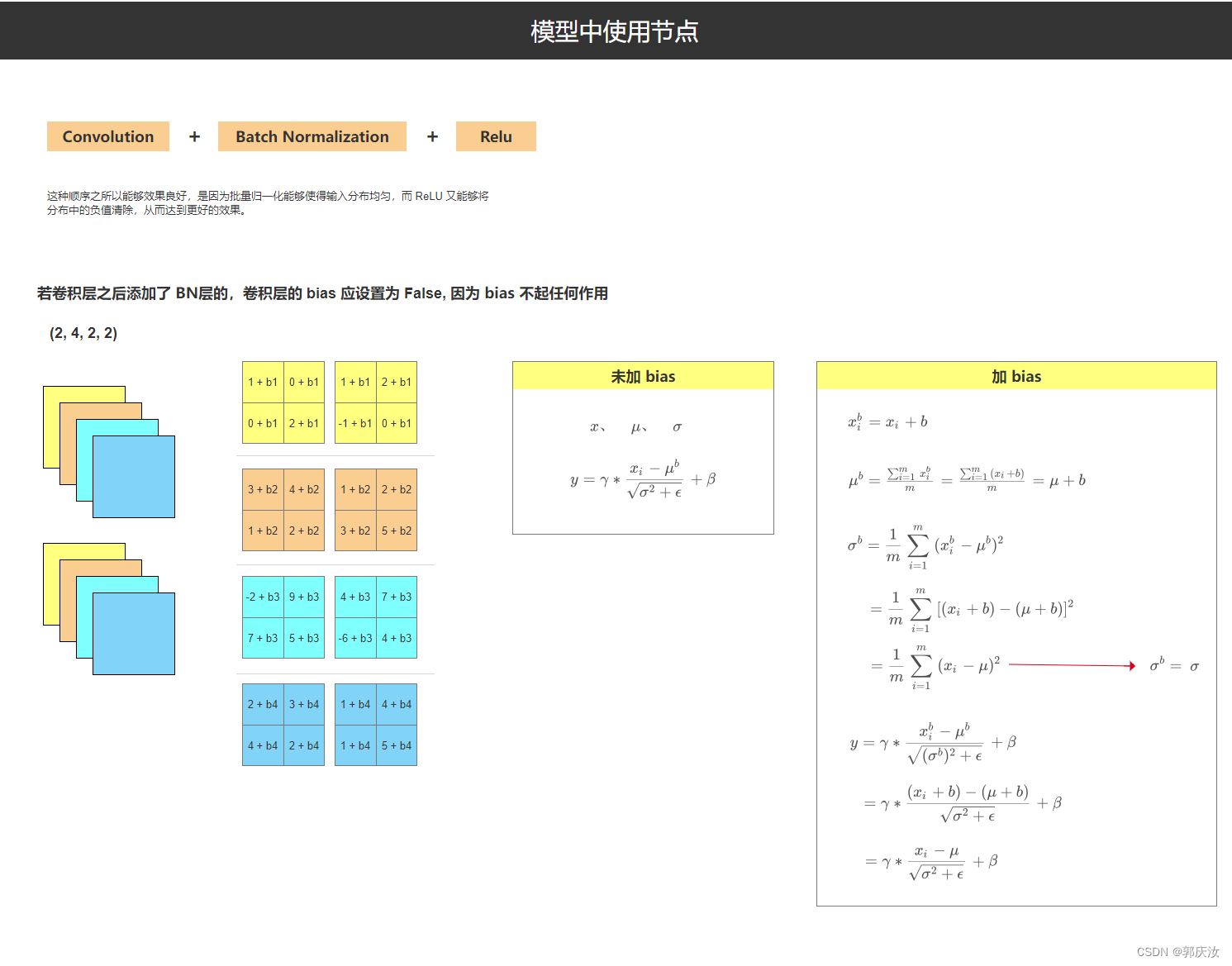
深度学习基础知识 Batch Normalization的用法解析

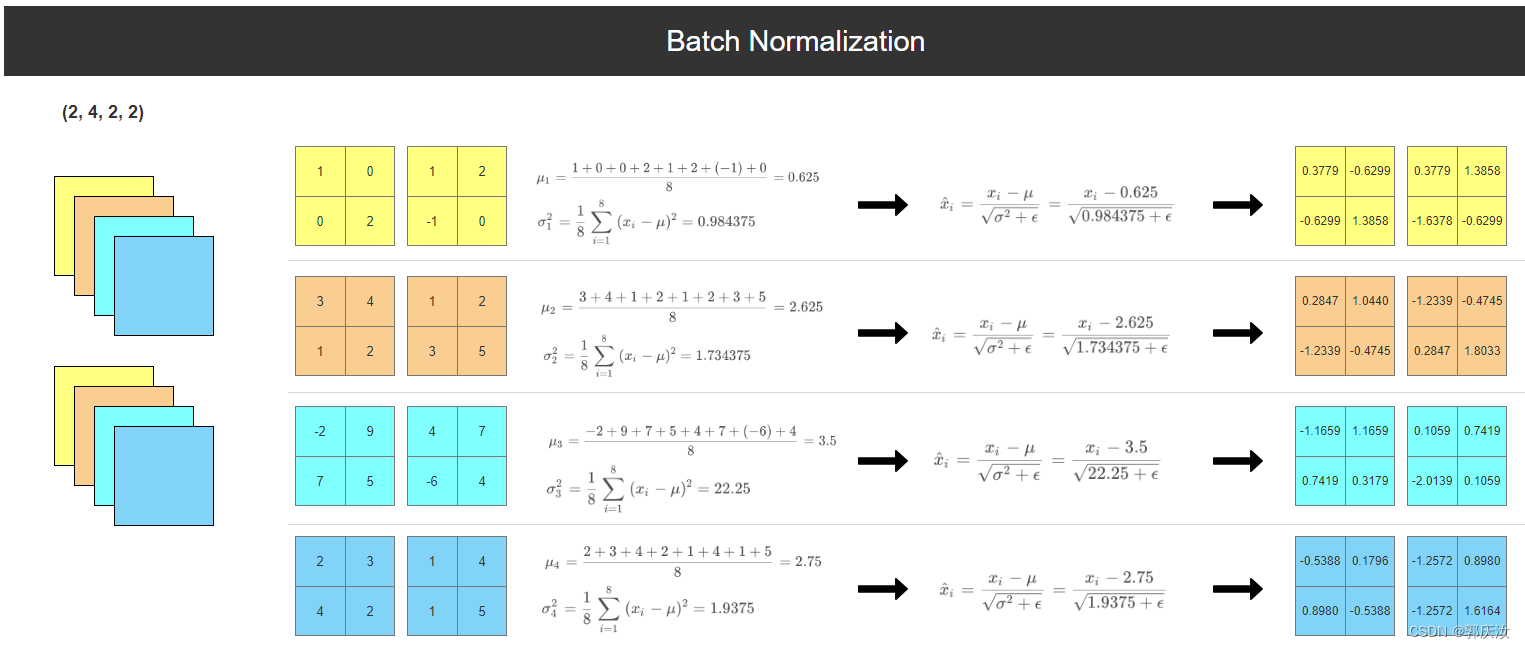
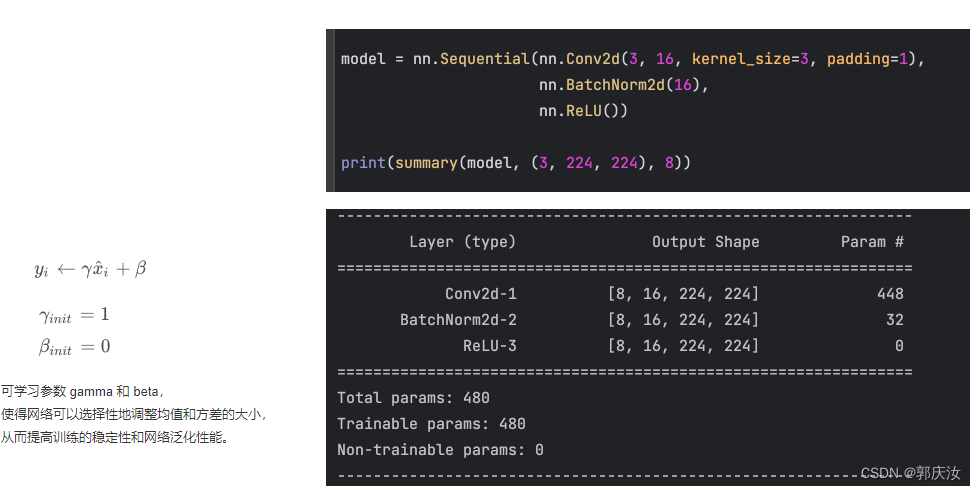
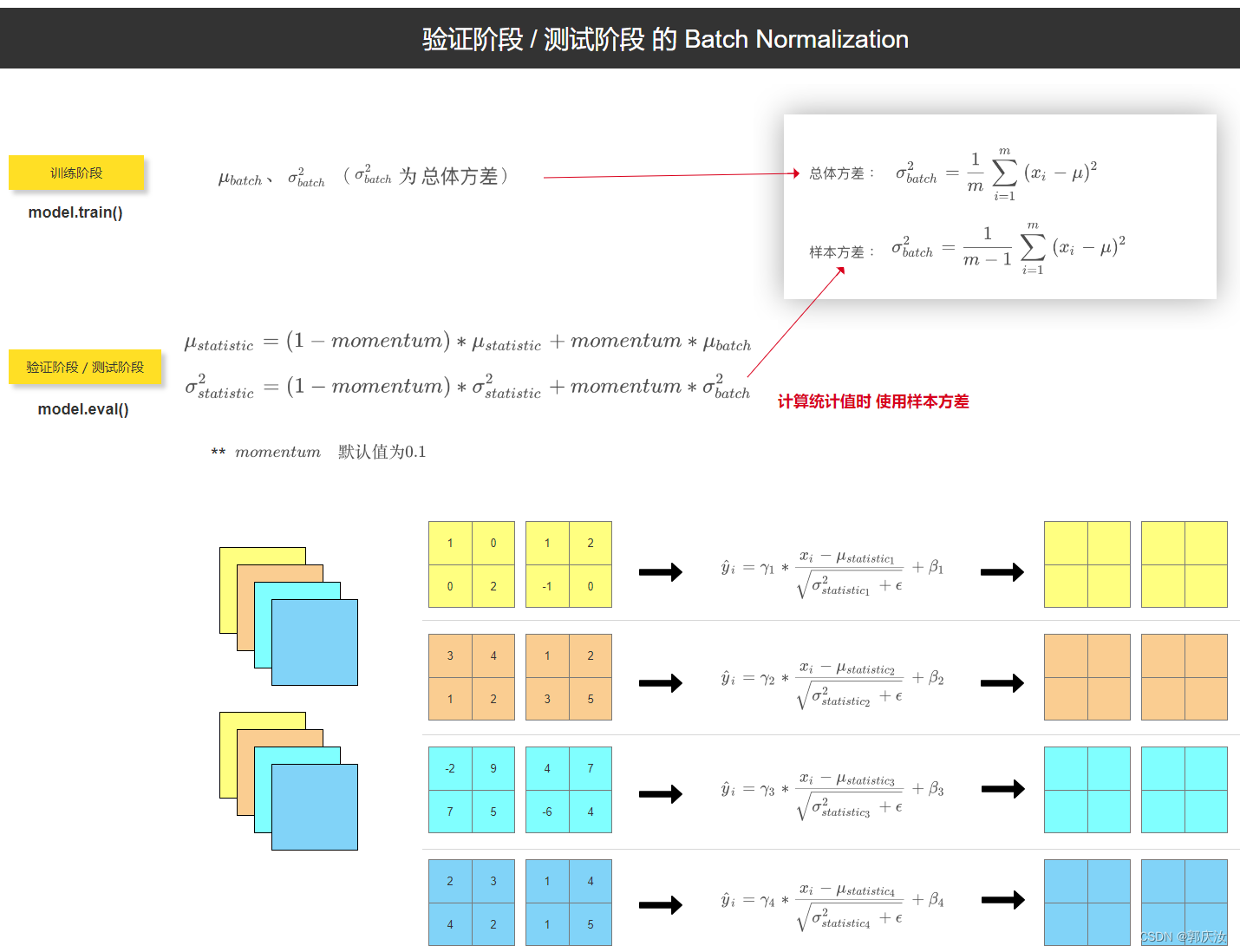
import numpy as np
import torch.nn as nn
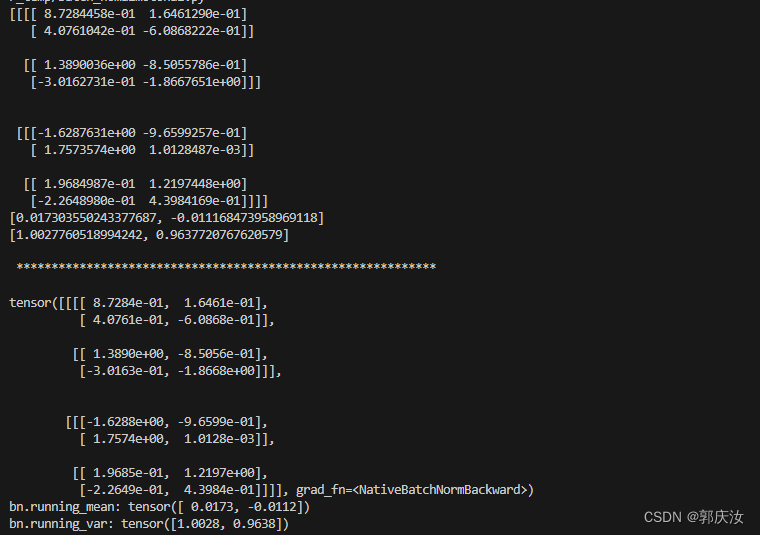
import torchdef bn_process(feature, mean, var):feature_shape = feature.shapefor i in range(feature_shape[1]):# [batch, channel, height, width]feature_t = feature[:, i, :, :] # 得到每一个channel的height和widthmean_t = feature_t.mean()# 总体标准差std_t1 = feature_t.std()# 样本标准差std_t2 = feature_t.std(ddof=1)# bn process# 这里记得加上eps和pytorch保持一致feature[:, i, :, :] = (feature[:, i, :, :] - mean_t) / np.sqrt(std_t1 ** 2 + 1e-5)# update calculating mean and varmean[i] = mean[i] * 0.9 + mean_t * 0.1var[i] = var[i] * 0.9 + (std_t2 ** 2) * 0.1print(feature)# 随机生成一个batch为2,channel为2,height=width=2的特征向量
# [batch, channel, height, width]
feature1 = torch.randn(2, 2, 2, 2)
# 初始化统计均值和方差
calculate_mean = [0.0, 0.0]
calculate_var = [1.0, 1.0]
# print(feature1.numpy())# 注意要使用copy()深拷贝
bn_process(feature1.numpy().copy(), calculate_mean, calculate_var)bn = nn.BatchNorm2d(2, eps=1e-5)
output = bn(feature1)
print(output)显示结果如下: