前面的两篇,从相对比较简单的锁的内容入手(也是干货满满),开始了go的系列。这篇开始,进入更核心的内容。我们知道,go应该是第一门在语言层面支持协程的编程语言(可能是我孤陋寡闻),goroutine也完全算的上是go的门面。golang围绕着goroutine构建了一整套用户态的调度体系,并不断演进至当前的GMP模型。接下来相当的一段时间,我们应该都会在介绍GMP以及调度机制中度过。
本篇呢,我们就从goroutine开始说起。之所以从goroutine开始说起,是因为从我的角度来说,相比M和P,G是最简单的。G完全就是一个用户态的任务,唯一要做的就是记录任务的状态,并管理任务(或者说被管理)。其中管理任务包括,选择一个ready的任务运行、将阻塞的任务挂在到相应的阻塞队列中、将ready的任务移动到就绪队列。
当然,实际的实现远远比这复杂,但不妨碍我们先忽略一些细节,比如gc相关的内容等,先将主干抽离出来,理解其设计主线。
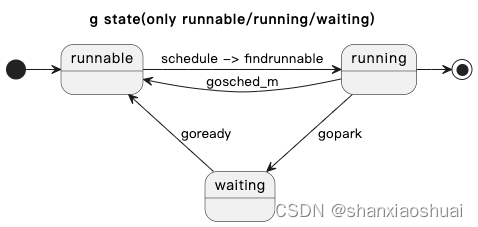
本文的内容主要是围绕下面的状态图,当然里面的内容不够全面。但就像前面说的,先理解主干,更多的细节在完整介绍完GMP后再进行补充。
对象
g
goroutine本质就是一个任务,可以被运行,可以等待,可以被调度。基于此,首先要有一个结构体,记录任务相关的信息。基本的信息包括任务的内容、任务的状态、运行任务所需的资源等。不只goroutine,包括其他一些计算机领域更广为人知的典型的任务,比如进程、线程等,都是如此。不过不同的任务,基于其自身的特性以及各自的迭代又会有特有的字段。
goroutine对应的对象如下。字段看上去不少,但是刨除一些gc、pprof(观测,不确定都是pprof相关)的字段,其实内容并不多,主要如下图所示。接下来我们一一介绍。
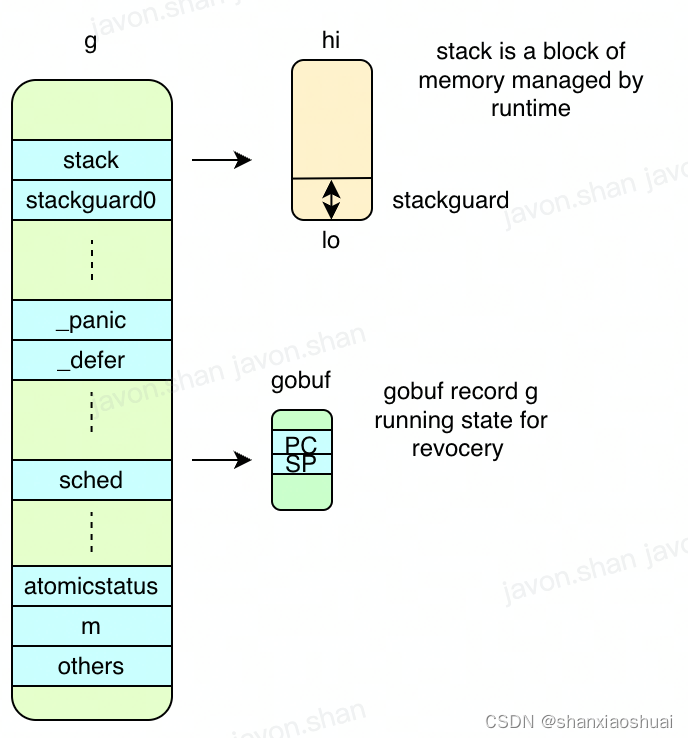
- 栈相关。
stack表示goroutine的栈,栈是一块从高向低增长的线性内存,所以用lo和hi两个指针完全可以表示。
type stack struct {lo uintptrhi uintptr
}
stackguard0的作用是为了判断栈的扩张。
goroutine初始化的时候只会分配固定大小的栈,并且初始化的栈一定不会分配太大(2KB)。当goroutine运行过程中分配的栈内存越来越多,栈向下增长超过lo+StackGuard时就需要对栈进行扩张。同时stackguard0还可以设置为stackPreempt,表示该协程需要被抢占。goroutine检查到stackPreempt后会主动调度退出运行。stackguard0被检查的时机就是在发生函数调用时,所以我们说goroutine主动调度的时机除了阻塞时,就是在函数调用时。
stackguard1的作用和stackguard0的作用完全相同,stackguard1用来做c的栈的判断,这块我是完全不懂。
- _panic和_defer。这是golang的panic和defer特性,其实现是绑定于goroutine的,和我之前想的不一样。后面可以开一篇单独介绍。
- 调度相关。sched字段在goroutine被调度时记录其状态,主要是sp和pc,这两个字段可以记录goroutine的运行状态。
type gobuf struct {sp uintptrpc uintptrg guintptrctxt unsafe.Pointerret uintptrlr uintptrbp uintptr // for framepointer-enabled architectures
}
- 其他。其他的字段比如atomicstatus、goid、m等相对比较简单,就不占篇幅在这里说。
g结构体如下。
// src/runtime2.go 407
type g struct {stack stack // offset known to runtime/cgostackguard0 uintptr // offset known to liblinkstackguard1 uintptr // offset known to liblink_panic *_panic // innermost panic - offset known to liblink_defer *_defer // innermost deferm *m // current m; offset known to arm liblinksched gobufsyscallsp uintptr // if status==Gsyscall, syscallsp = sched.sp to use during gcsyscallpc uintptr // if status==Gsyscall, syscallpc = sched.pc to use during gcstktopsp uintptr // expected sp at top of stack, to check in tracebackparam unsafe.Pointeratomicstatus uint32stackLock uint32 // sigprof/scang lock; TODO: fold in to atomicstatusgoid int64schedlink guintptrwaitsince int64 // approx time when the g become blockedwaitreason waitReason // if status==Gwaitingpreempt bool // preemption signal, duplicates stackguard0 = stackpreemptpreemptStop bool // transition to _Gpreempted on preemption; otherwise, just deschedulepreemptShrink bool // shrink stack at synchronous safe pointasyncSafePoint boolpaniconfault bool // panic (instead of crash) on unexpected fault addressgcscandone bool // g has scanned stack; protected by _Gscan bit in statusthrowsplit bool // must not split stackactiveStackChans boolparkingOnChan uint8// 下面都是观测及gc相关的,可以略过raceignore int8 // ignore race detection eventssysblocktraced bool // StartTrace has emitted EvGoInSyscall about this goroutinetracking bool // whether we're tracking this G for sched latency statisticstrackingSeq uint8 // used to decide whether to track this GrunnableStamp int64 // timestamp of when the G last became runnable, only used when trackingrunnableTime int64 // the amount of time spent runnable, cleared when running, only used when trackingsysexitticks int64 // cputicks when syscall has returned (for tracing)traceseq uint64 // trace event sequencertracelastp puintptr // last P emitted an event for this goroutinelockedm muintptrsig uint32writebuf []bytesigcode0 uintptrsigcode1 uintptrsigpc uintptrgopc uintptr // pc of go statement that created this goroutineancestors *[]ancestorInfo // ancestor information goroutine(s) that created this goroutine (only used if debug.tracebackancestors)startpc uintptr // pc of goroutine functionracectx uintptrwaiting *sudog // sudog structures this g is waiting on (that have a valid elem ptr); in lock ordercgoCtxt []uintptr // cgo traceback contextlabels unsafe.Pointer // profiler labelstimer *timer // cached timer for time.SleepselectDone uint32 // are we participating in a select and did someone win the race?goroutineProfiled goroutineProfileStateHoldergcAssistBytes int64
}
sudog
除了g对象外,goroutine还涉及到sudog的对象。sudog是为了goroutine的阻塞队列而封装的一层对象。sudog的封装在我看来是出于两点考虑:
- 一个goroutine可以阻塞在多个资源上,也就是可能存在于多个阻塞队列中。针对这种情况,做一层封装会简化并发操作,每个sudog都是独属于某个阻塞队列的。
- 阻塞队列本身即具有一定的数据结构,封装sudog可以将阻塞队列的结构和g本身隔离出来,相当于某种程度的分层。例如在之前介绍的golang的sync.Mutex实现中,就涉及到红黑树以及链表的结构。
// src/runtime2.go 338
type sudog struct {g *gnext *sudogprev *sudogelem unsafe.Pointer // data element (may point to stack)acquiretime int64releasetime int64ticket uint32isSelect boolsuccess boolparent *sudog // semaRoot binary treewaitlink *sudog // g.waiting list or semaRootwaittail *sudog // semaRootc *hchan // channel
}
g的调度
goroutine的调度通常涉及到三种情况(最基本的三种):
- goroutine处于running状态,主动调度;
- goroutine处于running状态,遇到阻塞时间,转换为waiting状态,触发调度;
- goroutine处于waiting状态,等待条件达成,转换为runnable状态,等待执行;
主动调度
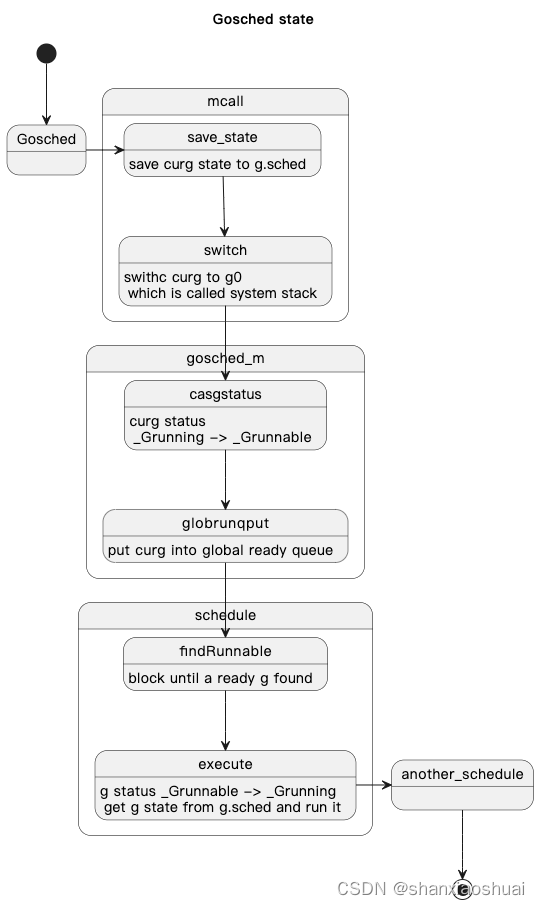
go的runtime包提供了显示调度的方法runtime.Gosched()。
其调用了mcall函数,并将gosched_m函数作为参数传入。
// src/proc.go 316
func Gosched() {checkTimeouts()mcall(gosched_m)
}
先看下mcall函数。mcall是用汇编写的,这里就不贴汇编代码,感兴趣的小伙伴可以自行了解下plan9。从注释里看,mcall做的事情是:
- 将curg的PC/SP保存至g->sched中。g->sched在第一小节中我们也提到过,是goroutine被调度时记录其状态的字段。其中主要是PC/SP两个字段,PC记录当前goroutine执行到哪条指令,SP记录的是栈顶。
- 从curg切换至g0。g0是和每个m绑定的,不会执行用户任务,只执行系统任务。通常也把切换至g0称为切换至系统栈。
- 将curg作为参数传入fn中。fn做的事通常是对curg做一些操作,然后调度至新的goroutine继续执行。实际上,我们上面说的几种调度的情况,只是通过不同的fn参数来实现。
mcall的这种实现实际也是一种代码复用和抽象的小技巧。
再回到gosched_m函数,实际是调用了goschedImpl函数。
goschedImpl中将curg的状态从_Grunning置为_Grunnable,因为这里是主动的调度,当前goroutine并没有被阻塞。
然后将curg和m进行解绑,并将curg塞到全局的阻塞队列中。
然后调用schedule函数。schedule会寻找到一个可执行的g,并切换至起执行。
流程图如下。

// Gosched continuation on g0.
func gosched_m(gp *g) {if trace.enabled {traceGoSched()}goschedImpl(gp)
}func goschedImpl(gp *g) {status := readgstatus(gp)if status&^_Gscan != _Grunning {dumpgstatus(gp)throw("bad g status")}casgstatus(gp, _Grunning, _Grunnable)dropg()lock(&sched.lock)globrunqput(gp)unlock(&sched.lock)schedule()
}
schedule是很核心的函数,行数也比较多。我们还是忽略一些细节(细节的部分我们在m和p都有一定的了解后再来补充),抽出主干,代码如下。
找到一个可执行的g,然后运行。
// src/proc.go 3185
// One round of scheduler: find a runnable goroutine and execute it.
// Never returns.
func schedule() {_g_ := getg()gp, inheritTime, tryWakeP := findRunnable() // blocks until work is availableexecute(gp, inheritTime)
}
execute会中会做状态的转换,然后运行gogo。gogo的参数是g->sched,gogo同样是汇编实现,其直接设置pc及sp将执行流切换至g。
func execute(gp *g, inheritTime bool) {_g_ := getg()_g_.m.curg = gpgp.m = _g_.mcasgstatus(gp, _Grunnable, _Grunning)gp.waitsince = 0gp.preempt = falsegp.stackguard0 = gp.stack.lo + _StackGuardif !inheritTime {_g_.m.p.ptr().schedtick++}gogo(&gp.sched)
}
goroutine阻塞
当goroutine运行遇到需要等待某些条件时,就会进入等待状态。将当前goroutine挂载到相应的阻塞队列,并触发调度。schedule的内容同上面没有变化,可见schedule是调度的核心,不同的调度方法只是在封装了在不同场景下的细节 。流程图如下。
func gopark(unlockf func(*g, unsafe.Pointer) bool, lock unsafe.Pointer, reason waitReason, traceEv byte, traceskip int) {if reason != waitReasonSleep {checkTimeouts() // timeouts may expire while two goroutines keep the scheduler busy}mp := acquirem()gp := mp.curgstatus := readgstatus(gp)if status != _Grunning && status != _Gscanrunning {throw("gopark: bad g status")}mp.waitlock = lockmp.waitunlockf = unlockfgp.waitreason = reasonmp.waittraceev = traceEvmp.waittraceskip = traceskipreleasem(mp)// can't do anything that might move the G between Ms here.mcall(park_m)
}
// park continuation on g0.
func park_m(gp *g) {_g_ := getg()if trace.enabled {traceGoPark(_g_.m.waittraceev, _g_.m.waittraceskip)}casgstatus(gp, _Grunning, _Gwaiting)dropg()if fn := _g_.m.waitunlockf; fn != nil {ok := fn(gp, _g_.m.waitlock)_g_.m.waitunlockf = nil_g_.m.waitlock = nilif !ok {if trace.enabled {traceGoUnpark(gp, 2)}casgstatus(gp, _Gwaiting, _Grunnable)execute(gp, true) // Schedule it back, never returns.}}schedule()
}
goroutine就绪
goroutine从等待状态转变为就绪状态应该是最简单的,因为其不涉及调度。只是将g的状态改变,并将g从阻塞队列移动至当前的就绪队列。流程图如下。
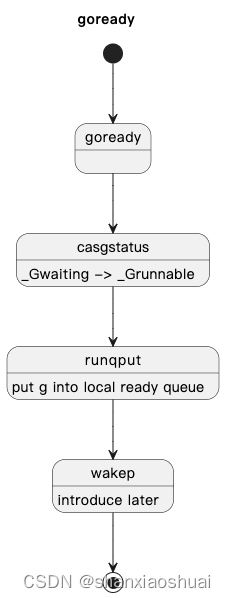
唯一有点意思的点在于wakep。wakep的作用是 当有新的g就绪,而当前系统的负载又很低时,确保有m和p来及时的运行g。这个后面在m和p的部分回详细介绍。
func goready(gp *g, traceskip int) {systemstack(func() {ready(gp, traceskip, true)})
}
// Mark gp ready to run.
func ready(gp *g, traceskip int, next bool) {if trace.enabled {traceGoUnpark(gp, traceskip)}status := readgstatus(gp)// Mark runnable._g_ := getg()mp := acquirem() // disable preemption because it can be holding p in a local varif status&^_Gscan != _Gwaiting {dumpgstatus(gp)throw("bad g->status in ready")}// status is Gwaiting or Gscanwaiting, make Grunnable and put on runqcasgstatus(gp, _Gwaiting, _Grunnable)runqput(_g_.m.p.ptr(), gp, next)wakep()releasem(mp)
}
本篇呢,对goroutine的介绍肯定不算面面俱到。毕竟,抛开M和P来讲G是很难讲全的。但是,我相信,读过本篇一定会对goroutine建立基本的认知。这种认知不够细节,但一定足够本质。就像文章开头说的,goroutine就是一个用户态的任务。我们自己其实也可以很轻易的实现一个任务管理的系统,这本质上就没有区别。当然,goroutine具备了很多的go的特性,肯定是复杂的多。




![[maven]关于pom文件中的<relativePath>标签](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/115b4b8e909c4a2a83fe5dd16f9f3944.png)