- string类的理解(以JDK8为例说明)
1.1的声明
public final class String
implements java.io.Serializable, Comparable<String>, CharSequence
final:String是不可被继承的
Serializable:可序列化的接口。凡是实现此接口的类的对象就可以通过网络或本地流进行数据的传输。
1.2内部声明的属性
private final char value[] ;//存储字符串数据的容器
>final : 指明此value数组一旦初始化,其地址就不可变。
Jdk9开始:
Private final char byte[] value;//存储字符串数据的容器
2.字符串常量的存储位置
字符串常量都存储在字符串常量池(StringTable)中
字符串常量池不允许存放两个相同的字符串常量。
字符串常量池,在不同的jdk版本中,
存放位置不同。jdk7之前:字符串常量池存放在方法区
jdk7及之后:字符串常量池存放在堆空间。
- String的不可变性的理解
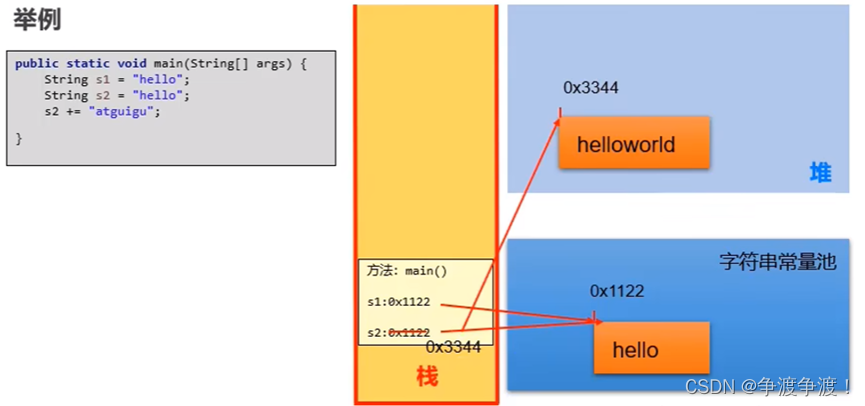
当对字符串变量重新赋值时,需要重新指定一个字符串常量的位置进行赋值,不能在原有位置置修改
* 当对现有的字符串进行拼接操作时,需要重新开辟空间保存拼接以后的字符串,不能在原有的位置修改
* 当调用字符串的repLace()替换现有的某个字符时,需要重新开辟空间保存修改以后的字符串,不能在原有的位置修改
代码:
package Test0704;public class StringDeno{public void test1(){String s1 = "hello"; //字面量的定义方式String s2 = "hello";System.out.println(s1 == s2);}/*** String 的不可变性* 当对字符串变量重新赋值时,需要重新指定一个字符串常量的位置进行赋值,不能在原有位置置修改* 当对现有的字符串进行拼接操作时,需要重新开辟空间保存拼接以后的字符串,不能在原有的位置修改* 当调用字符串的repLace()替换现有的某个字符时,需要重新开辟空间保存修改以后的字符串,不能在原有的位置修改*/public void test2(){String s1 = "hello";String s2 = "hello";s2 = "hi";System.out.println(s1);}public void test3(){String s1 = "hello";//在字符串常量池new了一个hello 地址gei了s1String s2 = "hello";//获取s1的地址值s2 += " world";System.out.println(s1);System.out.println(s2);}public void test4(){String s1 = "hello";String s2 = "hello";//将s2中的l转换成wString s3 = s2.replace("l","w");System.out.println(s1);System.out.println(s2);System.out.println(s3);}public static void main(String[] args) {// new StringDeno().test1();// new StringDeno().test2();// new StringDeno().test3();new StringDeno().test4();}}
- String实例化的两种方式
第1种方式:String s1 ="hello";
第2种方式: String s2 = new String("hello");
String s2 = new String("hello");在内存中创建了几个对象? 两个
个是堆空间中new的对象。另一个是在字符串常量池中生成的字面量
String的连接操作:+
情况1:常量+常量:结果仍然存储在字符串常量池中。注:此时的常量可能是字面量,也可能是final修饰的常量
情况2:常量+变量 或 变量+变量:都会通过new的方式创建一个新的字符串,返回堆空间中此字符串对象的地址
情况3:调用字符串的intern():返回的是字符串常量池中字面量的地址
string的构造器和常用方法
6.1 构造器
public string():初始化新创建的 string对象,以使其表示空字符序列。
String(String original): 初始化一个新创建的Strng对象,使其表示一个与参数相同的字符序列,
public string(char[] value) :通过当前参数中的字符数组来构造新的String。
public String(char[] value,int offset,int count):通过字符数组的一部分来构造新的String,
public String(byte[] bytes) :通过使用平台的**默认字符集**解码当前参数中的字节数组来构造新的String。
public String(byte[] bres,String charsetName)·:通过使用指定的字符集解码当前参数中的字节数组来构造新的String对象
基本数据类型---》转换成String
Int a = 3;//方式1String s1 = a +””;//方式2String s2 = String.valueof(num);String与char相互转换String str = “hello”//String àchar []:调用String的toCharArray()Char[] arr = str.toChatArray();For (int I = 0;i < arr.length ; i++){System.out.println(arr[i]);//char[] àString:调用String的构造器String str1 = new String(arr);System.out.println(str1);//hello