(1)92反转链表–中等
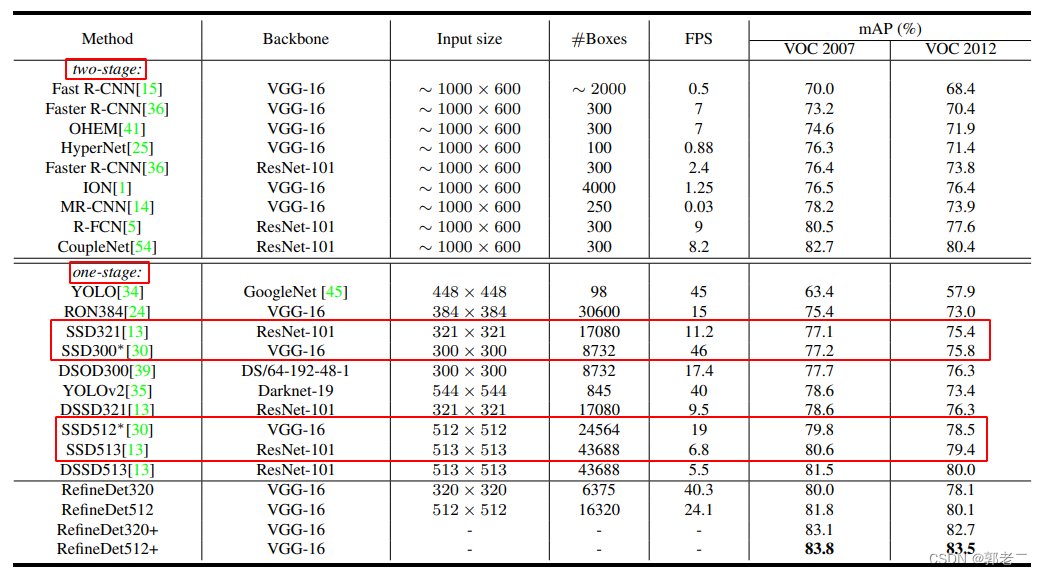
给你单链表的头指针 head 和两个整数 left 和 right ,其中 left <= right 。请你反转从位置 left 到位置 right 的链表节点,返回 反转后的链表 。
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* ListNode *next;* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}* };*/
class Solution {
public:ListNode* reverseBetween(ListNode* head, int left, int right) {ListNode* new_head = NULL;ListNode* next = head;ListNode* pre_head = NULL;ListNode* latter_head = NULL;ListNode* reversed_first_node = NULL;int count = 1;while(head){if(left == right) return head;else if(count < left){pre_head = next;next = next->next;count += 1;}else if (left <= count && count < right){//逆置的长度如果只有1的话,就不需要逆置//从最左边开始,没有pre_headif(left == count) reversed_first_node = next;if(left != 1) pre_head->next = next->next;else head = next->next;next->next = new_head;new_head = next;if(left == 1) next = head;else next = pre_head->next;count+=1;}else if (count == right){latter_head = next->next;if (left != 1) pre_head->next = latter_head;next->next=new_head;new_head = next;next = latter_head;//逆置完成,开始拼接if (left != 1) pre_head->next = new_head;reversed_first_node->next = latter_head;break;}}return head;}
};

(2)160相交链表–简单
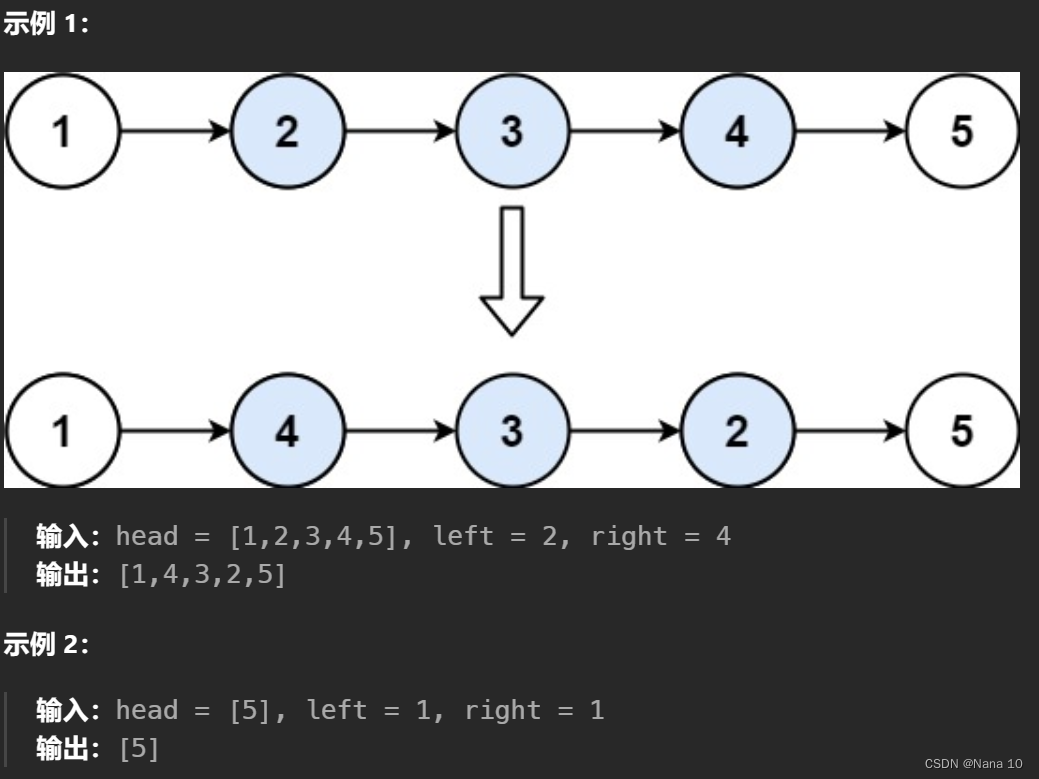
给你两个单链表的头节点 headA 和 headB ,请你找出并返回两个单链表相交的起始节点。如果两个链表不存在相交节点,返回 null 。
```cpp
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* ListNode *next;* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}* };*/
#include<iostream>
class Solution {
public:ListNode *getIntersectionNode(ListNode *headA, ListNode *headB) {if(headA == NULL or headB == NULL) return NULL;//_a标志从哪个点开始相同//_b标志正在检查哪个点ListNode* A_a = headA;ListNode* A_b = headA;ListNode* B_a = headB;ListNode* B_b = headB;//计算A和B的长度,方便末端对齐int count_A = 1;int count_B = 1;while(A_a){A_a = A_a->next;count_A++;}while(B_a){B_a = B_a->next;count_B++;}A_a = headA;B_a = headB;if(count_A > count_B){int len = count_A - count_B;while(len){A_a = A_a->next;len--;}A_b = A_a;}else if(count_A < count_B){int len = count_B - count_A;while(len){B_a = B_a->next;len--;}B_b = B_a;}cout<< A_a->val<< endl;cout<< B_a->val<< endl;//到此,两链表已经末端对齐while(A_b){//注意,是数值相等,不是指针相等if(A_b != B_b){A_a=A_b->next;A_b=A_b->next;B_a=B_b->next;B_b=B_b->next;}else{A_b = A_b->next;B_b = B_b->next;}}//cout<< A_a->val<< endl;return A_a;}
};

(3)142环形链表二–中等
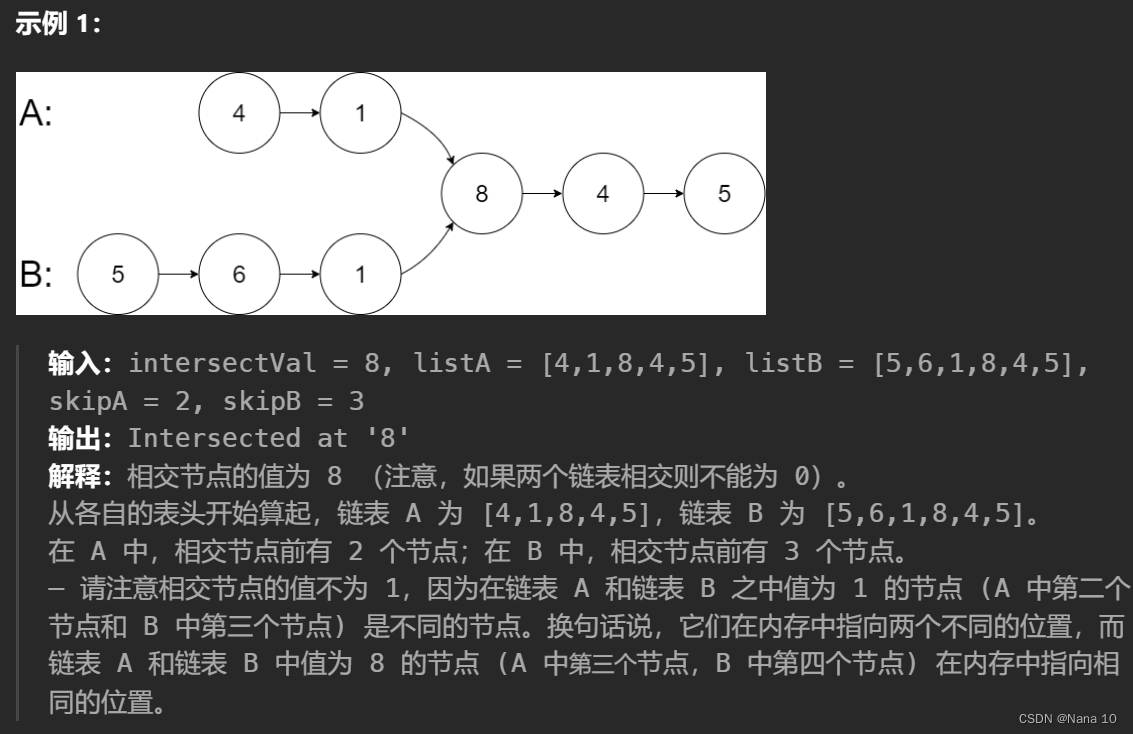
给定一个链表的头节点 head ,返回链表开始入环的第一个节点。 如果链表无环,则返回 null。
如果链表中有某个节点,可以通过连续跟踪 next 指针再次到达,则链表中存在环。 为了表示给定链表中的环,评测系统内部使用整数 pos 来表示链表尾连接到链表中的位置(索引从 0 开始)。如果 pos 是 -1,则在该链表中没有环。注意:pos 不作为参数进行传递,仅仅是为了标识链表的实际情况。
不允许修改 链表。
法一:利用集合
#include<iostream>
class Solution {
public:ListNode *detectCycle(ListNode *head) {std::set<ListNode*> nodeSet;if(head == NULL || head->next == NULL ) return NULL;while(head){//cout<< head->val << endl;//在集合的非最后一个元素处找到该节点,则说明已经加过该节点,则该点为循环的起始点if(nodeSet.find(head) != nodeSet.end())return head;nodeSet.insert(head);head = head->next;}return NULL;}
};

法二:快慢指针赛跑
就像跑800,如果有环,快指针肯定能再一次相遇慢指针。
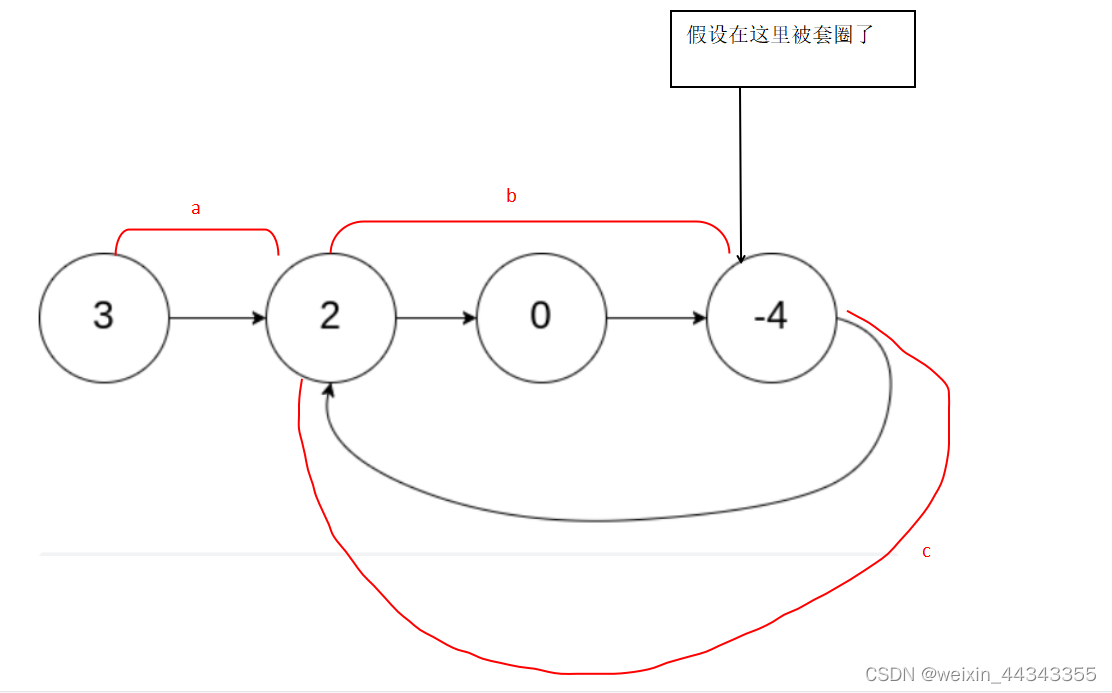
假设快指针每次走两步,慢指针每次走一步
在相同时间内,快指针走的距离是慢指针的两倍
a:起始点到环开始点的距离
b:环开始点到相遇点的距离
c:相遇点到环开始点的距离
快指针跑过的距离:a+b+c+b
慢指针跑过的距离:a+b
所以,a+b+c+b = 2*(a+b)
即:a = c
也就是说,从开始点和快慢指针相遇点一起开始向前走,一次走一格,如果到达了同一个点,即环开始的点
#include<iostream>
class Solution {
public:ListNode *detectCycle(ListNode *head) {if(head == NULL || head ->next == NULL) return NULL;//初始点位指向头结点ListNode* fastPoint = head->next->next;if(fastPoint == NULL) return NULL;cout<< fastPoint->val<< endl;//fastPoint = ;ListNode* slowPoint= head->next;//cout<<slowPoint->val<<endl;//slowPoint = head;while(fastPoint){//找到了相遇点就退出循环if(slowPoint == fastPoint) break;//快指针每次走两步,慢指针每次走一步slowPoint = slowPoint ->next;if(fastPoint -> next)fastPoint = fastPoint -> next -> next;else return NULL;}//cout<<slowPoint->val<<endl;if(fastPoint == NULL) return NULL;//如果走到了尽头,则说明没有环fastPoint = head;//*tmpPoint->next = &head;//tmpPoint回到头,开始以慢指针的速度开始走//两指针未相遇,就一直往前走while(fastPoint != slowPoint){fastPoint = fastPoint->next;slowPoint = slowPoint->next;}return slowPoint;}
};
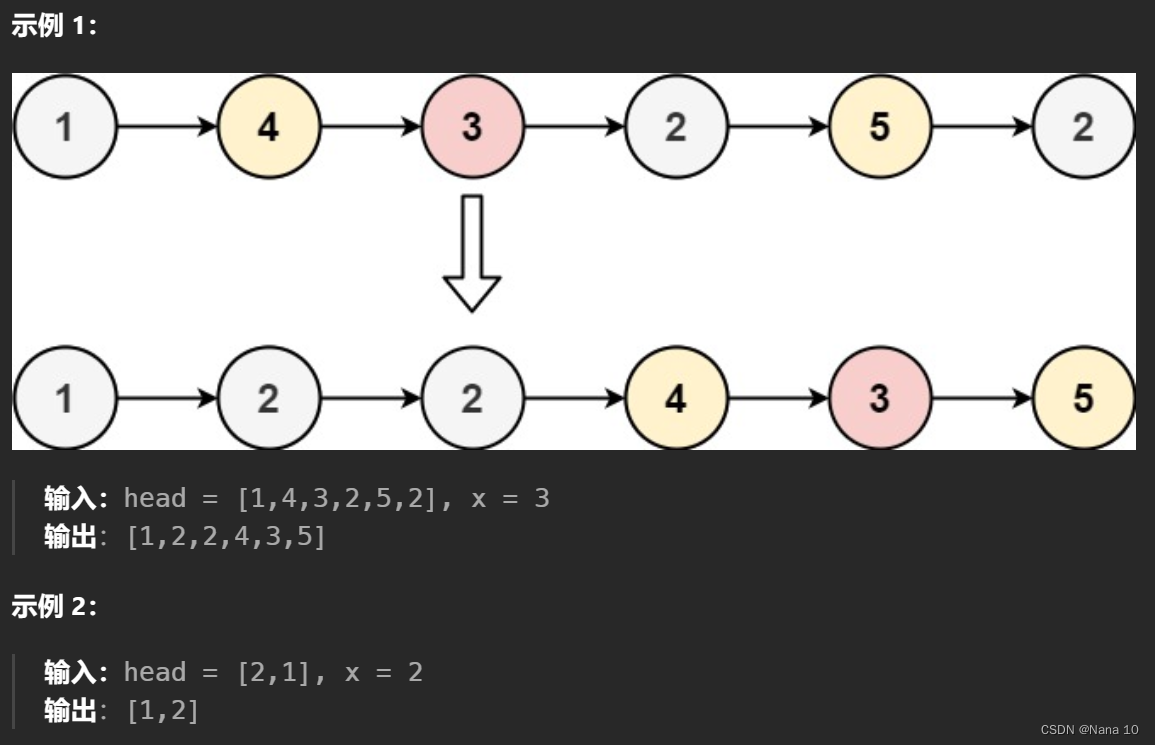
(4)86分隔链表–中等
给你一个链表的头节点 head 和一个特定值 x ,请你对链表进行分隔,使得所有 小于 x 的节点都出现在 大于或等于 x 的节点之前。
你应当 保留 两个分区中每个节点的初始相对位置。
class Solution {
public:ListNode* partition(ListNode* head, int x) {if(head == NULL || head->next ==NULL) return head;//设置两个临时头结点ListNode lessHead(0);ListNode moreHead(0);//对应指针分别指向这两个临时头结点ListNode* lessptr = &lessHead;ListNode* moreptr = &moreHead;while(head){//比x大的插入到moreptr后if(head->val>= x){moreptr->next = head;moreptr = head;}//比x小的插入到lessptr后else{lessptr->next = head;lessptr = head;}head = head->next;}//两个链表相连lessptr->next = moreHead.next;moreptr->next = NULL;return lessHead.next;}
};
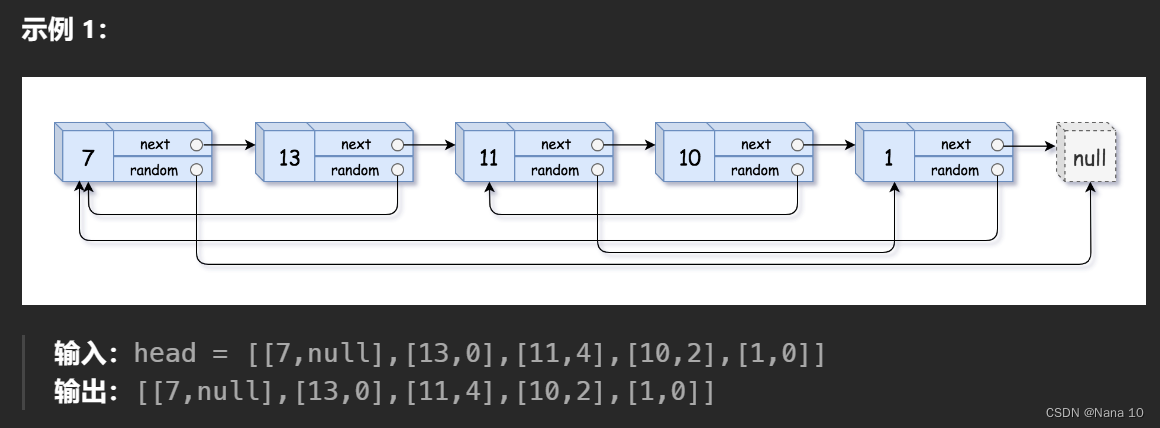
(5)138复制带随机指针的链表–中等
给你一个长度为 n 的链表,每个节点包含一个额外增加的随机指针 random ,该指针可以指向链表中的任何节点或空节点。
构造这个链表的 深拷贝。 深拷贝应该正好由 n 个 全新 节点组成,其中每个新节点的值都设为其对应的原节点的值。新节点的 next 指针和 random 指针也都应指向复制链表中的新节点,并使原链表和复制链表中的这些指针能够表示相同的链表状态。复制链表中的指针都不应指向原链表中的节点 。
例如,如果原链表中有 X 和 Y 两个节点,其中 X.random --> Y 。那么在复制链表中对应的两个节点 x 和 y ,同样有 x.random --> y 。
返回复制链表的头节点。
用一个由 n 个节点组成的链表来表示输入/输出中的链表。每个节点用一个 [val, random_index] 表示:
val:一个表示 Node.val 的整数。
random_index:随机指针指向的节点索引(范围从 0 到 n-1);如果不指向任何节点,则为 null 。
你的代码 只 接受原链表的头节点 head 作为传入参数。
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:Node* copyRandomList(Node* head) {vector<Node*> node_vec;//位置到节点的映射map<Node*, int> node_map;//地址到位置的映射Node* ptr = head;int i = 0;while(ptr){//生成新节点,放入列表node_vec.push_back(new Node(ptr->val));node_map[ptr] = i;i++;ptr = ptr->next;}node_vec.push_back(NULL);ptr= head;i=0;while(ptr){//新节点依次相连node_vec[i]->next = node_vec[i+1];if(ptr->random){//通过map,找出random到位置的映射int node = node_map[ptr->random];node_vec[i]->random = node_vec[node];}else node_vec[i]->random = NULL;ptr = ptr->next;i++;}return node_vec[0];}
};

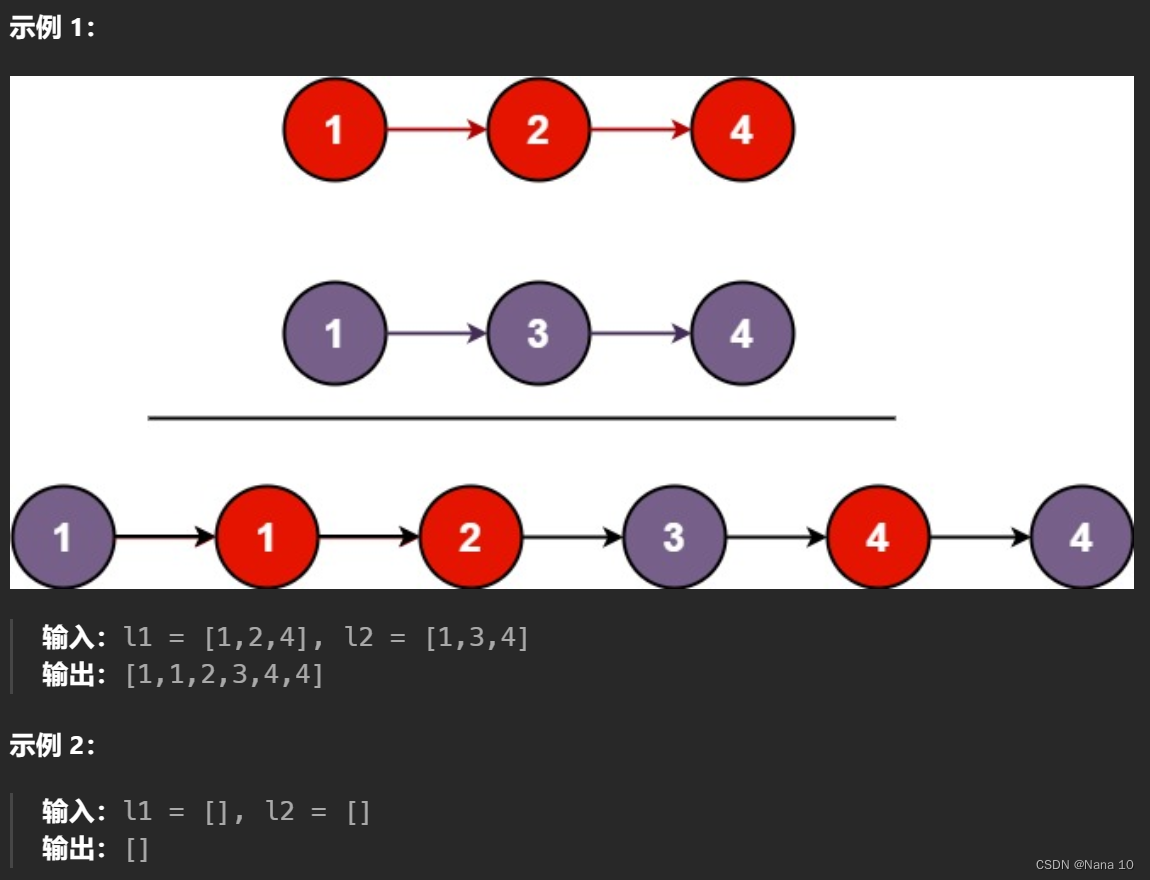
(6)21合并两个有序链表–简单
将两个升序链表合并为一个新的 升序 链表并返回。新链表是通过拼接给定的两个链表的所有节点组成的。
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* ListNode *next;* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}* };*/
class Solution {
public:ListNode* mergeTwoLists(ListNode* list1, ListNode* list2) {if(list1 == NULL ) return list2;if(list2 == NULL ) return list1;//设置一个头结点ListNode newnode(0);//newnode->val = 0;ListNode* newnodeHead = &newnode;//取两链表头结点,较小者插入新链表while(list1&&list2){if(list1->val <= list2->val){newnodeHead ->next = list1;list1 = list1->next;}else{newnodeHead ->next = list2;list2 = list2->next;}newnodeHead = newnodeHead->next;newnodeHead->next = NULL;}//将未空的链表直接接到新链表后if(list1 !=NULL){newnodeHead->next = list1;}else if(list2 !=NULL){newnodeHead->next = list2;}return newnode.next;}};

(7)23合并k个升序表–困难
给你一个链表数组,每个链表都已经按升序排列。
请你将所有链表合并到一个升序链表中,返回合并后的链表。

法一、二
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* ListNode *next;* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}* };*/#include<iostream>
class Solution {
public://自定义比较函数//如果不加static//非static成员函数在经过编译后编译器会他们添加一个this指针参数//变成bool cmp(Solution *this, const ListNode* a,const ListNode*b)//而标准库的sort()函数的第三个cmp函数指针参数中并没有这样this指针参数,因此会出现//cmp参数和sort()要求的参数不匹配,从而导致://error: reference to non-static member function must be called//static静态类成员函数是不需要this指针的,因此改为静态成员函数即可通过static bool cmp(const ListNode* a,const ListNode*b){return a->val < b->val;}ListNode* mergeKLists(vector<ListNode*>& lists) {//if (lists.size() == 0) return NULL;//else if (lists[0] == NULL&& lists.size() == 1) return NULL;//假设链表长度为n,有k个链表//方式1:链表两两合并//时间复杂度为:(n+n)+(2n+n)+...+((k-1)*n+n) = O(k^2*N)=O(kn*k)//方式2:放入vector中,将vector排序,再将各个节点相连//时间复杂度为:O(kn*logkn)//当kn很大的时候,logkn小于kvector<ListNode*> points;ListNode* ptr = NULL;int listsLength = lists.size();for(int i = 0; i<listsLength; i++){ptr = lists[i];while(ptr){points.push_back(ptr);//cout<<ptr->val<<endl;ptr = ptr->next;}}if(points.size() == 0) return NULL;std::sort(points.begin(),points.end(),cmp);listsLength = points.size();for(int i = 0; i<listsLength-1; i++){points[i]->next = points[i+1];}points[listsLength-1]->next = NULL;return points[0];}
};

法三:分治
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* ListNode *next;* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}* };*/#include<iostream>
class Solution {
public://法三,时间复杂度为O(kn*logkn),链表较长时便可看出效率ListNode* mergeTowLists(ListNode* a,ListNode*b){if(a == NULL) return b;if(b == NULL) return a;ListNode newhead(0);ListNode* ptr = &newhead;while(a&&b){if(a->val<=b->val){ptr->next = a;a = a->next;ptr = ptr->next;}else{ptr->next = b;b= b->next;ptr = ptr->next;}}if(a) ptr->next = a;else ptr->next = b;return newhead.next;}ListNode* mergeKLists(vector<ListNode*>& lists) {if (lists.size() == 0) return NULL;else if (lists.size() == 1) return lists[0];else if (lists.size() == 2) return mergeTowLists(lists[0],lists[1]);int mid = lists.size()/2;vector<ListNode*> sub_list1;vector<ListNode*> sub_list2;for(int i = 0; i< mid; i++) sub_list1.push_back(lists[i]);for(int i = mid; i< lists.size(); i++) sub_list2.push_back(lists[i]);ListNode* l1 = mergeKLists(sub_list1);ListNode* l2 = mergeKLists(sub_list2);return mergeTowLists(l1,l2);}
};