号,让其失效//两者都是写在脚本文件最前面//一般配合 if指令使用 或配合特性//2//#if//#elif//#else//#endif//和if语句规则一样,一般配合#define定义的符号使用//用于告诉编译器进行编译代码的流程控制//如果发现有Unity4这个符号 那么其中包含的代码 就会被编译器翻译//可以通过 逻辑或 和 逻辑与 进行多种符号的组合判断
#if Unity4Console.WriteLine("版本为Unity4");
#elif Unity2017 && IOSConsole.WriteLine("版本为Unity2017");//#warning 这个版本 不合法//#error 这个版本不准执行
#elseConsole.WriteLine("其它版本");
#endif//3//#warning//#error//告诉编译器//是报警告还是报错误//一般还是配合if使用#endregion}}//总结//预处理器指令//可以让代码还没有编译之前就可以进行一些预处理判断//在Unity中会用来进行一些平台或者版本的判断//决定不同的版本或者不同的平台使用不同的代码逻辑
}反射
using System;
using System.Reflection;
using System.Threading;namespace Lesson20_反射
{#region 知识点回顾//编译器是一种翻译程序//它用于将源语言程序翻译为目标语言程序//源语言程序:某种程序设计语言写成的,比如C#、C、C++、Java等语言写的程序//目标语言程序:二进制数表示的伪机器代码写的程序#endregion#region 知识点一 什么是程序集//程序集是经由编译器编译得到的,供进一步编译执行的那个中间产物//在WINDOWS系统中,它一般表现为后缀为·dll(库文件)或者是·exe(可执行文件)的格式//说人话://程序集就是我们写的一个代码集合,我们现在写的所有代码//最终都会被编译器翻译为一个程序集供别人使用//比如一个代码库文件(dll)或者一个可执行文件(exe)#endregion#region 知识点二 元数据//元数据就是用来描述数据的数据//这个概念不仅仅用于程序上,在别的领域也有元数据//说人话://程序中的类,类中的函数、变量等等信息就是 程序的 元数据//有关程序以及类型的数据被称为 元数据,它们保存在程序集中#endregion#region 知识点三 反射的概念//程序正在运行时,可以查看其它程序集或者自身的元数据。//一个运行的程序查看本身或者其它程序的元数据的行为就叫做反射//说人话://在程序运行时,通过反射可以得到其它程序集或者自己程序集代码的各种信息//类,函数,变量,对象等等,实例化它们,执行它们,操作它们#endregion#region 知识点四 反射的作用//因为反射可以在程序编译后获得信息,所以它提高了程序的拓展性和灵活性//1.程序运行时得到所有元数据,包括元数据的特性//2.程序运行时,实例化对象,操作对象//3.程序运行时创建新对象,用这些对象执行任务#endregionclass Test{private int i = 1;public int j = 0;public string str = "123";public Test(){}public Test(int i){this.i = i;}public Test( int i, string str ):this(i){this.str = str;}public void Speak(){Console.WriteLine(i);}}class Program{static void Main(string[] args){Console.WriteLine("反射");#region 知识点五 语法相关#region Type//Type(类的信息类)//它是反射功能的基础!//它是访问元数据的主要方式。 //使用 Type 的成员获取有关类型声明的信息//有关类型的成员(如构造函数、方法、字段、属性和类的事件)#region 获取Type//1.万物之父object中的 GetType()可以获取对象的Typeint a = 42;Type type = a.GetType();Console.WriteLine(type);//2.通过typeof关键字 传入类名 也可以得到对象的TypeType type2 = typeof(int);Console.WriteLine(type2);//3.通过类的名字 也可以获取类型// 注意 类名必须包含命名空间 不然找不到Type type3 = Type.GetType("System.Int32");Console.WriteLine(type3);#endregion#region 得到类的程序集信息//可以通过Type可以得到类型所在程序集信息Console.WriteLine(type.Assembly);Console.WriteLine(type2.Assembly);Console.WriteLine(type3.Assembly);#endregion#region 获取类中的所有公共成员//首先得到TypeType t = typeof(Test);//然后得到所有公共成员//需要引用命名空间 using System.Reflection;MemberInfo[] infos = t.GetMembers();for (int i = 0; i < infos.Length; i++){Console.WriteLine(infos[i]);}#endregion#region 获取类的公共构造函数并调用//1.获取所有构造函数ConstructorInfo[] ctors = t.GetConstructors();for (int i = 0; i < ctors.Length; i++){Console.WriteLine(ctors[i]);}//2.获取其中一个构造函数 并执行//得构造函数传入 Type数组 数组中内容按顺序是参数类型//执行构造函数传入 object数组 表示按顺序传入的参数// 2-1得到无参构造ConstructorInfo info = t.GetConstructor(new Type[0]);//执行无参构造 无参构造 没有参数 传nullTest obj = info.Invoke(null) as Test;Console.WriteLine(obj.j);// 2-2得到有参构造ConstructorInfo info2 = t.GetConstructor(new Type[] { typeof(int) });obj = info2.Invoke(new object[] { 2 }) as Test;Console.WriteLine(obj.str);ConstructorInfo info3 = t.GetConstructor(new Type[] { typeof(int), typeof(string) });obj = info3.Invoke(new object[] { 4, "444444" }) as Test;Console.WriteLine(obj.str);#endregion#region 获取类的公共成员变量//1.得到所有成员变量FieldInfo[] fieldInfos = t.GetFields();for (int i = 0; i < fieldInfos.Length; i++){Console.WriteLine(fieldInfos[i]);}//2.得到指定名称的公共成员变量FieldInfo infoJ = t.GetField("j");Console.WriteLine(infoJ);//3.通过反射获取和设置对象的值Test test = new Test();test.j = 99;test.str = "2222";// 3-1通过反射 获取对象的某个变量的值Console.WriteLine(infoJ.GetValue(test));// 3-2通过反射 设置指定对象的某个变量的值infoJ.SetValue(test, 100);Console.WriteLine(infoJ.GetValue(test));#endregion#region 获取类的公共成员方法//通过Type类中的 GetMethod方法 得到类中的方法//MethodInfo 是方法的反射信息Type strType = typeof(string);MethodInfo[] methods = strType.GetMethods();for (int i = 0; i < methods.Length; i++){Console.WriteLine(methods[i]);}//1.如果存在方法重载 用Type数组表示参数类型MethodInfo subStr = strType.GetMethod("Substring",new Type[] { typeof(int), typeof(int) });//2.调用该方法//注意:如果是静态方法 Invoke中的第一个参数传null即可string str = "Hello,World!";//第一个参数 相当于 是哪个对象要执行这个成员方法object result = subStr.Invoke(str, new object[] { 7, 5 });Console.WriteLine(result);#endregion#region 其它//Type;//得枚举//GetEnumName//GetEnumNames//得事件//GetEvent//GetEvents//得接口//GetInterface//GetInterfaces//得属性//GetProperty//GetPropertys//等等#endregion#endregion#region Assembly//程序集类//主要用来加载其它程序集,加载后//才能用Type来使用其它程序集中的信息//如果想要使用不是自己程序集中的内容 需要先加载程序集//比如 dll文件(库文件) //简单的把库文件看成一种代码仓库,它提供给使用者一些可以直接拿来用的变量、函数或类//三种加载程序集的函数//一般用来加载在同一文件下的其它程序集//Assembly asembly2 = Assembly.Load("程序集名称");//一般用来加载不在同一文件下的其它程序集//Assembly asembly = Assembly.LoadFrom("包含程序集清单的文件的名称或路径");//Assembly asembly3 = Assembly.LoadFile("要加载的文件的完全限定路径");//1.先加载一个指定程序集Assembly asembly = Assembly.LoadFrom(@"C:\Users\MECHREVO\Desktop\CSharp进阶教学\Lesson18_练习题\bin\Debug\netcoreapp3.1\Lesson18_练习题");Type[] types = asembly.GetTypes();for (int i = 0; i < types.Length; i++){Console.WriteLine(types[i]);}//2.再加载程序集中的一个类对象 之后才能使用反射Type icon = asembly.GetType("Lesson18_练习题.Icon");MemberInfo[] members = icon.GetMembers();for (int i = 0; i < members.Length; i++){Console.WriteLine(members[i]);}//通过反射 实例化一个 icon对象//首先得到枚举Type 来得到可以传入的参数Type moveDir = asembly.GetType("Lesson18_练习题.E_MoveDir");FieldInfo right = moveDir.GetField("Right");//直接实例化对象object iconObj = Activator.CreateInstance(icon, 10, 5, right.GetValue(null));//得到对象中的方法 通过反射MethodInfo move = icon.GetMethod("Move");MethodInfo draw = icon.GetMethod("Draw");MethodInfo clear = icon.GetMethod("Clear");Console.Clear();while(true){Thread.Sleep(1000);clear.Invoke(iconObj, null);move.Invoke(iconObj, null);draw.Invoke(iconObj, null);}//3.类库工程创建#endregion#region Activator//用于快速实例化对象的类//用于将Type对象快捷实例化为对象//先得到Type//然后 快速实例化一个对象Type testType = typeof(Test);//1.无参构造Test testObj = Activator.CreateInstance(testType) as Test;Console.WriteLine(testObj.str);//2.有参数构造testObj = Activator.CreateInstance(testType, 99) as Test;Console.WriteLine(testObj.j);testObj = Activator.CreateInstance(testType, 55, "111222") as Test;Console.WriteLine(testObj.j);#endregion#endregion}}//总结//反射//在程序运行时,通过反射可以得到其他程序集或者自己的程序集代码的各种信息//类、函数、变量、对象等等,实例化他们,执行他们,操作他们//关键类//Type//Assembly//Activator//对于我们的意义//在初中级阶段 基本不会使用反射//所以目前对于大家来说,了解反射可以做什么就行//很长时间内都不会用到反射相关知识点//为什么要学反射//为了之后学习Unity引擎的基本工作原理做铺垫//Unity引起的基本工作机制 就是建立在反射的基础上}练习题
using System;
using System.Reflection;namespace Lesson20_练习题
{class Program{static void Main(string[] args){Console.WriteLine("反射练习题");#region 练习题//新建一个类库工程//有一个Player类,有姓名,血量,攻击力,防御力,位置等信息//有一个无参构造函数//再新建一个控制台工程//通过反射的形式使用类库工程生成的dll程序集//实例化一个Player对象//加载类库生成的 程序集 dll库文件Assembly assembly = Assembly.LoadFrom(@"C:\Users\MECHREVO\Desktop\CSharp进阶教学\测试\bin\Debug\测试");Type[] types = assembly.GetTypes();for (int i = 0; i < types.Length; i++){Console.WriteLine(types[i]);}Type player = assembly.GetType("MrTang.Player");object obj = Activator.CreateInstance(player);Console.WriteLine(obj);#endregion}}
}特性
#define Fun
using System;
using System.Diagnostics;
using System.Runtime.CompilerServices;
using System.Runtime.InteropServices;namespace Lesson21_特性
{#region 知识点一 特性是什么//特性是一种允许我们向程序的程序集添加元数据的语言结构//它是用于保存程序结构信息的某种特殊类型的类//特性提供功能强大的方法以将声明信息与 C# 代码(类型、方法、属性等)相关联。//特性与程序实体关联后,即可在运行时使用反射查询特性信息//特性的目的是告诉编译器把程序结构的某组元数据嵌入程序集中//它可以放置在几乎所有的声明中(类、变量、函数等等申明)//说人话://特性本质是个类//我们可以利用特性类为元数据添加额外信息//比如一个类、成员变量、成员方法等等为他们添加更多的额外信息//之后可以通过反射来获取这些额外信息#endregion#region 知识点二 自定义特性//继承特性基类 Attribute[AttributeUsage(AttributeTargets.Class | AttributeTargets.Field, AllowMultiple = true, Inherited = false)]class MyCustomAttribute : Attribute{//特性中的成员 一般根据需求来写public string info;public MyCustomAttribute(string info){this.info = info;}public void TestFun(){Console.WriteLine("特性的方法");}}#endregion#region 知识点三 特性的使用//基本语法://[特性名(参数列表)]//本质上 就是在调用特性类的构造函数//写在哪里?//类、函数、变量上一行,表示他们具有该特性信息[MyCustom("这个是我自己写的一个用于计算的类")][MyCustom("这个是我自己写的一个用于计算的类")]class MyClass{[MyCustom("这是一个成员变量")]public int value;//[MyCustom("这是一个用于计算加法的函数")]//public void TestFun( [MyCustom("函数参数")]int a )//{//}public void TestFun(int a){}}#endregion#region 知识点四 限制自定义特性的使用范围//通过为特性类 加特性 限制其使用范围[AttributeUsage(AttributeTargets.Class | AttributeTargets.Struct, AllowMultiple = true, Inherited = true)]//参数一:AttributeTargets —— 特性能够用在哪些地方//参数二:AllowMultiple —— 是否允许多个特性实例用在同一个目标上//参数三:Inherited —— 特性是否能被派生类和重写成员继承public class MyCustom2Attribute : Attribute{}#endregion#region 知识点五 系统自带特性——过时特性//过时特性//Obsolete//用于提示用户 使用的方法等成员已经过时 建议使用新方法//一般加在函数前的特性class TestClass{//参数一:调用过时方法时 提示的内容//参数二:true-使用该方法时会报错 false-使用该方法时直接警告[Obsolete("OldSpeak方法已经过时了,请使用Speak方法", false)]public void OldSpeak(string str){Console.WriteLine(str);}public void Speak(){}public void SpeakCaller(string str, [CallerFilePath]string fileName = "", [CallerLineNumber]int line = 0, [CallerMemberName]string target = ""){Console.WriteLine(str);Console.WriteLine(fileName);Console.WriteLine(line);Console.WriteLine(target);}}#endregion#region 知识点六 系统自带特性——调用者信息特性//哪个文件调用?//CallerFilePath特性//哪一行调用?//CallerLineNumber特性//哪个函数调用?//CallerMemberName特性//需要引用命名空间 using System.Runtime.CompilerServices;//一般作为函数参数的特性#endregion#region 知识点七 系统自带特性——条件编译特性//条件编译特性//Conditional//它会和预处理指令 #define配合使用//需要引用命名空间using System.Diagnostics;//主要可以用在一些调试代码上//有时想执行有时不想执行的代码#endregion#region 知识点八 系统自带特性——外部Dll包函数特性//DllImport//用来标记非.Net(C#)的函数,表明该函数在一个外部的DLL中定义。//一般用来调用 C或者C++的Dll包写好的方法//需要引用命名空间 using System.Runtime.InteropServices#endregionclass Program{[DllImport("Test.dll")]public static extern int Add(int a, int b);[Conditional("Fun")]static void Fun(){Console.WriteLine("Fun执行");}static void Main(string[] args){Console.WriteLine("特性");#region 特性的使用MyClass mc = new MyClass();Type t = mc.GetType();//t = typeof(MyClass);//t = Type.GetType("Lesson21_特性.MyClass");//判断是否使用了某个特性//参数一:特性的类型//参数二:代表是否搜索继承链(属性和事件忽略此参数)if( t.IsDefined(typeof(MyCustomAttribute), false) ){Console.WriteLine("该类型应用了MyCustom特性");}//获取Type元数据中的所有特性object[] array = t.GetCustomAttributes(true);for (int i = 0; i < array.Length; i++){if( array[i] is MyCustomAttribute ){Console.WriteLine((array[i] as MyCustomAttribute).info);(array[i] as MyCustomAttribute).TestFun();}}TestClass tc = new TestClass();tc.OldSpeak("123");tc.Speak();tc.SpeakCaller("123123123123123");Fun();#endregion}}//总结://特性是用于 为元数据再添加更多的额外信息(变量、方法等等)//我们可以通过反射获取这些额外的数据 来进行一些特殊的处理//自定义特性——继承Attribute类// 系统自带特性:过时特性// 为什么要学习特性// Unity引擎中很多地方都用到了特性来进行一些特殊处理
}习题
using System;
using System.Reflection;namespace Lesson21_练习题
{class Program{static void Main(string[] args){Console.WriteLine("特性练习题");#region 练习题//为反射练习题中的Player对象//随便为其中一个成员变量加一个自定义特性//同样实现反射练习题中的要求//但是当在设置加了自定义特性的成员变量时,在控制台中打印一句//非法操作,随意修改XXX成员Assembly assembly = Assembly.LoadFrom(@"C:\Users\MECHREVO\Desktop\CSharp进阶教学\测试\bin\Debug\测试");Type[] types = assembly.GetTypes();for (int i = 0; i < types.Length; i++){Console.WriteLine(types[i]);}//得typeType playerType = assembly.GetType("MrTang.Player");//实例化object playerObj = Activator.CreateInstance(playerType);Console.WriteLine(playerObj);FieldInfo[] fields = playerType.GetFields();for (int i = 0; i < fields.Length; i++){Console.WriteLine(fields[i]);}//首先要得到我们自定特性的TypeType attribute = assembly.GetType("MrTang.MyCustomAttribute");//赋值名字FieldInfo fildStr = playerType.GetField("name");//得到的特性如果不为空 就证明有if(fildStr.GetCustomAttribute(attribute) != null){Console.WriteLine("非法操作,随意修改name成员");}else{//检测是否被自定义特性修饰 如果是 就不能修改 而是提示fildStr.SetValue(playerObj, "123123");}#endregion}}
}迭代器
using System;
using System.Collections;namespace Lesson22_迭代器
{#region 知识点一 迭代器是什么//迭代器(iterator)有时又称光标(cursor)//是程序设计的软件设计模式//迭代器模式提供一个方法顺序访问一个聚合对象中的各个元素//而又不暴露其内部的标识//在表现效果上看//是可以在容器对象(例如链表或数组)上遍历访问的接口//设计人员无需关心容器对象的内存分配的实现细节//可以用foreach遍历的类,都是实现了迭代器的#endregion#region 知识点二 标准迭代器的实现方法//关键接口:IEnumerator,IEnumerable//命名空间:using System.Collections;//可以通过同时继承IEnumerable和IEnumerator实现其中的方法class CustomList : IEnumerable, IEnumerator{private int[] list;//从-1开始的光标 用于表示 数据得到了哪个位置private int position = -1;public CustomList(){list = new int[] { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 };}#region IEnumerablepublic IEnumerator GetEnumerator(){Reset();return this;}#endregionpublic object Current{get{return list[position];}}public bool MoveNext(){//移动光标++position;//是否溢出 溢出就不合法return position < list.Length;}//reset是重置光标位置 一般写在获取 IEnumerator对象这个函数中//用于第一次重置光标位置public void Reset(){position = -1;}}#endregion#region 知识点三 用yield return 语法糖实现迭代器//yield return 是C#提供给我们的语法糖//所谓语法糖,也称糖衣语法//主要作用就是将复杂逻辑简单化,可以增加程序的可读性//从而减少程序代码出错的机会//关键接口:IEnumerable//命名空间:using System.Collections;//让想要通过foreach遍历的自定义类实现接口中的方法GetEnumerator即可class CustomList2 : IEnumerable{private int[] list;public CustomList2(){list = new int[] { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 };}public IEnumerator GetEnumerator(){for (int i = 0; i < list.Length; i++){//yield关键字 配合迭代器使用//可以理解为 暂时返回 保留当前的状态//一会还会在回来//C#的语法糖yield return list[i];}//yield return list[0];//yield return list[1];//yield return list[2];//yield return list[3];//yield return list[4];//yield return list[5];//yield return list[6];//yield return list[7];}}#endregion#region 知识点四 用yield return 语法糖为泛型类实现迭代器class CustomList<T> : IEnumerable{private T[] array;public CustomList(params T[] array){this.array = array;}public IEnumerator GetEnumerator(){for (int i = 0; i < array.Length; i++){yield return array[i];}}}#endregionclass Program{static void Main(string[] args){Console.WriteLine("迭代器");CustomList list = new CustomList();//foreach本质 //1.先获取in后面这个对象的 IEnumerator// 会调用对象其中的GetEnumerator方法 来获取//2.执行得到这个IEnumerator对象中的 MoveNext方法//3.只要MoveNext方法的返回值时true 就会去得到Current// 然后复制给 item//foreach (int item in list)//{// Console.WriteLine(item);//}//foreach (int item in list)//{// Console.WriteLine(item);//}CustomList<string> list2 = new CustomList<string>("123","321","333","555");foreach (string item in list2){Console.WriteLine(item);}foreach (string item in list2){Console.WriteLine(item);}}}
}//总结:
//迭代器就是可以让我们在外部直接通过foreach遍历对象中元素而不需要了解其结构
//主要的两种方式
//1.传统方式 继承两个接口 实现里面的方法
//2.用语法糖 yield return 去返回内容 只需要继承一个接口即可习题
using System;
using System.Collections;namespace Lesson22_练习题
{#region 练习题//请为一个自定义类//用两种方法让其可以被foreach遍历class CustomList : IEnumerable{private int[] list;public CustomList(){list = new int[] { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10 };}public IEnumerator GetEnumerator(){for (int i = 0; i < list.Length; i++){yield return list[i];}}}class CustomList2 : IEnumerable, IEnumerator{private string[] list;private int position = -1;public CustomList2(){list = new string[] { "123", "321", "666", "7777" };}public object Current{get{return list[position];}}public IEnumerator GetEnumerator(){Reset();return this;}public bool MoveNext(){++position;return position < list.Length;}public void Reset(){position = -1;}}#endregionclass Program{static void Main(string[] args){Console.WriteLine("迭代器练习题");
zCustomList list = new CustomList();foreach (int item in list){Console.WriteLine(item);}CustomList2 list2 = new CustomList2();foreach (string item in list2){Console.WriteLine(item);}foreach (string item in list2){Console.WriteLine(item);}}}
}特殊语法
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;namespace Lesson23_特殊语法
{class Person{private int money;public bool sex;public string Name{get => "唐老狮";set => sex = true;}public int Age{get;set;}public Person(int money){this.money = money;}public int Add(int x, int y) => x + y;public void Speak(string str) => Console.WriteLine(str);}class Program{static void Main(string[] args){Console.WriteLine("特殊语法");#region 知识点一 var隐式类型//var是一种特殊的变量类型//它可以用来表示任意类型的变量//注意://1.var不能作为类的成员 只能用于临时变量申明时// 也就是 一般写在函数语句块中//2.var必须初始化var i = 5;var s = "123";var array = new int[] { 1, 2, 3, 4 };var list = new List<int>();#endregion#region 知识点二 设置对象初始值//申明对象时 //可以通过直接写大括号的形式初始化公共成员变量和属性Person p = new Person(100) { sex = true, Age = 18, Name = "唐老狮" };Person p2 = new Person(200) { Age = 18 };#endregion#region 知识点三 设置集合初始值//申明集合对象时//也可以通过大括号 直接初始化内部属性int[] array2 = new int[] { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };List<int> listInt = new List<int>() { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 };List<Person> listPerson = new List<Person>() {new Person(200),new Person(100){Age = 10},new Person(1){sex = true, Name = "唐老狮"}};Dictionary<int, string> dic = new Dictionary<int, string>(){{ 1, "123" },{ 2, "222"}};#endregion#region 知识点四 匿名类型//var 变量可以申明为自定义的匿名类型var v = new { age = 10, money = 11, name = "小明" };Console.WriteLine(v.age);Console.WriteLine(v.name);#endregion#region 知识点五 可空类型//1.值类型是不能赋值为 空的//int c = null;//2.申明时 在值类型后面加? 可以赋值为空int? c = 3;//3.判断是否为空if( c.HasValue ){Console.WriteLine(c);Console.WriteLine(c.Value);}//4.安全获取可空类型值int? value = null;// 4-1.如果为空 默认返回值类型的默认值Console.WriteLine(value.GetValueOrDefault());// 4-2.也可以指定一个默认值Console.WriteLine(value.GetValueOrDefault(100));float? f = null;double? d = null;object o = null;if( o != null ){Console.WriteLine(o.ToString());}//相当于是一种语法糖 能够帮助我们自动去判断o是否为空//如果是null就不会执行tostring也不会报错Console.WriteLine(o?.ToString());int[] arrryInt = null;Console.WriteLine(arrryInt?[0]);Action action = null;//if (action != null)//{// action();//}action?.Invoke();#endregion#region 知识点六 空合并操作符// 空合并操作符 ??// 左边值 ?? 右边值// 如果左边值为null 就返回右边值 否则返回左边值// 只要是可以为null的类型都能用int? intV = null;//int intI = intV == null ? 100 : intV.Value;int intI = intV ?? 100;Console.WriteLine(intI);string str = null;str = str ?? "hahah";Console.WriteLine(str);#endregion#region 知识点七 内插字符串//关键符号:$//用$来构造字符串,让字符串中可以拼接变量string name = "唐老狮";int age = 18;Console.WriteLine($"好好学习,{name},年龄:{age}");#endregion#region 知识点八 单句逻辑简略写法//当循环或者if语句中只有 一句代码时 大括号可以省略if (true)Console.WriteLine("123123");for (int j = 0; j < 10; j++)Console.WriteLine(j);while (true)Console.WriteLine("123123");#endregion}}
}值和引用
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;namespace Lesson24_值和引用
{class Test{public static int TestI = 0;int b = 0;string str = "123";TestStrict ts = new TestStrict();public void Fun(){b = 1;}}struct TestStrict{public Test t;public int i;}class Program{static int b;static void Main(string[] args){Console.WriteLine("值和引用");#region 知识回顾//值类型//无符号:byte,ushort,uint,ulong//有符号:sbyte,short,int,long//浮点数:float,double,decimal//特殊:char,bool//枚举:enum//结构体:struct//引用类型//string//数组//class//interface//委托//值类型和引用类型的本质区别//值的具体内容存在栈内存上//引用的具体内容存在堆内存上#endregion#region 问题一 如何判断 值类型和引用类型//F12进到类型的内部去查看//是class就是引用//是struct就是值int i = 12;string str = "123";#endregion#region 问题二 语句块//命名空间// ↓//类、接口、结构体// ↓//函数、属性、索引器、运算符重载等(类、接口、结构体)// ↓//条件分支、循环//上层语句块:类、结构体//中层语句块:函数//底层的语句块: 条件分支 循环等//我们的逻辑代码写在哪里?//函数、条件分支、循环-中底层语句块中//我们的变量可以申明在哪里?//上、中、底都能申明变量//上层语句块中:成员变量//中、底层语句块中:临时变量#endregion#region 问题三 变量的生命周期//编程时大部分都是 临时变量//在中底层申明的临时变量(函数、条件分支、循环语句块等)//语句块执行结束 //没有被记录的对象将被回收或变成垃圾//值类型:被系统自动回收//引用类型:栈上用于存地址的房间被系统自动回收,堆中具体内容变成垃圾,待下次GC回收int i2 = 1;string str2 = "123";//{// int b = 1;//}//Console.WriteLine(b);//while(true)//{// int index = 1;//}//想要不被回收或者不变垃圾//必须将其记录下来//如何记录?//在更高层级记录或者//使用静态全局变量记录b = 0;if(true){b = 1;}int c = 10;Test.TestI = c;//Game g = new Game();//while(true)//{//}#endregion#region 问题四 结构体中的值和引用//结构体本身是值类型//前提:该结构体没有做为其它类的成员//在结构体中的值,栈中存储值具体的内容//在结构体中的引用,堆中存储引用具体的内容//引用类型始终存储在堆中//真正通过结构体使用其中引用类型时只是顺藤摸瓜TestStrict ts = new TestStrict();#endregion#region 问题五 类中的值和引用//类本身是引用类型//在类中的值,堆中存储具体的值//在类中的引用,堆中存储具体的值//值类型跟着大哥走,引用类型一根筋Test t = new Test();#endregion#region 问题六 数组中的存储规则//数组本身是引用类型//值类型数组,堆中房间存具体内容//引用类型数组,堆中房间存地址int[] arrayInt = new int[5];object[] objs = new object[5];#endregion#region 问题七 结构体继承接口//利用里氏替换原则,用接口容器装载结构体存在装箱拆箱TestStruct obj1 = new TestStruct();obj1.Value = 1;Console.WriteLine(obj1.Value);TestStruct obj2 = obj1;obj2.Value = 2;Console.WriteLine(obj1.Value);Console.WriteLine(obj2.Value);ITest iObj1 = obj1;//装箱 value 1ITest iObj2 = iObj1;iObj2.Value = 99;Console.WriteLine(iObj1.Value);Console.WriteLine(iObj2.Value);TestStruct obj3 = (TestStruct)iObj1;//拆箱#endregion}}interface ITest{int Value{get;set;}}struct TestStruct : ITest{int value;public int Value {get{return value;}set{this.value = value;}}}}俄罗斯方块实战
需求分析
开始场景结束场景复用贪吃蛇
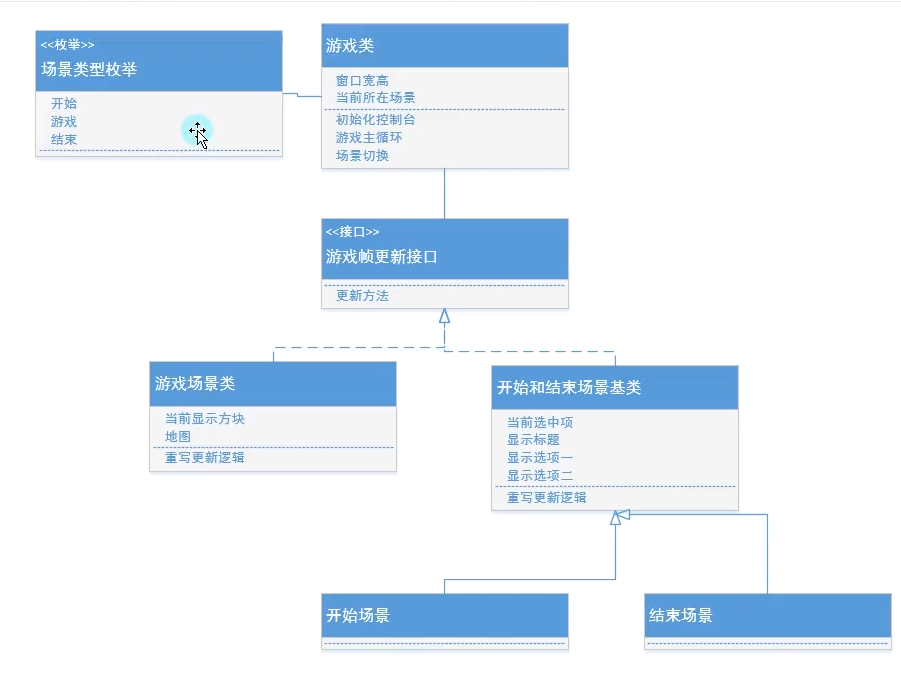
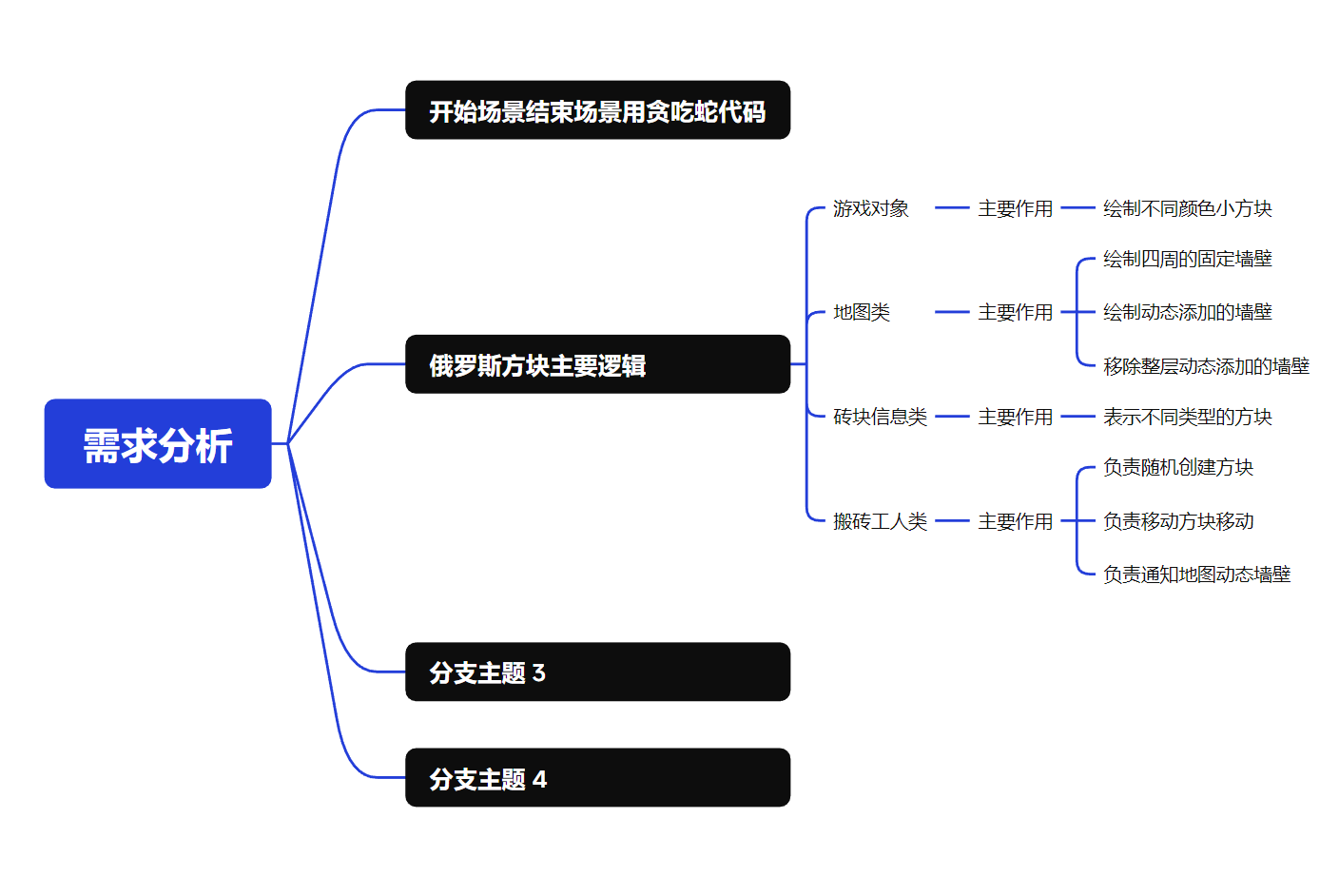
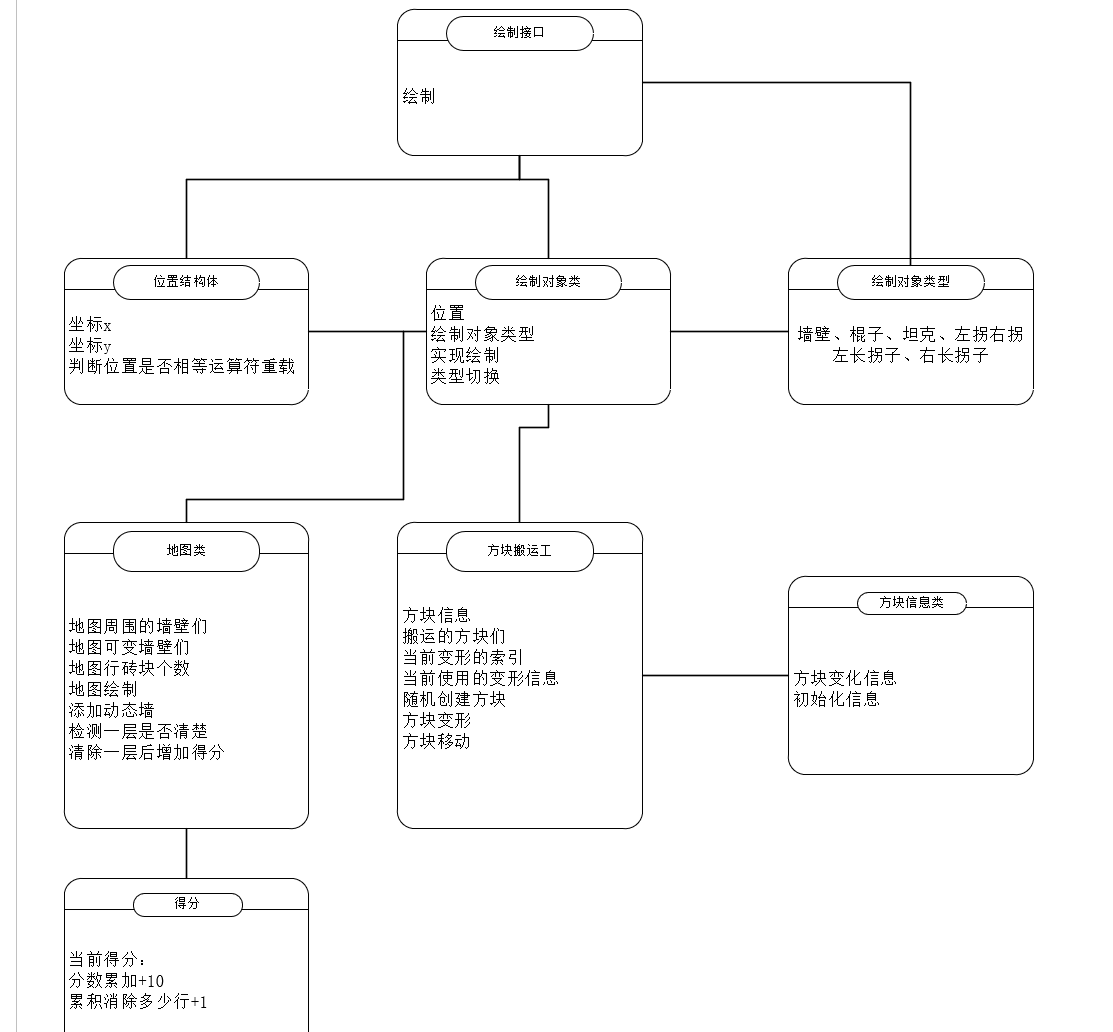
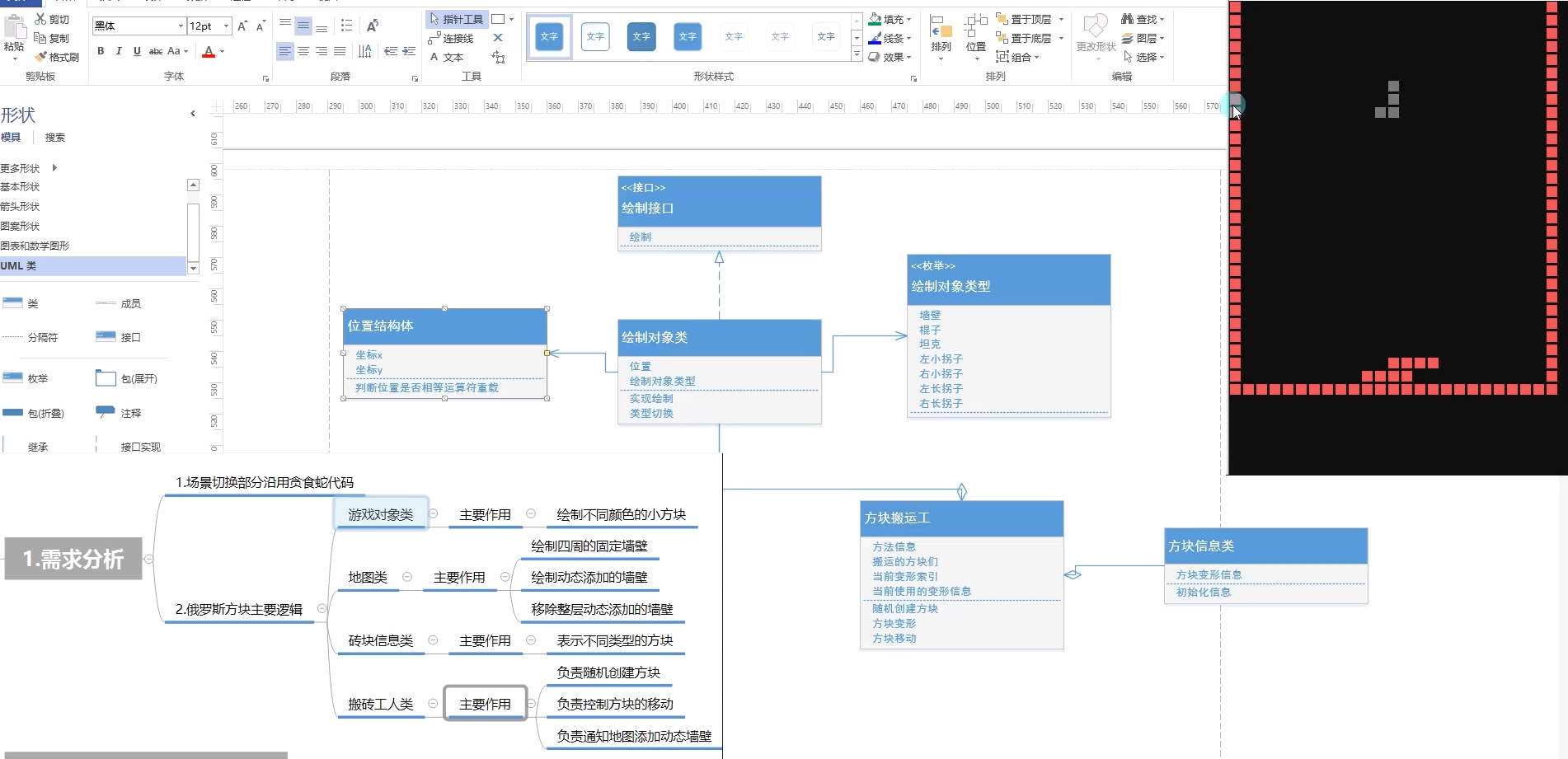
项目文件
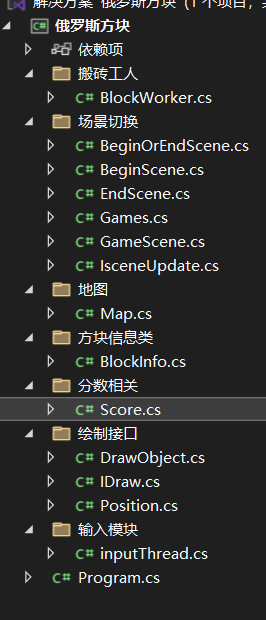
BeginOrEndScene
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using 俄罗斯方块;
namespace 俄罗斯方块
{abstract class BeginOrEndScene : IsceneUpdate{protected int nowSelIndex = 0;protected string strTitle;protected string StrOne;public abstract void EnterJDoSomthing();public void Update(){// 开始或结束游戏逻辑//选择当前选项,监听键盘输入Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.White;// 显示标题Console.SetCursorPosition(Game.w/2-strTitle.Length,5);Console.Write(strTitle);Console.SetCursorPosition(Game.w / 2 - StrOne.Length, 8);Console.ForegroundColor = nowSelIndex==0?ConsoleColor.Red:ConsoleColor.White;Console.Write(StrOne);Console.SetCursorPosition(Game.w / 2 -4, 10);Console.ForegroundColor = nowSelIndex == 1 ? ConsoleColor.Red : ConsoleColor.White;Console.Write("结束游戏");switch (Console.ReadKey(true).Key){case ConsoleKey.W:--nowSelIndex;if (nowSelIndex <0){nowSelIndex = 0;}break;case ConsoleKey.A:++nowSelIndex;if (nowSelIndex >1){nowSelIndex = 1;}break;case ConsoleKey.S:++nowSelIndex;if (nowSelIndex > 1){nowSelIndex = 1;}break;case ConsoleKey.D:--nowSelIndex;if (nowSelIndex < 0){nowSelIndex = 0;}break;case ConsoleKey.J:EnterJDoSomthing();break;}// 显示下方选项// 检测输入}}
}BeginScene
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;namespace 俄罗斯方块
{internal class BeginScene : BeginOrEndScene{public BeginScene() {strTitle = "俄罗斯方块";StrOne = "开始游戏";}public override void EnterJDoSomthing(){// 按J键做什么if (nowSelIndex == 0){Game.ChangeScene(E_SceneType.Game);}else {Environment.Exit(0);}}}
}EndScene
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;namespace 俄罗斯方块
{internal class EndScene : BeginOrEndScene{public EndScene() {strTitle = "结束游戏";StrOne = "回到开始界面";}public override void EnterJDoSomthing(){// 按J键做什么if (nowSelIndex == 0){Game.ChangeScene(E_SceneType.Begin);}else{Environment.Exit(0);}}}
}Games
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;namespace 俄罗斯方块
{enum E_SceneType{ /// <summary>/// 开始/// </summary>Begin,/// <summary>/// 游戏/// </summary>Game,/// <summary>/// 结束/// </summary>End}class Game{public const int w = 50;public const int h = 35;public static IsceneUpdate nowSecene;public Game(){Console.CursorVisible = false;Console.SetWindowSize(w, h);Console.SetBufferSize(w, h);ChangeScene(E_SceneType.Begin);}public void Start() {while (true){if (nowSecene != null){nowSecene.Update();}}}public static void ChangeScene(E_SceneType type){// 切场景之前把上一个场景绘制清理Console.Clear();switch (type){case E_SceneType.Begin:nowSecene = new BeginScene();break;case E_SceneType.Game:nowSecene = new GameScene();break;case E_SceneType.End:nowSecene = new EndScene();break;}}}}GameScene
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;namespace 俄罗斯方块
{class GameScene : IsceneUpdate{Map map;BlockWorker blockWorker;Score Score;//Thread inputThread;//public bool isRunning = true;public GameScene(){map = new Map(this);blockWorker = new BlockWorker();Score = new Score(this);// 添加输入时间监听inputThread.Instance.inputEvent += CheckInputThread;//inputThread = new Thread(CheckInputThread);//inputThread.IsBackground = true;//inputThread.Start();}private void CheckInputThread(){//while (isRunning)//{if (Console.KeyAvailable){lock (blockWorker){switch (Console.ReadKey(true).Key){case ConsoleKey.LeftArrow:if (blockWorker.IsChange(E_Change_Type.left, map)){blockWorker.Change(E_Change_Type.left);}break;case ConsoleKey.RightArrow:if (blockWorker.IsChange(E_Change_Type.right, map)){blockWorker.Change(E_Change_Type.right);}break;case ConsoleKey.A:if (blockWorker.IsMoveRL(E_Change_Type.left, map)){blockWorker.MoveRl(E_Change_Type.left);}break;case ConsoleKey.D:if (blockWorker.IsMoveRL(E_Change_Type.right, map)){blockWorker.MoveRl(E_Change_Type.right);}break;case ConsoleKey.S:if (blockWorker.IsAutoMove(map)){blockWorker.AutoMoveDown();}break;}//Score.ScoreLine = map.updateScore();//Score.ScoreNum = map.GetScore();}}}public void StopThread(){// 移除事件监听inputThread.Instance.inputEvent-=CheckInputThread;}public void Update(){lock (blockWorker){/* Console.ReadKey(true);Game.ChangeScene(E_SceneType.End);*/map.IDraw();blockWorker.IDraw();if (blockWorker.IsAutoMove(map)){blockWorker.AutoMoveDown();}//Score.DrawScore(0, 0);if (map.cleared){Score.DrawScore(map.GetScore(),map.updateScore());map.cleared = false;}}// 线程休眠Thread.Sleep(100);}// }
}IsceneUpdate.cs
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;namespace 俄罗斯方块
{// 场景更新接口internal interface IsceneUpdate{void Update();}
}Map
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;namespace 俄罗斯方块
{internal class Map:IDraw{// 固定墙壁private List<DrawObject> walls = new List<DrawObject>();// 动态墙壁public List<DrawObject> dynamicWalls = new List<DrawObject>();private GameScene nowGameScene;// 记录垮掉的行次数public int ScoreCount;public int Score;// 快速得到地图边界public int w;public int h;// 跨层//记录有多少方块private int[] recordInfo; // 重载无参构造初始化固定墙壁public Map(GameScene scene) {this.nowGameScene = scene;h= Game.h-6;// 代表每行计数的初始化,默认都为0recordInfo = new int[h];// 动态墙壁的宽容量w = 0;// 横向for (int i = 0; i < Game.w; i+=2){walls.Add(new DrawObject(E_DrawType.wall, i, Game.h - 6));walls.Add(new DrawObject(E_DrawType.wall, i, Game.h-1));++w;}w -= 2;// 纵向for (int i = 0; i < Game.h; i += 1){walls.Add(new DrawObject(E_DrawType.wall, 0, i));walls.Add(new DrawObject(E_DrawType.wall, Game.w-2,i));}}public void IDraw(){// 绘制固定墙壁for (int i = 0; i < walls.Count; i++){walls[i].Draw();}// 绘制动态墙壁for (int i = 0; i < dynamicWalls.Count; i++){dynamicWalls[i].Draw();}}// 清除动态墙壁public void ClearDraw() {for (int i = 0; i < dynamicWalls.Count; i++){dynamicWalls[i].ClearDraw();}}/// <summary>/// 提供给外部动态添加方块的函数/// </summary>/// <param name="walls"></param>public void AddWall(List<DrawObject> walls){for (int i = 0; i < walls.Count; i++){walls[i].ChangType(E_DrawType.wall);dynamicWalls.Add(walls[i]);// 在动态墙壁添加出发现位置满了就结束if (walls[i].Position.y <= 0){// 关闭输入线程this.nowGameScene.StopThread();Game.ChangeScene(E_SceneType.End);return;}// 添加动态墙壁计数//根据索引来得到行recordInfo[h - 1 - walls[i].Position.y] += 1;}// 先把之前的动态小方块擦掉ClearDraw();CheckClear();IDraw();}public bool cleared = false;public void CheckClear(){// 添加一个待移除记录列表List<DrawObject> tmpClearList = new List<DrawObject>();//要选择记录行中有多少个方块的容器//数组//判断这个一行是否满(方块)//遍历数组 检测数组里面存的数//是不是w-2for (int i = 0; i < recordInfo.Length; i++){// 满足条件才证明满了if (recordInfo[i] == w){// 这一行的虽有小方块移除for (int j = 0; j < dynamicWalls.Count; j++){//当前动态方块y计算在那一行,如果行号和当前所以一直就证明应该移除if (i == (h - dynamicWalls[j].Position.y-1)){// 移除// 添加一个移除记录列表tmpClearList.Add(dynamicWalls[j]);}//要这一行上的所有小方块下移一个单位else if ((h - dynamicWalls[j].Position.y - 1)>i){++dynamicWalls[j].Position.y;}}//移除待移除的小方块for (int j = 0; j < tmpClearList.Count; j++){dynamicWalls.Remove(tmpClearList[j]); }//记录小方块的数量数组从上到下迁移for (int j = i; j < recordInfo.Length-1; j++){recordInfo[j] = recordInfo[j + 1];}// 置空最顶的计数recordInfo[recordInfo.Length - 1] = 0;// 垮掉一行ScoreTime+1// 垮掉一行后,再次从头判断一次cleared =true; CheckClear();break;}}}}
}BlockInfo
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;namespace 俄罗斯方块.方块信息类
{internal class BlockInfo{// 方块信息坐标private List<Position[]> list;public BlockInfo(E_DrawType type) {//list 初始化才能装东西list = new List<Position[]>();switch (type){case E_DrawType.Cube:// list添加形状信息list.Add(new Position[3] {new Position(2,0),new Position(0,1),new Position(2,1)});break;case E_DrawType.Line:list.Add(new Position[3] {new Position(0, -1),new Position(0, 1),new Position(0, 2),});list.Add(new Position[3] {new Position(-4, 0),new Position(-2, 0),new Position(2, 0),});list.Add(new Position[3] {new Position(0, -2),new Position(0, -1),new Position(0, 1),});list.Add(new Position[3] {new Position(-2, 0),new Position(2, 0),new Position(4, 0),});break;case E_DrawType.Tank:list.Add(new Position[3] {new Position(-2, 0),new Position(2, 0),new Position(0, 1),});list.Add(new Position[3] {new Position(0,-1),new Position(-2,0),new Position(0,1)});list.Add(new Position[3] {new Position(0,-1),new Position(-2,0),new Position(2,0)});list.Add(new Position[3] {new Position(0,-1),new Position(2,0),new Position(0,1)});break;case E_DrawType.Left_Ladder:list.Add(new Position[3]{new Position(0,-1),new Position(2,0),new Position(2,1)});list.Add(new Position[3]{new Position(2,0),new Position(0,1),new Position(-2,1)});list.Add(new Position[3]{new Position(-2,-1),new Position(-2,0),new Position(0,1)});list.Add(new Position[3]{new Position(0,-1),new Position(2,-1),new Position(-2,0)});break;case E_DrawType.Right_Ladder:list.Add(new Position[3]{new Position(0,-1),new Position(-2,0),new Position(-2,1)});list.Add(new Position[3]{new Position(-2,-1),new Position(0,-1),new Position(2,0)});list.Add(new Position[3]{new Position(2,-1),new Position(2,0),new Position(0,1)});list.Add(new Position[3]{new Position(0,1),new Position(2,1),new Position(-2,0)});break;case E_DrawType.Left_Long_Ladder:list.Add(new Position[3]{new Position(-2,-1),new Position(0,-1),new Position(0,1)});list.Add(new Position[3]{new Position(2,-1),new Position(-2,0),new Position(2,0)});list.Add(new Position[3]{new Position(0,-1),new Position(2,1),new Position(0,1)});list.Add(new Position[3]{new Position(2,0),new Position(-2,0),new Position(-2,1)});break;case E_DrawType.Right_Long_Ladder:list.Add(new Position[3]{new Position(0,-1),new Position(0,1),new Position(2,-1)});list.Add(new Position[3]{new Position(2,0),new Position(-2,0),new Position(2,1)});list.Add(new Position[3]{new Position(0,-1),new Position(-2,1),new Position(0,1)});list.Add(new Position[3]{new Position(-2,-1),new Position(-2,0),new Position(2,0)});break;default:break;}} /// <summary>/// 提供给外部啊根据索引位置快速获取位置偏移信息/// </summary>/// <param name="index"></param>/// <returns></returns>public Position[] this[int index]{get {if (index < 0){return list[0];}else if (index >= list.Count){return list[list.Count - 1];}elsereturn list[index];}}public int Count { get => list.Count; }}
}Score.cs
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;namespace 俄罗斯方块
{// 画出得分internal class Score : Map{protected String SumScoreName;protected String ScoreLineName;public int ScoreNum;public int ScoreLine;int ScoreInit = 0;int LineInit = 0;public Score(GameScene scene) : base(scene){// 显示得分位置,地图边界在map里面SumScoreName = "分数:";ScoreLineName = "行数:";#region 计算得分// 消除一行得分+10,行数+1#endregionConsole.SetCursorPosition(2, Game.h - 4);Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Red;Console.Write(SumScoreName);Console.SetCursorPosition(2, Game.h - 3);Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Red;Console.Write(ScoreLineName);// 初始化分数0 Console.SetCursorPosition(7, Game.h - 4);Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.White;Console.Write(ScoreInit);Console.SetCursorPosition(7, Game.h - 3);Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.White;Console.Write(LineInit);}public void DrawScore(int ScoreNum, int ScoreLine){// 显示实际得分Console.SetCursorPosition(7, Game.h - 4);Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.White;Console.Write(ScoreNum);Console.SetCursorPosition(7, Game.h - 3);Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.White;Console.Write(ScoreLine);}public int updateScore(){return ++ScoreCount;}public int GetScore(){return Score += 10;}// 判断是否消除一行public void Isclear(){DrawScore(GetScore(), updateScore());}}}BlockWorker
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Diagnostics.CodeAnalysis;
using System.Linq;
using System.Numerics;
using System.Runtime.CompilerServices;
using System.Security.Cryptography;
using System.Security.Cryptography.X509Certificates;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using 俄罗斯方块.方块信息类;namespace 俄罗斯方块
{enum E_Change_Type{left,right,}internal class BlockWorker : IDraw{// 方块们private List<DrawObject> blocks;// 记录各个方块的信息private Dictionary<E_DrawType, BlockInfo> blockInfoDict;private BlockInfo nowBlockInfo;// 当前形态索引private int nowInfoIndex;public BlockWorker(){// 初始化撞开信息blockInfoDict = new Dictionary<E_DrawType, BlockInfo>(){{ E_DrawType.Cube ,new BlockInfo(E_DrawType.Cube)},{ E_DrawType.Line ,new BlockInfo(E_DrawType.Line)},{ E_DrawType.Tank ,new BlockInfo(E_DrawType.Tank)},{ E_DrawType.Left_Ladder ,new BlockInfo(E_DrawType.Left_Ladder)},{ E_DrawType.Right_Ladder ,new BlockInfo(E_DrawType.Right_Ladder)},{ E_DrawType.Left_Long_Ladder ,new BlockInfo(E_DrawType.Left_Long_Ladder)},{ E_DrawType.Right_Long_Ladder ,new BlockInfo(E_DrawType.Right_Long_Ladder)},};// 随机方块RandomCratBlock();}public void IDraw(){for (int i = 0; i < blocks.Count; i++){blocks[i].Draw();}}public void RandomCratBlock(){// 随机方块的类型Random r = new Random();E_DrawType type = (E_DrawType)r.Next(1, 8);// 每次创建一个砖块其实就是创建4个小方形blocks = new List<DrawObject>(){new DrawObject(type),new DrawObject(type),new DrawObject(type),new DrawObject(type),};// 初始化方块的位置blocks[0].Position = new Position(24, -5);// 把方块信息存起来nowBlockInfo = blockInfoDict[type];// 随机形态nowInfoIndex = r.Next(0, nowBlockInfo.Count);// 取出一种形态坐标信息Position[] positions = nowBlockInfo[nowInfoIndex];for (int i = 0; i < positions.Length; i++){// 取出来的pos相对原点方块的坐标blocks[i + 1].Position = blocks[0].Position + positions[i];}}#region 变形相关// 清除public void ClearDraw(){for (int i = 0; i < blocks.Count; i++){blocks[i].ClearDraw();}}public void Change(E_Change_Type type){// 变之前擦除ClearDraw();switch (type){case E_Change_Type.left:--nowInfoIndex;if (nowInfoIndex < 0){nowInfoIndex = nowBlockInfo.Count - 1;}break;case E_Change_Type.right:++nowInfoIndex;if (nowInfoIndex >= nowBlockInfo.Count){nowInfoIndex = 0;}break;default:break;}// 得到索引目的是得到对应形态的位置偏移信息//用于设置另外三个小方块Position[] positions = nowBlockInfo[nowInfoIndex];for (int i = 0; i < positions.Length; i++){// 取出来的pos相对原点方块的坐标blocks[i + 1].Position = blocks[0].Position + positions[i];}// 变之后再绘制IDraw();}public bool IsChange(E_Change_Type type, Map map){int nowIndex = nowInfoIndex;switch (type){case E_Change_Type.left:--nowIndex;if (nowIndex < 0){nowIndex = nowBlockInfo.Count - 1;}break;case E_Change_Type.right:++nowIndex;if (nowIndex >= nowBlockInfo.Count){nowIndex = 0;}break;default:break;}// 通过临时索引判断是否超出边界Position[] Nowpositions = nowBlockInfo[nowIndex];// 判断是否超出地图边界Position tempPostion;for (int i = 0; i < Nowpositions.Length; i++){// 判断左右边界和下边界tempPostion = blocks[0].Position + Nowpositions[i];if (tempPostion.x < 2 || tempPostion.x >= Game.w - 2 || tempPostion.y >= map.h){return false;}}// 判断是否和地图上的动态方块重合for (int i = 0; i < Nowpositions.Length; i++){tempPostion = blocks[0].Position + Nowpositions[i];for (int j = 0; j < map.dynamicWalls.Count; j++){if (tempPostion == map.dynamicWalls[j].Position){return false;}}}return true;}#endregion#region 方块左右移动/// <summary>/// 方块左右移动函数/// </summary>/// <param name="type"></param>public void MoveRl(E_Change_Type type){// 动之前得到坐标擦除ClearDraw();// 根据传入的类型,决定左右移动// 左 x-2,y0,右x+2,y0Position movePosition = new Position(type == E_Change_Type.left ? -2 : 2, 0);for (int i = 0; i < blocks.Count; i++){blocks[i].Position += movePosition;}IDraw();}// 判断是否可以移动public bool IsMoveRL(E_Change_Type type, Map map){// 判断左右边界重合// 得到左右的偏移位置Position movePosition = new Position(type == E_Change_Type.left ? -2 : 2, 0);// 动过之后结果不能直接改小方块的位置Position position;for (int i = 0; i < blocks.Count; i++){position = blocks[i].Position + movePosition;if (position.x < 2 || position.x >= Game.w - 2){return false;}}// 要不要和动态方块重合for (int i = 0; i < blocks.Count; i++){position = blocks[i].Position + movePosition;for (int j = 0; j < map.dynamicWalls.Count; j++){if (position == map.dynamicWalls[j].Position){return false;}}}return true;}#endregion#region 自动向下移动/// <summary>/// 自动移动/// </summary>public void AutoMoveDown(){ClearDraw();Position downMove = new Position(0, 1);for (int i = 0; i < blocks.Count; i++){blocks[i].Position += downMove;//blocks[i].Position.y += 1;}IDraw();}public bool IsAutoMove(Map map){// 用临时变量存储下一次移动的位置用于重合判断Position position;Position downMove = new Position(0, 1);for (int i = 0; i < blocks.Count; i++){position = blocks[i].Position + downMove;if (position.y >= map.h){// 停下map.AddWall(blocks);// 随机创建新的方块RandomCratBlock();return false;}}// 动态方块for (int i = 0; i < blocks.Count; i++){position = blocks[i].Position + downMove;for (int j = 0; j < map.dynamicWalls.Count; j++){if (position == map.dynamicWalls[j].Position){// 停下map.AddWall(blocks);// 随机创建新的方块RandomCratBlock();return false;}}}return true;}#endregion}
}DrawObject
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;namespace 俄罗斯方块
{/// <summary>/// 绘制方块/// </summary>enum E_DrawType{/// <summary>/// 墙壁/// </summary>wall,/// <summary>/// 正方形/// </summary>Cube,/// <summary>/// 长的/// </summary>Line,/// <summary>/// 坦克/// </summary>Tank,/// <summary>/// 左/// </summary>Left_Ladder,/// <summary>/// 右/// </summary>Right_Ladder,/// <summary>/// 左长/// </summary>Left_Long_Ladder,/// <summary>/// 右长/// </summary>Right_Long_Ladder,}internal class DrawObject : IDraw{public Position Position;public E_DrawType type;public DrawObject(E_DrawType type){this.type = type;}public DrawObject(E_DrawType type, int x, int y) : this(type){this.Position = new Position(x, y);}public void Draw(){if (Position.y<0){return;}Console.SetCursorPosition(Position.x, Position.y);switch (type){case E_DrawType.wall:Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Red;break;case E_DrawType.Cube:Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Green;break;case E_DrawType.Line:Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Blue;break;case E_DrawType.Tank:Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Yellow;break;case E_DrawType.Left_Ladder:Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.DarkGray;break;case E_DrawType.Right_Ladder:Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.DarkGray;break;case E_DrawType.Left_Long_Ladder:Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Gray;break;case E_DrawType.Right_Long_Ladder:Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Gray;break;default:break;}Console.Write("卐");}public void ClearDraw(){if (Position.y<0){return;}Console.SetCursorPosition(Position.x, Position.y);Console.Write(" ");}/// <summary>/// 切换方块类型,搬砖掉落到墙壁上转为墙壁/// </summary>public void ChangType(E_DrawType type){this.type = type;}void IDraw.IDraw(){throw new NotImplementedException();}}
}IDraw
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;namespace 俄罗斯方块
{internal interface IDraw{void IDraw();}
}Position
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;namespace 俄罗斯方块
{internal class Position{public int x;public int y;public Position(int x, int y){this.x = x;this.y = y;}public static bool operator ==(Position p1, Position p2) {if (p1.x== p2.x&&p1.y==p2.y){return true;}return false;}public static bool operator !=(Position p1, Position p2){if (p1.x == p2.x && p1.y == p2.y){return false;}return true;}public static Position operator +(Position p1, Position p2){Position position = new Position(p1.x+p2.x,p1.y+p2.y);return position;}}}inputThread
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;namespace 俄罗斯方块
{internal class inputThread{Thread inputThead;public event Action inputEvent;private static inputThread instance = new inputThread();public static inputThread Instance{get { return instance; }}private inputThread(){inputThead = new Thread(InputCheck);inputThead.IsBackground = true;inputThead.Start();}public void InputCheck() {while (true){inputEvent?.Invoke();}}// 线程}
}显示清除最后









![折腾笔记[6]-使用rust绘制三维画面](https://img2024.cnblogs.com/blog/1048201/202501/1048201-20250118233358578-443459944.png)