Kafka 生产者
发送流程
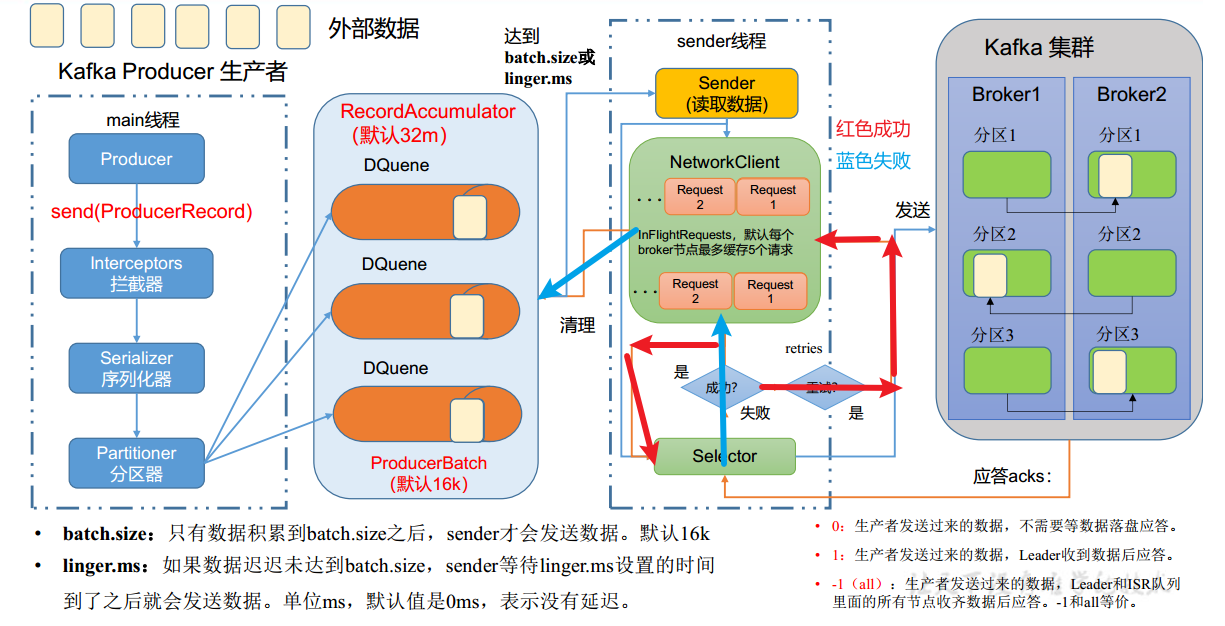
消息发送过程中涉及到两个线程——main线程和Sender线程
main线程
-
使用serializer(并非java默认)序列化数据,使用partitioner确认发送分区
-
在main线程中创建了一个双端队列RecordAccumulator,main线程将批次数据发送给RecordAccumulator。创建批次数据是从内存池中分配内存,在发送成功后释放到内存池
-
Sender线程不断从RecordAccumulator中拉取消息发送给kafka Broker
-
一个分区创建一个DQuene,在内存中完成RecordAccumulator(缓冲队列)的创建(总大小默认32M),每批次大小默认16K
sender线程
-
数据到达batch.size护着linger.ms之后,sender线程开始发送数据
-
sender创建请求队列(每个broker一个),默认最多缓存5个请求
-
发送完成后等待broker的ack应答
- 0,表示不需要等待落盘
- 1,表示等待leader收到数据后应答
- -1(all),表示等待leader和ISR队列中的所有节点收到数据后应答
-
发送成功则sender清除队列,并清理RecordAccumulator中每一个分区的数据,失败则重试再次发送
生产者相关参数
-
bootstrap.servers ,连接的broker清单
-
key.serializer 和 value.serializer,指定发送消息的 key 和 value 的序列化类型
-
buffer.memory RecordAccumulator,缓冲区总大小,默认 32m
-
batch.size 缓冲区一批数据最大值,默认 16k。适当增加该值,可 以提高吞吐量,但是如果该值设置太大,会导致数据 传输延迟增加。
-
linger.ms,如果数据迟迟未达到 batch.size,sender 等待 linger.time 之后就会发送数据。单位 ms,默认值是 0ms,表示没 有延迟。生产环境建议该值大小为 5-100ms 之间。
-
acks
-
0:生产者发送过来的数据,不需要等数据落盘应答。
-
1:生产者发送过来的数据,Leader 收到数据后应答。
-
-1(all):生产者发送过来的数据,Leader+和 isr 队列 里面的所有节点收齐数据后应答。默认值是-1,-1 和 all 是等价的。
-
-
max.in.flight.requests.per.connection,允许最多没有返回 ack 的次数,默认为 5,开启幂等性要保证该值是 1-5 的数字。
-
retries,当消息发送出现错误的时候,系统会重发消息。
- retries 表示重试次数。默认是 int 最大值,2147483647。
- 如果设置了重试,还想保证消息的有序性,需要设置 MAX_IN_FLIGHT_REQUESTS_PER_CONNECTION=1 否则在重试此失败消息的时候,其他的消息可能发送 成功了。
-
retry.backoff.ms,两次重试之间的时间间隔,默认是 100ms。
-
enable.idempotence,是否开启幂等性,默认 true,开启幂等性。
-
compression.type,生产者发送的所有数据的压缩方式。默认是 none,也 就是不压缩。 支持压缩类型:none、gzip、snappy、lz4 和 zstd。
异步发送
异步发送指的是外部数据向RecordAccumulator发送数据的过程
不带回调的异步发送
maven依赖
<dependency><groupId>org.apache.kafka</groupId><artifactId>kafka-clients</artifactId><version>3.0.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency><groupId>org.slf4j</groupId><artifactId>slf4j-simple</artifactId><version>1.7.25</version><scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
发送demo
import java.util.Properties;
import org.apache.kafka.clients.producer.KafkaProducer;
import org.apache.kafka.clients.producer.ProducerConfig;
import org.apache.kafka.clients.producer.ProducerRecord;
import org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringSerializer;public class CustomerProducer {public static void main(String[] args) {//创建配置对象Properties properties = new Properties();properties.put(ProducerConfig.BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS_CONFIG, "master:9092,slave1:9092");//key,value序列化properties.put(ProducerConfig.KEY_SERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG, StringSerializer.class.getName());properties.put(ProducerConfig.VALUE_SERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG, StringSerializer.class.getName());//创建kafka对象KafkaProducer<String, String> kafkaProducer = new KafkaProducer<>(properties);//发送数据for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {kafkaProducer.send(new ProducerRecord<>("first", "hello" + i));}kafkaProducer.close();}
}
带回调函数的异步发送
回调函数会在producer收到ack时调用,有两个参数
- 元数据信息(RecordMetadata)和异常信息(Exception)
- 如果 Exception 为 null,说明消息发 送成功,如果 Exception 不为 null,说明消息发送失败
- 回调中获取的metadata来自于
RecordAccumulator
import java.util.Properties;
import org.apache.kafka.clients.producer.Callback;
import org.apache.kafka.clients.producer.KafkaProducer;
import org.apache.kafka.clients.producer.ProducerConfig;
import org.apache.kafka.clients.producer.ProducerRecord;
import org.apache.kafka.clients.producer.RecordMetadata;
import org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringSerializer;public class CustomerProducerCallback {public static void main(String[] args) {//创建配置对象Properties properties = new Properties();properties.put(ProducerConfig.BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS_CONFIG, "master:9092,slave1:9092");//key,value序列化properties.put(ProducerConfig.KEY_SERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG, StringSerializer.class.getName());properties.put(ProducerConfig.VALUE_SERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG, StringSerializer.class.getName());// tls 连接// properties.put("security.protocol", "SSL");// properties.put("sasl.mechanism", "SCRAM-SHA-512");//创建kafka对象KafkaProducer<String, String> kafkaProducer = new KafkaProducer<>(properties);//发送数据for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {kafkaProducer.send(new ProducerRecord<>("first", "hello" + i), new Callback() {@Overridepublic void onCompletion(RecordMetadata recordMetadata, Exception e) {if (e == null){System.out.println("topic:"+recordMetadata.topic()+" partition:"+recordMetadata.partition());}}});}kafkaProducer.close();}
}output:
[main] INFO org.apache.kafka.clients.producer.ProducerConfig - ProducerConfig values: acks = -1batch.size = 16384bootstrap.servers = [localhost:9092, localhost:9092]buffer.memory = 33554432client.dns.lookup = use_all_dns_ipsclient.id = producer-1compression.type = noneconnections.max.idle.ms = 540000delivery.timeout.ms = 120000enable.idempotence = trueinterceptor.classes = []key.serializer = class org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringSerializerlinger.ms = 0max.block.ms = 60000max.in.flight.requests.per.connection = 5max.request.size = 1048576metadata.max.age.ms = 300000metadata.max.idle.ms = 300000metric.reporters = []metrics.num.samples = 2metrics.recording.level = INFOmetrics.sample.window.ms = 30000partitioner.class = class com.example.MyPartitionerreceive.buffer.bytes = 32768reconnect.backoff.max.ms = 1000reconnect.backoff.ms = 50request.timeout.ms = 30000retries = 2147483647retry.backoff.ms = 100sasl.client.callback.handler.class = nullsasl.jaas.config = nullsasl.kerberos.kinit.cmd = /usr/bin/kinitsasl.kerberos.min.time.before.relogin = 60000sasl.kerberos.service.name = nullsasl.kerberos.ticket.renew.jitter = 0.05sasl.kerberos.ticket.renew.window.factor = 0.8sasl.login.callback.handler.class = nullsasl.login.class = nullsasl.login.refresh.buffer.seconds = 300sasl.login.refresh.min.period.seconds = 60sasl.login.refresh.window.factor = 0.8sasl.login.refresh.window.jitter = 0.05sasl.mechanism = GSSAPIsecurity.protocol = PLAINTEXTsecurity.providers = nullsend.buffer.bytes = 131072socket.connection.setup.timeout.max.ms = 30000socket.connection.setup.timeout.ms = 10000ssl.cipher.suites = nullssl.enabled.protocols = [TLSv1.2, TLSv1.3]ssl.endpoint.identification.algorithm = httpsssl.engine.factory.class = nullssl.key.password = nullssl.keymanager.algorithm = SunX509ssl.keystore.certificate.chain = nullssl.keystore.key = nullssl.keystore.location = nullssl.keystore.password = nullssl.keystore.type = JKSssl.protocol = TLSv1.3ssl.provider = nullssl.secure.random.implementation = nullssl.trustmanager.algorithm = PKIXssl.truststore.certificates = nullssl.truststore.location = nullssl.truststore.password = nullssl.truststore.type = JKStransaction.timeout.ms = 60000transactional.id = nullvalue.serializer = class org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringSerializer[main] INFO org.apache.kafka.common.utils.AppInfoParser - Kafka version: 3.0.0
[main] INFO org.apache.kafka.common.utils.AppInfoParser - Kafka commitId: 8cb0a5e9d3441962
[main] INFO org.apache.kafka.common.utils.AppInfoParser - Kafka startTimeMs: 1687969802272
[kafka-producer-network-thread | producer-1] INFO org.apache.kafka.clients.Metadata - [Producer clientId=producer-1] Cluster ID: MqCwKFtET36BCuCusypwCg
[main] INFO org.apache.kafka.clients.producer.KafkaProducer - [Producer clientId=producer-1] Closing the Kafka producer with timeoutMillis = 9223372036854775807 ms
topic:first partition:0
topic:first partition:0
topic:first partition:0
topic:first partition:0
topic:first partition:0
同步发送
外部数据发送到RecordAccumulator之后,需要等到全部发送到kafka集群才会发送下一批
public class CustomerProducerSync {public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {//创建配置对象Properties properties = new Properties();properties.put(ProducerConfig.BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS_CONFIG, "master:9092,slave1:9092");//key,value序列化properties.put(ProducerConfig.KEY_SERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG, StringSerializer.class.getName());properties.put(ProducerConfig.VALUE_SERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG, StringSerializer.class.getName());//创建kafka对象KafkaProducer<String, String> kafkaProducer = new KafkaProducer<>(properties);//发送数据for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {kafkaProducer.send(new ProducerRecord<>("first", "hello" + i)).get(); //添加get即成为同步发送}kafkaProducer.close();}
}
生产者分区策略
生产者为什么要分区
-
便于合理使用存储资源, 每个Partition在一个Broker上存储, 可以把海量的数据按照分区切割成一块一块数据存储在多台Broker上。 合理控制分区的任务, 可以实现负载均衡的效果。
-
提高并行度, 生产者可以以分区为单位发送数据;消费者可以以分区为单位进行消费数据。
DefaultPartitioner,默认分区器的策略
if partition is specified in th record, use it
if no partition is specified but a key is present choose a partition based on a hash of the key
if no partition or key is present choose the sticky partition that changes when the batch is full
对于PreducerRecord类,存在多种构造方法
- 如果指定partition,则发送到对应分区
- 如果未指定partition,但是指定key,通过将key的hash和topic的partition数进行取余得到partition的值
- 未指定partition和key,采用sticky partition(黏性分区),即随机选择一个分区并尽可能保持使用该分区。等到此分区的batch已满(到达16K)或者已完成,再随机选择一个分区(和上一次不同)使用
自定义分区器如下
public class MyPartitioner implements Partitioner {@Overridepublic int partition(String s, Object key, byte[] bytes, Object value, byte[] bytes1, Cluster cluster) {int partition;String v = value.toString();if(v.contains("hello"))partition = 1;else partition = 0;return partition;}@Overridepublic void close() {}@Overridepublic void configure(Map<String, ?> map) {}
}//在CustomerProducer中添加配置信息
properties.put(ProducerConfig.PARTITIONER_CLASS_CONFIG,MyPartitioner.class.getName());
生产者提升吞吐量
- batch.size 设置批次大小,默认16k
- linger.ms 等待时间默认为0(batchsize不起作用),修改为5-100ms
- compression.type 压缩数据
- RecordAccumulator 缓冲区大小默认32m,修改为64m,但是太大会导致较高的延迟
//在CustomerProducer中添加配置信息,在输出的日志中都能看到
// batch.size: 批次大小, 默认 16K
properties.put(ProducerConfig.BATCH_SIZE_CONFIG,16384);
// linger.ms: 等待时间,默认 0
properties.put(ProducerConfig.LINGER_MS_CONFIG,1);
// RecordAccumulator: 缓冲区大小, 默认 32M: buffer.memory
properties.put(ProducerConfig.BUFFER_MEMORY_CONFIG,33554432);
//默认none,可配置gzip,snappy,lz4,zstd
properties.put(ProducerConfig.COMPRESSION_TYPE_CONFIG,"snappy");
数据的可靠性
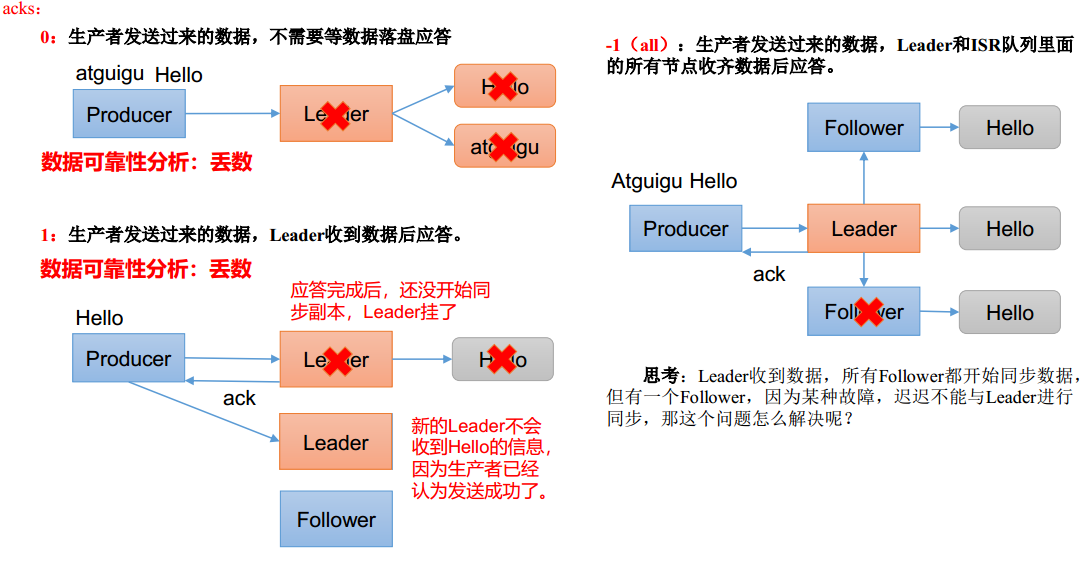
ACK应答级别
https://kafka.apache.org/documentation/#producerconfigs_acks
-
ack = 0,leader数据不落盘就应答。此时如果leader故障,内存中的数据会丢失,生产环境不适用
-
ack = 1,leader数据落盘但没有同步到follower就应答,常用于传输日志
-
ack = -1,leader数据落盘并等待同步到所有follower在应答,和钱相关可靠性要求比较高的场景
ISR对列
对于ack为-1的情况,如果leader收到数据,所有follower开始同步数据,但某个follower出现故障迟迟不能回复,如何解决?
- leader维护了一个动态的in-sync replica set(ISR),即和leader保持同步的follwer-leader集合(leader:0, isr:0,1,2)
- 如果follower长时间未向leader发送通信请求或同步数据,follower将被提出ISR,时间阈值由replica.lag.time.max.ms参数设定,默认30s
数据可靠性分析
- 实际上,如果分区副本设置为1,或者ISR应答的最小副本数量为1(min.insync.replicas默认为1),和ack=1的效果一样,仍然有丢失数据的风险
数据完全可靠条件 = A C K 级别设置为 − 1 + 分区副本大于等于 2 + I S R 中应答的最小副本数大于等于 2 数据完全可靠条件 = ACK级别设置为-1+分区副本大于等于2+ISR中应答的最小副本数大于等于2 数据完全可靠条件=ACK级别设置为−1+分区副本大于等于2+ISR中应答的最小副本数大于等于2
//在CustomerProducer中添加配置信息,在输出的日志中都能看到
// 设置 acks
properties.put(ProducerConfig.ACKS_CONFIG,1);
// 重试次数 retries,默认是 int 最大值, 2147483647
properties.put(ProducerConfig.RETRIES_CONFIG,3);
数据重复分析
对于ack=-1的配置,如果leader收到数据并同步到follower之后,但是还没有进行应答,突然宕机。此时会选举新的leader,producer会发送同样的数据造成数据重复

数据传递语义
-
至少一次(at least once)
ACK级别设置为-1+分区副本 >= 2+ISR中应答的最小副本数>=2- 至少一次(at least once)保证数据不丢失,但不保证数据不重复
-
最多一次(at most once)
- ACK为 0
- 最多一次(at most once)保证数据不重复,但是不保证数据不丢
-
精确一次(exactly once):
开启幂等性+至少一次(ACK级别设置为-1+分区副本>=2+ISR中应答的最小副本数>=2)
幂等性
幂等性能够保证无论producer向broker发送多少数据,始终保证broker只持久化一条数据
精确一次 ( e x a c t l y o n c e ) = 幂等性 + 至少一次 ( A C K ( − 1 ) + 分区副本 > = 2 + I S R 中应答的最小副本数 > = 2 ) 精确一次(exactly once) = 幂等性 + 至少一次(ACK(-1)+分区副本>=2+ISR中应答的最小副本数>=2) 精确一次(exactlyonce)=幂等性+至少一次(ACK(−1)+分区副本>=2+ISR中应答的最小副本数>=2)
幂等性判断重复数据的标准,具有<PID,partition,seqnumber>相同主键的消息提交时,broker只会持久化一条,其中的PID是kafka每次重启都会分配新的,partition表示分区号,sequence number单调递增
-
幂等性只能保证单分区单会话内不重复,kafka重启后pid会重置
-
开启参数enable.Idempotence,默认开启为true,kafka在内存中直接将重复的数据删除

重启之后还是可能产生重复数据,需要使用生产者事务
事务原理
由于幂等性只能保证在单分区和会话保证数据不重复,因此需要事务的来实现
- 开启事务,必须开启幂等性
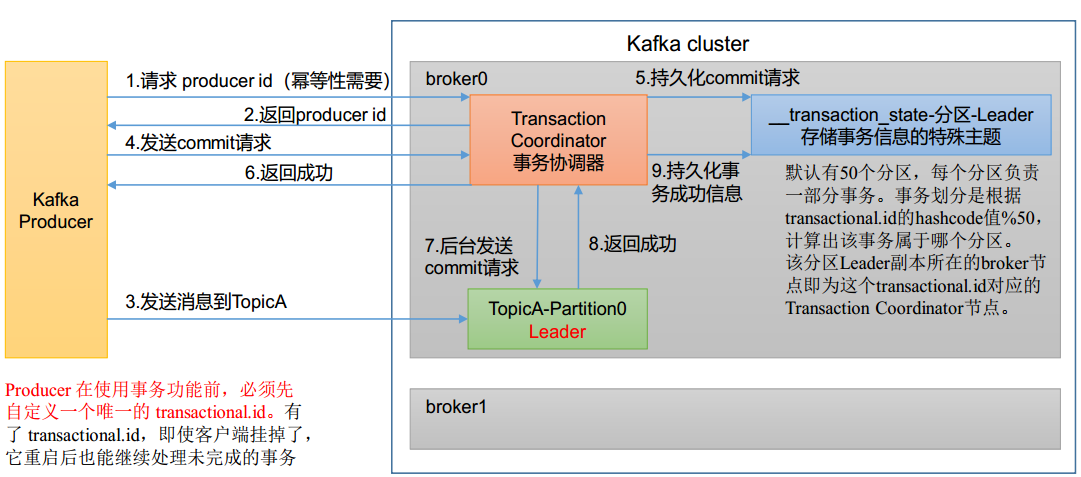
kafka事务的api
// 1 初始化事务
void initTransactions();
// 2 开启事务
void beginTransaction() throws ProducerFencedException;
// 3 在事务内提交已经消费的偏移量(主要用于消费者)
void sendOffsetsToTransaction(Map<TopicPartition, OffsetAndMetadata> offsets,
String consumerGroupId) throws
ProducerFencedException;
// 4 提交事务
void commitTransaction() throws ProducerFencedException;
// 5 放弃事务(类似于回滚事务的操作)
void abortTransaction() throws ProducerFencedException;
使用事务保证消息的仅一次发送
//重要:手动指定事务id
properties.put(ProducerConfig.TRANSACTIONAL_ID_CONFIG,"transaction_id_0");
//创建kafka对象
KafkaProducer<String, String> kafkaProducer = new KafkaProducer<>(properties);
kafkaProducer.initTransactions();
kafkaProducer.beginTransaction();
try {for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {kafkaProducer.send(new ProducerRecord<>("first", "world" + i), new Callback() {@Overridepublic void onCompletion(RecordMetadata recordMetadata, Exception e) {if (e == null) {System.out.println("topic:" + recordMetadata.topic() + " partition:" + recordMetadata.partition());}}}).get();}//发送数据kafkaProducer.commitTransaction();
} catch (Exception e) {kafkaProducer.abortTransaction();
} finally {kafkaProducer.close();
}
数据有序
- producer在不同分区内产生数据,无法保证有序
- 单分区内,有序(有条件)
- 多分区,分区之间无序。多分区有序,需要在comsumer端收到所有数据后进行整体重排序
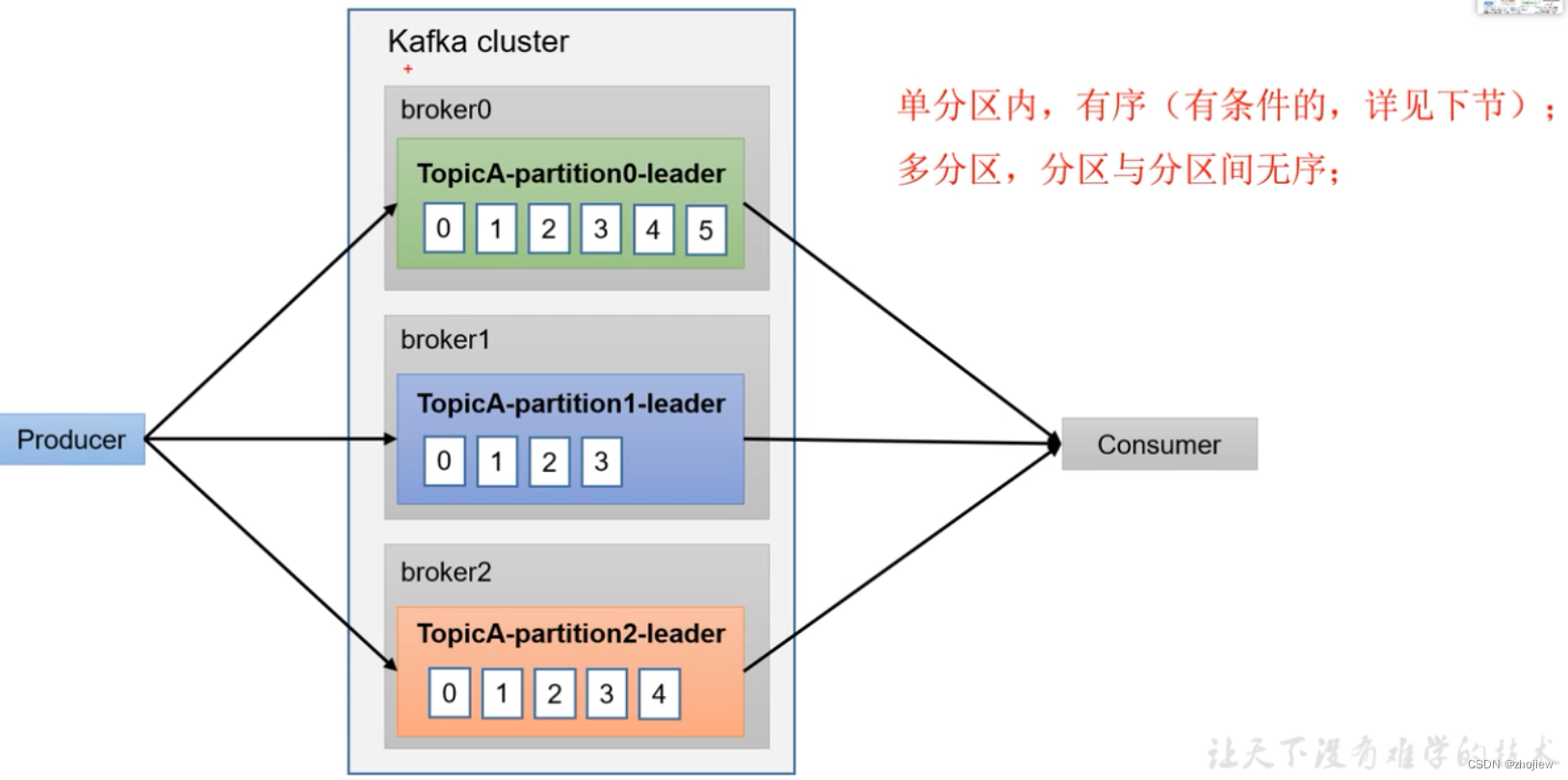
数据乱序
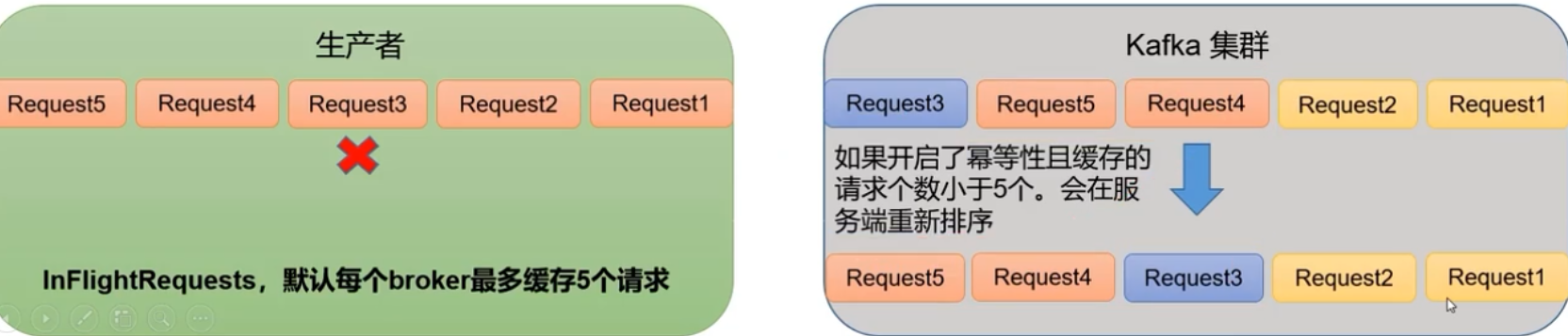
kafka在1.x版本之前保证数据单分区有序,条件是max.in.flight.requests.per.connection =1(不需要考虑幂等性)
kafka在1.x版本之后
-
未开启幂等性,
max.in.flight.requests.per.connection =1 -
开启幂等性,
max.in.flight.requests.per.connection <= 5。原因:开启幂等性后kafka服务端会缓存producer发来的最近5个request的元数据,通过重新排序来保证有序