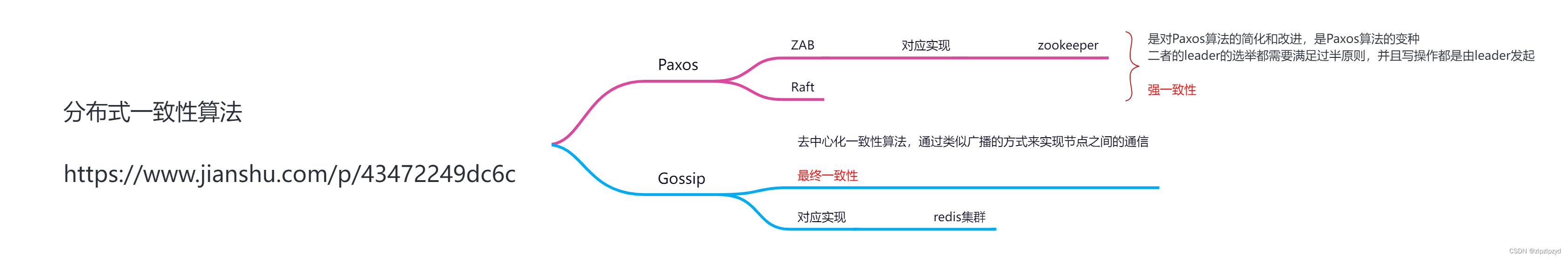
以官方给的例程,重新梳理,以供理解NLopt的使用。

问题被定义为:
min x ∈ R 2 x 2 s u b j e c t t o x 2 ≥ 0 , x 2 ≥ ( a 1 x 1 + b 1 ) 3 , a n d x 2 ≥ ( a 2 x 1 + b 2 ) 3 f o r p a r a m e t e r s a 1 = 2 , b 1 = 0 , a 2 = − 1 , b 2 = 1. \begin{gathered} \min_{\mathbf{x}\in\mathbb{R}^2}\sqrt{x_2} \\ \mathrm{subject~to~}x_2\geq0,x_2\geq(a_1x_1+b_1)^3,\mathrm{and~}x_2\geq(a_2x_1+b_2)^3 \\ \mathrm{for~parameters~a_{1}=2,~b_{1}=0,~a_{2}=-1,~b_{2}=1.} \end{gathered} x∈R2minx2subject to x2≥0,x2≥(a1x1+b1)3,and x2≥(a2x1+b2)3for parameters a1=2, b1=0, a2=−1, b2=1.
使用步骤如下:
- 创建nlopt对象
- 设置上下边界
- 设置不等式约束
- 设置优化目标
- 设置迭代停止条件,参考传送门
- 设置算法起始点
- 执行优化函数
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
#include "nlopt.h"
#include <stdlib.h>
#define INF (1.0/0.0)typedef struct {double a, b;
} my_constraint_data; // 约束参数// 目标函数
int item_count = 0;
double myfunc(unsigned n, const double *x, double *grad, void *my_func_data)
{++item_count;if (grad) {grad[0] = 0.0;grad[1] = 0.5 / sqrt(x[1]);}return sqrt(x[1]);
}// 约束函数
double myconstraint(unsigned n, const double *x, double *grad, void *data)
{my_constraint_data *d = (my_constraint_data *) data;double a = d->a, b = d->b;if (grad) {grad[0] = 3 * a * (a*x[0] + b) * (a*x[0] + b);grad[1] = -1.0;}return ((a*x[0] + b) * (a*x[0] + b) * (a*x[0] + b) - x[1]);}int main()
{// 创建nlopt对象nlopt_opt opt;opt = nlopt_create(NLOPT_LD_MMA, 2); /* algorithm and dimensionality */// 设置上下边界double lb[2] = {-HUGE_VAL, 0 }; /* lower bounds */double ub[2] = {INF, INF};nlopt_set_lower_bounds(opt, lb);nlopt_set_upper_bounds(opt, ub);// 设置优化目标nlopt_set_min_objective(opt, myfunc, NULL);// 添加不等式约束my_constraint_data data[2] = { {2,0}, {-1,1} }; // a1=2,b1=0 a2=-1,b2=1nlopt_add_inequality_constraint(opt, myconstraint, &data[0], 1e-8); // 1e-8是约束的可选容差nlopt_add_inequality_constraint(opt, myconstraint, &data[1], 1e-8);// 优化参数x的相对容差nlopt_set_xtol_rel(opt, 1e-4);double x[2] = { 1.234, 5.678 }; /* `*`some` `initial` `guess`*` */double minf; /* `*`the` `minimum` `objective` `value,` `upon` `return`*` */// 执行优化if (nlopt_optimize(opt, x, &minf) < 0) {printf("nlopt failed!\n");}else {printf("found minimum at f(%g,%g) = %0.10g\n", x[0], x[1], minf);}printf("found minimum after %d evaluations\n", item_count);// 销毁对象nlopt_destroy(opt);return 0;
}
案例2:
#include<iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include <iomanip>
#include <nlopt.hpp>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
using namespace std;
using namespace nlopt;
/** main.c** Created on: Oct 9, 2018* Author: lgh*/
#define INF (1.0/0.0)
int i=0;//目标函数;
double utility(unsigned n, const double *x, double *grad, void *data)
{if(grad){grad[0]=2*x[0];grad[1]=2*x[1];grad[2]=1.0;grad[3]=2*x[3];}printf("迭代次数 i= %d, x[0]=%f, x[1]= %f,x[2]= %f,x[3]= %f,f(x1,x2,x3,x4)=%f\n",i++,x[0],x[1],x[2],x[3],x[0]*x[0]+x[1]*x[1]+x[2]+x[3]*x[3]+10);return ( x[0]*x[0]+x[1]*x[1]+x[2]+x[3]*x[3]+10 );
}//等式限制条件;
double constraint(unsigned n, const double *x, double *grad, void *data)
{if(grad){grad[0]= 1.0;grad[1]= 1.0;grad[2]= 1.0;grad[3]= 1.0;}return (x[0]+x[1]+x[2]+x[3]);
}//不等式限制条件;
double inconstraint(unsigned n, const double *x, double *grad, void *data)
{if(grad){grad[0]= -2*x[0];grad[1]= -2*x[1];}return (-x[0]*x[0]-x[1]*x[1]-100);
}int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{double tol=1e-8;double lb[4]={-INF,-INF,-INF,-INF}; //x1、x2的下边界;double ub[4]={INF,INF,INF,INF};double x[4]={1, 1, 1, 1}; //给x1、x2赋予初始值;double f_max;nlopt_opt opter=nlopt_create( NLOPT_LD_SLSQP, 4);//设置自变量下限;nlopt_set_lower_bounds(opter, lb);// 目标函数;nlopt_set_min_objective(opter, utility, NULL);// 不等式约束;nlopt_add_inequality_constraint(opter, inconstraint, NULL, tol);// 等式约束;nlopt_add_equality_constraint(opter, constraint, NULL, tol);// 停止时需要的条件;nlopt_set_xtol_rel(opter, tol);// 开始优化;nlopt_result result=nlopt_optimize(opter, x, &f_max);if (result){printf("目标函数最大值=%g, x=(%g,%g)\n", f_max, x[0], x[1], x[2], x[3]);}//freenlopt_destroy(opter);return 0;
}
参考链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/derek-dhb/p/17497953.html