Java的控制流程
1. Scanner对象
- Java.util.Scanner 是Java5的新特性,我们可以通过Scanner类来获取用户的输入。
- 基本语法: Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in);
- 通过Scanner类的next() 与nextLine()方法获取输入的字符串,在读取我们一般需要 使用 hasNext() 与 hasNextLine() 判断是否还有输入的数据。
- next()
- 一定要读取到有效字符后才可以结束输入
- 对输入有效字符之前的空白,next()方法会自动去掉空格
- 只有输入有效字符之后才将其后面输入的空白作为分隔符或者结束符
- next()不能得到带有空格的字符串
- nextLine()
- 以回车为结束符,也就是说nextLine()方法返回的是输入回车之前的所有字符
- 可以获得空白
- next()
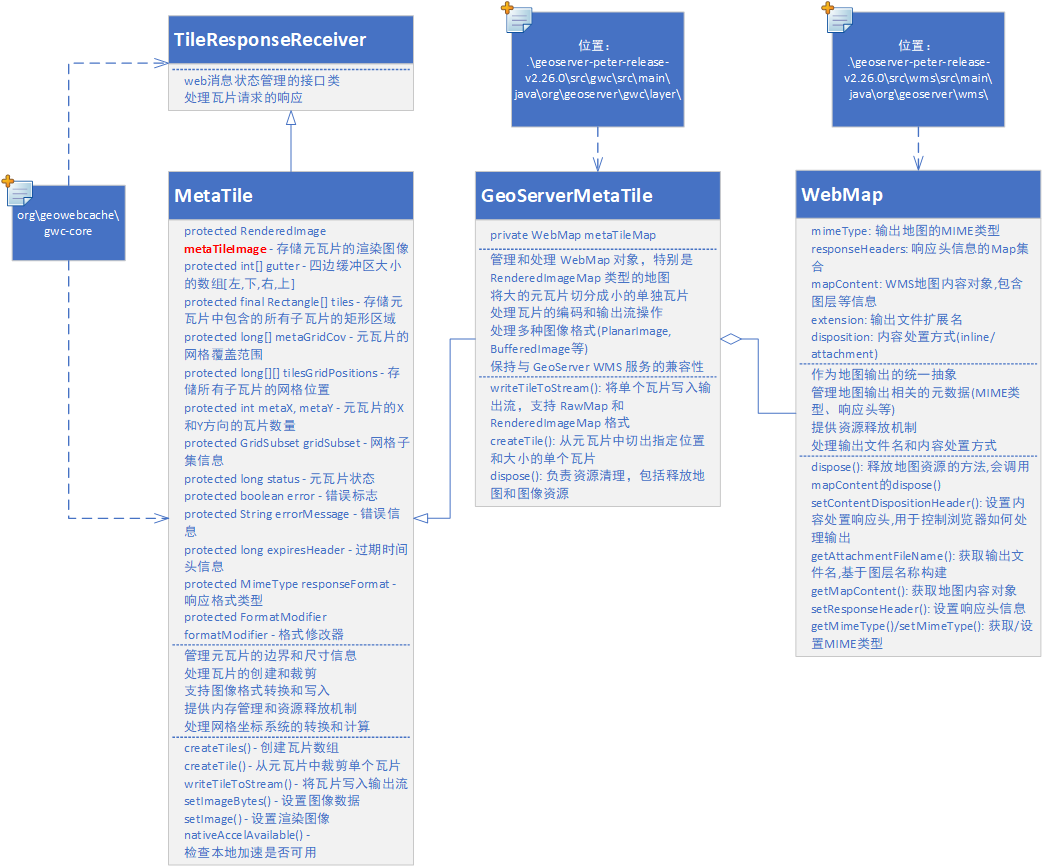
package com.yehuan.scanner;import java.util.Scanner;public class Dome01 {public static void main(String[] args) {//创建一个扫描器对象,用于接收键盘数据Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);System.out.println("使用next方式接收:");//判断用户有没有输入字符串if (scanner.hasNext()){//使用next方式接收String str = scanner.next();//程序会等待用户输入完毕System.out.println("输出的内容是:"+str);}//凡是属于IO流的类如果不关闭会一直占用资源,要养成好习惯用完就关掉。scanner.close();}
}Scanner进阶应用
package com.yehuan.scanner;import java.util.Scanner;public class Dome04 {public static void main(String[] args) {Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);System.out.println("请输入整数:");int i = 0;float f = 0.0f;if(scanner.hasNextInt()){i = scanner.nextInt();System.out.println("您输入的整数数据是:"+i);}else {System.out.println("输入的数据不是整数!");}System.out.println("请输入小数:");if(scanner.hasNextFloat()){f = scanner.nextFloat();System.out.println("您输入的小数数据是:"+f);}else {System.out.println("输入的数据不是小数!");}scanner.close();}
}案例
我们可以输入多个数据,并求其总和与平均数,每输入一个数据用回车确认,通过输入非数字来结束输入并输出执行结果
package com.yehuan.scanner;import java.util.Scanner;public class Dome05 {public static void main(String[] args) {//我们可以输入多个数据,并求其总和与平均数,每输入一个数据用回车确认,通过输入非数字来结束输入并输出执行结果Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);double sum = 0;int m = 0;while (scanner.hasNextDouble()){double x = scanner.nextDouble();m = m + 1;sum = sum + x;System.out.println("你输入了第"+m+"个数据,然后当前结果sum="+sum);}System.out.println(m+"个数据和为"+sum);System.out.println(m+"个数据的平均值为:"+(sum / m));}
}2.顺序结构
- Java的结构就是顺序结构,除非特别指明,否则就按照顺序一句一句执行。
- 顺序结构是最简单的算法结构。
- 语句与语句之间,框与框之间是按照从上到下的顺序进行的,它是由若干个依次执行的处理步骤组成的,它是任何一个算法都离不开的一种基本算法结构。
package com.yehuan.struct;
//顺序结构
public class Dome01 {public static void main(String[] args) {System.out.println("hello1");System.out.println("hello2");System.out.println("hello3");System.out.println("hello4");System.out.println("hello5");}
}按照顺序输出
hello1
hello2
hello3
hello4
hello5
3.选择结构
1.if 单选择结构
package com.yehuan.struct;import java.util.Scanner;
//if 单选择结构
public class IfDome01 {public static void main(String[] args) {Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);System.out.println("请输入内容:");String s = scanner.nextLine();//equals:判断字符串是否相等if(s.equals("Hello")){System.out.println(s);}System.out.println("End");scanner.close();}
}2.if 双选择结构
package com.yehuan.struct;import java.util.Scanner;
//if双选择结构
public class IfDome02 {public static void main(String[] args) {//考试分数大于60分就是及格,否则就是不及格Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);System.out.println("请输入成绩");int score = scanner.nextInt();if(score>60){System.out.println("及格");}else {System.out.println("不及格");}scanner.close();}
}3.if 多选择结构
package com.yehuan.struct;import java.util.Scanner;
//if 多选择结构
public class IfDome03 {public static void main(String[] args) {Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);/** if语句至多有1个else语句,else语句在所有的else if语句之后* if语句可以有若干个else if语句,它们必须在else语句之前* 一旦其中一个else if 语句检测为true ,其它的else if以及else语句都将跳过执行。* */System.out.println("请输入成绩");int score = scanner.nextInt();if(score==100){System.out.println("恭喜满分!");}else if(score<100 && score>=90){System.out.println("A级");}else if(score<90 && score>=80){System.out.println("B级");}else if(score<80 && score>=70){System.out.println("C级");}else if(score<70 && score>=60){System.out.println("D级");}else if(score<60 && score>=0){System.out.println("不及格");}else{System.out.println("成绩不合法");}scanner.close();}
}
4.switch多选择结构
- 多选择结构还有一个实现方式就是switch case语句
- switch case 语句判断一个变量与一系列值中某个是否相等,每个值称为一个分支。
- switch语句中的变量类型中可以是:byte、short、int、char、String(jdk7新特性)
- 通时case标签必须为字符串常量或字面量
案例1:
package com.yehuan.struct;public class SwitchDome01 {public static void main(String[] args) {//case 穿透 //switch 匹配一个具体的值char grade = 'F';switch (grade){case 'A':System.out.println("优秀");break;//可选case 'B':System.out.println("良好");case 'C':System.out.println("及格");break;//可选case 'D':System.out.println("再接再厉");break;//可选case 'E':System.out.println("挂科");break;//可选default:System.out.println("未知");}}
}
案例2:
package com.yehuan.struct;public class SwitchDome02 {public static void main(String[] args) {String name = "夜欢";//JDK7的新特性,表达式结果可以是字符串!!!//字符的本质还是数字//反编译 Java----class(字节码文件) ---- 反编译(IDEA)switch (name){case "秦江":System.out.println("秦江");break;case "夜欢":System.out.println("夜欢");break;default:System.out.println("弄啥咧!");}}
}
4.while循环
语法结构:
while(布尔表达式){
//循环内容
}
- 只要布尔表达式为true,循环就会一直执行下去
- 我们大多数情况是会让循环停止下来的,我们需要一个让表达式失效的方式来结束循环
- 少部分情况需要循环一直执行,比如服务器请求响应监听等
- 当循环条件一直为true时,就会变为死循环
例
package com.yehuan.struct;public class WhileDome02 {public static void main(String[] args) {//计算1加到100int i = 0;int sum = 0;while (i<=100){sum = sum + i;i++;}System.out.println(sum);}
}
do...while循环
-
do...while 循环和while循环相似,不同的是,do...while循环至少会执行一次
do{
//循环内容
}while(布尔表达式)
-
while先判断后执行。do...while是先执行后判断
例;
package com.yehuan.struct;public class DoWhileDome01 {public static void main(String[] args) {int i = 0;int sum = 0;do{sum = sum + i;i++;}while (i<=100);System.out.println(sum);}
}
5.For循环
-
for循环语句是支持迭代的一种通用结构,是最有效、最灵活的循环结构。
-
for循环执行的次数是在执行前就确定的
-
语法格式:
for(初始化;布尔表达式;更新){
//代码语句
}
练习1:计算0到100之间的奇数和偶数的和
package com.yehuan.struct;public class ForDome02 {public static void main(String[] args) {//练习1:计算0到100之间的奇数和偶数的和int oddSum = 0;int evenSum = 0;for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {if(i%2!=0){//奇数oddSum = oddSum + i;}else{//偶数evenSum += i;}}System.out.println(oddSum);System.out.println(evenSum);}
}
练习2:输出1-1000之间能被5整除的数,并且每行输出3个
package com.yehuan.struct;public class ForDome03 {public static void main(String[] args) {//练习2:输出1-1000之间能被5整除的数,并且每行输出3个for (int i = 1; i < 1000; i++) {if(i%5==0){System.out.print(i+"\t");}if(i%(5*3)==0){System.out.println();//System.out.print("\n");}}//println: 输出完会换行//print: 输出完不会换行}
}
练习3:打印九九乘法表
package com.yehuan.struct;public class ForDome04 {public static void main(String[] args) {//练习3:打印九九乘法表for (int j = 1; j <= 9; j++) {for (int i = 1; i <= j; i++) {System.out.print(i+"*"+j+"="+(j*i)+"\t");}System.out.println();}}
}
增强for循环
- 主要用于数组或集合的增强型for循环
- 格式:
for(声明语句 :表达式)
{
//代码句子
}
package com.yehuan.struct;public class ForDemo05 {public static void main(String[] args) {int[] numbers = {10,20,30,40,50};//定义了一个数组for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {System.out.println(numbers[i]);}System.out.println("==============================");//遍历数组的元素for (int x:numbers){System.out.println(x);}}
}
6.break 和 continue
- break在任何循环语句的主题部分,均可以使用break控制循环的流程。break用于强行退出循环,不执行循环中剩余的语句。(break语句也在switch语句中使用)
- continue语句用于终止某次循环,跳过当前这次循环,接着执行下一次循环
(一个辞职一个请假)_
package com.yehuan.struct;public class BreakDome01 {public static void main(String[] args) {int i = 0;while (i<100){i++;System.out.println(i);if(i==30){break;}}System.out.println("123");}
}
package com.yehuan.struct;public class ContinueDome01 {public static void main(String[] args) {int i = 0;while (i<100){i++;if (i%10==0){System.out.println();continue;}System.out.println(i);}}
}
练习:打印三角形
package com.yehuan.struct;public class TestDome01 {public static void main(String[] args) {//打印三角形 5行for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {for (int j = 5; j >= i; j--) {System.out.print(" ");}for (int j = 1; j <= i; j++) {System.out.print("*");}for (int j = 1;j < i ; j++){System.out.print("*");}System.out.println();}}
}







![[日志] 打印异常堆栈信息的技巧](https://blog-static.cnblogs.com/files/johnnyzen/cnblogs-qq-group-qrcode.gif?t=1679679148)