AC截图
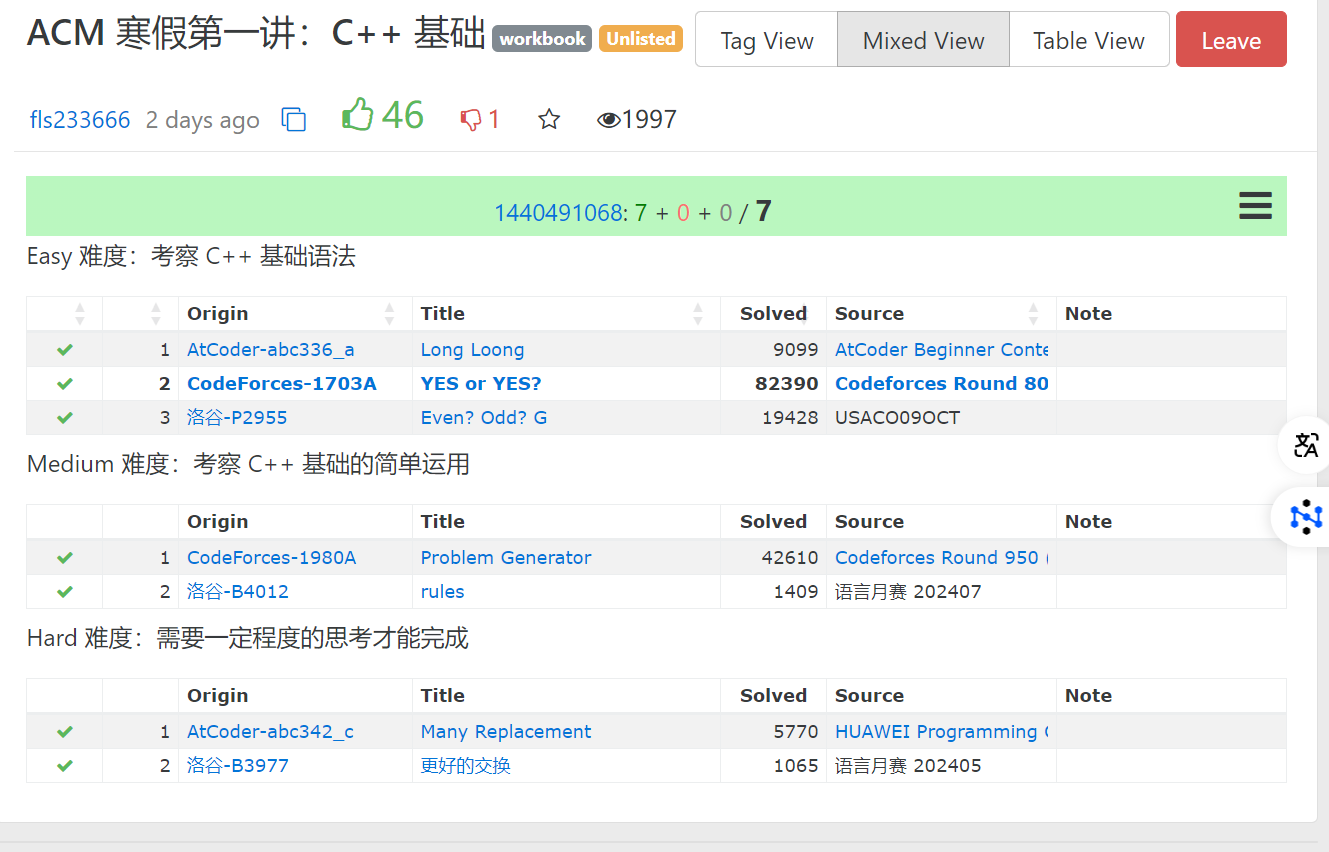
1、Long Loong
本题易知字符串开头为L,结尾为ng,唯一不同的是中间o的个数,于是想到用3个字符串拼接得到目标字符串。(直接用for循环输出似乎更简单)
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;int main()
{int n;cin >> n;string str = "L";string temp(n,'o');str = str + temp + "ng";cout << str << endl;return 0;
}
2、YES or YES?
需要检验的字符串每个只有3字符,因此直接遍历字符串是完全可以的。判断每个对应位字符是否为yes对应字母的大小写,若不是则直接输出no并跳出,若未输出no则输出yes。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;int main()
{ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);int t;cin >> t;string s;while (t--){cin >> s;if (s[0] != 'y' && s[0] != 'Y'){cout << "no" << endl;continue;}if (s[1] != 'e' && s[1] != 'E'){cout << "no" << endl;continue;}if (s[2] != 's' && s[2] != 'S'){cout << "no" << endl;continue;}cout << "yes" << endl;}return 0;
}
3、Even? Odd? G
本题只需要判断奇偶数,但是数据范围达到了10^60,溢出了所有基本数据类型,因此需要使用高精度,用string来接受读入的整数。最后只需要判断字符串最后一位是奇是偶即可。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;int main()
{ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);int n;cin >> n;string num;while (n--){cin >> num;int len = num.size();int t = num[len-1] - '0';if (t % 2 == 0) cout << "even" << endl;else cout << "odd" << endl;}return 0;
}
4、Problem Generator
本题需要知道A到G中还需要添加的题目总数。由于A到G只有7种题目,因此只需使用桶来记录每种题目的出现次数,并与所需轮数进行比较。
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;int cnt[10];int main()
{ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);int t;cin >> t;while (t--){int n,m;string a;cin >> n >> m;cin >> a;memset(cnt,0,sizeof(cnt));for (int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++){int temp = a[i] - 'A' + 1;cnt[temp]++;}long long sum = 0;for (int i = 1 ; i <= 7 ; i++){sum += max(0,m-cnt[i]);}cout << sum << endl; }return 0;
}
5、rules
本题只需要考虑代号k是否在每天中出现半数以上次数。边读入边计数,若k出现次数满足要求,则天数计数器+1,所有数据读入完再判断天数是否满足要求即可。需要注意的是当人数或天数为奇数时,除2时需向上取整。
#include <iostream>
#include <math.h>
using namespace std;int main()
{ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);int n,m,k;cin >> n >> m >> k;int sum = 0;for (int i = 1 ; i <= m ; i++){int cnt = 0; for (int j = 1 ; j <= n ; j++){int t;cin >> t;if (t == k) cnt++;}if (cnt >= ceil(n/2.0)) sum++;} if (sum >= ceil(m/2.0)) cout << "YES" << endl;else cout << "NO" << endl;return 0;
}
6、Many Replacement
直观地按题意模拟复杂度为O(n*q),题目要卡一定超时,考虑优化。由于本题并不关心中间过程字符串长什么样,只需要知道所有替换操作后的字符串,因此每步只需要知道对应字母的变化即可。在每次操作中,将所有指向被替换字母的字母更改为指向替换字母。在所有操作结束后,逐一遍历字符串中的字符,并输出该字符所指向的字母。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;int id[100];int main()
{ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);int n,q;string s;cin >> n >> s >> q;for (int i = 97 ; i <= 122 ; i++) id[i] = i;for (int i = 1 ; i <= q ; i++){char c,d;cin >> c >> d;for (int j = 97 ; j <= 122 ; j++){if (id[j] == c){id[j] = d;}} }for (int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++){cout << (char)id[s[i]];}return 0;
}
7、更好的交换
按题目要求暴力模拟一定超时,仍需要优化。首先想到行列变化是否会互相影响。举了几个例子后,得到行列变化并不会互相影响,于是本题思路就和上一题类似,用数组记录对应位置的行和列是原矩阵中的哪行哪列,每次操作只需要交换这个用于记录的数组。最后遍历矩阵中的每个位置,输出该行该列记录的是原矩阵中的哪一位置即可。
#include <iostream>
#include <unordered_map>
using namespace std;const int N = 1e3 + 10;
int arr[N][N];
int to0[N]; //列
int to1[N]; //行
unordered_map<int,int> mp;int main()
{ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);int n,m;cin >> n >> m;for (int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i++){for (int j = 1 ; j <= n ; j++){cin >> arr[i][j];}}for (int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i++){to0[i] = to1[i] = i;}while (m--){int type,x,y; //0列 1行 cin >> type >> x >> y;if (type == 0){swap(to0[x],to0[y]);}else{swap(to1[x],to1[y]);} }for (int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i++){for (int j = 1 ; j <= n ; j++){int x = to1[i];int y = to0[j];cout << arr[x][y] << " ";}cout << endl;}return 0;
}