目录
一、异常
1.异常概述
1.1认识异常
1.2Java异常体系结构
2.Java异常处理机制
2.1异常处理
2.2捕获异常
2.2.1使用try-catch捕获异常
2.2.2使用try-catch-finally处理异常
2.2.3使用多重catch处理异常
2.3抛出异常
2.3.1使用throws声明抛出异常
2.3.2使用throw抛出异常
2.4自定义异常
2.5异常链
一、异常
1.异常概述
1.1认识异常
异常是指程序在运行过程中出现的非正常情况。
public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) {int i=1,j=0,res;System.out.println("begin");res=i/j;//算术运算异常System.out.println("end");}}
一旦程序发生异常将会立即结束,因此“end”没有输出。
1.2Java异常体系结构
异常在Java中被封装成了各种异常类。
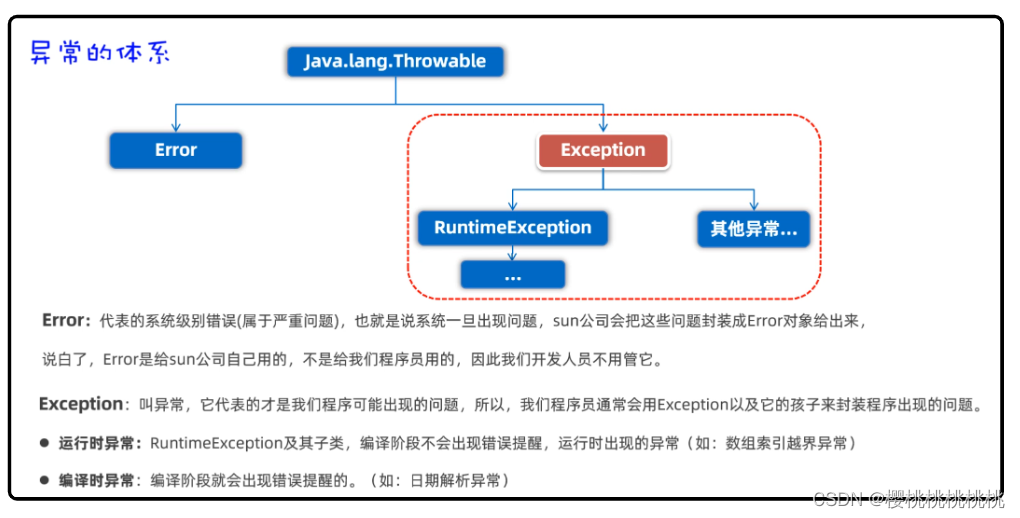
程序中常见的异常:
| Exception | 设计时异常 | 异常层次结构的根类 |
| IOException | 设计时异常 | IO异常的根类,属于非运行时异常 |
| FileNotFoundException | 设计时异常 | 文件操作时,找不到文件 |
| RuntimeException | 运行时异常 | 运行时异常的根类,RuntimeException及其子类,不要求必须处理 |
| ArithmeticException | 运行时异常 | 算术运算异常 |
| lllegalArgumentException | 运行时异常 | 方法接收到非法参数 |
| ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException | 运行时异常 | 数组越界访问异常 |
| NullPointerException | 运行时异常 | 尝试访问null对象的成员时发生的空指针异常 |
| ArrayStoreException | 运行时异常 | 数据存储异常,写数组操作时,对象或数据类型不兼容 |
| ClassCastException | 运行时异常 | 类型转换异常 |
| IIIegalThreadStateException | 运行时异常 | 试图非法改变线程状态,例如试图启动一个已经运行的线程 |
| NumberFormatException | 运行时异常 | 数据格式异常,试图把一字符串非法转换成数值 |
2.Java异常处理机制
2.1异常处理
Java中的异常处理机制依靠5个关键字:try、catch、finally、throw、throws。这些关键字提供了两种异常处理方式:
(1)用try、catch、finally来捕获和处理异常
try块中包含可能会抛出异常的代码
catch块中用户捕获和处理指定类型的异常
finally块中的代码无论是否发生异常都会被执行,通常用于释放资源或清理操作
(2)使用throw、throws来抛出异常
throw关键字用于手动抛出异常对象。
throws关键字用于在方法声明中指定可能抛出的异常类型,表示该方法可能会抛出该类型的异常,由调用者来处理。
2.2捕获异常
2.2.1使用try-catch捕获异常
public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) {try {int i=1,j=0,res;System.out.println("begin");res=i/j;System.out.println("end");}catch (Exception e){System.out.println("caught");e.printStackTrace();}System.out.println("over");}}- 如果try语句块中的所有语句正常执行完毕,没有发生异常,那么catch语句块中的所有语句将被忽略。
- 如果try语句块在执行过程中发生异常,并且这个异常与catch语句块中声明的异常类型匹配,那么try语句块中剩下的代码都将被忽略,相应的catch语句块将会被执行。匹配是指catch中所处理的异常类型与try中发生的异常类型完全一致或者是它的父类。
- 如果try语句块在执行过程中发生异常,而抛出的异常在catch语句块中没有被声明,那么程序立即终止运行,程序被强迫退出。
- catch语句块中可以加入用戶自定义处理信息,也可以调用异常对象的方法输出异常信息,常用的方法如下:
void prinStackTrace() :输出异常的堆栈信息。堆栈信息包括程序运行到当前类的执行流程,它将输出从方法调用处到异常抛出处的方法调用的栈序列。
String getMessage() :返回异常信息描述字符串,该字符串描述了异常产生的原因,是 printStackTrace() 输出信息的一部分。
2.2.2使用try-catch-finally处理异常
无论try块中是否发生异常,finally语句块中的代码总能被执行。
public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) {try {int i=1,j=0,res;System.out.println("begin");res=i/j;System.out.println("end");}catch (ArithmeticException e){System.out.println("caught");e.printStackTrace();}finally {System.out.println("finally");}System.out.println("over");}}- 如果try语句块中所有语句正常执行完毕,程序不会进入catch语句块执行,但是finally语句块会被执行。
- 如果try语句块在执行过程中发生异常,程序会进入到catch语句块捕获异常, finally语句块也会被执行。
- try-catch-finally结构中try语句块是必须存在的,catch、finally语句块为可选,但两者至少出现其中之一。
即使在catch语句块中存在return语句,finally语句块中的语句也会执行。发生异常时的执行顺序是,先执行catch语句块中return之前的语句,再执行finally语句块中的语句,最后执行catch语句块中的return语句退出。
finally语句块中语句不执行的唯一情况是在异常处理代码中执行了 System.exit(1) ,退出Java虚拟机。
public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) {try {int i=1,j=0,res;System.out.println("begin");res=i/j;System.out.println("end");}catch (ArithmeticException e){System.out.println("caught");e.printStackTrace();System.exit(1);}finally {System.out.println("finally");}System.out.println("over");}}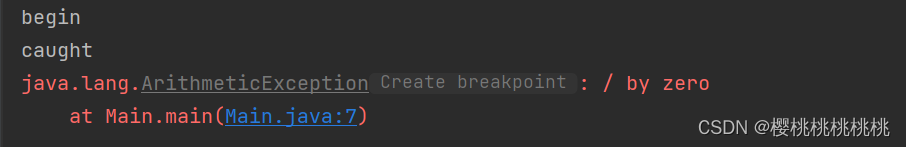
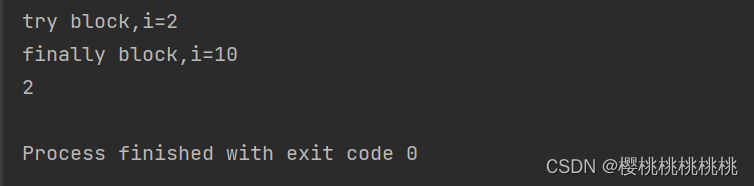
public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) {System.out.println(method());}private static int method() {int i=1;try {i++;//2System.out.println("try block,i="+i);//try block,i=2return i;//2}catch (Exception e){i++;System.out.println("catch block,i="+i);}finally {i=10;System.out.println("finally block,i="+i);//finally block,i=10}return i;}
}
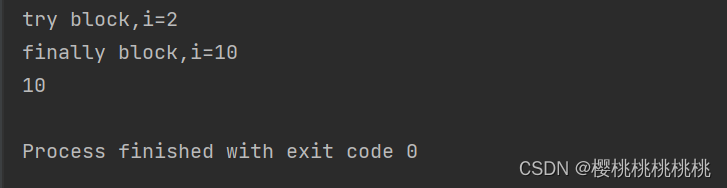
public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) {System.out.println(method());}private static int method() {int i=1;try {i++;System.out.println("try block,i="+i);//try block,i=2return i;}catch (Exception e){i++;System.out.println("catch block,i="+i);return i;}finally {i=10;System.out.println("finally block,i="+i);//finally block,i=10return i;//10}}
}
2.2.3使用多重catch处理异常
catch语句块的排列顺序必须是从子类到父类,最后一个一般是Exception类。这是因为在异常处理中,catch语句块会按照从上到下的顺序进行匹配,系统会检测每个catch语句块处理的异常类型,并执行第一个与异常类型匹配的catch语句块。如果将父类异常放在前面,子类异常的catch语句块将永远不会被执行,因为父类异常的catch语句块已经处理了异常。
一旦系统执行了与异常类型匹配的catch语句块,并执行其中的一条catch语句后,其后的catch语句块将被忽略,程序将继续执行紧随catch语句块的代码。
子类异常应该放在前面,父类异常应该放在后面。
import java.util.InputMismatchException;
import java.util.Scanner;public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) {Scanner input=new Scanner(System.in);try {System.out.println("计算开始:");int i,j,res;System.out.println("请输入被除数:");i=input.nextInt();System.out.println("请输入除数:");j=input.nextInt();res=i/j;System.out.println(i+"/"+j+"="+res);System.out.println("计算结束");}catch (InputMismatchException e){System.out.println("除数和被除数都必须是整数!");}catch (ArithmeticException e){System.out.println("除数不能为0!");}catch (Exception e){System.out.println("其他异常"+e.getMessage());}finally {System.out.println("感谢使用本程序!");}System.out.println("程序结束!");}}第一种:被除数发生异常

第二种:除数发生异常

第三种:除数为0

2.3抛出异常
2.3.1使用throws声明抛出异常
如果在一个方法体内抛出了异常,并希望调用者能够及时地捕获异常,Java语言中通过关键字throws声明某个方法可能抛出的各种异常,以通知调用者。throws可以同时声明多个异常,之间用逗号隔开。
import java.util.InputMismatchException;
import java.util.Scanner;public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) {try {divide();}catch (InputMismatchException e){System.out.println("除数和被除数都必须是整数!");}catch (ArithmeticException e){System.out.println("除数不能为0!");}catch (Exception e){System.out.println("其他异常"+e.getMessage());}finally {System.out.println("感谢使用本程序!");}System.out.println("程序结束!");}private static void divide() throws Exception{Scanner input=new Scanner(System.in);System.out.println("计算开始:");int i,j,res;System.out.println("请输入被除数:");i=input.nextInt();System.out.println("请输入除数:");j=input.nextInt();res=i/j;System.out.println(i+"/"+j+"="+res);System.out.println("计算结束");}}2.3.2使用throw抛出异常
在Java语言中,可以使用throw关键字来自行抛出异常。
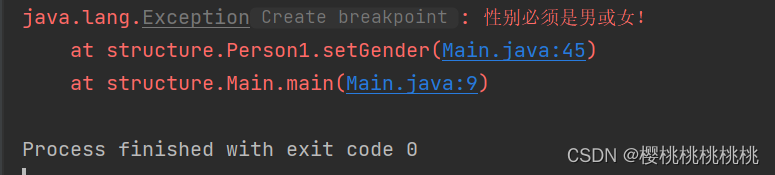
package structure;public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) {Person1 person=new Person1();try {person.setName("扈三娘");person.setAge(18);person.setGender("男女");person.print();}catch (Exception e){e.printStackTrace();}}
}
class Person1{private String name="";private int age=0;private String gender="男";public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public int getAge() {return age;}public void setAge(int age) {this.age = age;}public String getGender() {return gender;}public void setGender(String gender) throws Exception{if ("男".equals(gender)||"女".equals(gender)){this.gender = gender;}else {throw new Exception("性别必须是男或女!");}}public void print(){System.out.println("姓名:"+this.name+"性别:"+this.gender+"年龄:"+this.age);}
}
- 如果 throw 语句抛出的异常是 Checked 异常,则该 throw 语句要么处于 try 块里,显式捕获该异常,要么放在一个带 throws 声明抛出的方法中,即把该异常交给该方法的调用者处理;
- 如果 throw 语句抛出的异常是 Runtime 异常,则该语句无须放在 try 块里,也无须放在带 throws 声明抛出的方法中;程序既可以显式使用 try...catch来捕获并处理该异常,也可以完全不理会该异常,把该异常交给该方法调用者处理。
- 自行抛出Runtime 异常比自行抛出Checked 异常的灵活性更好。同样,抛出 Checked 异常则可以让编译器提醒程序员必须处理该异常。
throw和throws的区别:
1.作用不同:throw用于程序员自行产生并抛出异常,throws用于声明该方法内抛出了异常。
2.使用位置不同:throw位于方法体内部,可以作为单独的语句使用;throws必须跟在方法参数列表的后面,不能单独使用。
3.内容不同:throw抛出一个异常对象,只能是一个;throws后面跟异常类,可以跟多个。
2.4自定义异常
当JDK中的异常类型不能满足程序的需要时,可以自定义异常类。步骤:
①定义异常类,并继承Exception或者RuntimeException。
②编写异常类的构造方法,向父类构造方法传入异常描述信息,并继承父类的其他实现方法。
③实例化自定义异常对象,并在程序中使用throw抛出。
package structure;public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) {Person1 person=new Person1();try {person.setName("扈三娘");person.setAge(18);person.setGender("男女");person.print();}catch (GenderException e){e.printStackTrace();}}
}
//自定义异常类
class GenderException extends Exception{public GenderException(String message){super(message);}
}
class Person1{private String name="";private int age=0;private String gender="男";public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public int getAge() {return age;}public void setAge(int age) {this.age = age;}public String getGender() {return gender;}public void setGender(String gender) throws GenderException{if ("男".equals(gender)||"女".equals(gender)){this.gender = gender;}else {throw new GenderException("性别必须是男或女!");}}public void print(){System.out.println("姓名:"+this.name+"性别:"+this.gender+"年龄:"+this.age);}
}
自定义异常可能是编译时异常,也可能是运行时异常 。
1.如果自定义异常类继承Excpetion,则是编译时异常。
特点:方法中抛出的是编译时异常,必须在方法上使用throws声明,强制调用者处理。
2.如果自定义异常类继承RuntimeException,则运行时异常。
特点:方法中抛出的是运行时异常,不需要在方法上用throws声明。
2.5异常链
有时候我们会捕获一个异常后再抛出另一个异常。
顾名思义就是将异常发生的原因一个传一个串起来,即把底层的异常信息传给上层,这样逐层抛出。
在要抛出的对象中使用 initCause() 方法,添加上一个产生异常的信息; getCause() 可以获取当前异常对象的上一个异常对象。